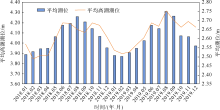
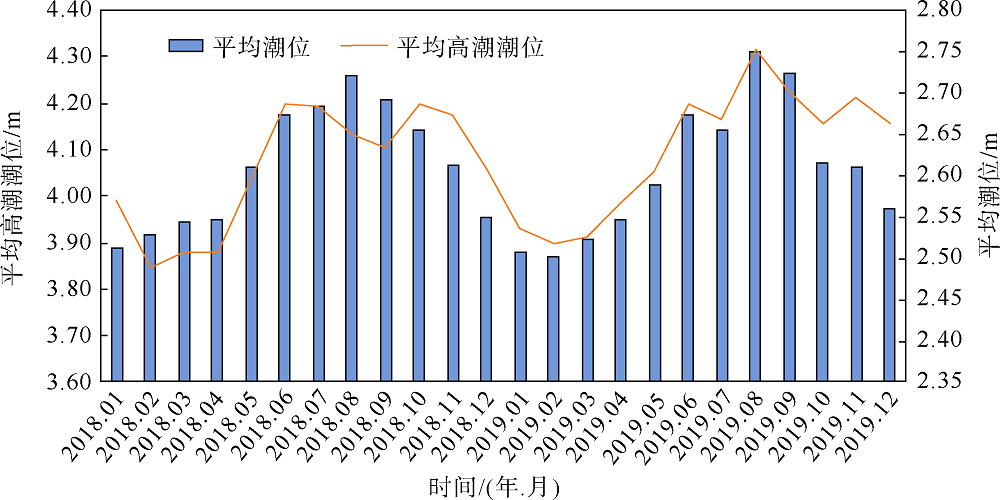
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 51-60.doi: 10.11978/2021096CSTR: 32234.14.2021096
• Marine geomorphology • Previous Articles Next Articles
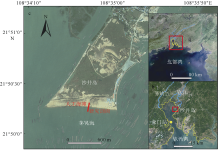
Changes of the artificial beach profile in the Qinzhou Bay
FENG Bingbin1,2( ), WANG Riming3,4, LI Shushi3, HUANG Hu3(
), WANG Riming3,4, LI Shushi3, HUANG Hu3( ), HU Baoqing1
), HU Baoqing1
- 1. Key Laboratory of Beibu Gulf Environmental Change and Resource Use, Ministry of Education (Nanning Normal University), Nanning 530000, China
2. School of Geography and Planning (Nanning Normal University), Nanning 530000, China
3. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Marine Disaster Research in Beibu Gulf (Beibu Gulf University), Qinzhou 535011, China
4. Qinzhou Key Laboratory of Environmental and Ecological Restoration (Beibu Gulf University), Qinzhou 535011, China
-
Received:2021-07-28Revised:2021-10-28Online:2022-07-10Published:2021-10-25 -
Contact:HUANG Hu E-mail:FengBingbin@163.com;mrhuanghu@126.com -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province(2018JJD150005);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41930537);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41666003);Guangxi Key Research and Development Program(AB21076016)
CLC Number:
- P737.13
Cite this article
FENG Bingbin, WANG Riming, LI Shushi, HUANG Hu, HU Baoqing. Changes of the artificial beach profile in the Qinzhou Bay[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 51-60.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
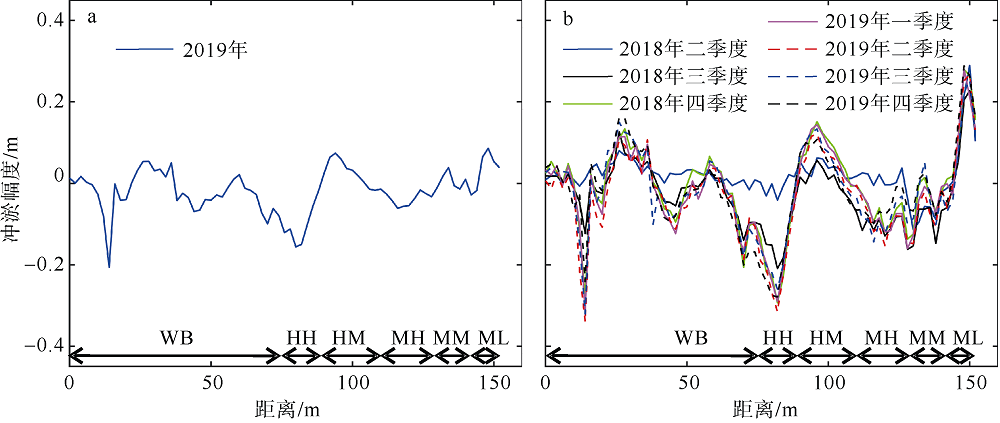
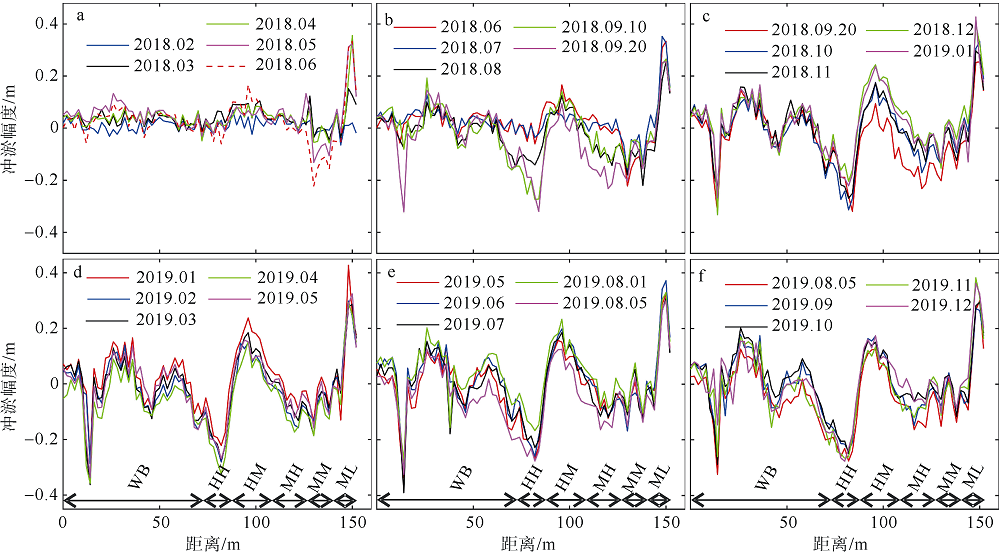
