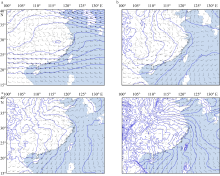
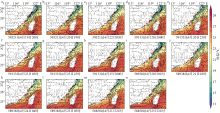
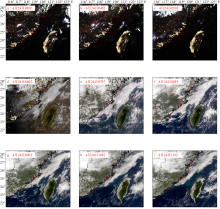
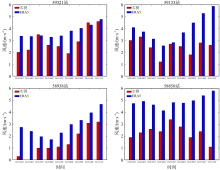
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 79-93.doi: 10.11978/2023050CSTR: 32234.14.2023050
• Marine Meteorology • Previous Articles Next Articles
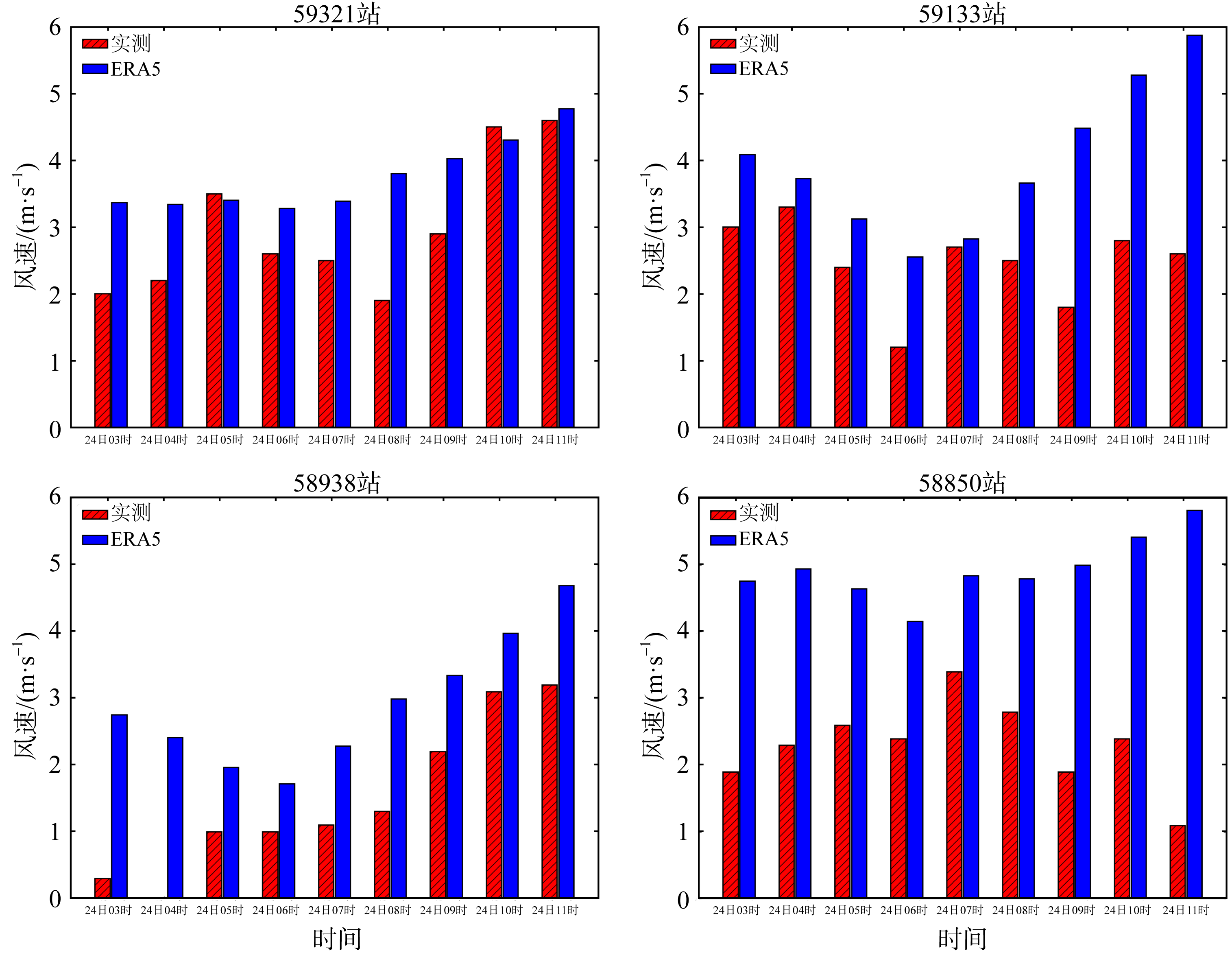
Process and characteristics of occurrence and dissipation of sea fog in the west coast of the Taiwan Strait based on coastal automatic weather station*
LIAO Kuo1,2( ), LI Kailin1,2(
), LI Kailin1,2( ), DANG Haofei1,2, LIN Bin3, ZHAO Dongzhi4, LI Hui5
), DANG Haofei1,2, LIN Bin3, ZHAO Dongzhi4, LI Hui5
- 1. Fujian Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Fuzhou 350007, China
