热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 206-216.doi: 10.11978/2024132CSTR: 32234.14.2024132
近30年来涠洲岛海域海水磷含量变化及其影响因素——来自高分辨率珊瑚记录的证据
- 1.中国地质大学(武汉)海洋学院, 湖北 武汉 430070
2.广西大学海洋学院, 广西南海珊瑚礁研究重点实验室, 广西 南宁 530004
-
收稿日期:2024-06-27修回日期:2024-07-29出版日期:2025-05-10发布日期:2025-06-04 -
通讯作者:姜伟 -
作者简介:陈裕月(2000—), 女, 硕士研究生, 海洋科学专业, 主要从事海洋地质方面研究。email: chenyuyue@cug.edu.cn
-
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2023YFF0804801); 国家自然科学基金项目(41976059)
Changes and controlling factors of seawater phosphorus in Weizhou Island over the past 30 years: Insights from high-resolution coral records
CHEN Yuyue1( ), JIANG Wei2(
), JIANG Wei2( ), YANG Haodan2, YU Kefu2
), YANG Haodan2, YU Kefu2
- 1. College of Marine Science and Technology, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan 430070, China
2. Guangxi Laboratory on the Study of Coral Reefs in the South China Sea, School of Marine Sciences, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
-
Received:2024-06-27Revised:2024-07-29Online:2025-05-10Published:2025-06-04 -
Contact:JIANG Wei -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2023YFF0804801); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976059)
摘要:
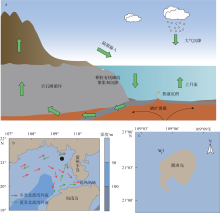
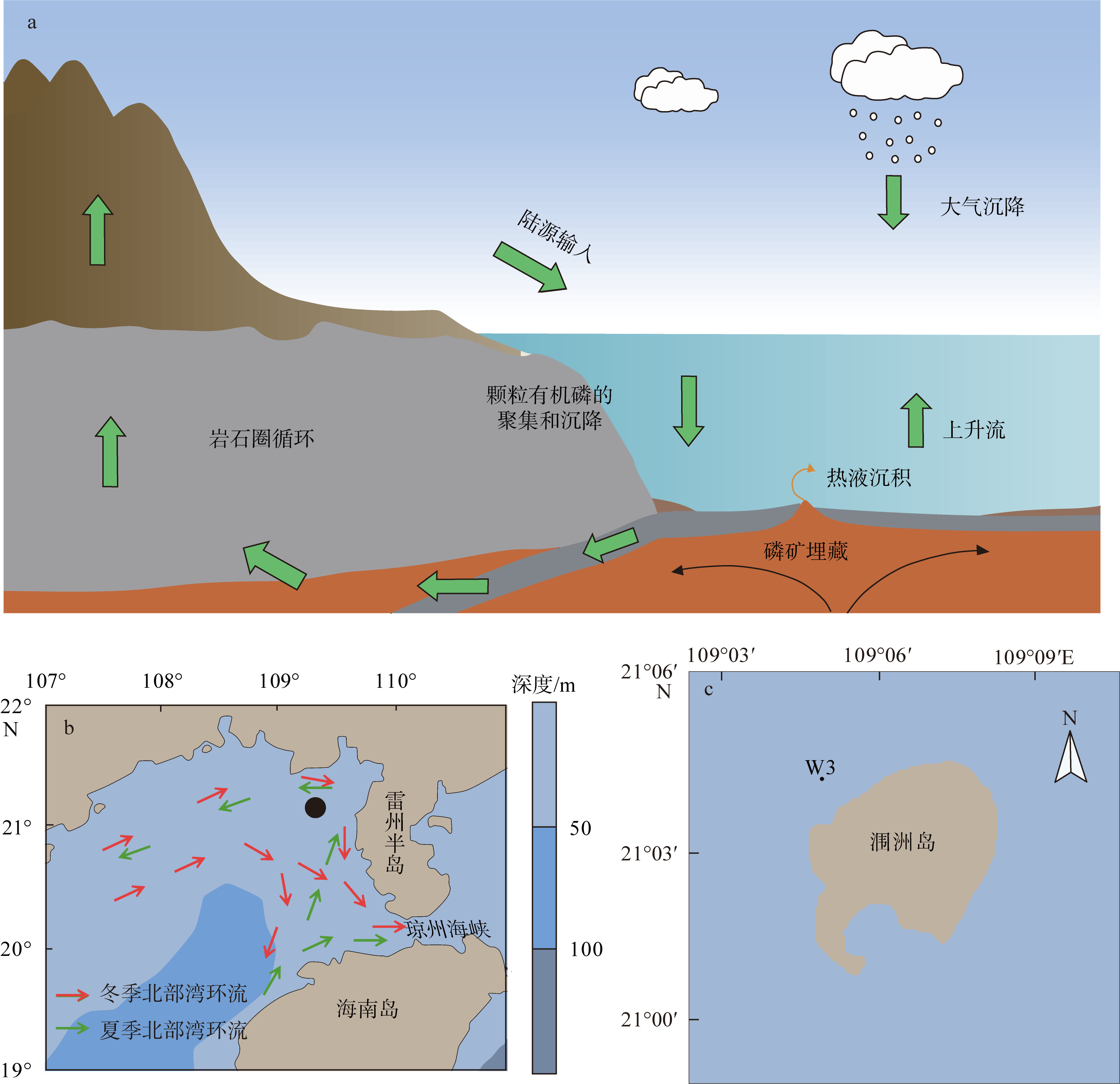
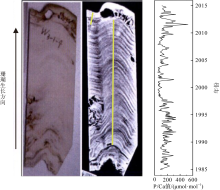
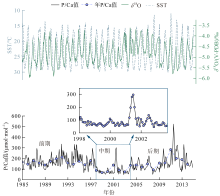
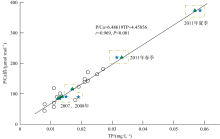
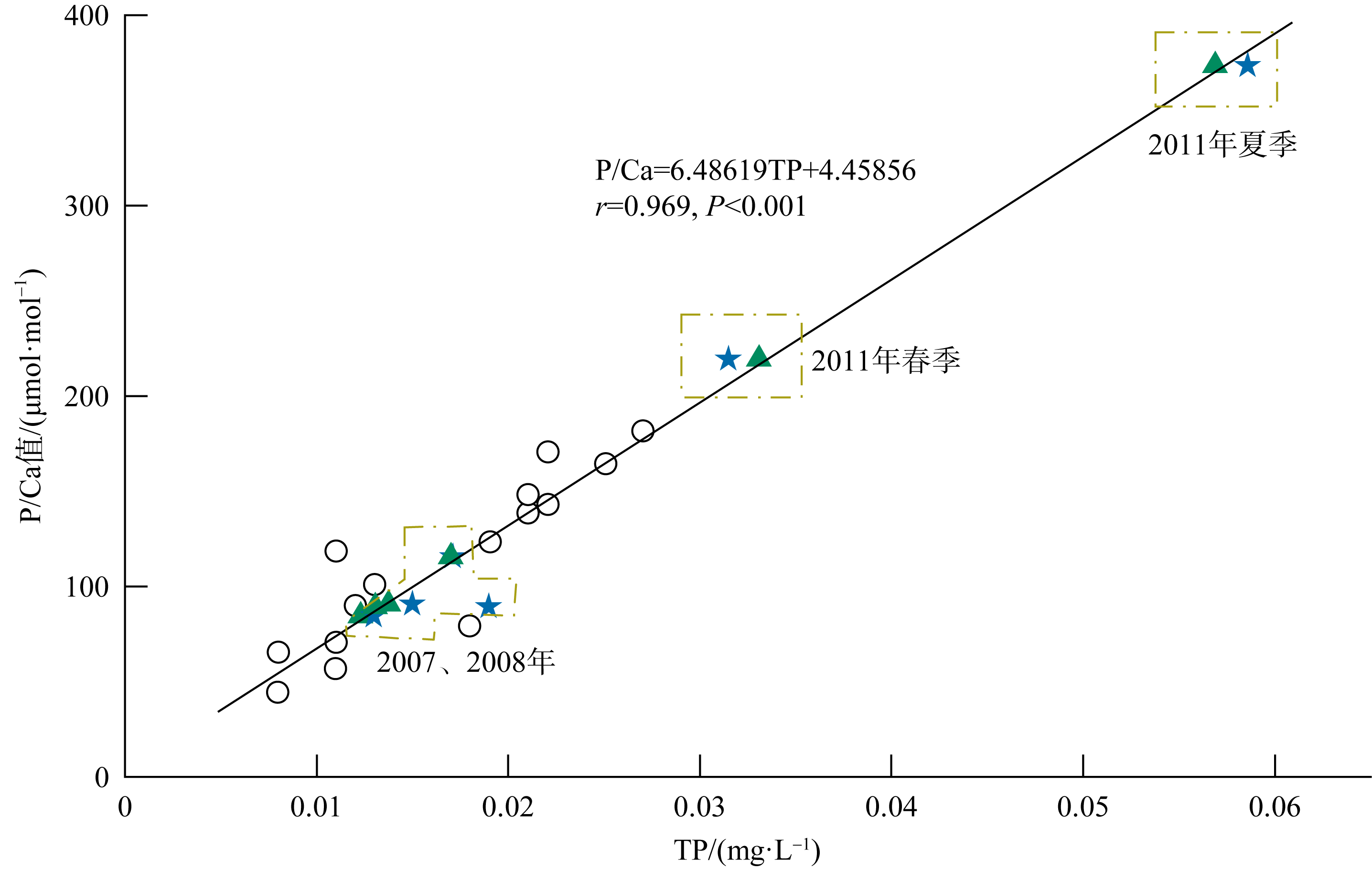
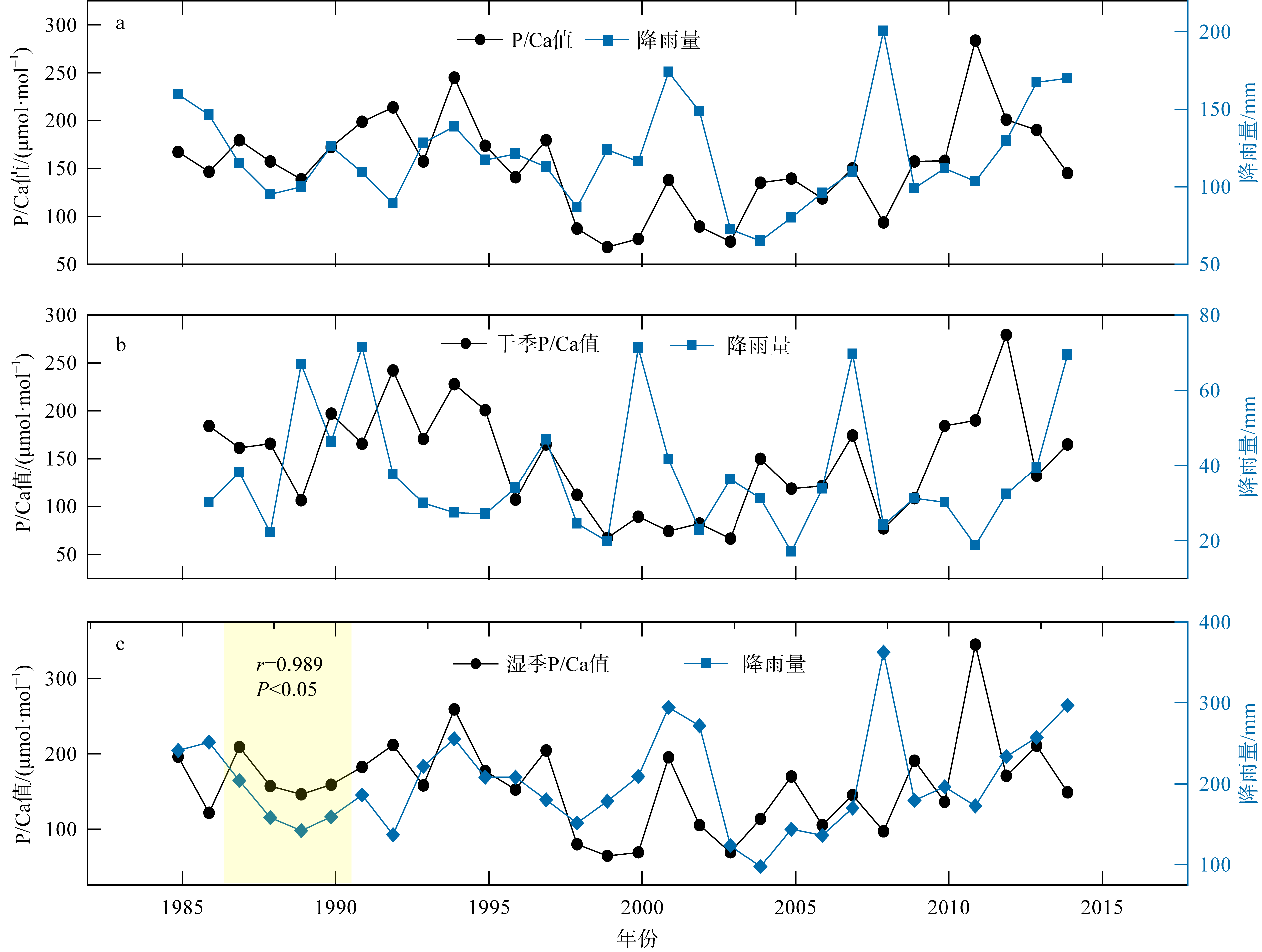