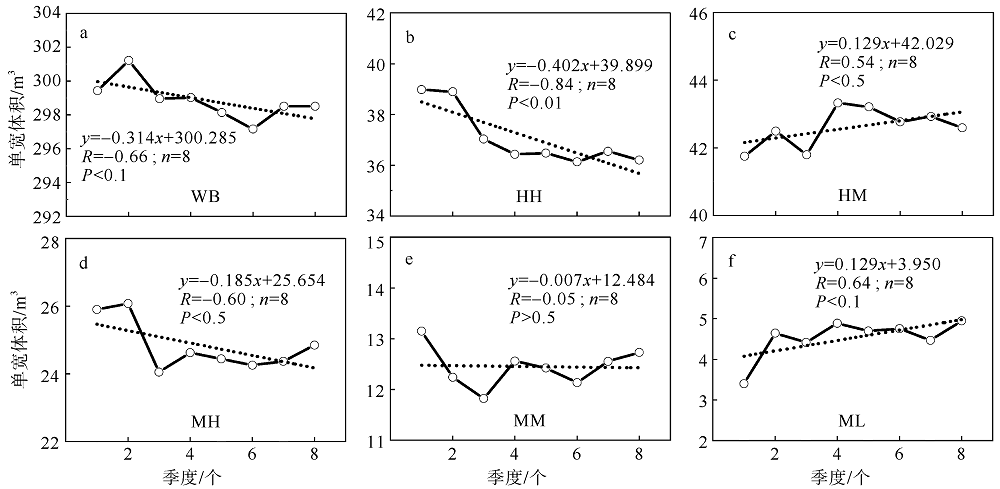
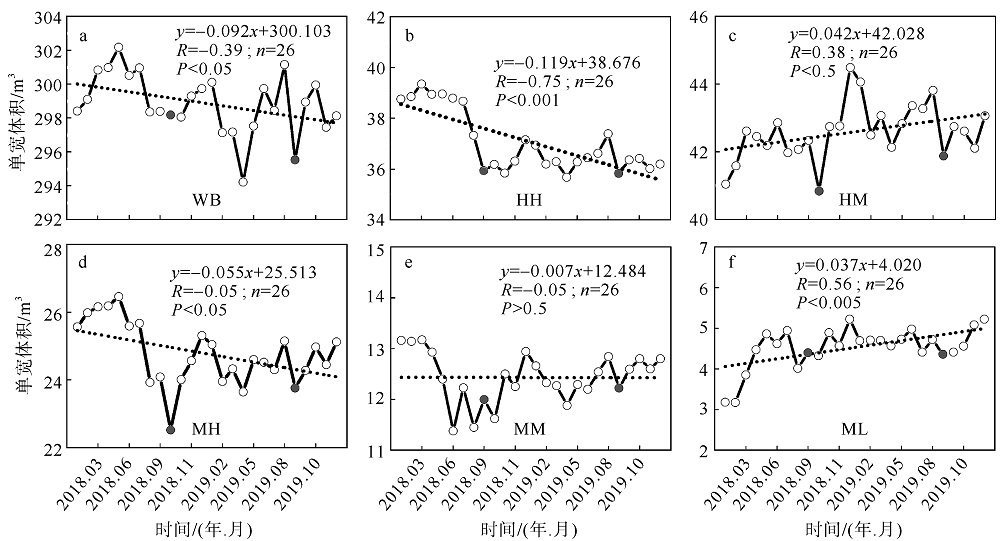
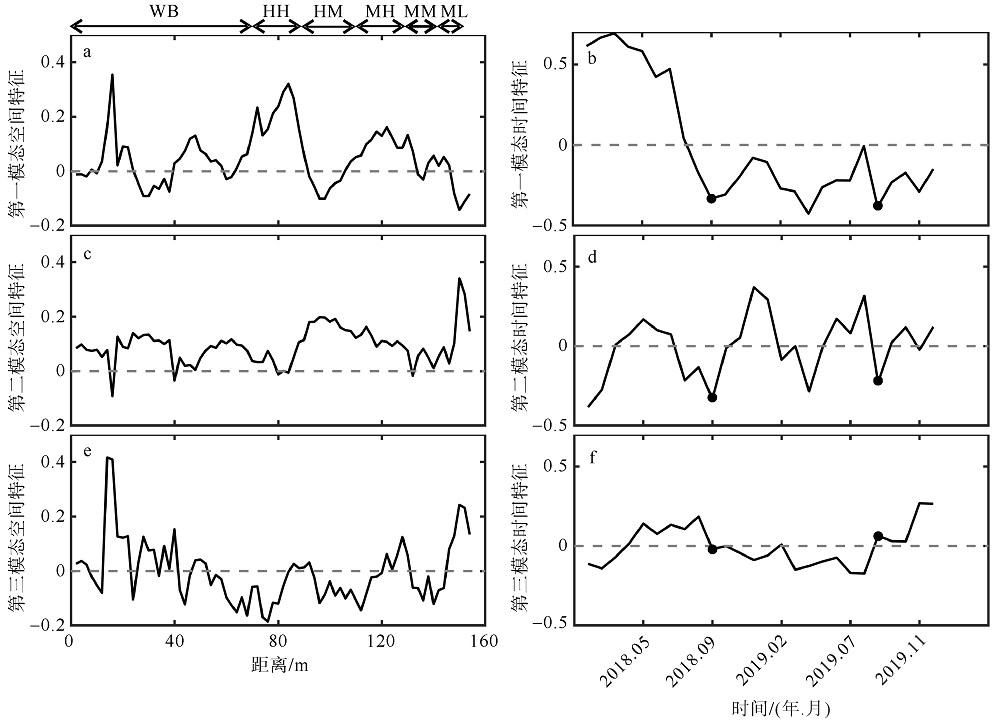
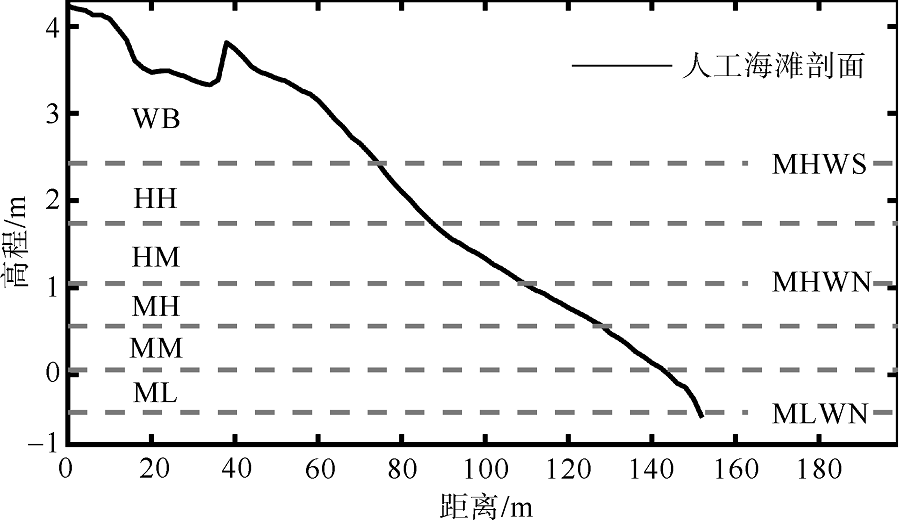
Fig. 2
The artificial beach profile division zone (MHWS: mean high water level of spring tide; MHWN: mean high water level of neap tide; MLWN: mean low water level of neap tide; WB: mean spring tide high water level up the beach zone; HH: high high tide zone; HM: high middle tide zone; MH: middle high tide zone; MM: middle middle tide zone; ML: middle low tide zone"
| [1] | 蔡锋, 刘根, 2019. 我国海滩养护修复的发展与技术创新[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 38(4): 452-463. |
| CAI FENG, LIU GEN, 2019. Beach nourishment development and technological innovations in China: an overview[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 38(4): 452-463. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 曹惠美, 蔡锋, 陈峰, 2009. 厦门滨海沙滩的养护与海洋旅游业发展的探讨[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 26(7): 58-62. |
| CAO HUIMEI, CAI FNEG, CHEN FENG, 2009. The conservation of coastal beaches and development of marine tourism of Xiamen city[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 26(7): 58-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 陈坚, 蔡锋, 许江, 等, 2002. 厦门岛东北部海滩回填重塑研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 21(2): 243-251. |
| CHEN JIAN, CAI FENG, XU JIANG, et al, 2002. Study on beach filling and reconstruction on northeast coast of Xiamen Island[J]. Journal of oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 21(2): 243-251. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 戴志军, 陈子燊, 欧素英, 2002. 粤东汕尾岬间海滩剖面月内日变化过程特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 21(1): 27-32. |
