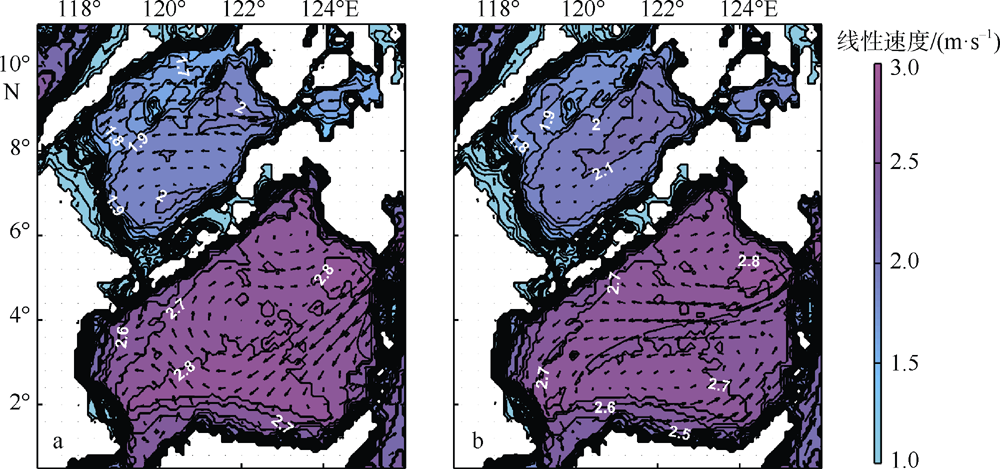
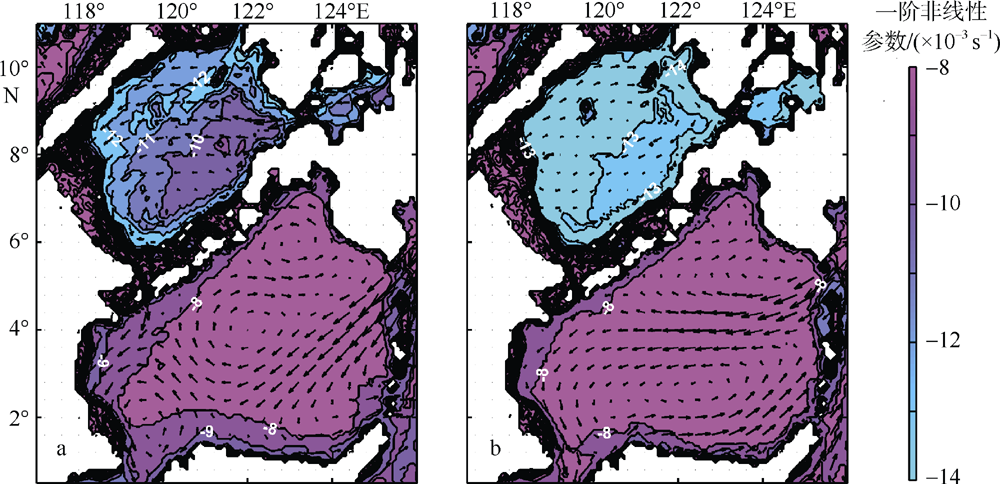
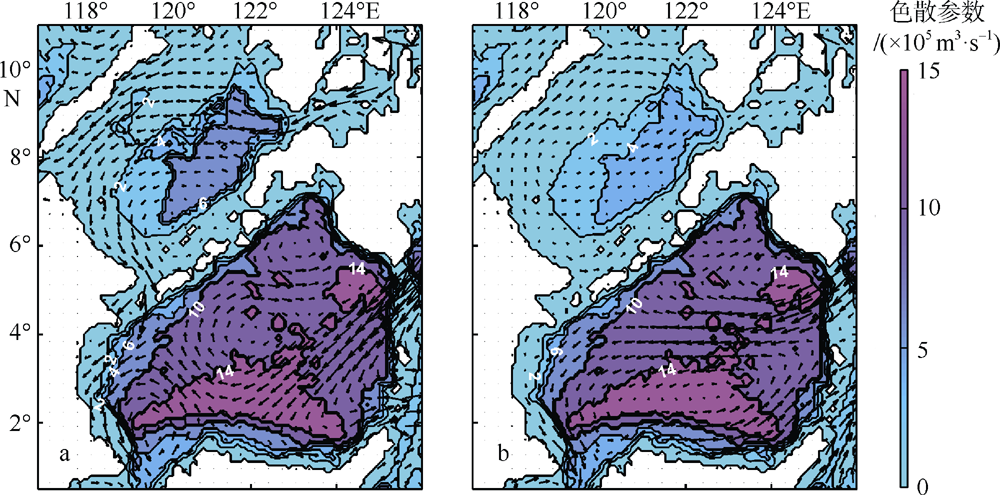
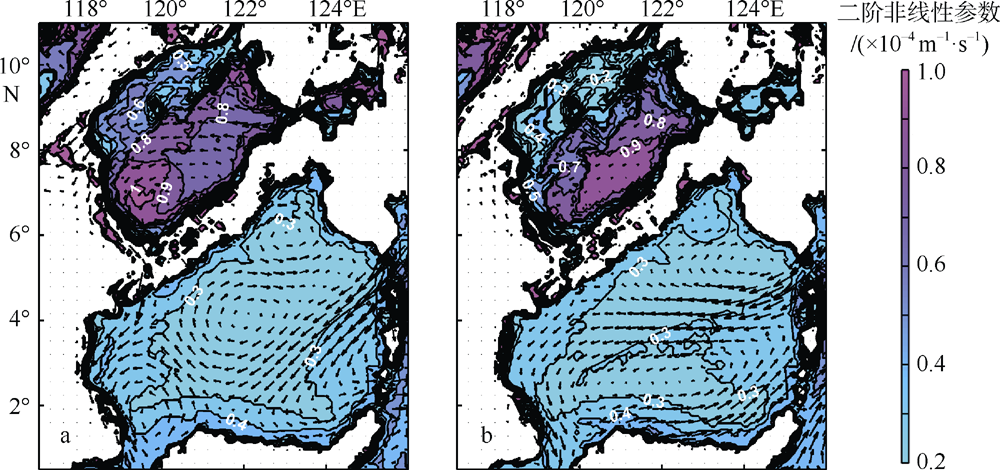
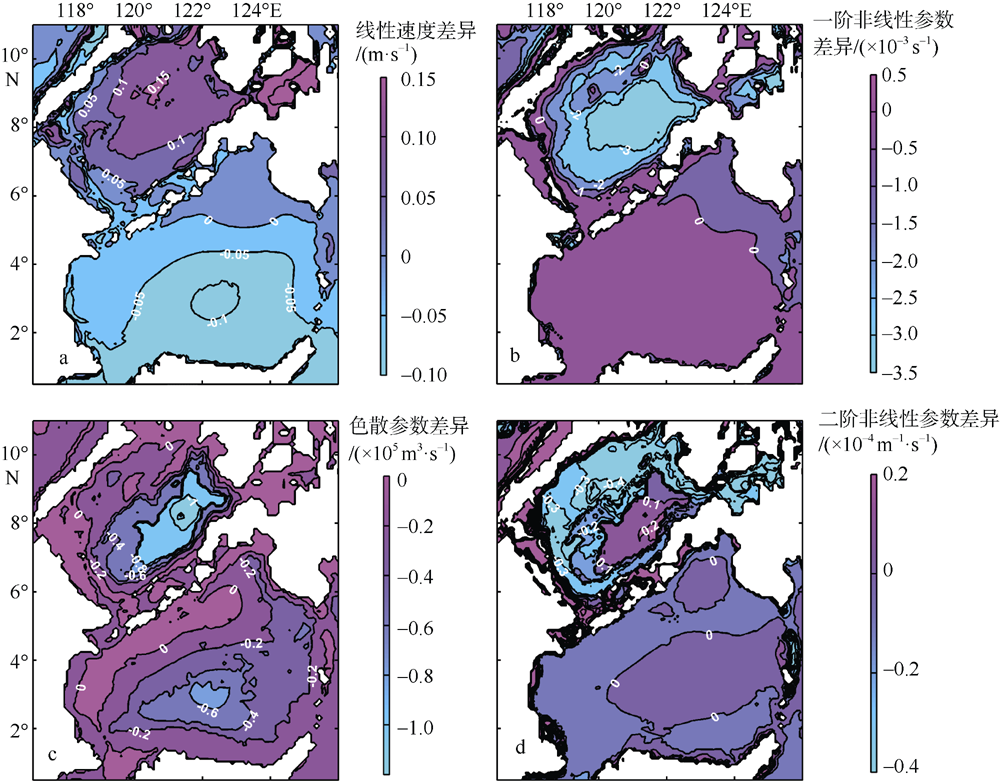
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 132-142.doi: 10.11978/2021183CSTR: 32234.14.2021183
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatial-temporal variations of the dynamic parameters of internal solitary waves in the Sulu-Celebes Sea
XIE Jieshuo1,2( ), GONG Yankun1,2, NIU Jianwei1,2, HE Yinghui1,2, CHEN Zhiwu1,2, XU Jiexin1,2, CAI Shuqu1,2(
), GONG Yankun1,2, NIU Jianwei1,2, HE Yinghui1,2, CHEN Zhiwu1,2, XU Jiexin1,2, CAI Shuqu1,2( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, 511458, China
-
Received:2021-12-24Revised:2022-03-17Online:2022-11-10Published:2022-04-19 -
Contact:CAI Shuqu E-mail:xiejieshuo@126.com;caisq@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China(42130404);Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China(41776008);Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, CAS(QYZDJ-SSW-DQC034);Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0304);Special