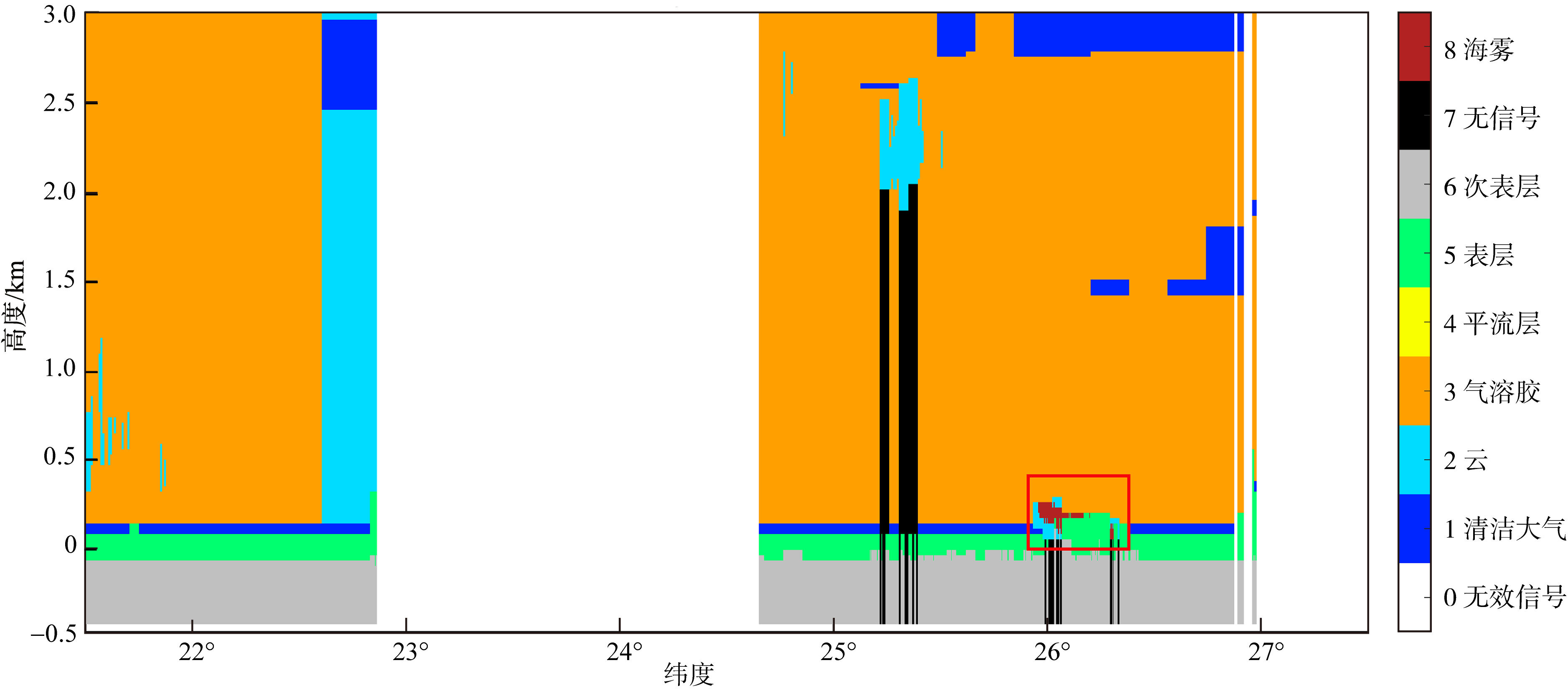
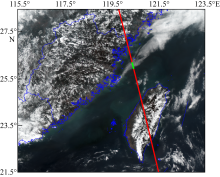
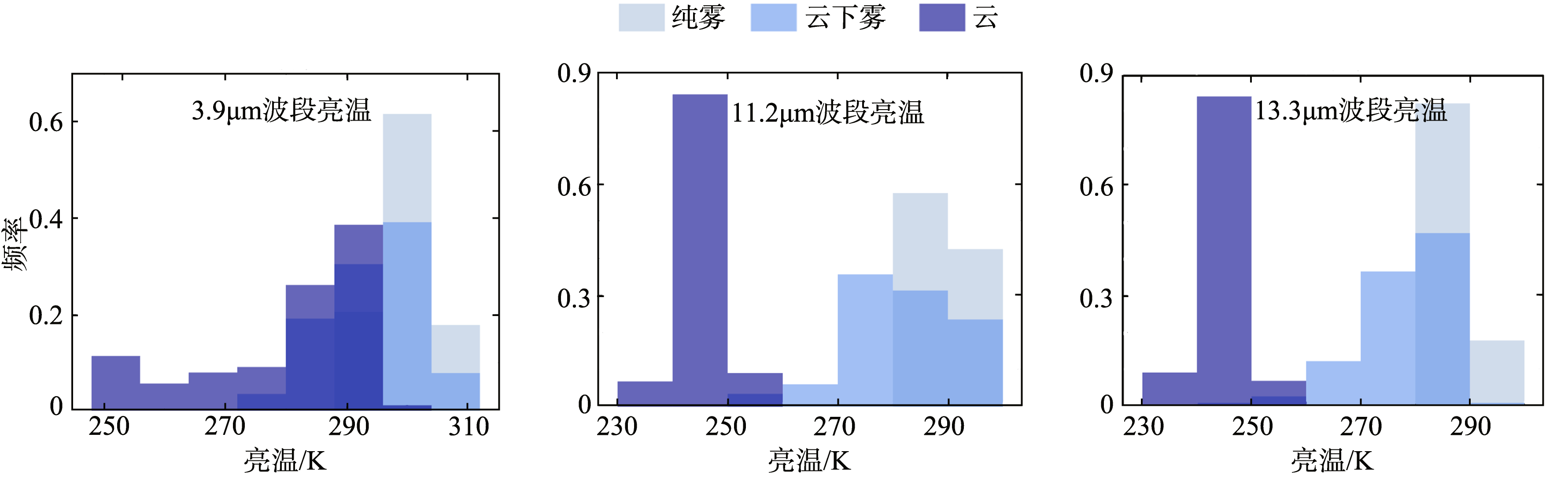
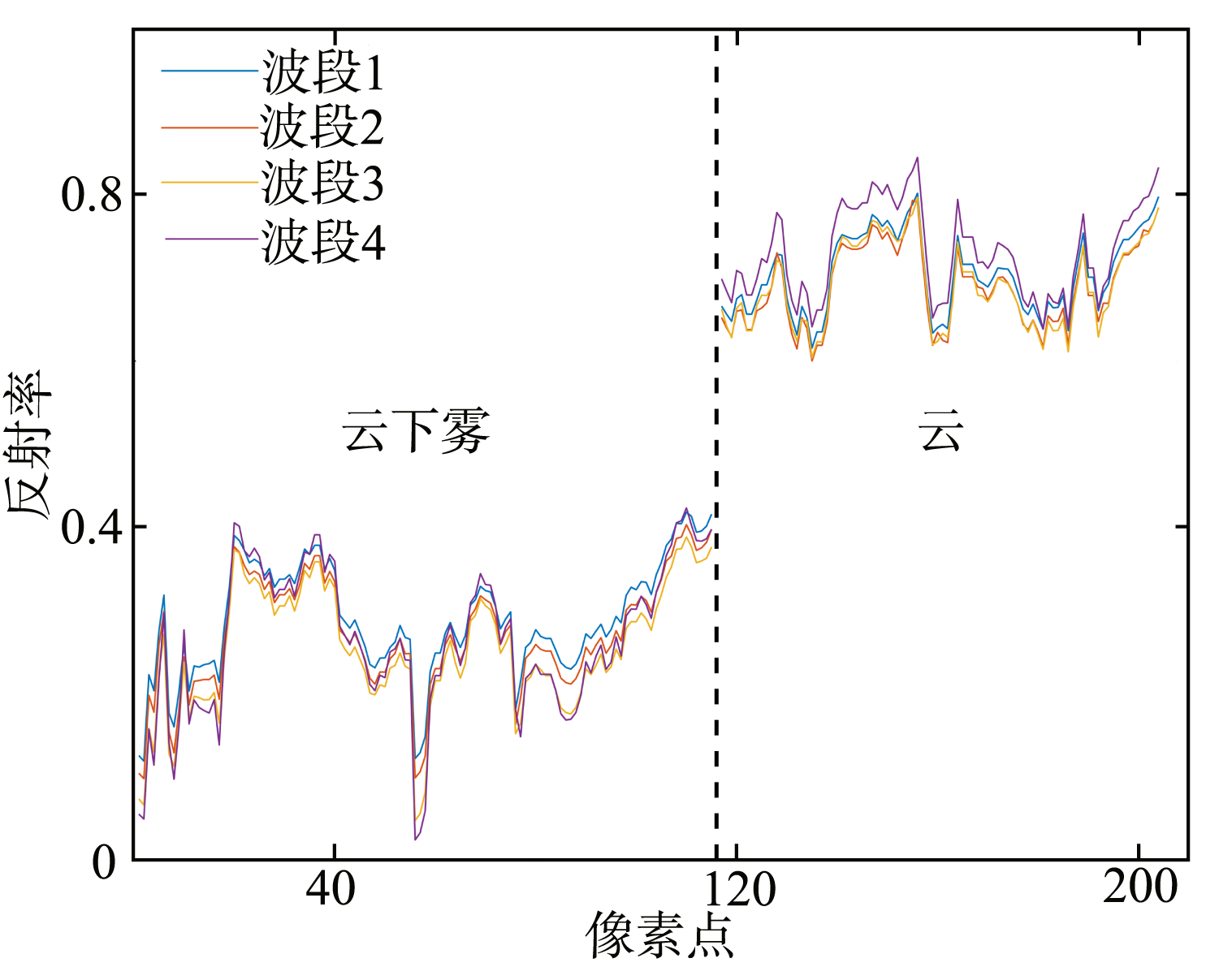
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 104-112.doi: 10.11978/2022215CSTR: 32234.14.2022215
• Marine Meteorology • Previous Articles Next Articles
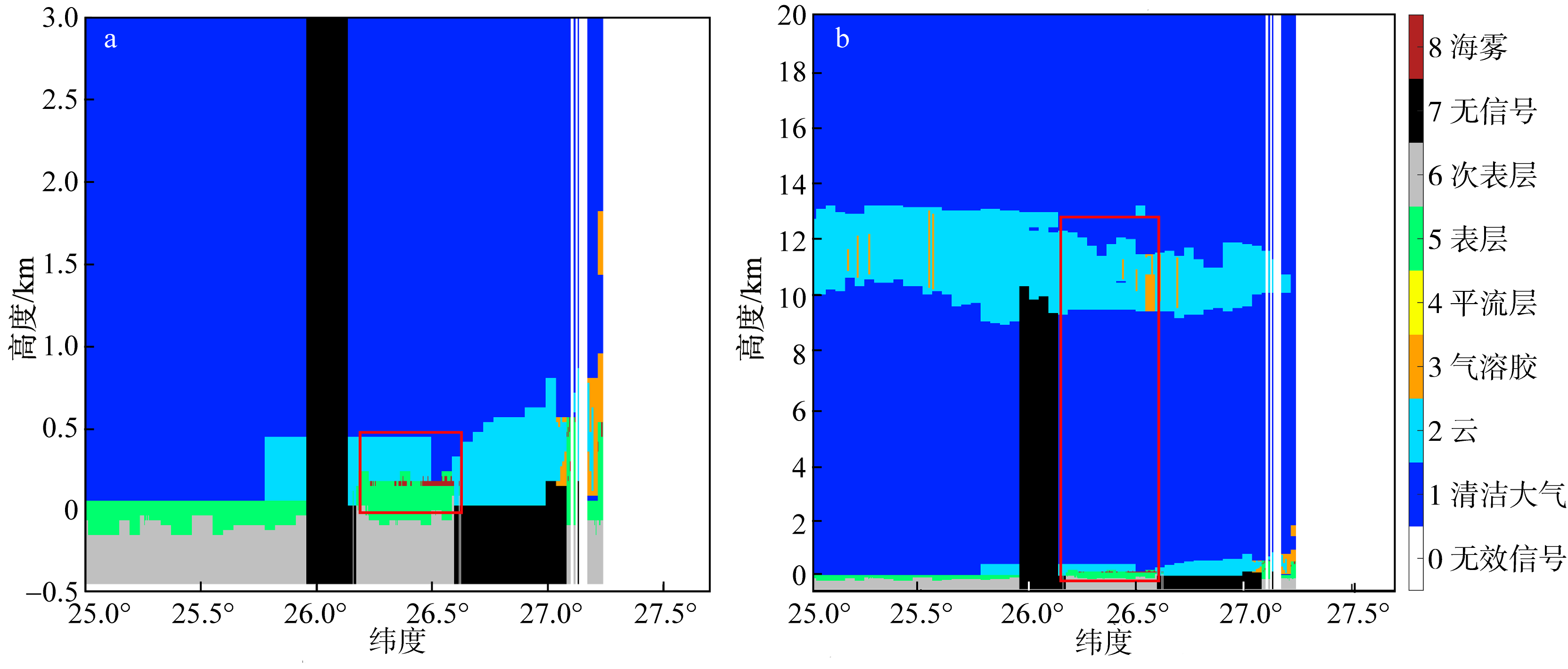
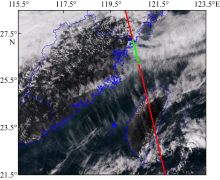
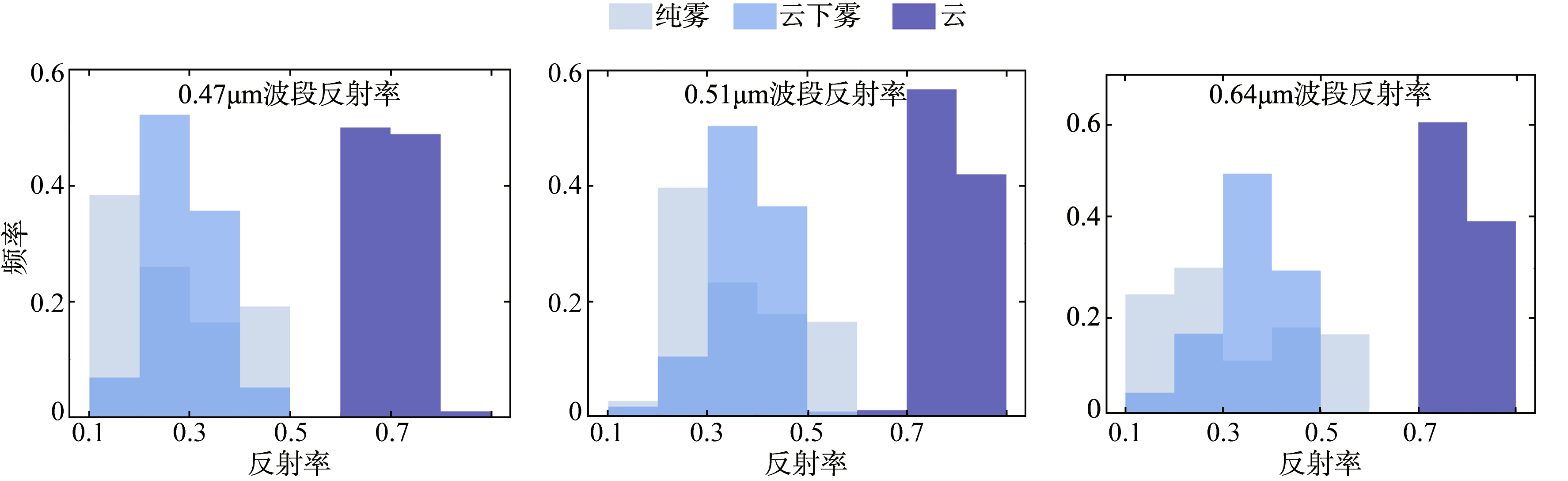
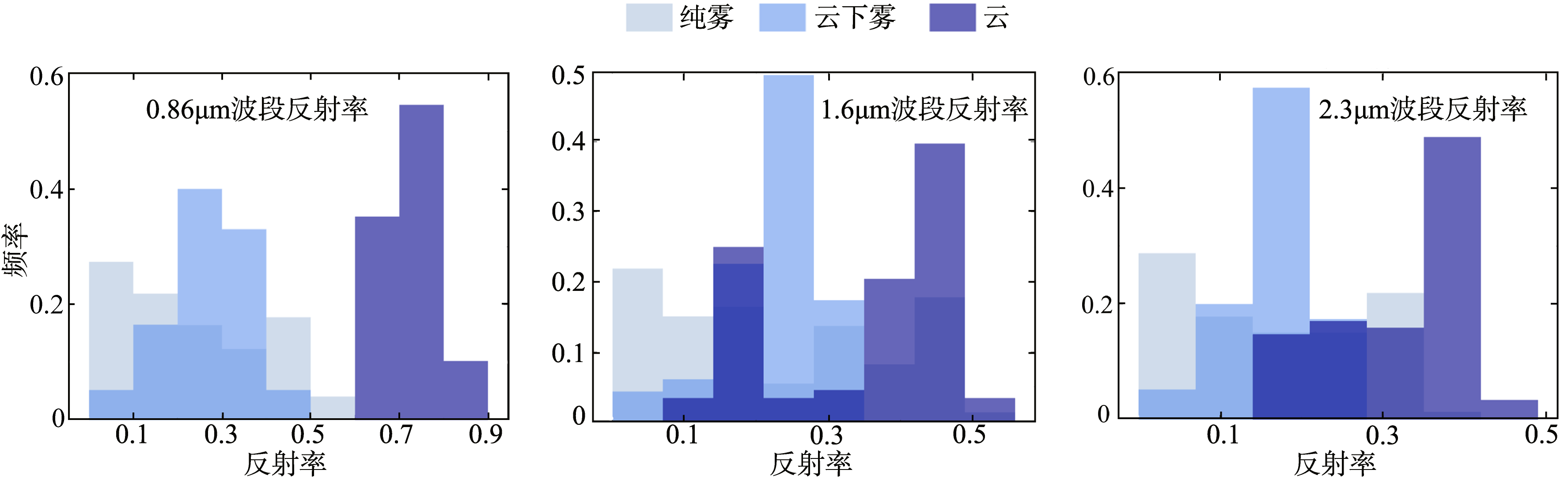
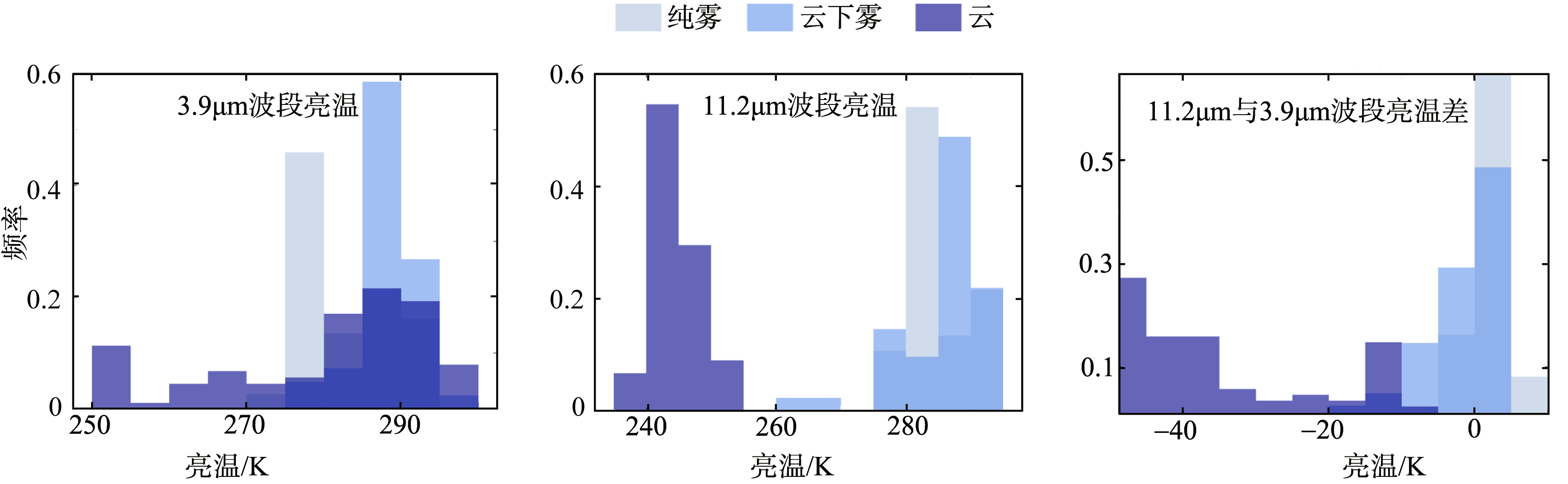
CALIOP remote sensing monitoring of the Fujian sea fog and spectral characteristics analysis of subcloud fog based on Himawari-8
HU Chenyue1( ), QIU Zhongfeng1, LIAO Kuo2(
), QIU Zhongfeng1, LIAO Kuo2( ), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao3
), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao3
- 1. Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2. Fujian Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Fuzhou 350008, China