| DAI ZHIJUN, CHEN ZISHEN, OU SUYING, 2002. Characteristics of daily variation processes over a month for beach profiles between headlands in Shanwei, eastern Guangdong[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 21(1): 27-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 戴志军, 李春初, 2008. 华南弧形海岸动力地貌过程[M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社: 5-31. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | 董德信, 李谊纯, 陈宪云, 等, 2015. 海洋工程对钦州湾岸线地形及泥沙冲淤的影响[J]. 广西科学, 22(3): 266-273. |
| DONG DEXIN, LI YICHUN, CHEN XIANYUN, et al, 2015. Impacts of ocean engineering on shoreline, topography and deposition-erosion environment in Qinzhou gulf[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 22(3): 266-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 董丽红, 梁书秀, 孙昭晨, 2012. 海滩养护理论与试验研究进展[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 29(5): 44-51. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | 郭俊丽, 时连强, 童宵岭, 等, 2018. 浙江朱家尖岛东沙海滩对热带风暴“娜基莉”的响应及风暴后的恢复[J]. 海洋学报, 40(9): 137-147. |
| GUO JUNLI, SHI LIANQIANG, TONG XIAOLING, et al, 2018. The response to tropical storm Nakri and the restoration of Dongsha Beach in Zhujiajian Island, Zhejiang province[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 40(9): 137-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 季小梅, 张永战, 朱大奎, 2007. 三亚海岸演变与人工海滩设计研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 27(5): 853-860. |
| JI XIAOMEI, ZHANG YONGZHAN, ZHU DAKUI, 2007. Evolution of Sanya coast and artificial beach design[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 27(5): 853-860. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 雷刚, 刘根, 蔡锋, 2013. 厦门岛会展中心海滩养护及其对我国海岸防护的启示[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 32(3): 305-315. |