project by Department of natural resources of Guangdong Province([2020]017);Youth Science and Technology Innovation Talent of Guangdong TeZhi Plan(2019TQ05H519);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2020A1515010495);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021A1515012538);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021A1515011613)
CLC Number:
- P731.24
Cite this article
XIE Jieshuo, GONG Yankun, NIU Jianwei, HE Yinghui, CHEN Zhiwu, XU Jiexin, CAI Shuqu. Spatial-temporal variations of the dynamic parameters of internal solitary waves in the Sulu-Celebes Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 132-142.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | 李子木, 蔡树群, 陈举, 等, 2014. 2010-2011年吕宋海峡西侧潜标观测的初步分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(1): 10-16. |
|
LI ZIMU, CAI SHUQUN, CHEN JU, et al, 2014. Preliminary analysis of observations by deep submersible mooring in west Luzon Strait during 2010 to 2011[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 33(1): 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.01.002 |
|
| [2] | 孙丽娜, 张杰, 孟俊敏, 2018. 基于遥感与现场观测数据的南海北部内波传播速度[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 49(3): 471-480. |
| SUN LINA, ZHANG JIE, MENG JUNMIN, 2018. On propagation velocity of internal solitary waves in the northern South China Sea with remote sensing and in-situ observations data[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 49(3): 471-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 张涛, 张旭东, 2020. 基于MODIS和VIIRS遥感图像的苏禄-苏拉威西海内孤立波特征研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(5): 991-1000. |
| ZHANG TAO, ZHANG XUDONG, 2020. Characteristics on internal solitary waves in the sulu-celebes sea based on MODIS and VIIRS remote sensing images[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 51(5): 991-1000. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] |
ALFORD M H, PEACOCK T, MACKINNON J A, et al, 2015. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea[J]. Nature, 521(7550): 65-69.