2. Wuyishan National Climatological Observation, Wuyishan 354300, China
3. Pingtan Meteorological Bureau, Pingtan 350400, China
4. Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
5. Beijing Kunyu Tianxin Science and Technology Ltd, Beijing 100010, China
-
Received:2023-04-20Revised:2020-06-01Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-19 -
Supported by:East China Collaborative Innovation Fund for Meteorological Science and Technology(QYHZ202110); Innovative Development Project of China Meteorological Administration 2022(CXFZ2022P010); Advanced Program for FY Satellite Applications 2022(FY-APP-2022.0610)
Cite this article
LIAO Kuo, LI Kailin, DANG Haofei, LIN Bin, ZHAO Dongzhi, LI Hui. Process and characteristics of occurrence and dissipation of sea fog in the west coast of the Taiwan Strait based on coastal automatic weather station*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 79-93.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
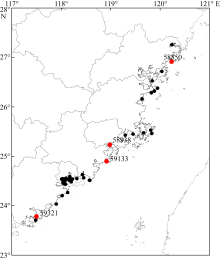
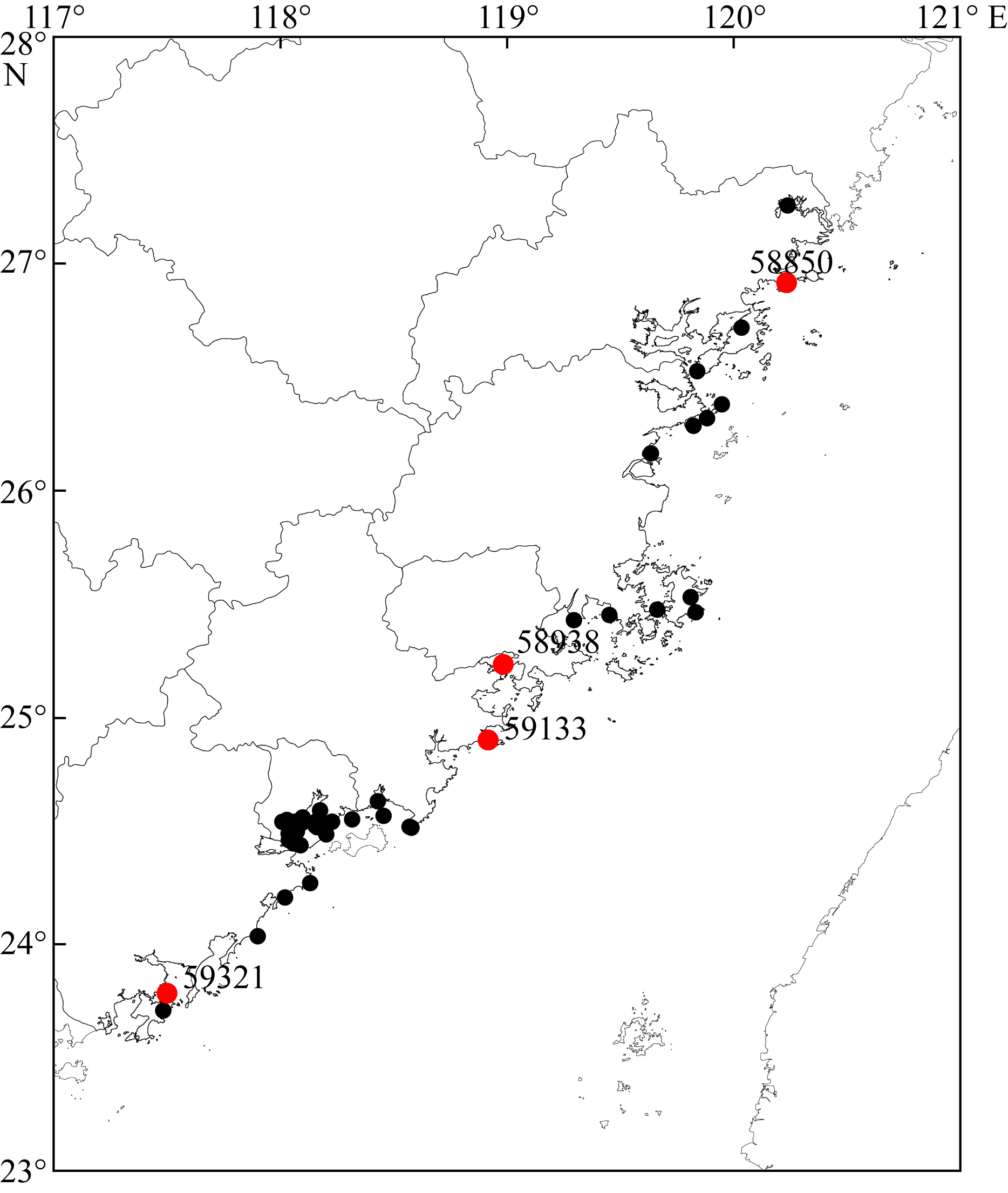
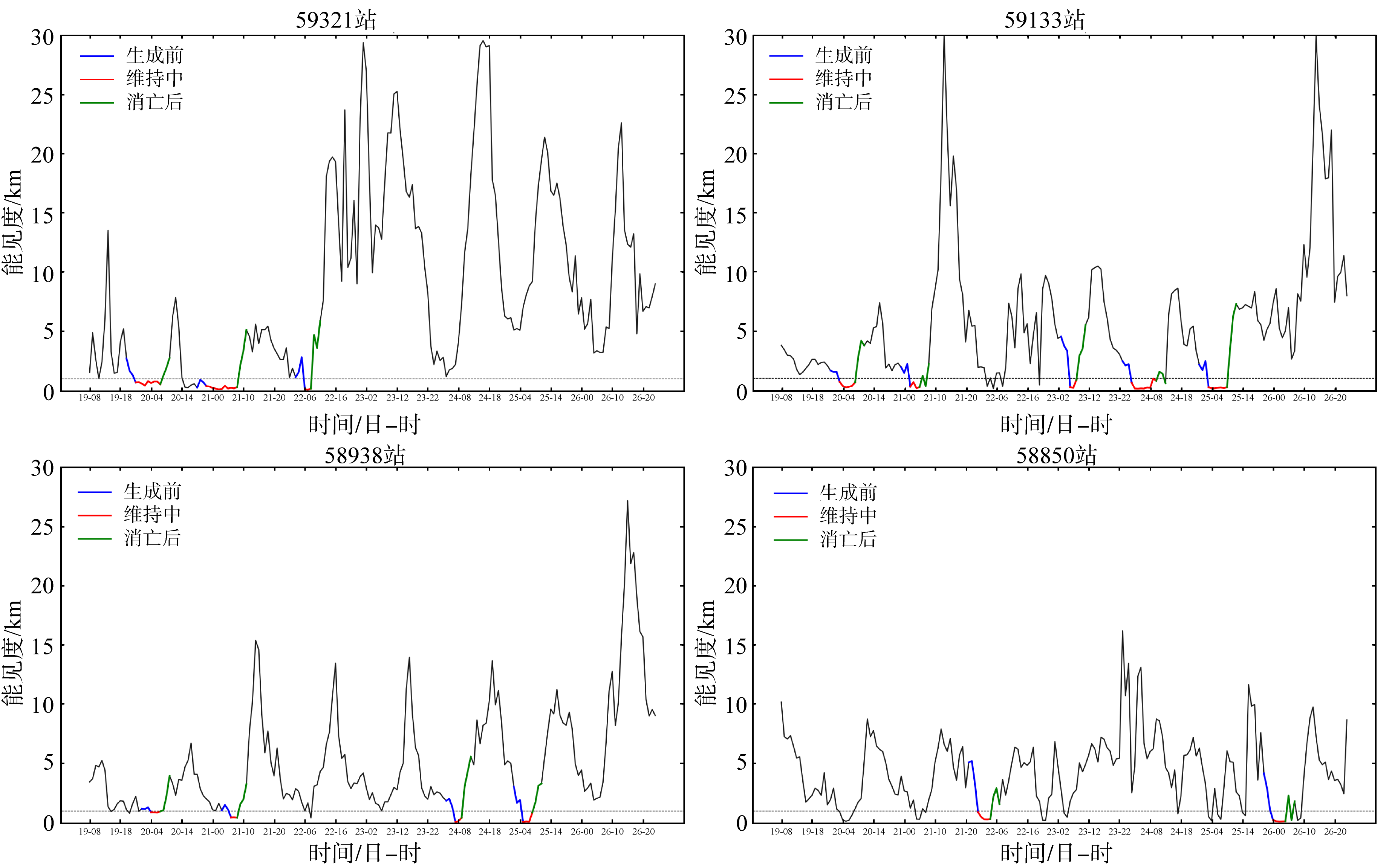
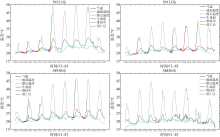
Tab.1
Time of occurrence and dissipation of sea fog at Automatic weather station"
| 站号 | 次数 | 海雾时间 | 海雾生成时间 | 海雾消亡时间 | 海雾持续时间/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59321 | 1 | 4月19日23时—20日07时 | 19日20时 | 20日10时 | 9 |
| 2 | 4月20日22时—21日08时 | 20日19时 | 21日11时 | 11 | |