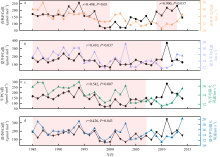
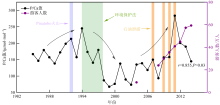
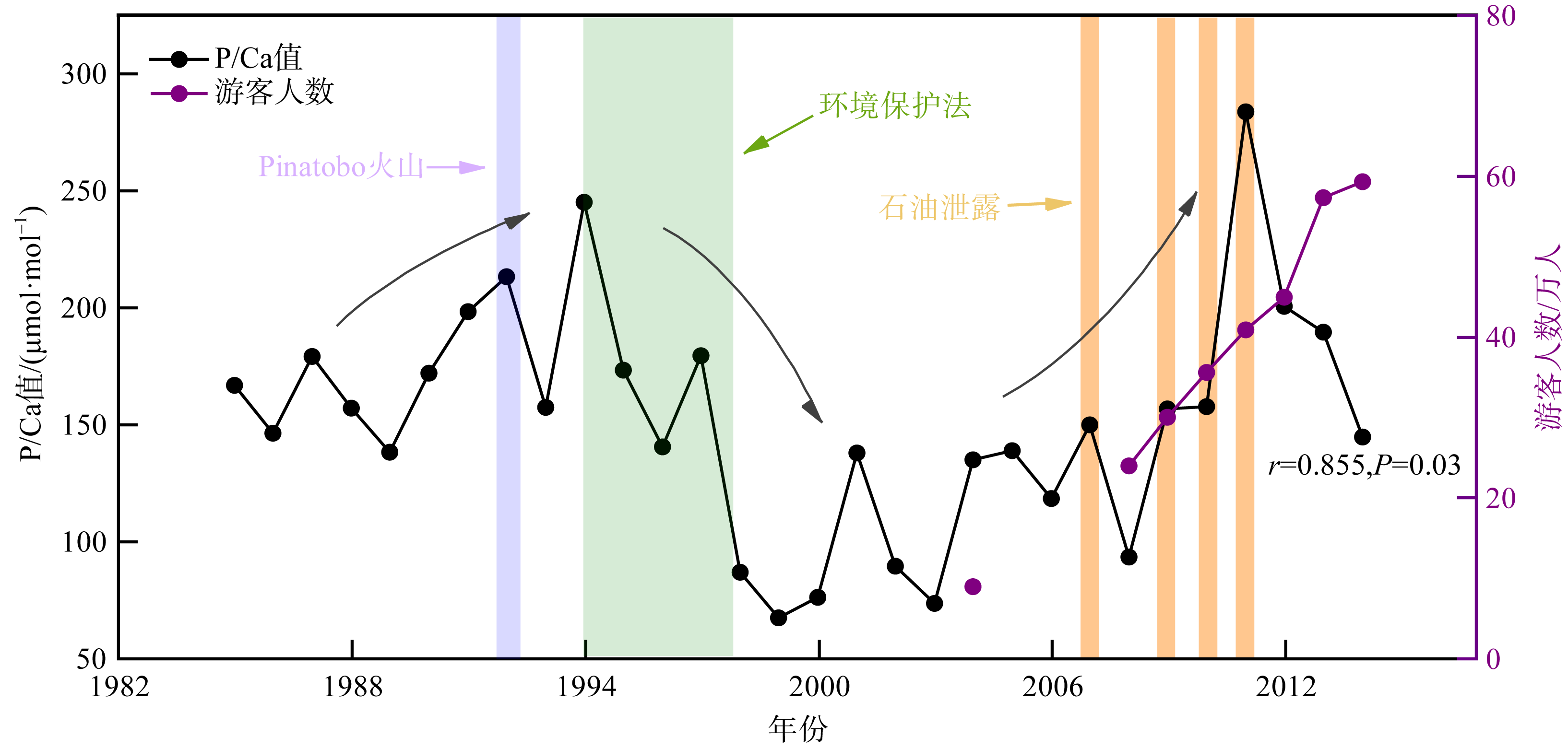
表层海水磷(P)含量变化是评价海洋生态系统营养含量的重要参数, 对地球环境演变过程起到重要调节作用。涠洲岛是我国最大最年轻的火山岛, 海水表层P含量变化缺乏长时间尺度记录, 影响因子尚未明确。珊瑚骨骼P/Ca是反演海水P含量的可靠指标, 被广泛用于重建高分辨率海水P含量变化历史。本研究以涠洲岛西北部连续生长珊瑚为研究对象, 基于珊瑚氧同位素建立1985—2015年的年龄框架, 重建1985—2014年月分辨率的珊瑚P/Ca变化历史。不同年份的珊瑚P/Ca值及其季节变化较大, 在1998—2003年之间珊瑚P/Ca值较低, 普遍低于年平均值。珊瑚P/Ca比值变化与季风强度变化存在极大相关性(P<0.05), 季风、台风盛行期珊瑚P/Ca值明显增加, 说明海表风速是该区域海水P含量变化的主控因素。此外, 火山爆发、石油泄露以及旅游业的发展也会造成P含量短暂性升高, 但影响时长有限。降雨量年际变化及干湿季变化与P/Ca值相关性不显著, 说明陆源物质对海水P含量变化的影响有限。
中图分类号:
- X145
引用本文
陈裕月, 姜伟, 杨浩丹, 余克服. 近30年来涠洲岛海域海水磷含量变化及其影响因素——来自高分辨率珊瑚记录的证据[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 206-216.
