Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 29-41.doi: 10.11978/2022265CSTR: 32234.14.2022265
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristic statistics and analysis of internal waves in the continental slope area west of the Dongsha Plateau on the northern South China Sea in the autumn of 2021*
XIE Botao1( ), HUANG Bigui1, YANG Wei2,3(
), HUANG Bigui1, YANG Wei2,3( ), LI Ruixiang2,3, ZHANG Yan2,3, LIU Tongmu2,3, LI Xiangyi2,3
), LI Ruixiang2,3, ZHANG Yan2,3, LIU Tongmu2,3, LI Xiangyi2,3
- 1. China National Offshore Oil Corporation Research Institute, Beijing 100028, China
2. South China Sea Marine Survey Center, Ministry of Natural Resources, Guangzhou 510300, China
3. Key Laboratory of Marine Environment Survey Technology and Application, Ministry of Natural Resources, Guangzhou 510300, China
-
Received:2022-12-28Revised:2023-03-09Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-03-14 -
Supported by:Key-Area Research and Development Project of Guangdong Province(2020B111102003); Study on Internal Wave Zoning and Engineering Parameters in the North of the South China Sea(YXKY-ZX 10 2021); Key Technologies of Refined Environmental Prediction and Parameter Zoning for Offshore Oil and Gas Fields(YXKY-ZX 07 2020); Research on Deepwater Marine Environmental Monitoring and Data Platform(KJGG2022-0202)
Cite this article
XIE Botao, HUANG Bigui, YANG Wei, LI Ruixiang, ZHANG Yan, LIU Tongmu, LI Xiangyi. Characteristic statistics and analysis of internal waves in the continental slope area west of the Dongsha Plateau on the northern South China Sea in the autumn of 2021*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 29-41.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
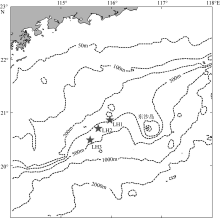
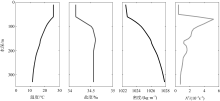
Location information, observation period, instrument, and sample depth of moorings at the sites LH1-LH3"
| 站位 | 经度 | 纬度 | 水深/m | 观测设备 | 观测时段 | 流速剖面深度范围/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LH1 | 115°58.230′E | 20°51.605′N | 368 | 300 & 150kHz ADCP | 08.28—11.03 | 12~328 |
| LH2 | 115°44.422′E | 20°42.006′N | 378 | 4*300 & 600kHz ADCP 4* SBE37 & 15* SBE 56 | 08.27—10.29 | 12~370 |
| LH3 | 115°34.828′E | 20°28.774′N | 440 | 2* 300kHz ADCP | 09.02—11.05 | 12~180 |
Tab. 2
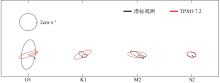
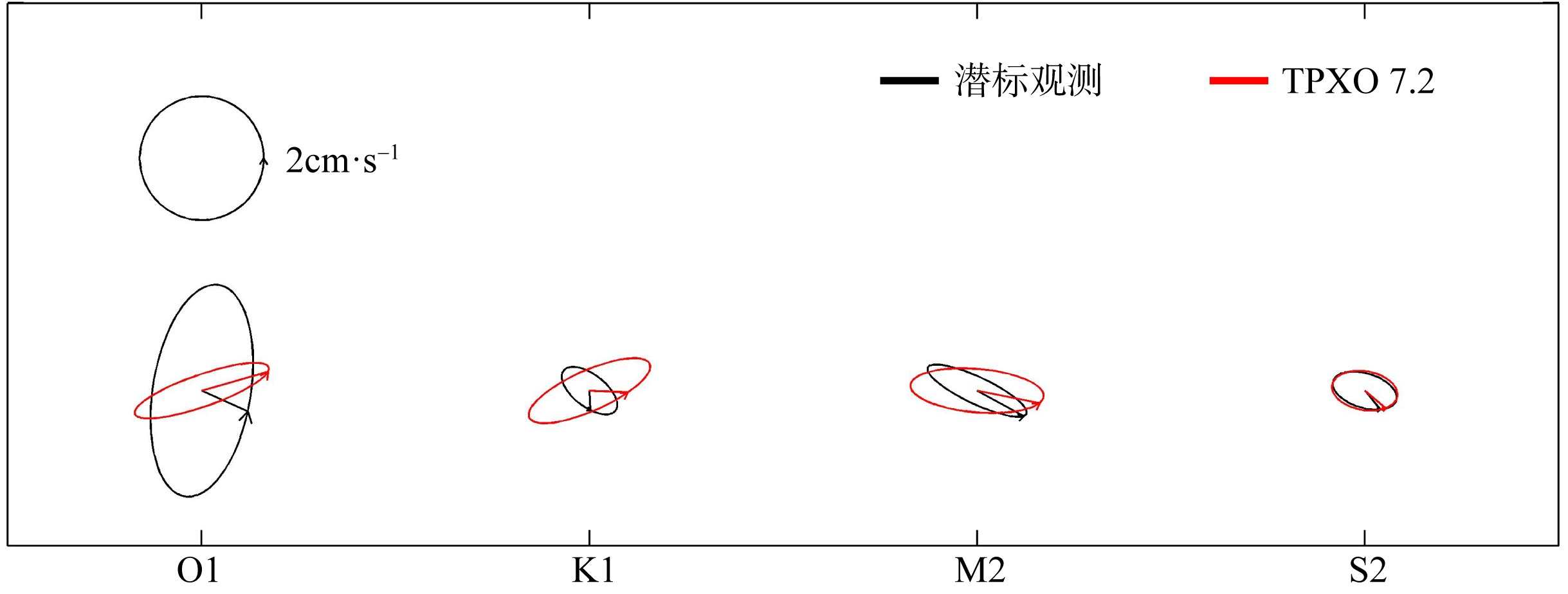
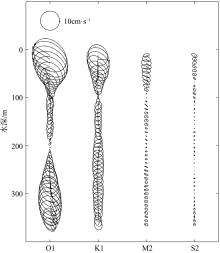
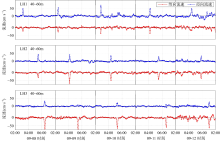
Ellipse parameters of the principal diurnal and semidiurnal barotropic and baroclinic tidal constituents of LH2"
| 长轴/(cm·s-1) | 短轴/(cm·s-1) | 倾角/° | 相位/° | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 正压潮流 | 3.5 | 1.6 | 81 | 97 | |
| TPXO 7.2 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 19 | 15 | ||
| 斜压潮流 | 25m | 21.3 | -14.9 | 137 | 340 | |