| 3 | 4月22日06时—22日08时 | 22日03时 | 22日11时 | 3 | |
| 59133 | 1 | 4月20日03时—20日07时 | 20日00时 | 20日10时 | 5 |
| 2 | 4月21日02时—21日07时 | 20日23时 | 21日08时 | 6 | |
| 3 | 4月23日06时—23日08时 | 23日03时 | 23日11时 | 3 | |
| 4 | 4月24日03时—24日10时 | 24日00时 | 24日13时 | 8 | |
| 5 | 4月25日03时—25日09时 | 25日00时 | 25日12时 | 7 | |
| 58938 | 1 | 4月20日04时—20日07时 | 20日01时 | 20日10时 | 4 |
| 2 | 4月21日06时—21日08时 | 21日03时 | 21日11时 | 3 | |
| 3 | 4月24日07时—24日09时 | 24日04时 | 24日12时 | 3 | |
| 4 | 4月25日05时—25日08时 | 25日02时 | 25日11时 | 4 | |
| 58850 | 1 | 4月22日00时—22日04时 | 21日21时 | 22日07时 | 5 |
| 2 | 4月26日00时—26日04时 | 25日21时 | 26日07时 | 5 |
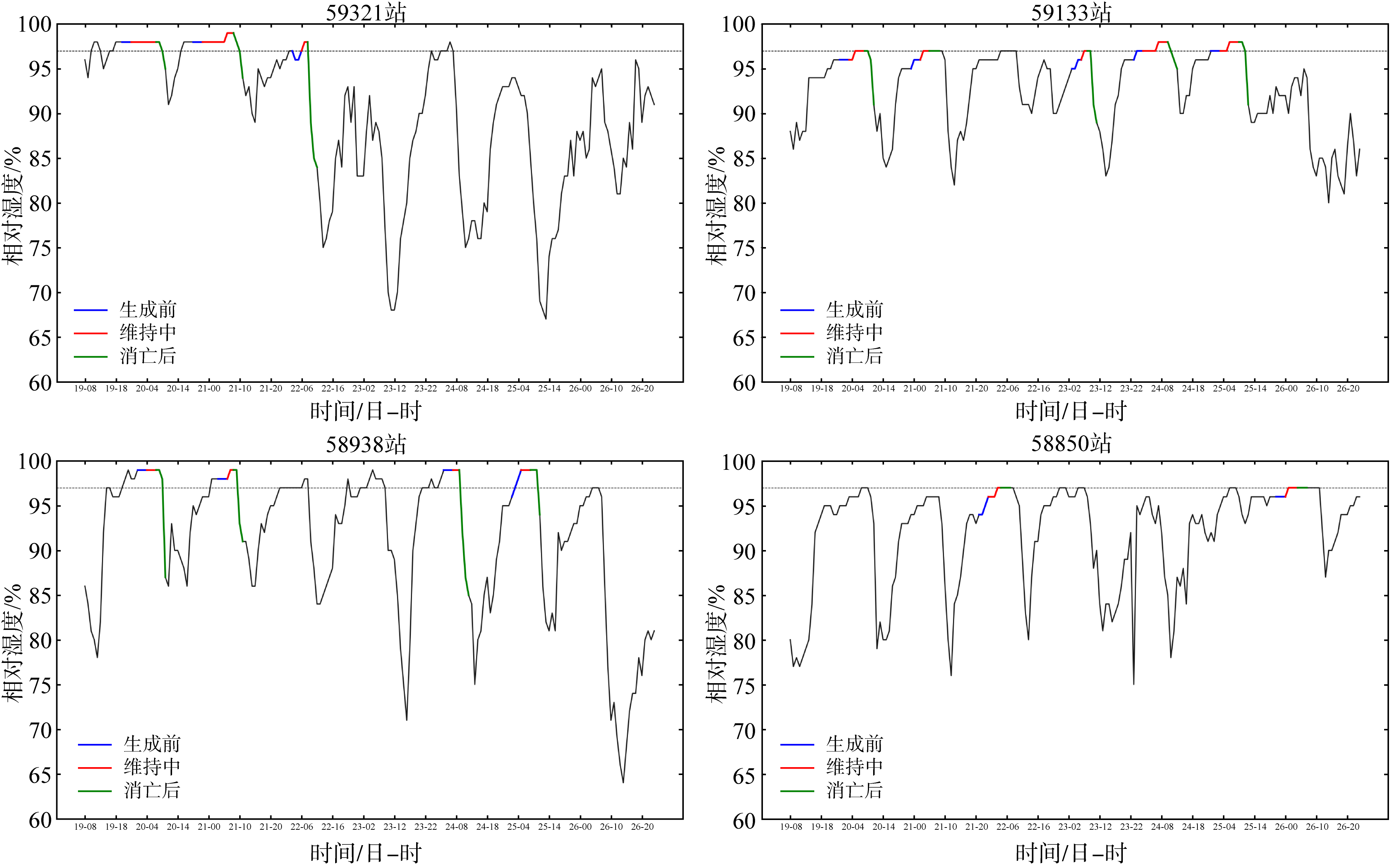
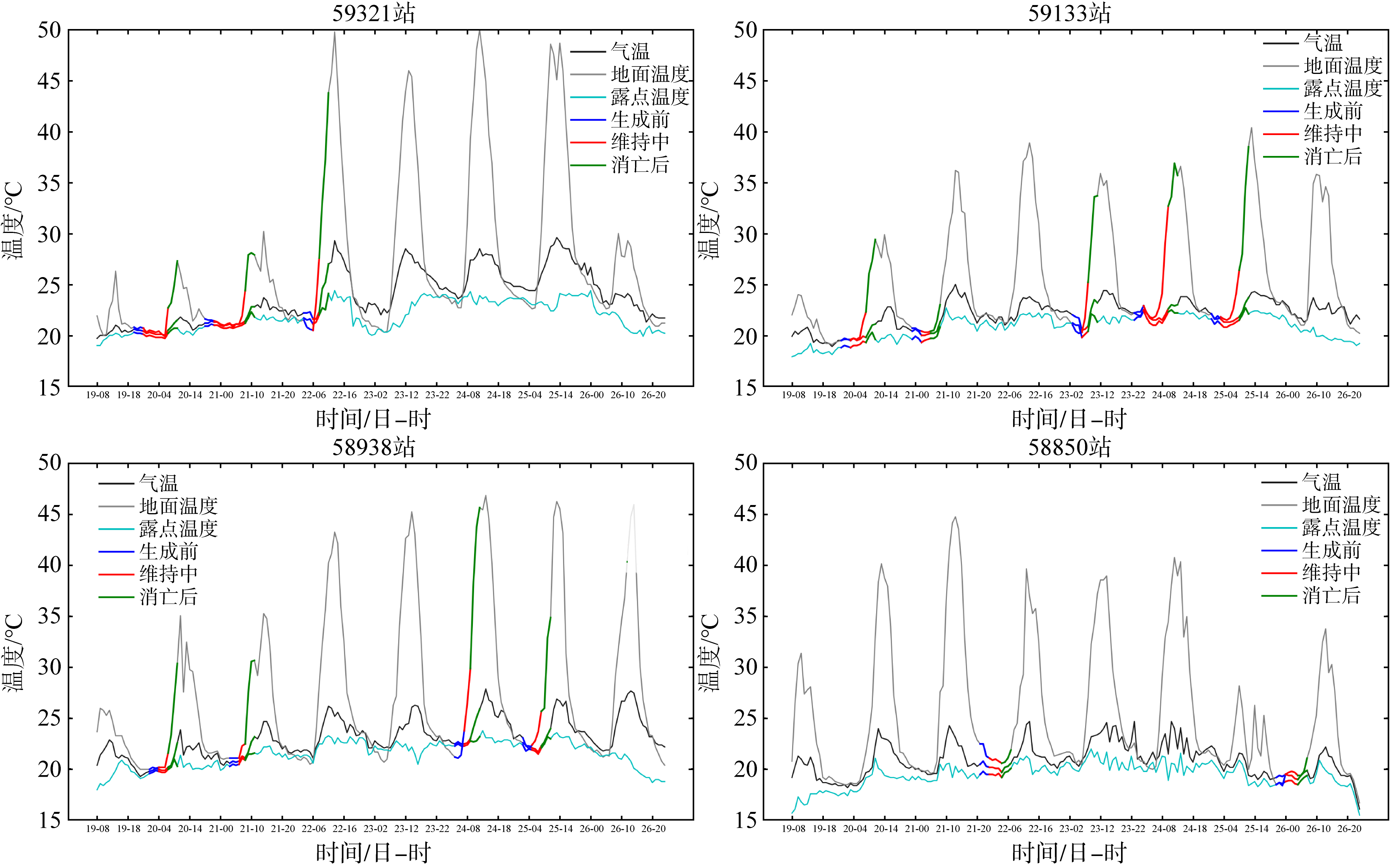
Tab. 2
Three temperature differences during sea fog progress (unit:℃)"
