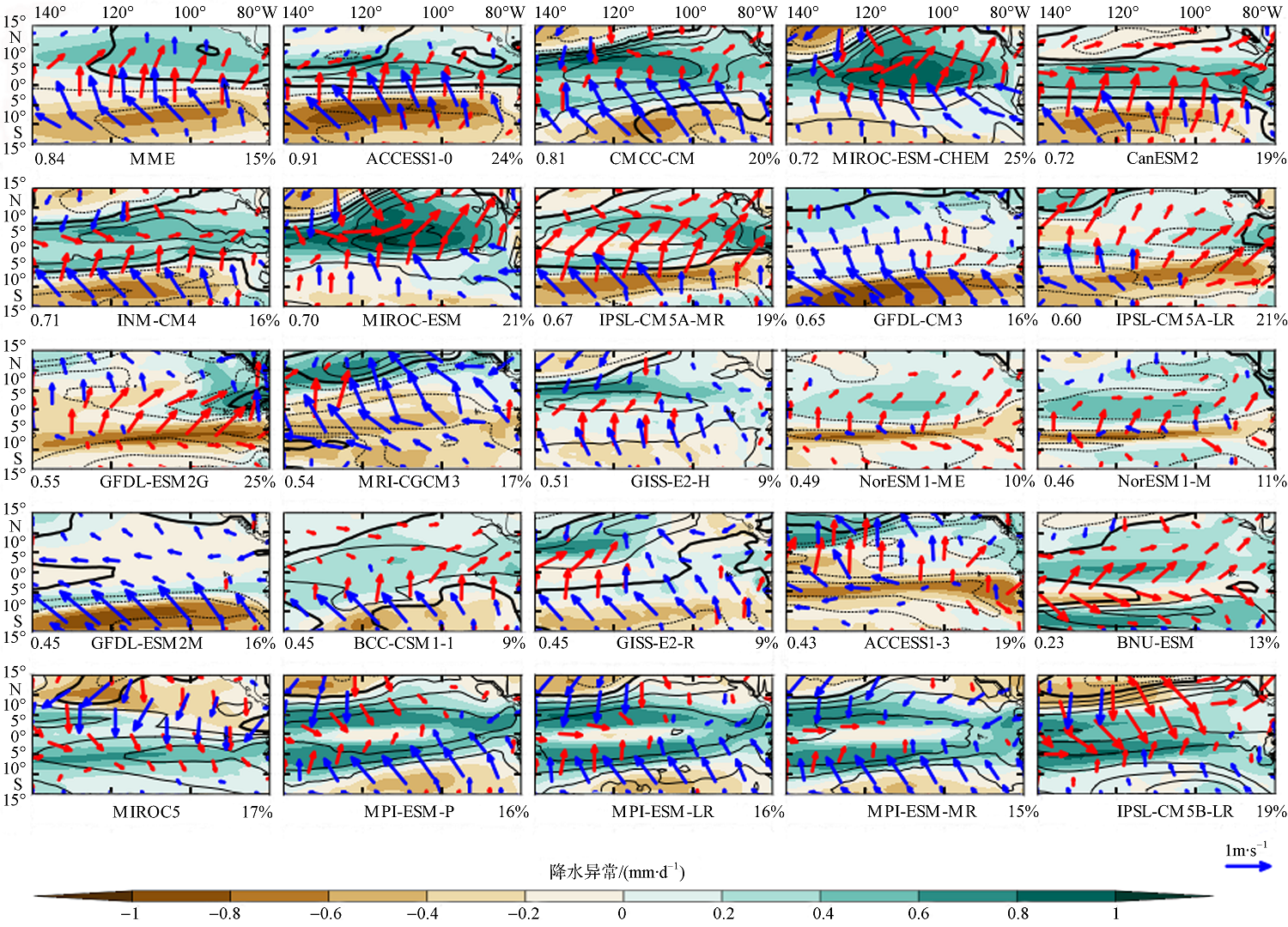
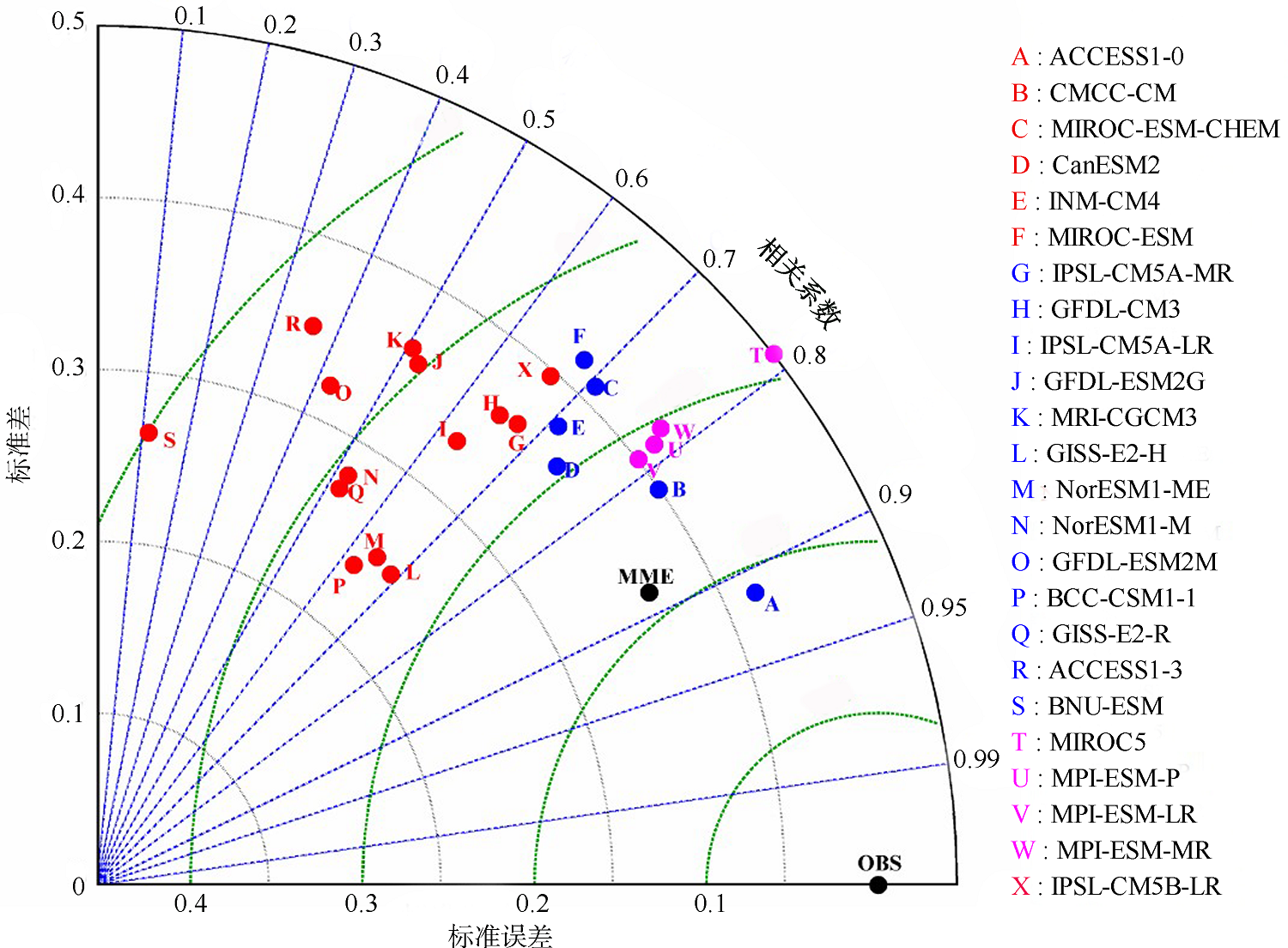
