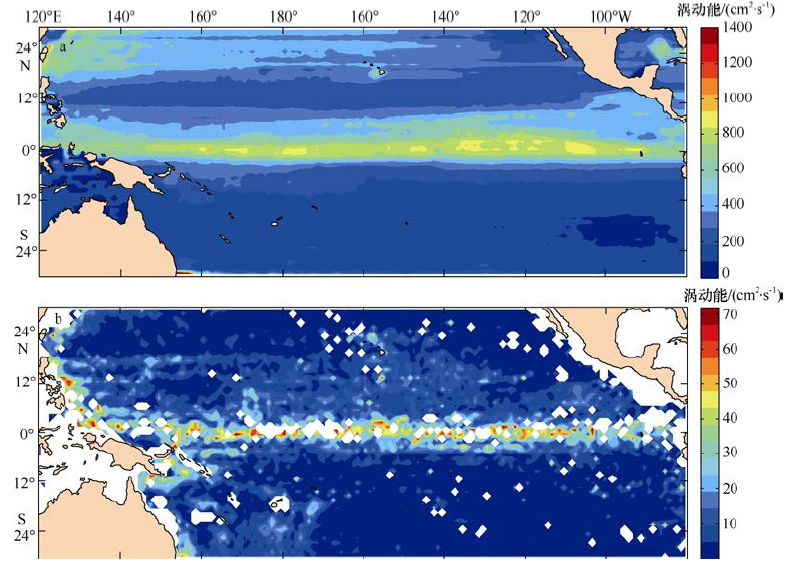
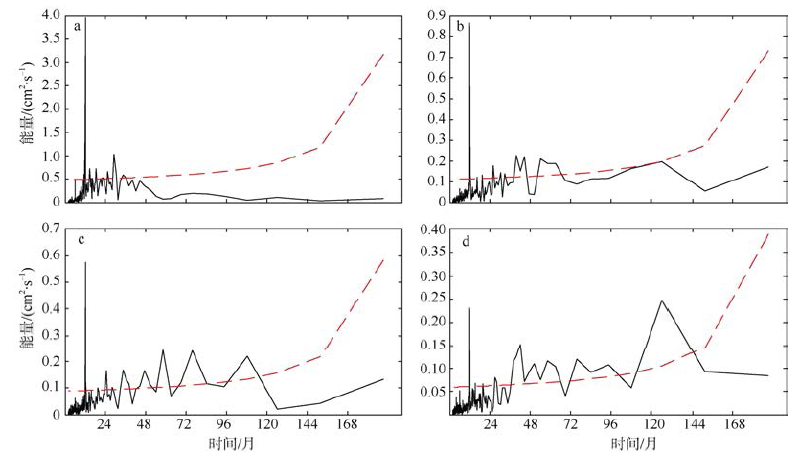
| [1] |
谢基平, 2005. 利用ARGO浮标提取中层海流信息研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学.
|
|
XIE JIPING, 2005. A study on the acquirablity of mid-depth current information by the Argo float[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Informarion (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
张涟漪, 杜岩, 郑少军, 等, 2016. 南印度洋表层副热带环流的漂流示踪[J]. 科学通报, 61(33): 3596-3605.
|
|
ZHANG LIANYI, DU YAN, ZHENG SHAOJUN, et al, 2016. Subtropical surface circulation in the southern Indian Ocean derived from surface drifters[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 61(33): 3596-3605 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
张人禾, 朱江, 许建平, 等, 2013. Argo大洋观测资料的同化及其在短期气候预测和海洋分析中的应用[J]. 大气科学, 37(2): 411-424.
|
|
ZHANG RENHE, ZHU JIANG, XU JIANPING, et al, 2013. Argo global ocean data assimilation and its applications in short-term climate prediction and oceanic analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 37(2): 411-424 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
CRAVATTE S, KESSLER W S, MARIN F, 2012. Intermediate zonal jets in the tropical Pacific Ocean observed by Argo floats[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42(9): 1475-1485.
|
| [5] |
DE MEY P, MÉNARD Y, 1989. Synoptic analysis and dynamical adjustment of GEOS 3 and Seasat altimeter eddy fields in the northwest Atlantic[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 94(C5): 6221-6230.
|
| [6] |
DUTRIEUX P, 2009. Tropical western Pacific currents and the origin of intraseasonal variability below the thermocline[D]. Manoa: University of Hawaii.