| 站点 | 生消过程 | LST-T变化区间 | LST-Td变化区间 | T-Td变化区间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59321 | 生成前 | -1.7~0.4 | -1~0.7 | 0.3~0.7 |
| 过程中 | -0.1~2.2 | -0.6~5.6 | 0~0.5 | |
| 消亡后 | 2.4~16.8 | 2.7~19.7 | 0.3~2.9 | |
| 59133 | 生成前 | -1.5~0.3 | -0.8~1.1 | 0.5~0.8 |
| 过程中 | -0.4~10.1 | 0~10.4 | 0~0.7 | |
| 消亡后 | 1.7~14.8 | 2.2~16.4 | 0.3~1.9 | |
| 58938 | 生成前 | 0.0~0.5 | 0.2~0.8 | 0.2~0.3 |
| 过程中 | 0.2~0.4 | 0.4~0.7 | 0.2~0.3 | |
| 消亡后 | 1~7.9 | 1.2~10.1 | 0.2~2.3 | |
| 58850 | 生成前 | -0.7~2 | -0.2~2.7 | 0.7~1 |
| 过程中 | 0~0.9 | 0.7~1.8 | 0.5~0.7 | |
| 消亡后 | 0~1.3 | 0.5~1.8 | 0.5~0.5 |
| [1] |