3. Suqian Environmental Monitoring Center, Suqian 223800, China
-
Received:2022-10-09Revised:2022-12-14Online:2023-07-10Published:2022-12-19 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976165)
Cite this article
HU Chenyue, QIU Zhongfeng, LIAO Kuo, ZHAO Dongzhi, WU Daomao. CALIOP remote sensing monitoring of the Fujian sea fog and spectral characteristics analysis of subcloud fog based on Himawari-8[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 104-112.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
郝姝馨, 郝增周, 黄海清, 等, 2021. 基于Himawari-8数据的夜间海雾识别[J]. 海洋学报, 43(11): 166-180.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
李琦, 蔡淼, 周毓荃, 等, 2021. 基于探空云识别方法的云垂直结构分布特征[J]. 大气科学, 45(6): 1161-1172.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
李昀英, 王汉杰, 2000. 台湾海峡地区雾形成的天气类型分析[J]. 热带海洋, (4): 65-70.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
刘柏鑫, 李栋梁, 2018. 我国云量时空变化特征及其与副热带夏季风北边缘带关系研究[J]. 气象, 44(3): 382-395.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
刘少军, 吴胜安, 李伟光, 等, 2017. 基于 FY-3B 卫星资料的中国南海海区 1-3 月海雾时空分布特征研究[J]. 海洋气象学报, 37(4): 85-90.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
马静, 于芸, 魏立新, 2012. 东海近海海雾日变化特征及生成的水文气象条件分析[J]. 海洋预报, 29(6): 58-65.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
孙艺, 杨悦, 甄晴, 2020. CALIPSO卫星资料的春夏季黄海海雾高度特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 37(3): 54-61.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
田永杰, 2016. 基于风云 2 号静止卫星数据的白天海雾监测算法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
张春桂, 蔡义勇, 张加春, 2009. MODIS 遥感数据在我国台湾海峡海雾监测中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 20(1): 8-16.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
张春桂, 何金德, 马治国, 2013. 福建沿海海雾的卫星遥感监测[J]. 中国农业气象, 34(3): 366-373.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
张春桂, 林炳青, 2018. 基于 FY-2E 卫星数据的福建沿海海雾遥感监测[J]. 国土资源遥感, 30(1): 7-13.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
张苏平, 鲍献文, 2018. 近十年中国海雾研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 359-366.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
