Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 93-107.doi: 10.11978/2024048CSTR: 32234.14.2024048
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of tidal hydrodynamics characteristics of the Shuangyue Bay Lagoon system in Huizhou, Guangdong based on modified harmonic analysis model using the credo of smoothness
WANG Yajun1,2( ), ZHANG Siyi1,2, OU Suying1,2,3,4, CAI Huayang1,2,3,4(
), ZHANG Siyi1,2, OU Suying1,2,3,4, CAI Huayang1,2,3,4( ), ZHU Xinyu1,2, ZHU Lei5
), ZHU Xinyu1,2, ZHU Lei5
- 1. Institute of Estuarine and Coastal Research, School of Ocean Engineering and Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
2. State and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Estuarine Hydraulic Technology, Guangzhou 510275, China
3. Guangdong Provincial Engineering Research Center of Coasts, Islands and Reefs, Guangzhou 510275, China
4. Southern Laboratory of Ocean Science and Engineering (Zhuhai), Zhuhai 519000, China
5. School of Ocean Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510275, China
-
Received:2024-03-01Revised:2024-03-26Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-02-10 -
Contact:CAI Huayang -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(52279080); Guangdong Provincial Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Project Regional Joint Fund -Youth Project(2020A1515110367)
CLC Number:
- P731.22
Cite this article
WANG Yajun, ZHANG Siyi, OU Suying, CAI Huayang, ZHU Xinyu, ZHU Lei. Analysis of tidal hydrodynamics characteristics of the Shuangyue Bay Lagoon system in Huizhou, Guangdong based on modified harmonic analysis model using the credo of smoothness[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 93-107.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab.1