| 105m | 5.6 | -1.4 | 118 | 335 | ||
| 200m | 2.0 | -1.0 | 66 | 25 | ||
| 300m | 13.6 | -9.7 | 116 | 163 | ||
| 350m | 13.4 | -9.5 | 117 | 188 | ||
| K1 | 正压潮流 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 142 | 247 | |
| TPXO 7.2 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 24 | 59 | ||
| 斜压潮流 | 25m | 13.3 | -10.2 | 132 | 127 | |
| 105m | 1.7 | -0.8 | 96 | 161 | ||
| 200m | 4.4 | -4.2 | 170 | 226 | ||
| 300m | 5.8 | -5.2 | 144 | 312 | ||
| 350m | 5.6 | -4.1 | 112 | 330 | ||
| M2 | 正压潮流 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 155 | 194 | |
| TPXO 7.2 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 175 | 199 | ||
| 斜压潮流 | 25m | 4.6 | -3.0 | 176 | 131 | |
| 105m | 0.5 | 0.1 | 61 | 263 | ||
| 200m | 1.0 | -0.2 | 149 | 282 | ||
| 300m | 2.2 | -1.0 | 9 | 149 | ||
| 350m | 1.9 | -1.3 | 136 | 12 | ||
| S2 | 正压潮流 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 163 | 232 | |
| TPXO 7.2 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 170 | 225 | ||
| 斜压潮流 | 25m | 1.9 | -1.7 | 34 | 244 | |
| 105m | 1.6 | -0.6 | 137 | 43 | ||
| 200m | 0.4 | -0.2 | 156 | 5 | ||
| 300m | 0.5 | -0.2 | 8 | 141 | ||
| 350m | 1.4 | -0.8 | 95 | 316 | ||
Tab. 3
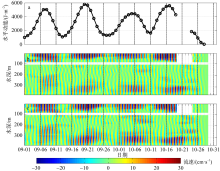
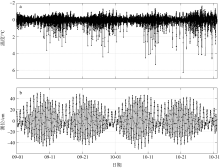
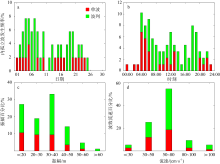
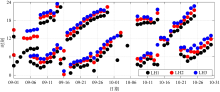
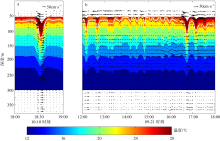
Statistics of the occurrence time, wave-induced velocity and direction, duration for the ISWs along LH1-LH2-LH3 during 8-12 September 2021"
| 站位 | 日期 | 时间 | 波致流速/(cm·s-1) | 波致流向/° | 持续时间/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LH1 | 09-08 | 03:10 | 54.3 | 332 | 22 |
| 09-09 | 02:26 | 58.1 | 329 | 20 | |
| 09-10 | 02:50 | 80.8 | 332 | 18 | |
| 09-11 | 04:12 | 65.3 | 323 | 20 | |
| 09-12 | 04:26 | 46.1 | 343 | 20 | |
| LH2 | 09-08 | 05:26 | 55.6 | 325 | 26 |
| 09-09 | 04:10 | 88.0 | 302 | 24 | |
| 09-10 | 04:20 | 64.1 | 307 | 22 | |
| 09-11 | 05:28 | 53.6 | 300 | 26 | |
| 09-12 | 05:52 | 49.7 | 313 | 20 | |
| LH3 | 09-08 | 06:26 | 83.0 | 294 | 30 |
| 09-09 | 05:26 | 72.2 | 269 | 26 | |
| 09-10 | 05:18 | 70.1 | 287 | 22 | |
| 09-11 | 06:38 | 64.2 | 278 | 20 | |
| 09-12 | 07:04 | 76.3 | 293 | 28 |
| [1] |
蔡树群, 何建玲, 谢皆烁, 2011. 近10年来南海孤立内波的研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 26(7): 703-710.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
蒋暑民, 戴德君, 乔方利, 等, 2019. 南海北部陆架海域内潮特征的观测研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(1): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
石新刚, 刘耀华, 兰志刚, 等, 2013. 南海北部流花海域内孤立波特征研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(6): 22-27.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.06.004 |
|
|
|
| [4] |