doi: 10.1038/nature14399 |
| [5] | APEL J, OSTROSKY L, STEPANYANTS Y, et al, 2006. Internal solitons in the ocean[R]. Technical Report, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. WHOI-2006-04. |
| [6] |
APEL J R, HOLBROOK J R, LIU A K, et al, 1985. The Sulu Sea internal soliton experiment[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 15(12): 1625-1651.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1985)015<1625:TSSISE>2.0.CO;2 |
| [7] |
BAI XIAOLIN, LIU ZHIYU, ZHENG QUANAN, et al, 2019. Fission of shoaling internal waves on the northeastern shelf of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(7): 4529-4545.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014437 |
| [8] | CAI SHUQUN, HE YINGHUI, WANG SHENGAN, et al, 2009. Seasonal upper circulation in the Sulu Sea from satellite altimetry data and a numerical model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 114(C3): C03026. |
| [9] |
CAI SHUQUN, HE YINGHUI, 2010. Association of the Sulu Sea surface circulation with the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 81(4): 335-340.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.02.010 |
| [10] |
CAI SHUQUN, XIE JIESHUO, HE JIANLING, 2012. An overview of internal solitary waves in the South China Sea[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 33(5): 927-943.
doi: 10.1007/s10712-012-9176-0 |
| [11] |
CAI SHUQUN, XIE JIESHUO, XU JIEXIN, et al, 2014. Monthly variation of some parameters about internal solitary waves in the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 84: 73-85.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2013.10.008 |
| [12] |
CHEN LIANG, ZHENG QUANAN, XIONG XUEJUN, et al, 2019. Dynamic and statistical features of internal solitary waves on the continental slope in the northern South China Sea derived from mooring observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(6): 4078-4097.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014843 |
| [13] |
CHENG XUHUA, XIE SHANGPING, DU YAN, et al, 2016. Interannual-to-decadal variability and trends of sea level in the South China Sea[J]. Climate Dynamics, 46(9-10): 3113-3126.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-015-2756-1 |
| [14] |
CHO C, NAM S H, SONG H, 2016. Seasonal variation of speed and width from kinematic parameters of mode-1 nonlinear internal waves in the northeastern East China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(8): 5942-5958.
doi: 10.1002/2016JC012035 |
| [15] |
CHOI W, CAMASSA R, 1999. Fully nonlinear internal waves in a two-fluid system[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 396: 1-36.
doi: 10.1017/S0022112099005820 |
| [16] |
DU YAN, QU TANGDONG, 2010. Three inflow pathways of the Indonesian throughflow as seen from the simple ocean data assimilation[J]. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 50(2): 233-256.
doi: 10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2010.04.001 |
| [17] | GONG YANKUN, XIE JIESHUO, XU JIEXIN, et al, 2022. Oceanic internal solitary waves at the Indonesian submarine wreckage site[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 41(3): 109-113. |
| [18] | GORDON A L, HUBER B A, METZGER E J, et al, 2012. South China Sea throughflow impact on the Indonesian throughflow[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(11): L11602. |
| [19] |
GRIMSHAW R, PELINOVSKY E, TALIPOVA T, et al, 2004. Simulation of the transformation of internal solitary waves on oceanic shelves[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 34(12): 2774-2791.
doi: 10.1175/JPO2652.1 |
| [20] |
GRIMSHAW R, PELINOVSKY E, TALIPOVA T, 2007. Modelling internal solitary waves in the coastal ocean[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 28(4): 273-298
doi: 10.1007/s10712-007-9020-0 |
| [21] |
GRIMSHAW R, GUO CHUNCHENG, HELFRICH K, et al, 2014. Combined effect of rotation and topography on shoaling oceanic internal solitary waves[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 44(4): 1116-1132.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-13-0194.1 |
| [22] |
GUO C, CHEN X, 2014. A review of internal solitary wave dynamics in the northern South China Sea[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 121: 7-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2013.04.002 |
| [23] |
HAN WEIQING, MOORE A M, LEVIN J, et al, 2009. Seasonal surface ocean circulation and dynamics in the Philippine archipelago region during 2004-2008[J]. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 47(1-3): 114-137.