| LEI GANG, LIU GEN, CAI FENG, 2013. Enlightenment to China's coastal protection from the coast beach nourishment at Huizhan Zhongxin of Xiamen Island[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 32(3): 305-315. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 黎树式, 黄鹄, 戴志军, 2017. 近60年来广西北部湾气候变化及其适应研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 34(4): 50-55. |
| LI SHUSHI, HUANG HU, DAI ZHIJUN, 2017. Climate change and its adaptation in Beibu Gulf of Guangxi in recent 60 years[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 34(4): 50-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 刘建涛, 王刚, 陈文超, 等, 2018. 北戴河西海滩潜堤岬头养滩功效研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (3): 113-119. |
| LIU JIANTAO, WNAG GANG, CHEN WENCHAO, et al, 2018. Protective effect of submerged headland on west beach, Beidaihe[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (3): 113-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 毛龙江, 张永战, 魏灵, 等, 2006. 海南岛三亚湾海滩研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(3): 477-484. |
| MAO LONGJIANG, ZHANG YONGZHAN, WEI LING, et al, 2006. Study on beach characteristics in Sanya area of Hainan Island[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 26(3): 477-484. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 邱若峰, 庄振业, 赵友鹏, 等, 2014. 海滩养护的功效和寿命——以北戴河海滩养护工程为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 30(3): 26-33. |
| QIU RUOFNEG, ZHUANG ZHENYE, ZHAO YOUPENG, et al, 2014. Beidaihe beach nourishment: a case study of beach nourishment project in Beidaihe[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 30(3): 26-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 杨燕雄, 张甲波, 刘松涛, 2014. 秦皇岛海滩养护工程的实践与方法[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 30(3): 1-15. |