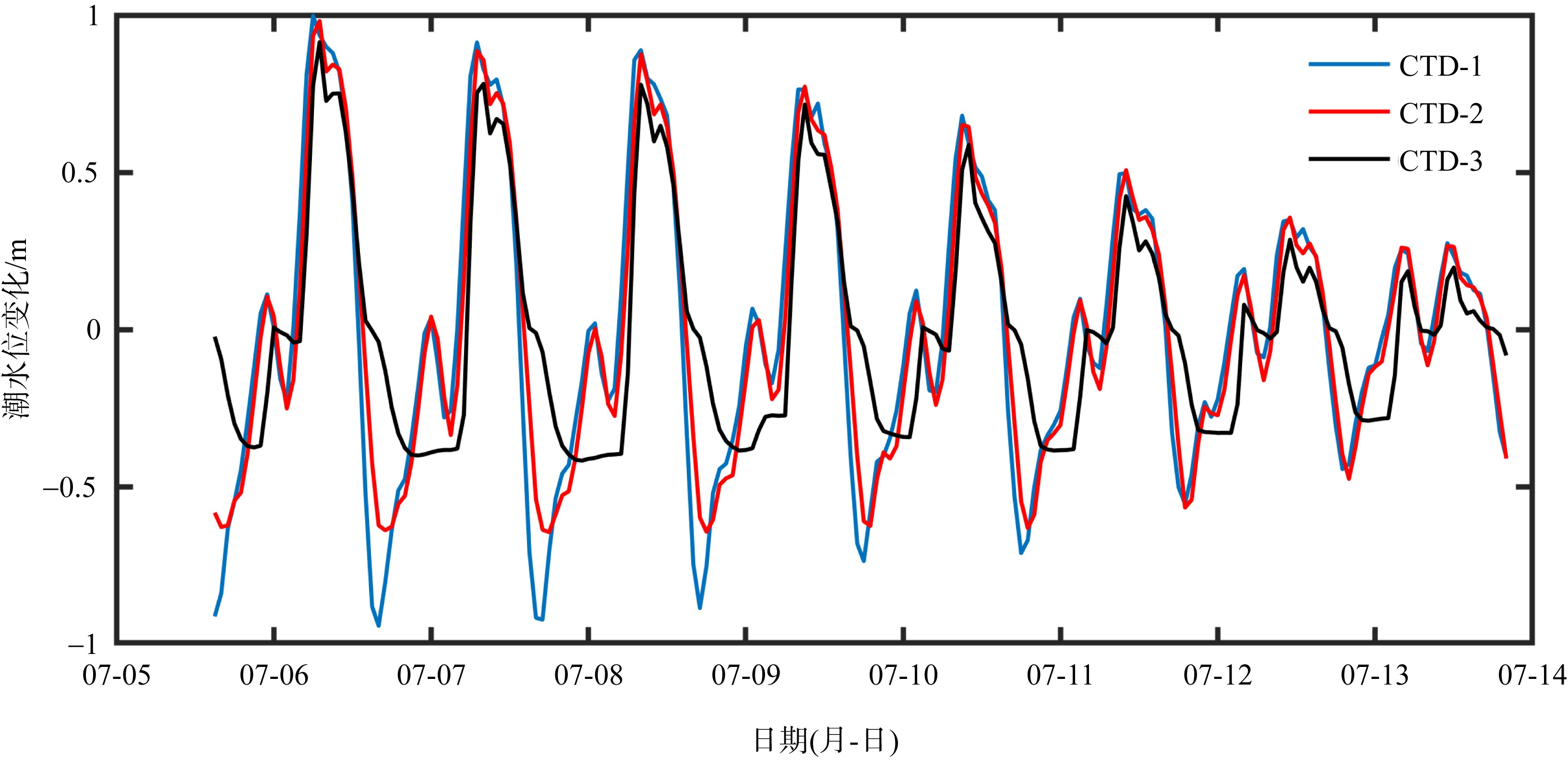
Layout of CTD-Diver observation station in the Shuangyue Bay Lagoon, Huizhou, Guangdong province"
| 编号 | 位置 | 经度 | 纬度 | 测量时间 | 时间长度/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTD-1 | 潟湖口门 | 114°53'24" E | 22°34'30"N | 2020-07-03, 16:00—2020-08-19, 16:00 | 1129 |
| 2022-08-22, 16:00—2022-11-09, 15:00 | 1896 | ||||
| 2022-11-10, 10:00—2023-04-25, 6:00 | 3981 | ||||
| 2023-06-19, 10:00—2023-12-02, 8:00 | 3983 | ||||
| CTD-2 | 潟湖中段 | 114°52'37"E | 22°36'29"N | 2020-07-04, 9:00—2020-08-19, 8:00 | 1104 |
| 2022-08-22, 16:00—2022-11-09, 15:00 | 1896 | ||||
| 2022-11-10, 10:00—2023-04-25, 6:00 | 3981 | ||||
| 2023-06-19, 10:00—2023-12-02, 8:00 | 3983 | ||||
| CTD-3 | 潟湖上段 | 114°53'31"E | 22°37'26"N | 2020-07-03, 16:00—2020-8-19, 16:00 | 1129 |
Tab. 2
Statistics of tidal characteristic parameters at three stations along the Shuangyue Bay Lagoon during the observed period"
| 特征值 | CTD-1 | CTD-2 | CTD-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均涨潮潮差/m | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.54 | |
| 平均落潮潮差/m | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.49 | |
| 平均潮差/m | 0.69 | 0.64 | 0.52 | |
| 最大涨潮潮差/m | 1.17 | 1.09 | 1.01 | |
| 最大落潮潮差/m | 1.87 | 1.57 | 1.19 | |
| 平均潮波振幅/m | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.25 | |
| 特征值 | 潟湖近口段 | 潟湖中上段 | ||
| 衰减率绝对值/(10-4·m-1) | 0.14 | 2.84 | ||
| 高潮位传播速度/(m·s-1) | 5.25 | 1.91 | ||
| 低潮位传播速度/(m·s-1) | 3.13 | 0.62 | ||
| 平均传播速度/(m·s-1) | 3.06 | 0.34 | ||
Tab. 3
Comparison of tidal harmonic constants at three stations along the Shuangyue Bay Lagoon during the observed period in 2020"
