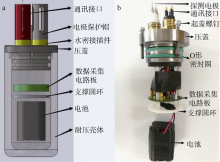
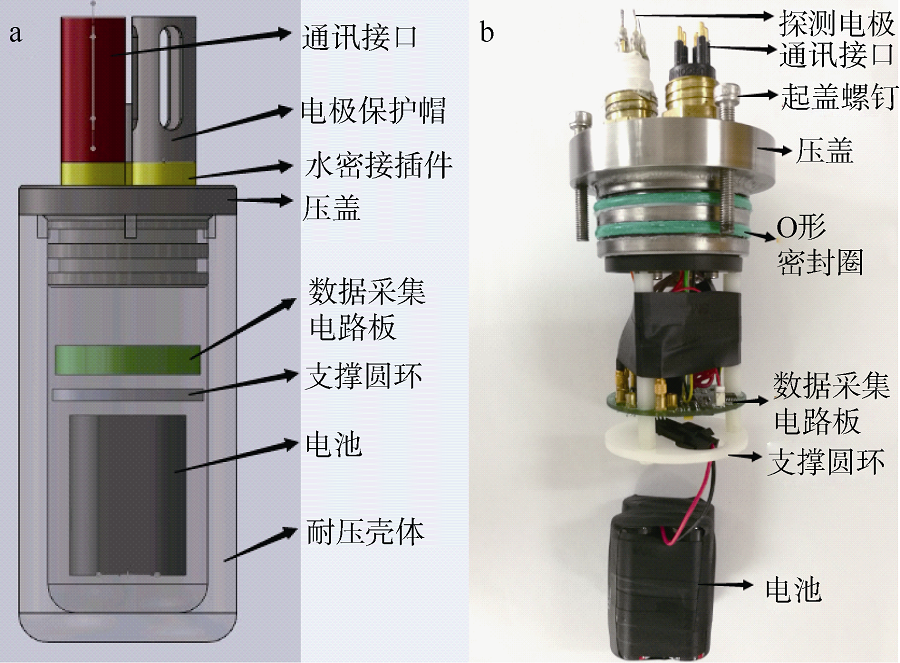
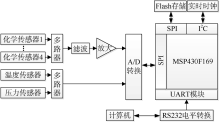
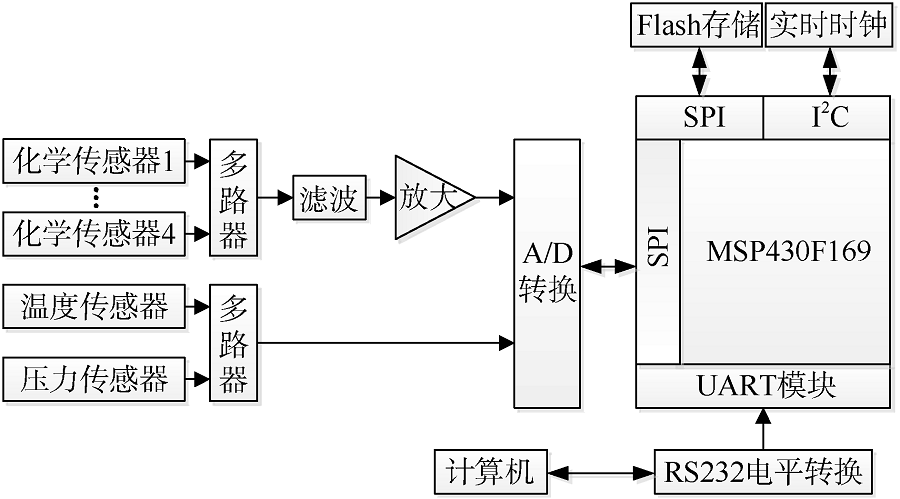
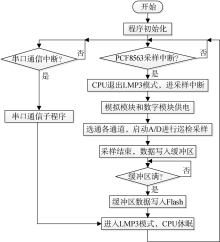