doi: 10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2008.10.007 |
| [24] |
HAO ZHANJIU, XU ZHENHUA, FENG MING, et al, 2021. Spatiotemporal variability of mesoscale eddies in the Indonesian Seas[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(5): 1017.
doi: 10.3390/rs13051017 |
| [25] |
HE YINGHUI, FENG MING, XIE JIESHUO, et al, 2017. Spatiotemporal variations of mesoscale eddies in the Sulu Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(10): 7867-7879.
doi: 10.1002/2017JC013153 |
| [26] |
HELFRICH K R, MELVILLE W K, 2006. Long nonlinear internal waves[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 38(1): 395-425.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.38.050304.092129 |
| [27] |
HUANG XIAODONG, CHEN ZHAOHUI, ZHAO WEI, et al, 2016. An extreme internal solitary wave event observed in the northern South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 6: 30041.
doi: 10.1038/srep30041 pmid: 27444063 |
| [28] |
HURLBURT H E, METZGER E J, SPRINTALL J, et al, 2011. Circulation in the Philippine archipelago simulated by 1/12° and 1/25° global HYCOM and EAS NCOM[J]. Oceanography, 24(1): 28-47.
doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2011.02 |
| [29] |
JACKSON C R, ARVELYNA Y, ASANUMA I, 2011. High-frequency nonlinear internal waves around the Philippines[J]. Oceanography 24(1): 90-99.
doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2011.06 |
| [30] |
JIA T, LIANG J J, LI X M, et al, 2018. SAR Observation and numerical simulation of internal solitary wave refraction and reconnectionbehind the Dongsha Atoll[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(1): 74-89.
doi: 10.1002/2017JC013389 |
| [31] |
JOSEPH R I, 1977. Solitary waves in a finite depth fluid[J]. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 10(12): L225-L227.
doi: 10.1088/0305-4470/10/12/002 |
| [32] |
KAO T W, PAN F S, RENOUARD D, 1985. Internal solitons on the pycnocline: Generation, propagation, and shoaling and breaking over a slope[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 159: 19-53.
doi: 10.1017/S0022112085003081 |
| [33] | KLYMAK J M, PINKEL R, LIU C T, et al, 2006. Prototypical solitons in the South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(11): L11607. |
| [34] |
KOOP C G, BUTLER G, 1981. An investigation of internal solitary waves in a two-fluid system[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 112: 225-251.
doi: 10.1017/S0022112081000372 |
| [35] | KORTEWEG D J, DE VRIES G, 1895. XLI. On the change of form of long waves advancing in a rectangular canal, and on a new type of long stationary waves[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 39(240): 422-443. |
| [36] |
LAI ZHIGANG, JIN GUANGZHEN, HUANG YONGMAO, et al, 2019. The generation of nonlinear internal waves in the South China Sea: A three-dimensional, nonhydrostatic numerical study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(12): 8949-8968.
doi: 10.1029/2019JC015283 |
| [37] |
LI MINGTING, WEI JUN, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2019. Exploring the importance of the Mindoro-Sibutu Pathway to the upper-layer circulation of the South China Sea and the Indonesian Throughflow[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(7): 5054-5066.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014910 |
| [38] |
LI QIANG, WANG BING, CHEN XU, et al, 2016. Variability of nonlinear internal waves in the South China Sea affected by the Kuroshio and mesoscale eddies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(4): 2098-2118.
doi: 10.1002/2015JC011134 |
| [39] |
LI XIAOFENG, JACKSON C R, PICHEL W G, 2013. Internal solitary wave refraction at Dongsha Atoll, South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(12): 3128-3132.