| 潮汐 | CTD-1 | CTD-2 | CTD-3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 振幅η/cm | 迟角 | 振幅η/cm | 迟角 | 振幅η/cm | 迟角 | ||||||||
| MHACS | CHA | MHACS | CHA | MHACS | MHACS | CHA | CHA | MHACS | CHA | MHACS | CHA | ||
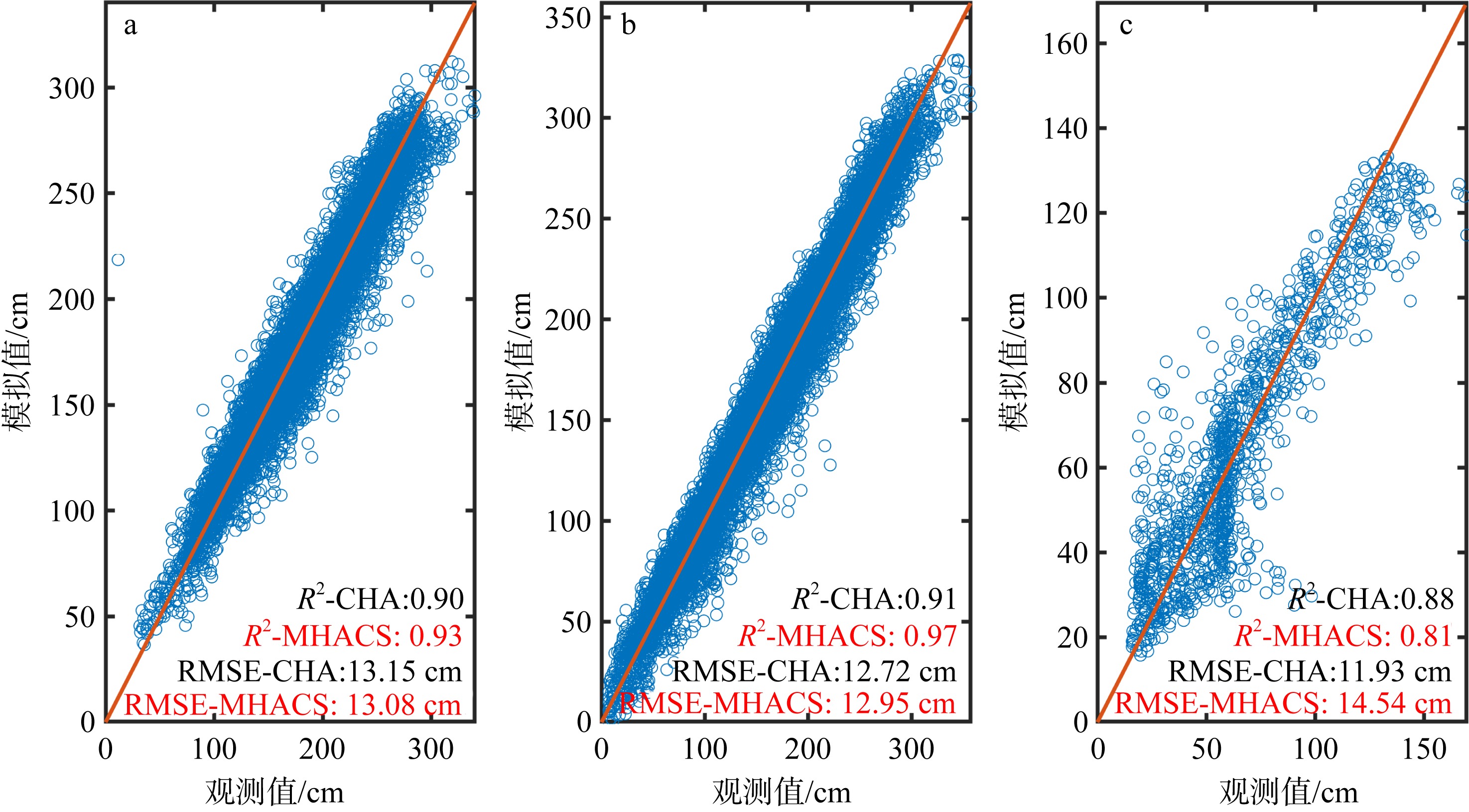
| M2 | 29.77 | 30.18 | 239.75° | 240.90° | 27.01 | 26.83 | 252.73° | 253.02° | 11.55 | 12.72 | 580.83° | 428.05° | |
| S2 | 10.48 | 9.14 | 265.09° | 277.41° | 8.15 | 6.81 | 283.12° | 292.45° | 2.32 | 2.70 | 519.24° | 545.93° | |
| N2 | 5.50 | 5.55 | 230.61° | 259.75° | 5.04 | 5.14 | 248.42° | 247.99° | 2.45 | 3.18 | 565.30° | 610.42° | |
| K2 | 2.78 | - | 268.82° | - | 2.14 | - | 289.21° | - | 0.71 | - | 503.20° | - | |
| K1 | 32.38 | 37.00 | 288.34° | 301.69° | 30.18 | 36.63 | 298.42° | 308.78° | 25.95 | 29.59 | 296.38° | 316.75° | |
| O1 | 28.21 | 24.83 | 241.35° | 239.68° | 26.49 | 23.54 | 252.60° | 250.55° | 22.94 | 19.91 | 251.36° | 268.11° | |
| P1 | 10.49 | - | 281.40° | - | 9.72 | - | 291.69° | - | 8.38 | - | 290.80° | - | |
| Q1 | 4.38 | 3.89 | 232.83° | 216.41° | 4.44 | 4.34 | 247.50° | 231.97° | 3.67 | 3.21 | 237.83° | 249.69° | |
| M4 | 11.21 | 12.14 | 260.08° | 261.56° | 9.90 | 10.32 | 282.65° | 283.72° | 2.12 | 3.31 | 282.65° | 286.37° | |
| MS4 | 5.07 | - | 339.08° | - | 4.16 | - | 376.70° | - | 0.69 | - | 376.70° | - | |
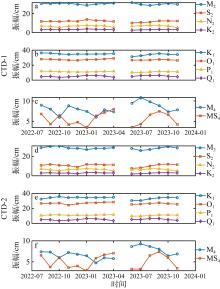
Fig. 4
Monthly variation of tidal amplitude during the observed period from 2022 to 2023. Panels (a), (b), and (c) show the amplitudes of CTD-1 for the semi-diurnal tide, diurnal tide, and shallow water tidal components, respectively. Panels (d), (e), and (f) display the amplitudes of CTD-2 for the semi-diurnal tide, diurnal tide, and shallow water tidal components, respectively"

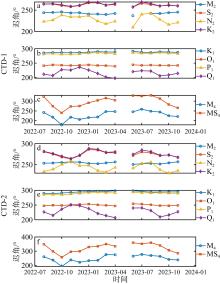
Fig. 5