|
| [7] |
FIRING E, 1987. Deep zonal currents in the central equatorial Pacific[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 45(4): 791-812.
|
| [8] |
FRAILE-NUEZ E, HERNÁNDEZ-GUERRA A, 2006. Wind-driven circulation for the eastern North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre from Argo data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(3): L03601.
|
| [9] |
GOULD J, ROEMMICH D, WIJFFELS S, et al, 2004. Argo profiling floats bring new era of in situ ocean observations[J]. EOS Transactions American Geophysical Union, 85(19): 185-191.
|
| [10] |
HOGAN P J, HURLBURT H E, 2005. Sensitivity of simulated circulation dynamics to the choice of surface wind forcing in the Japan/East Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 52(11-13): 1464-1489.
|
| [11] |
HU DUNXIN, CUI MAOCHANG, 1991. The Western Boundary Current of the pacific and its role in the climate[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 9(1): 1-14.
|
| [12] |
HURLBURT H E, HOGAN P J, 2000. Impact of 1/8° to 1/64° resolution on Gulf Stream model-data comparisons in basin-scale subtropical Atlantic Ocean models[J]. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 32(3-4): 283-329.
|
| [13] |
KASHINO Y, ESPAÑA N, SYAMSUDIN F, et al, 2009. Observations of the North Equatorial Current, Mindanao Current, and Kuroshio current system during the 2006/07 El Niño and 2007/08 La Niña[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 65(3): 325-333.
|
| [14] |
LEBEDEV K V, YOSHINARI H, MAXIMENKO N A, et al, 2007. Velocity data assessed from trajectories of Argo floats at parking level and at the sea surface[R]. IPRC Technical Note No. 4(2): 1-16.
|
| [15] |
MARIN F, KESTENARE E, DELCROIX T, et al, 2010. Annual reversal of the equatorial intermediate current in the Pacific: observations and model diagnostics[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 40(5): 915-933.
|
| [16] |
OLLITRAULT M, RANNOU J P, 2013. ANDRO: an Argo-based deep displacement dataset[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 30(4): 759-788.
|
| [17] |
PARK J J, KIM K, 2013. Deep currents obtained from Argo float trajectories in the Japan/East Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 85: 169-181.
|
| [18] |
PARK J J, KIM K, CRAWFORD W R, 2004. Inertial currents estimated from surface trajectories of ARGO floats[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(13): L13307.
|
| [19] |
PARK J J, KIM K, KING B A, et al, 2005. An advanced method to estimate deep currents from profiling floats[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 22(8): 1294-1304.
|
| [20] |
QIU BO, CHEN SHUIMING, RUDNICK D L, et al, 2015. A new paradigm for the North Pacific subthermocline low-latitude western boundary current system[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 45(9): 2407-2423.
|
| [21] |
QIU BO, CHEN SHUIMING, SASAKI H, 2013a. Generation of the north equatorial undercurrent jets by triad baroclinic Rossby wave interactions[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 43(12): 2682-2698.
|
| [22] |
QIU BO, RUDNICK D L, CHEN SHUIMING, et al, 2013b. Quasi-stationary North Equatorial Undercurrent jets across the tropical North Pacific Ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(10): 2183-2187.
|
| [23] |
RHINES P B, 1975. Waves and turbulence on a beta-plane[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 69(3): 417-443.
|
| [24] |
ROEMMICH D, BELBÉOCH M, BELCHI P J V, et al, 2009. Argo: the challenge of continuing 10 years of progress[J]. Oceanography, 22(3): 26-35.
|
| [25] |
ROEMMICH D H, DAVIS R E, RISER S C, et al, 2004 [2017-01-02]. The ARGO Project: global ocean observations for understanding and prediction of climate variability. Report for calendar year 2004 [R/OL]. .
|
| [26] |
TOOLE J M, ZOU E, MILLARD R C, 1988. On the circulation of the upper waters in the western equatorial Pacific Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 35(9): 1451-1482.
|
| [27] |
XIE JIPING, ZHU JIANG, 2008. Estimation of the surface and mid-depth currents from Argo floats in the Pacific and error analysis[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 73(1-2): 61-75.
|
 ), Yan DU1,2(
), Yan DU1,2( ), Tianyu WANG1,2, Qiang XIE1,3
), Tianyu WANG1,2, Qiang XIE1,3