doi: 10.1002/grl.50614 |
| [40] |
LIAO GUANGHONG, XU XIAOHUA, LIANG CHUJIN, et al, 2014. Analysis of kinematic parameters of internal solitary waves in the northern South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 94: 159-172.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2014.10.002 |
| [41] |
LIU BINGQING, D’SA E J, 2019. Oceanic internal waves in the Sulu-Celebes Sea under Sunglint and Moonglint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 57(8): 6119-6129.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2904402 |
| [42] |
NAGAI T, HIBIYA T, 2015. Internal tides and associated vertical mixing in the Indonesian Archipelago[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 120(5): 3373-3390.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC010592 |
| [43] | QU TANGDONG, SONG Y T, 2009. Mindoro Strait and Sibutu Passage transports estimated from satellite data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(9): L09601. |
| [44] |
SEGUR H, HAMMACK J L, 1982. Soliton models of long internal waves[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 118: 285-304.
doi: 10.1017/S0022112082001086 |
| [45] |
TESSLER Z D, GORDON A L, JACKSON C R, 2012. Early stage soliton observations in the Sulu Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42(8): 1327-1336.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-11-0165.1 |
| [46] |
WANG CAIXIA, WANG XIN, DA SILVA J C B, 2019. Studies of internal waves in the strait of Georgia based on remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(1): 96.
doi: 10.3390/rs11010096 |
| [47] | WANG JUAN, HUANG WEIGEN, YANG JINGSONG, et al, 2013. Study of the propagation direction of the internal waves in the South China Sea using satellite images[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 32(5): 42-50. |
| [48] |
XIE JIESHUO, HE YINGHUI, CHEN ZHIWU, et al, 2015. Simulations of internal solitary wave interactions with mesoscale eddies in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 45(12): 2959-2978.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-15-0029.1 |
| [49] |
XIE JIESHUO, HE YINGHUI, LÜ HAIBIN, et al, 2016. Distortion and broadening of internal solitary wavefront in the northeastern South China Sea deep basin[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(14): 7617-7624.
doi: 10.1002/2016GL070093 |
| [50] | XIE JIESHUO, FANG WENDONG, HE YINGHUI, et al, 2021. Variation of internal solitary wave propagation induced by the typical oceanic circulation patterns in the northern South China Sea deep basin[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(15): e2021GL093969. |
| [51] | XU ZHENHUA, WANG YANG, LIU ZHIQIANG, et al, 2021. Insight into the dynamics of the radiating internal tide associated with the Kuroshio Current[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 126(6): e2020JC017018. |
| [52] |
YUAN C, GRIMSHAW R, JOHNSON E, et al, 2018. Topographic effect on oblique internal wave-wave interactions[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 856: 36-60.
doi: 10.1017/jfm.2018.678 |
| [53] | ZHANG XUDONG, ZHANG TAO, LI XIAOFENG, 2020. Satellite observation of tansmeridional propagating internal waves in the Celebes Sea[C]// IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE: 6961-6964. |
| [54] | ZHANG Z, FRINGER O B, RAMP S R, 2011. Three-dimensional, nonhydrostatic numerical simulation of nonlinear internal wave generation and propagation in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C5): C05022. |
| [55] |
ZHAO XIAOYU, XU ZHENHUA, FENG MING, et al, 2021. Satellite investigation of semidiurnal internal tides in the Sulu-Sulawesi seas[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(13): 2530.
doi: 10.3390/rs13132530 |
| [1] | LI Zi-mu, CAI Shu-qun, CHEN Ju, CHEN Rong-yu, WANG Dong-xiao, DU Yan. Preliminary analysis of observations by deep submersible mooring in west Luzon Strait during 2010 to 2011 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 10-16. |
| [2] | SHI Xin-gang, LIU Yao-hua, LAN Zhi-gang, SONG Ji-wen, HE Qi, LEI Fang-hui, WANG Jun-qin, HUANG Bi-gui, ZHU Xue-ming. The characteristics of internal solitary waves at Liuhua in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(6): 22-27. |
|
||