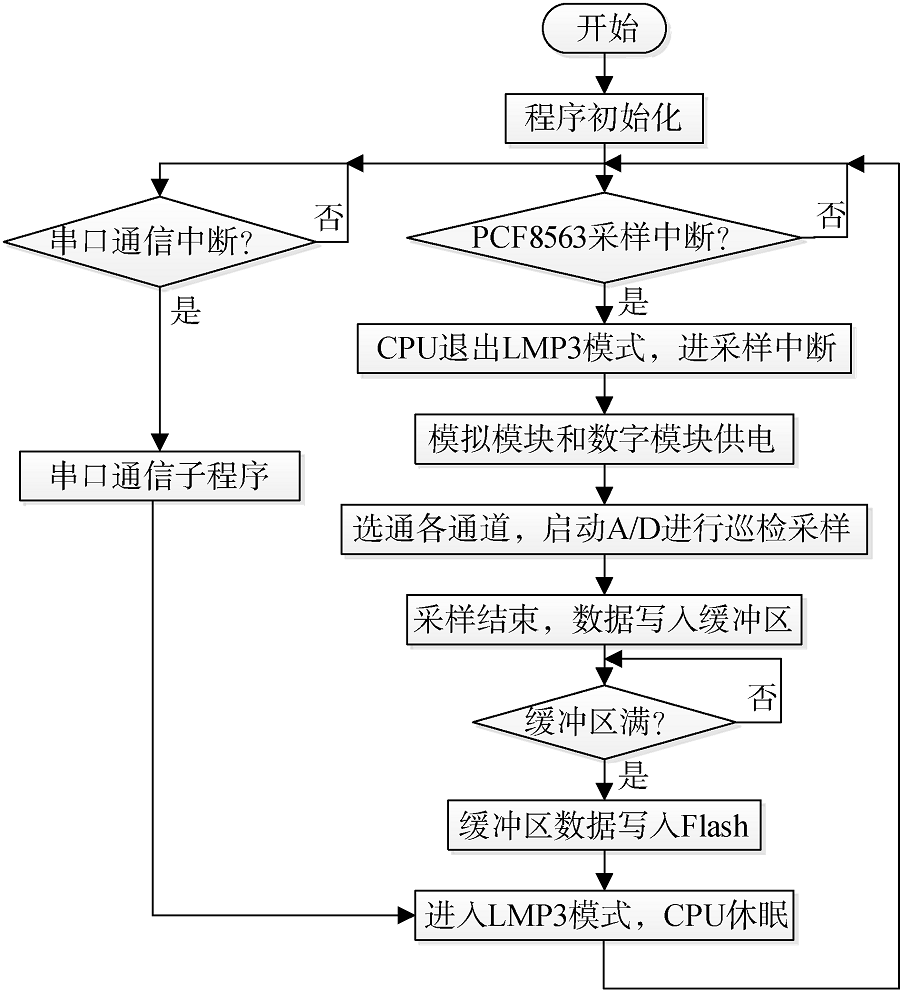
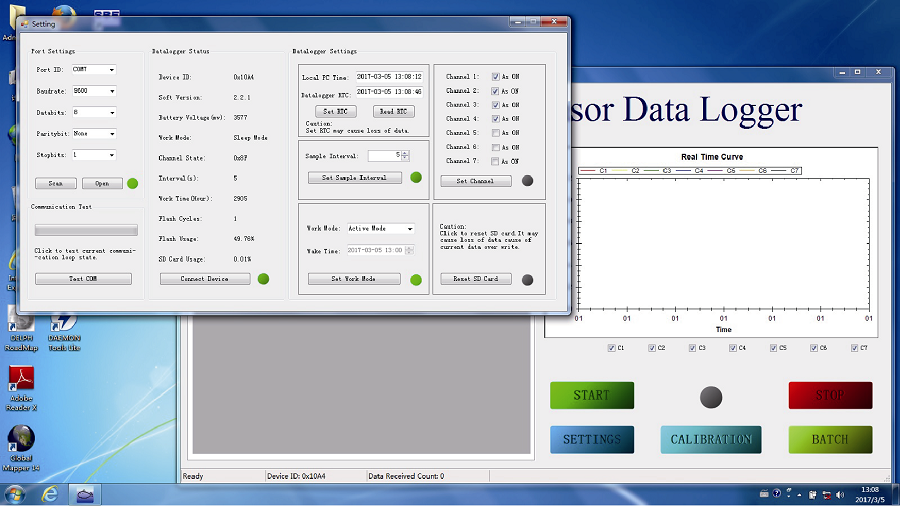
| [1] |
韩沉花, 2011. 用于海洋碳酸盐体系参数测定的微电极的研制与应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 90-128.