白彬人, 2006. 中国近海沿岸海雾规律特征、机理及年际变化的研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈千盛, 1986. 台湾岛和福建沿岸的雾[J]. 台湾海峡, 5(2): 101-106.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈玉珍, 黄玉藻, 1999. 湄洲湾海雾的初步分析[J]. 台湾海峡, 18(1): 49-54.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
郭丽君, 郭学良, 2016. 北京2009-2013年期间持续性大雾的类型、垂直结构及物理成因[J]. 大气科学, 40(2): 296-310.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
韩美, 高珊, 曾瑾瑜, 等, 2016. 台湾海峡西岸海雾研究现状与未来发展方向[J]. 气象科技, 44(6): 928-937.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
郝姝馨, 2022. 基于新一代静止气象卫星的夜间海雾跟踪监测与分析研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
何秀恋, 林荣惠, 王双才, 等, 2012. 福建南部一次初春大雾过程分析[J]. 海洋预报, 29(4): 60-64.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
胡晨悦, 丘仲锋, 廖廓, 等, 2023. 福建海雾的CALIOP遥感监测及基于Himawari-8的云下雾光谱特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(4): 104-112.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
黄彬, 郭云谦, 张增海, 2014. 海雾历史检索数据库的设计和实现[J]. 气象科技, 42(1): 94-98.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
黄辉军, 黄健, 刘春霞, 等, 2013. 用近地层温差因子改进广东沿海海雾区域预报[J]. 热带气象学报, 29(6): 907-914.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
黄惠镕, 韩美, 潘宁, 等, 2019. 福建一次春季海雾的边界层特征及其成因分析[J]. 海峡科学, 147(3): 12-15+25 (in Chinese).
|
| [12] |
李昀英, 王汉杰, 2000. 台湾海峡地区雾形成的天气类型分析[J]. 热带海洋, 19(4): 65-70.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
廖晨菲, 冯志明, 高聪晖, 等, 2022. 福建沿海一次持续性海雾过程的边界层特征分析[J]. 海峡科学, 187(7): 9-13 (in Chinese).
|
| [14] |
林丽萱, 郑中凯, 郑颖青, 等, 2021. 2014-2020年福州地区沿岸雾日特征分析[J]. 海峡科学, 174(6): 44-46 (in Chinese).