张效谦, 梁鑫峰, 田纪伟, 2005. 南海北部450m以浅水层内潮和近惯性运动研究[J]. 科学通报, 50(18): 2027-2031.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1175/2010JPO4388.1 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-11-073.1 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1038/nature14399 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.833226 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1007/s10712-012-9176-0 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2017.03.005 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014843 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v119.10 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.836998 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.5670/oceanog |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2013.04.002 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-17-0209.1 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-16-0111.1 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1175/2010JPO4500.1 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.840839 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1029/2018GL078372 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102422 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1029/2012JC008212 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2014.03.002 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v121.11 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2014.916442 |
| [1] | ZHANG Xinwen, LIN Guanying, LI Ruixiang, YANG Wei, LIU Tongmu, ZHOU Baocheng, YIN Liqiang, DING Yibo. Design and application of internal solitary wave monitoring system based on the Tiantong communication [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 180-189. |
| [2] | XIE Jieshuo, GONG Yankun, NIU Jianwei, HE Yinghui, CHEN Zhiwu, XU Jiexin, CAI Shuqu. Spatial-temporal variations of the dynamic parameters of internal solitary waves in the Sulu-Celebes Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 132-142. |
| [3] | MA Mengzhen, LI Qian, WU Zhengchao, CHEN Yinchao, YU Jiancheng. Underwater glider observation of oxygen minimum zone in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
| [4] | FANG Zhou, YAN Sheng-fu, WANG Xu. Comparative study of three wave-generating methods for internal solitary waves in a two-layer fluid [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(4): 31-36. |
| [5] | LI Zi-mu, CAI Shu-qun, CHEN Ju, CHEN Rong-yu, WANG Dong-xiao, DU Yan. Preliminary analysis of observations by deep submersible mooring in west Luzon Strait during 2010 to 2011 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 10-16. |
| [6] | SHI Xin-gang, LIU Yao-hua, LAN Zhi-gang, SONG Ji-wen, HE Qi, LEI Fang-hui, WANG Jun-qin, HUANG Bi-gui, ZHU Xue-ming. The characteristics of internal solitary waves at Liuhua in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(6): 22-27. |
|
||