Monthly variation of tidal phase during the observed period from 2022 to 2023. Panels (a), (b), and (c) represent tidal phases for the semi-diurnal tide, diurnal tide, and shallow water tidal components of CTD-1, respectively. Panels (d), (e), and (f) depict tidal phases for the semi-diurnal tide, diurnal tide, and shallow water tidal components of CTD-2, respectively"

Tab. 4
The averaged tidal harmonic constants at three stations along the Shuangyue Bay Lagoon during the entire observed periods"
| 分潮 | CTD-1 | CTD-2 | CTD-3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 振幅η/cm | 迟角φ | 振幅η/cm | 迟角φ | 振幅η/cm | 迟角φ | |
| M2 | 29.90 | 240.45° | 27.74 | 253.33° | 11.55 | 580.83° |
| S2 | 11.21 | 264.35° | 9.45 | 279.17° | 2.32 | 519.24° |
| N2 | 6.17 | 229.93° | 5.78 | 245.56° | 2.45 | 565.30° |
| K2 | 3.03 | 267.37° | 2.54 | 283.01° | 0.71 | 503.20° |
| K1 | 33.45 | 288.18° | 31.94 | 296.38° | 25.95 | 304.74° |
| O1 | 27.77 | 241.61° | 26.55 | 251.36° | 22.94 | 257.65° |
| P1 | 10.86 | 281.88° | 10.31 | 290.80° | 8.38 | 297.66° |
| Q1 | 4.81 | 228.72° | 4.77 | 237.83° | 3.67 | 251.72° |
| M4 | 11.21 | 260.08° | 9.90 | 265.47° | 2.12 | 597.32° |
| MS4 | 5.07 | 339.08° | 4.16 | 350.00° | 0.69 | 677.48° |
Tab.5
Tidal wave celerity${{C}_{A}}$and tidal wave amplitude gradient δ changes along the course of the lagoon"
| 分潮 | CTD-1至CTD-2 | CTD-2至CTD-3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ${{C}_{A}}$/(m·s-1) | $\delta $/(10-6 m-1) | ${{C}_{A}}$/(m·s-1) | $\delta $/(10-6 m-1) | |
| M2 | 3.25 | -0.14 | 0.07 | -3.05 |
| S2 | 2.92 | -0.33 | 0.09 | -4.49 |
| N2 | 2.63 | -0.13 | 0.07 | -2.99 |
| K2 | 2.78 | -0.34 | 0.10 | -4.19 |
| K1 | 2.65 | -0.09 | 1.35 | -0.77 |
| O1 | 2.07 | -0.09 | 1.66 | -0.54 |