| YANG YANXIONG, ZHANG JIABO, LIU SONGTAO, 2014. What we have learnt from the beach nourishment project in Qinhuangdao[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 30(3): 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 张振克, 2002. 美国东海岸海滩养护工程对中国砂质海滩旅游资源开发与保护的启示[J]. 海洋地质动态, 18(3): 23-27. |
| ZHANG ZHENKE, 2002. Discussions on development and protection of touring resources of China’s sandy beaches from beach nourishment engineering done for American east coast[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 18(3): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 周军, 庄振业, 李建华, 等, 2014. 潮滩上的人造沙滩——潍坊滨海旅游区沙滩构建始末[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 30(3): 64-70. |
| ZHOU JUN, ZHUANG ZHENYE, LI JIANHUA, et al, 2014. An artificial beach on tidal flat: construction of Weifang artificial beach[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 30(3): 64-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 朱嘉, 刘建辉, 蔡晓琼, 2014. 珠江口外伶仃岛海滩修复研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 31(11): 36-40. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | AUBREY D G, INMAN D L, WINANT C D, 1980. The statistical prediction of beach changes in Southern California[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 85(C6): 3264-3276. |
| [20] | BENASSAI E, GENTILOMO M, RAGONE A, et al, 1997. Littoral restoration by means of protected beach nourishment, recent Italian works[J]. PIANC Bulletin, 94: 43-55. |
| [21] |
DAI ZHIJUN, LIU J T, FU GUI, et al, 2013. A thirteen-year record of bathymetric changes in the North Passage, Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary[J]. Geomorphology, 187: 101-107.
doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.01.004 |
| [22] | DAVISON A T, NICHOLLS R J, LEATHERMAN S P, 1992. Beach nourishment as a coastal management tool: An annotated bibliography on developments associated with the artificial nourishment of beaches[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 8(4): 984-1022. |
| [23] | DEAN R G, 1991. Equilibrium beach profiles: characteristics and applications[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 7(1): 53-84. |
| [24] |
DEAN R G, YOO C H, 1994. Beach nourishment in presence of seawall[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 120(3): 302-316.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1994)120:3(302) |
| [25] |
HANSON H, BRAMPTON A, CAPOBIANCO M, et al, 2002. Beach nourishment projects, practices, and objectives—an European overview[J]. Coastal Engineering, 47(2): 81-111.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-3839(02)00122-9 |
| [26] | LEE P Z F, 1994. The submarine equilibrium profile: a physical model[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 10(1): 1-17. |
| [27] | OTVOS E G, 2004. Beach aggradation following hurricane landfall: Impact comparisons from two contrasting hurricanes, Northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 20(1): 326-339. |
| [28] |
SHU GAO, COLLINS M, CROSS J, 1998. Equilibrium coastal profiles: II. Evidence from EOF analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 16(3): 193-205.
doi: 10.1007/BF02848723 |
| [29] |
VOUSDOUKAS M I, RANASINGHE R, MENTASCHI L, et al, 2020. Sandy coastlines under threat of erosion[J]. Nature Climate Change, 10(3): 260-263.
doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0697-0 |
| [30] |
WEI WEN, CHANG YUANPIN, DAI ZHIJUN, 2014. Streamflow changes of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River in the recent 60 years: Impacts of the East Asian summer monsoon, ENSO, and human activities[J]. Quaternary International, 336: 98-107.
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.10.064 |
| [1] | TANG Chaoli, TAO Xinhua, WEI Yuanyuan, DAI Congming, WEI Heli. Spatiotemporal modal analysis and prediction of surface temperature in East Asia and the Western Pacific* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 183-192. |
| [2] | LI Ao, FENG Yang, WANG Yuntao, XUE Huijie. Spatiotemporal variation of water area with high chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea based on OC-CCI data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 77-89. |
| [3] | Shibing ZHU,Danni HU,Huiling ZHANG,Chunhua ZENG,Zhehua LI,Zhiqiang LI. Analysis of short-term temporal and spatial changes and sedimentary dynamics at the middle section of Haikou Bay Beach * [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 77-85. |
| [4] | Xia WANG,Wendong FANG,Rongyu CHEN. Intra-seasonal variability of sea level anomalies and their propagation features in the northern South China Sea from 25 years of satellite altimetry data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 1-12. |
| [5] | LI Gang, LI Chong-yin, JIANG Xiao-hua, ZHANG Ying, LIU Kai, TAN Yan-ke, BAI Tao. Analysis of spatiotemporal variability of global sea surface temperature anomalies during 1900~2009 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(4): 12-22. |
| [6] | L? Ke-wei, HU Jian-yu, YANG Xiao-yi. Spatial patterns in seasonal variability of sea surface wind over the South China Sea and its adjacent ocean [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(6): 41-47. |
| [7] | LIU Xin, WANG Jing, CHENG Xu-hua, YAN Tong. The temporal and spatial evolution of chlorophyll-a concentration in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(4): 42-48. |
| [8] | WU Xiao-fen,XU Jian-ping,ZHANG Qi-long,LIU Zeng-hong,. CSEOF analysis of the upper ocean heat content over tropical western Pacific [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(6): 37-46. |
|
||