赵耀天, 吴东, 2020. CALIOP、CPR 数据在探测海雾中的应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 50(10): 125-133.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.2151/jmsj.2016-009 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1007/s00024-007-0213-8 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.3390/electronics9020311 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.3390/rs12091521 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1364/OE.454570 pmid: 35472986 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1175/2009JTECHA1281.1 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2014.09.021 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.3390/rs13051042 |
| [1] | LIAO Kuo, LI Kailin, DANG Haofei, LIN Bin, ZHAO Dongzhi, LI Hui. Process and characteristics of occurrence and dissipation of sea fog in the west coast of the Taiwan Strait based on coastal automatic weather station* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 79-93. |
| [2] | WANG Yu, HU Chenyue, QIU Zhongfeng, ZHAO Dongzhi, WU Daomao, LIAO Kuo. Research on the multi-source satellite daytime sea fog detection technology based on cloud characteristics* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 15-28. |
| [3] | Xiaolong HUANG, Zhiyou JING, Ruixi ZHENG, Xu ZHANG. Analysis of submesoscale characteristics of summer upwelling fronts in the western South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(3): 1-9. |
| [4] | LI Xue, FU Dongyang, ZHANG Ying, LIU Dazhao, DING Youzhuan, WANG Wenfang, LUAN Hong, JIANG Chengfei. The impacts of super typhoon Rammasun on the environment of the northwestern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(6): 19-28. |
| [5] | GUAN Wei, CHEN Jiajie, XU Zhaoli. The distribution and seasonal variation of fish populations in the southwest waters of the Nanri Islands and their relationships with the variation of water masses* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(3): 65-71. |