| P1 | 2.42 | -0.10 | 1.64 | -0.76 |
| Q1 | 2.13 | -0.02 | 0.72 | -0.97 |
| M4 | 3.71 | -0.24 | 0.14 | -4.80 |
| MS4 | 2.26 | -0.38 | 0.15 | -5.29 |
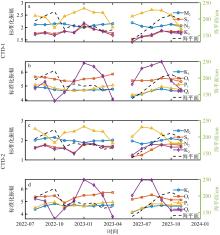
Fig. 6
The monthly variations of the standardized amplitudes of the eight major tidal components. (a) and (b) represent the semi-diurnal and diurnal tidal standardized amplitudes of CTD-1, respectively; (c) and (d) show the normalized amplitudes of the semi-diurnal and diurnal tides of CTD-2, respectively"
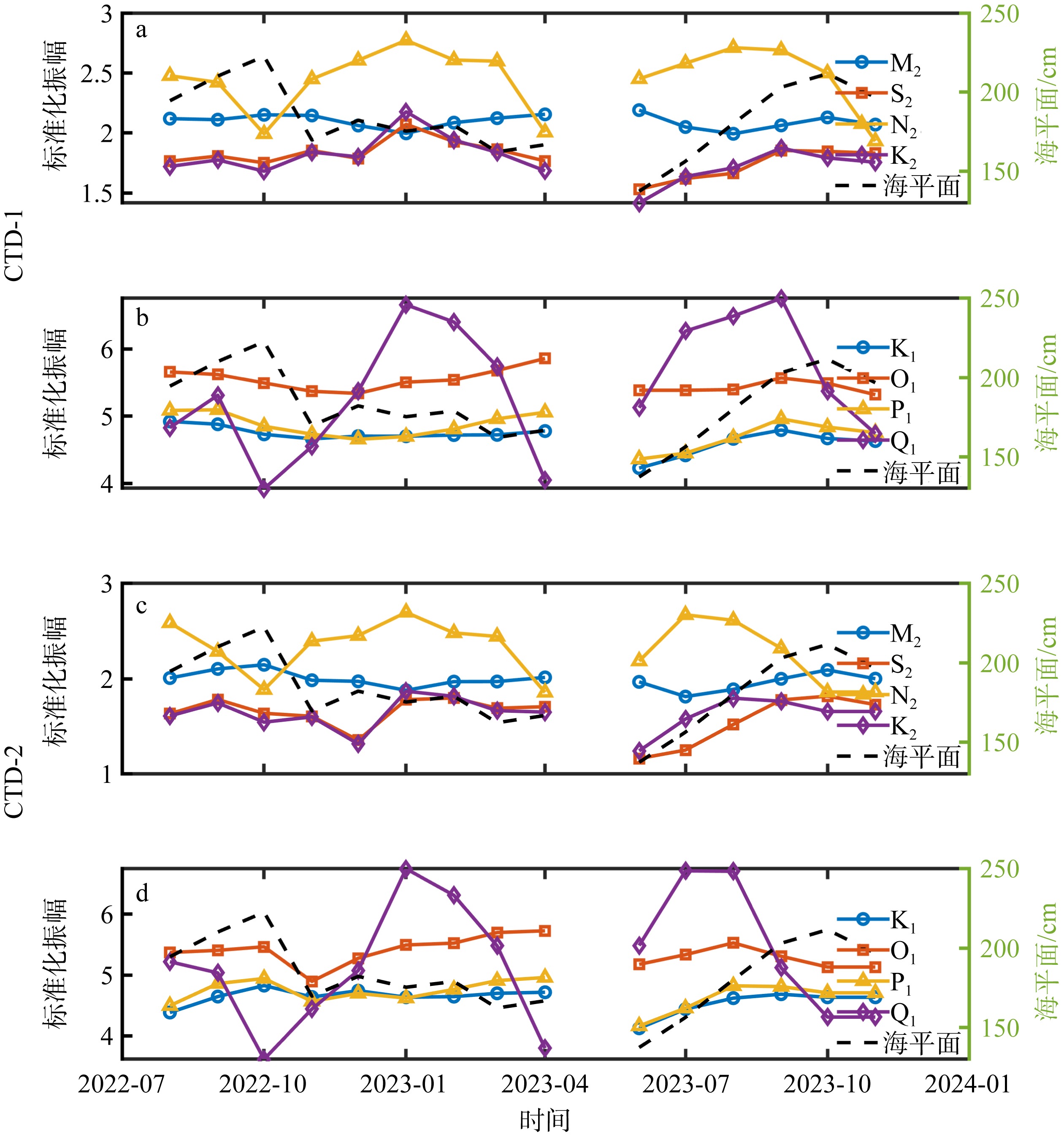
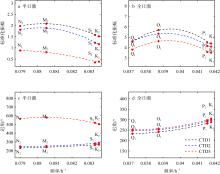
Fig. 7
The relationship between the tidal amplitude, phase, and frequency of the Shuangyue Bay Lagoon during all observed periods. (a) The standardized amplitude of the semi-diurnal tide in the lagoon; (b) the standardized amplitude of the diurnal tide in the lagoon; (c) the phase of the semi-diurnal tide in the lagoon, and (d) the phase of the diurnal tide in the lagoon"

| [1] |
陈浩, 2011. 粤西水东湾沙坝—潟湖海岸近期变化研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
丛新, 匡翠萍, 武云龙, 等, 2022. 侵蚀浪条件下沉水植被对沙坝—潟湖海岸的冲淤影响研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(4): 31-37.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
戴志军, 施伟勇, 陈浩, 2011. 沙坝—潟湖海岸研究进展与展望[J]. 上海国土资源, 32(3): 12-17.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
季荣耀, 罗宪林, 陆永军, 等, 2007. 粤西博贺沙坝潟湖海岸体系形成发育与现代演变[J]. 海洋工程, 25(3): 103-108.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
姜来想, 2010. 1973-2009年山东半岛沿岸潟湖遥感监测与变迁分析[D]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
李春初, 罗宪林, 张镇元, 等, 1986. 粤西水东沙坝潟湖海岸体系的形成演化[J]. 科学通报, 31(20): 1579-1582 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
李长均, 2019. 双月湾康养旅游特色小镇发展策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