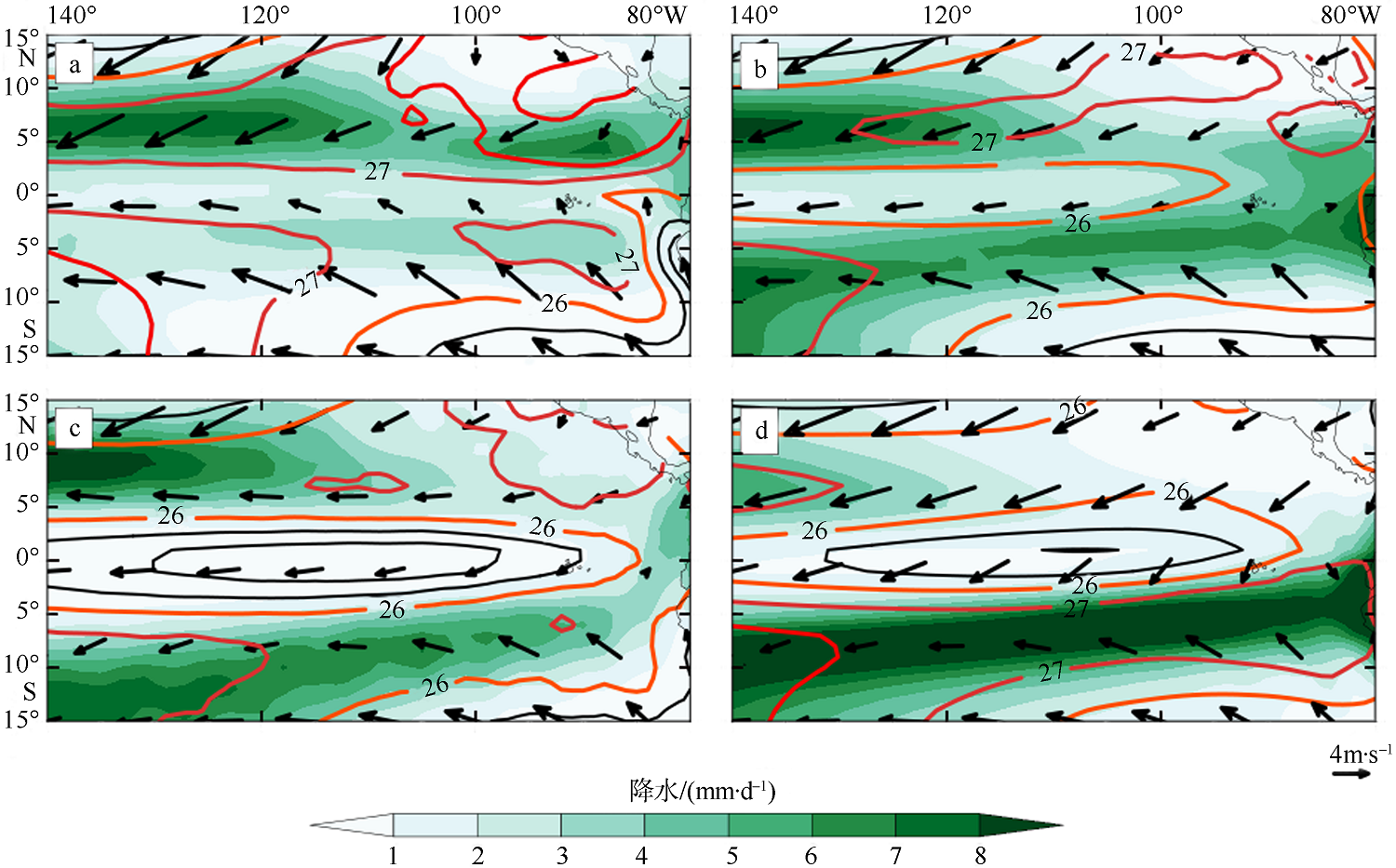
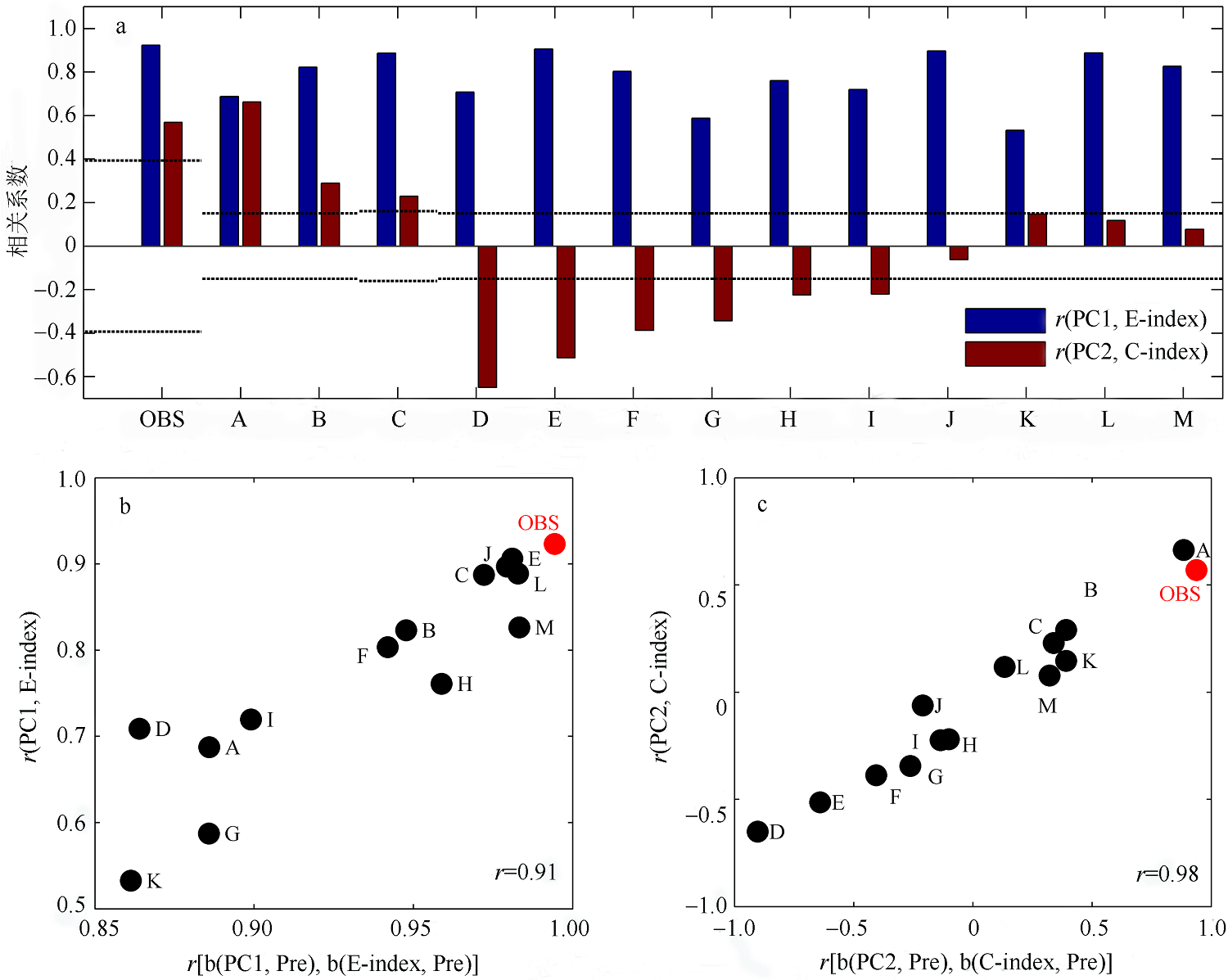
| [1] |
BELLUCCI A, GUALDI S, NAVARRA A, 2010. The Double-ITCZ Syndrome in Coupled General Circulation Models: The Role of Large-Scale Vertical Circulation Regimes[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(5):1127-1145.
doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI3002.1
|
| [2] |
CHIODI A M, HARRISON D E, 2013. El Niño impacts on seasonal U.S. atmospheric circulation,temperature, and precipitation anomalies: The OLR-event perspective[J]. Journal of Climate, 26(3):822-837.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00097.1
|
| [3] |
DEE D P, UPPALA S M, SIMMONS A J, et al, 2011. The ERA-Interim reanalysis:configuration and performance of the data assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 137:553-597.
doi: 10.1002/qj.828
|
| [4] |
HIRAHARA S, ISHII M, FUKUDA Y, 2014. Centennial-scale sea surface temperature analysis and its uncertainty[J]. Journal of Climate , 27(1):57-75.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00837.1
|
| [5] |
JOHNSON N C, KOSAKA Y, 2016. The impact of eastern equatorial Pacific convection on the diversity of boreal winter El Niño teleconnection patterns[J]. Climate Dynamics, 47(12):3737-3765.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-016-3039-1
|
| [6] |
LENGAIGNE M, VECCHI G A, 2010. Contrasting the termination of moderate and extreme El Niño events in coupled general circulation models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 35(2-3):299-313.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-009-0562-3
|
| [7] |
OUESLATI B, BELLON G, 2015. The double ITCZ bias in CMIP5 models: interaction between SST, large-scale circulation and precipitation[J]. Climate Dynamics, 44(3-4):585-607.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-015-2468-6
|
| [8] |
PENG QIHUA, XIE SHANGPING, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2019. Coupled ocean-atmosphere dynamics of the 2017 extreme coastal El Nino[J]. Nature Communications, 10(1):298.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08258-8
pmid: 30655541
|
| [9] |
PENG QIHUA, XIE SHANGPING, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2020. Eastern Pacific Wind Effect on the Evolution of El Niño: Implications for ENSO Diversity[J]. Journal of Climate, 33(8):3197-3212.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0435.1
|
| [10] |
TAKAHASHI K, MONTECINOS A, GOUBANOVA K, et al, 2011. ENSO regimes: Reinterpreting the canonical and Modoki El Niño[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(10):L10704.
|
| [11] |
TAYLOR K E, 2001. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(D7):7183-7192.
doi: 10.1029/2000JD900719
|
| [12] |
TAYLOR K E, STOURFFER R J, MEEHL G A, 2012. An Overview of CMIP5 and the Experiment Design[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 93(4):485-498.
doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1
|
| [13] |
WANG CHUNZAI, XIE SHANG-PING, CARTON JA, 2004. A global survey of ocean-atmosphere interaction and climate variability[M]// WANG CHUNZAI, XIE SHANGPING, CARTON J A. Earth’s Climate: The Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction. America: AGU Geophysical Monograph Series, 147:1-19.
|
| [14] |
XIE SHANGPING, ARKIN P A, 1997. Global precipitation:A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 78(11):2539-2558.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<2539:GPAYMA>2.0.CO;2
|
| [15] |
XIE SHANGPING, PENG QIHUA, KAMAE Y, et al, 2018. Eastern Pacific ITCZ dipole and ENSO diversity[J]. Journal of Climate, 31(11):4449-4462.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0905.1
|
| [16] |
ZHANG XIAOXIAO, LIU HAILONG, ZHANG MINGHUA, 2015. Double ITCZ in Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Models: From CMIP3 to CMIP5[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(20):8651-8659.
doi: 10.1002/2015GL065973
|
 ), ZHENG Xiaotong1,2,3
), ZHENG Xiaotong1,2,3