|
|
HAN CHENHUA, 2011. Fabrication and application of microelectrode for measuring ocean carbonate system parameters[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 90-128 (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
栾锡武, 秦蕴珊, 2002. 现代海底热液活动的调查研究方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 17(4): 592-597.
|
|
LUAN XIWU, QIN YUNSHAN, 2002. Survey methods of modern hydrothermal activity[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 17(4): 592-597 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
潘依雯, 叶瑛, 韩沉花, 2010. 用于深海极端环境下的pH电极制备方法改进[J]. 海洋学报, 32(2): 73-79.
|
|
PAN YIWEN, YE YING, HAN CHENHUA, 2010. An improved approach of pH electrode preparation for application in the deep-sea environment[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 32(2): 73-79 (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
潘依雯, 武光海, 秦华伟, 等, 2012. 基于多参数化学传感器的海底热液探测方法研究[J]. 海洋学报, 34(2): 179-184.
|
|
PAN YIWEN, WU GUANGHAI, QIN HUAWEI, et al, 2012. The research on hydrothermal vent detection with the multiparameter chemical sensor[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(2): 179-184 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
全国压力容器标准化技术委员会. JB 4732-1995 钢制压力容器分析设计标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1995.
|
| [6] |
孙训方, 方孝淑, 关来泰, 等, 2002. 材料力学[M]. 4版. 高等教育出版社..
|
| [7] |
陶春辉, 李怀明, 金肖兵, 等, 2014. 西南印度洋脊的海底热液活动和硫化物勘探[J]. 科学通报, 59(19): 1812-1822.
|
|
TAO CHUNHUI, LI HUAIMING, JIN XIAOBING, et al, 2014. Seafloor hydrothermal activity and polymetallic sulfide exploration on the southwest Indian ridge[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(19): 2266-2276 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
杨微, 秦华伟, 2009. 基于MSP430的深海低功耗数据采集系统[J]. 机电工程, 26(5): 16-19.
|
|
YANG WEI, QIN HUAWEI, 2009. Low power-consumption deep-sea data logger based on MSP430[J]. Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Magazine, 26(5): 16-19 (in Chinese ).
|
| [9] |
翟世奎, 李怀明, 于增慧, 等, 2007. 现代海底热液活动调查研究技术进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 22(8): 769-776.
|
|
ZHAI SHIKUI, LI HUAIMING, YU ZENGHUI, et al, 2007. Advances in the investigation technology of modern seafloor hydrothermal activities[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 22(8): 769-776 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
BAKER E T, HAYMON R M, RESING J A, et al, 2008. High-resolution surveys along the hot spot-affected Galápagos Spreading Center: 1. Distribution of hydrothermal activity[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 9(9): Q09003.
|
| [11] |
BAKER E T, MILBURN H B, 1997. MAPR: A new instrument for hydrothermal plume mapping[J]. Ridge Events, 8(1): 23-25.
|
| [12] |
CHEN YING, YE YING, YANG CANJUN, 2005. Integration of real-time chemical sensors for deep sea research[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 19(1): 129-137.
|
| [13] |
GILLESPIE L J, 1920. Reduction potentials of bacterial culture and of water-logged soils[J]. Soil Science, 9(4): 199-216.
|
| [14] |
PAN YIWEN, SEYFRIED JR W E, 2008. Experimental and theoretical constraints on pH measurements with an iridium oxide electrode in aqueous fluids from 25 to 175℃ and 25 MPa[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 37(8): 1051-1062.
|
| [15] |
SUDARIKOV S M, ROUMIANTSEV A B, 2000. Structure of hydrothermal plumes at the Logatchev vent field, 14°45′N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge: evidence from geochemical and geophysical data[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 101(3-4): 245-252.
|
 ), Zhuo TAO1(
), Zhuo TAO1( ), Huaiming LI2, Xihe YUE2, Zhen CAI3, Sheng CHEN1, Hongwei ZHOU2, Ying YE3
), Huaiming LI2, Xihe YUE2, Zhen CAI3, Sheng CHEN1, Hongwei ZHOU2, Ying YE3