| [6] | XIA Li-hua, WU Hui-ming, LIU Ming, LENG Dian-song, LI Ting-ting. Characteristic analysis of storm surges along Fujian coast associated with tropical cyclones [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(3): 40-45. |
| [7] | LIN Rui, ZHANG Cai-yun, LI Yan. Satellite observation of the temporal and spatial variation of sea surface diurnal warming in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 17-27. |
| [8] | XU Jin-dian, CAI Shang-zhan, XUAN Li-li, QIU Yun, ZHOU Xi-wu, ZHU Da-yong. Observational study on summertime upwelling in coastal seas between eastern Guangdong and southern Fujian [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 1-9. |
| [9] | YANG Ding-tian, LIU Su-min, SHAN Xiu-juan. Progress in detecting seagrass carbon flux over optically shallow water using satellite remote sensing [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(6): 108-114. |
| [10] | YANG Qi, OU Jian-jun, LI Yong-ping. An objective forecast method for sea fog over the Yangshan Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 59-64. |
| [11] | WANG Xin-xin, YANG Jian-hong, ZHAO Dong-zhi, WANG Xiang, SUN Guang-lun. Assessment of Aquarius/SAC-D salinity data accuracy in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 23-28. |
| [12] | YANG He-qun,YANG Yin-ming. Progress in objective position methods of tropical cyclone center using satellite remote sensing [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(2): 15-27. |
| [13] | YAO Yue,XU Hui-ping. Preliminary application of remote sensing: reclamation on Fujian coast and its effects on marine environment [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(1): 72-78. |
| [14] | WANG Wen-qi,DONG Qiang,SHANG Shao-ling,WU Jing-yu,LEE Zhong-ping. An evaluation of two semi-analytical ocean color algorithms for waters off South China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(5): 35-42. |
| [15] | YANG Ding-tian. Investigating internal waves east of the Hainan Island using optical satellite remote sensing data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(5): 29-34. |
|
||