缪红兵, 乔璐璐, 仲毅, 等, 2022. 人类活动和自然演变共同驱动下黄河三角洲海域潮波及物质输运变化[J]. 海洋学报, 44(9): 73-86.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
邱秀芳, 李博, 王博芝, 等, 2023. 珠江河网典型横向汊道径潮动力时空差异性分析—以“南沙—南华”横向汊道为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(4): 77-90.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
孙阳, 2021. 近50年来天鹅湖沙坝海岸地貌演变[J]. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版), 37(4): 366-373.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
孙宗勋, 赵焕庭, 1992. 大亚湾大鹏澳菱角石水下沿岸沙坝成因[J]. 海洋通报, 11(2): 45-49.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
谢梅芳, 张萍, 杨昊, 等, 2021. 珠江“伶仃洋河口湾—虎门—潮汐通道”的潮波传播特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(4): 1-13.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
辛红雨, 谢强, 王卫强, 2022. 东印度沿岸流的季节变化及其热盐输运[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(2): 38-51.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
杨红强, 谭飞, 徐辉龙, 等, 2022. 环礁潟湖沉积物重建南沙群岛小冰期以来的热带气旋活动[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(6): 171-182.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
杨世伦, 1989. 我国潮汐沼泽的类型及其开发利用[J]. 自然资源, 11(1): 29-34 (in Chinese).
|
| [16] |
英晓明, 严金辉, 赵明利, 2023. 惠州大亚湾海域风暴潮期间溢油情景模拟研究[J]. 海洋预报, 40(5): 81-89.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
余建奎, 任宗海, 战超, 等, 2022. 山东荣成天鹅湖沙坝水下岸坡地貌冲淤演变分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(4): 61-70.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
张乔民, 陈欣树, 王文介, 等, 1995. 华南海岸沙坝瀉湖型潮汐汊道口门地貌演变[J]. 海洋学报, 17(2): 69-77 (in Chinese).
|
| [19] |