|
| [15] |
林卫华, 蒋荣复, 王正廷, 2008. 湄洲湾海雾的发生规律和成因分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 26(3): 71-76.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
马治国, 张春桂, 陈家金, 等, 2011. 福建省沿海雾的气候变化特征分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 32(增1): 69-73.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
孟宪贵, 郭俊建, 韩永清, 2018. ERA5再分析数据适用性初步评估[J]. 海洋气象学报, 38(1): 91-99.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
牛生杰, 陆春松, 吕晶晶, 等, 2016. 近年来中国雾研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 6(2): 6-19.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
苏鸿明, 1998. 台湾海峡海雾的气候分析[J]. 台湾海峡, 17(1): 25-28.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
涂石飞, 韩利国, 徐峰, 等, 2019. 华南海雾研究进展[J]. 海洋气象学报, 39(4): 12-20.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
王彬华, 1983. 海雾[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [22] |
王博妮, 张雪蓉, 濮梅娟, 等, 2019. 一次平流雾的形成和传播特征研究[J]. 气象, 45(3): 395-406.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
翁国玲, 黄志刚, 陈宏, 等, 2015. 1961—2010年平潭大雾的年际特征及雾季环流分析[J]. 海洋预报, 32(1): 79-86.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
肖艳芳, 张杰, 崔廷伟, 等, 2017. 海雾卫星遥感监测研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 41(12): 146-154.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
衣立, 2015. 黄海海雾/层云的空间分布及云底高度遥感方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
张春桂, 蔡义勇, 张加春, 2009. MODIS遥感数据在我国台湾海峡海雾监测中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 20(1): 8-16.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
张春桂, 何金德, 马治国, 2013. 福建沿海海雾的卫星遥感监测[J]. 中国农业气象, 34(3): 366-373.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
张春桂, 林炳青, 2018. 基于FY-2E卫星数据的福建沿海海雾遥感监测[J]. 自然资源遥感, 30(1): 7-13.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
张苏平, 刘飞, 孔扬, 2014. 一次春季黄海海雾和东海层云关系的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 45(2): 341-352.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
张伟, 陈德花, 胡雅君, 等, 2021. 闽南沿海一次春季海雾过程微物理特征分析[J]. 气象, 47(2): 157-169.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
张曦, 牛生杰, 魏锦成, 等, 2016. 厦门春季海雾天气分类及典型个例宏微观结构分析[J]. 气象科学, 36(1): 121-127.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
张悦, 樊曙先, 张舒婷, 等, 2015. 海峡西岸一次雾过程微结构及其起伏特征研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 31(3): 385-394.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
张振顺, 李岩招, 蔡世旺, 2015. 闽东海雾观测及其预报[J]. 科技创新与生产力, (7): 54-56 (in Chinese).
|
| [34] |
郑凤琴, 周绍毅, 韦晶晶, 等, 2020. 北部湾海雾特点及海陆大雾差异分析[J]. 气象科技, 48(5): 717-722.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
郑泽华, 张伟, 陈德花, 2021. 2020年5月5日凌晨福建中南沿海海雾过程特征及成因分析[J]. 海峡科学, 171(3): 3-10 (in Chinese).
|
| [36] |
中国气象局, QX/T113-2010. 霾的观测和预报等级[S]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
|
China Meteorological Administration, 2010. Observation and forecasting levels of haze[S]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press (in Chinese).
|
|
| [37] |
周发琇, 1988. 海雾及其分类[J]. 海洋预报, (1): 78-84 (in Chinese).
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1002/qj.v146.730 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1994)075<0229:FOTUWC>2.0.CO;2 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1007/s00343-015-4030-0 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118523 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1029/2017JD028088 |
| [44] |
|
| [1] | WANG Yu, HU Chenyue, QIU Zhongfeng, ZHAO Dongzhi, WU Daomao, LIAO Kuo. Research on the multi-source satellite daytime sea fog detection technology based on cloud characteristics* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 15-28. |
| [2] | HU Chenyue, QIU Zhongfeng, LIAO Kuo, ZHAO Dongzhi, WU Daomao. CALIOP remote sensing monitoring of the Fujian sea fog and spectral characteristics analysis of subcloud fog based on Himawari-8 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 104-112. |
| [3] | YANG Qi, OU Jian-jun, LI Yong-ping. An objective forecast method for sea fog over the Yangshan Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 59-64. |
|
||