郑哲昊, 庄伟, 孙振宇, 等, 2020. 大亚湾及其邻近海域冬季温度、盐度的分布及日变化特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 39(1): 71-79.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [1] | SONG Jiacheng, QI Hongshuai, ZHANG Chi, CAI Feng, YIN Hang. Analysis of energy dissipation process of wave propagation in beach foreshore under the influence of tide [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 146-153. |
| [2] | KUANG Min, YAO Yu, CHEN Xianjin, ZHANG Qiming, JIANG Changbo. Laboratory study of wave processes over reef coasts under the impact of an excavation pit with varying pit locations [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 14-21. |
| [3] | XU Xiao, TAO Aifeng, LI Xueding, ZHENG Xiangjing, LIN Yinan. Analysis of Wave Characteristics in the Central Taiwan Strait Based on Measured Data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 12-20. |
| [4] | Yu YAO, Tiancheng HE, Zhengjiang TANG, Changbo JIANG. Laboratory study on the effect of varying reef-flat width on wave transformation and wave-induced setup [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 13-19. |
| [5] | Bin DENG, Yao TANG, Changbo JIANG, Mengfei WANG. Air entrainment and bubble movement processes in breaking waves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 33-40. |
| [6] | Zhishen CHEN, Weiyong SHI, Jianfei LU. Comparative analysis on four recurrence levels of joint distribution of wave height and period* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 18-23. |
| [7] | Yi YIN, Lifang JIANG, Zhixu ZHANG, Hongbing YU, Hailong WANG. Statistical analysis of wave characteristics in the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(4): 60-66. |
| [8] | YAO Yu, YUAN Wan-cheng, DU Rui-chao, JIANG Chang-bo. Experimental study of reef crest’s effects on wave transformation and wave-induced setup over fringing reefs [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(6): 19-25. |
|
||