CHEN Yuyue, JIANG Wei, YANG Haodan, YU Kefu. Changes and controlling factors of seawater phosphorus in Weizhou Island over the past 30 years: Insights from high-resolution coral records[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(3): 206-216.
表1
不同海域珊瑚P/Ca值对比"
| 海域 | 物种 | P/Ca值/(μmol·mol-1) | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 涠洲岛 | Porites | 93.37~283.58 | 本研究 |
| 地中海COBAS97a | Desmophyllum dianthus | 125.8~139.4 | Montagna et al, |
| 西太平洋G16505 | 714.1~731.2 | ||
| 大亚湾 | Porites sp. | 38.6~190.8 | Chen et al, |
| 巴拿马湾 | Pavona gigantea | 4.1~10.3 | Chen et al, |
| 列斯库拉索岛 | Montastrea | 11.4~52.7 | |
| 澳大利亚大堡礁 | Porites | 65.4 | Alibert et al, |
| [1] |
陈圆, 青尚敏, 2013. 广西北部湾海洋油污染影响与应急管理浅析[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 30(3): 104-108 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
郭芳, 2015. 广西涠洲岛是如何成为“违建岛”的[J]. 中国经济周刊, (43): 34-37 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
何本茂, 黎广钊, 韦蔓新, 等, 2013. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁海域氮磷比值季节变化与浮游生物结构的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(4): 64-72.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.04.010 |
|
|
|
| [4] |
况雪源, 苏志, 涂方旭, 2007. 广西气候区划[J]. 广西科学, 14(3): 278-283.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
李嘉琪, 白爱娟, 蔡亲波, 2018. 西沙群岛和涠洲岛气候变化特征及其与近岸陆地的对比[J]. 热带地理, 38(1): 72-81.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003003 |
|
|
|
| [6] |
李君光,2009-06-08(001). 环境状况有喜有忧[N]. 北海日报 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
李敏, 2009. 南海海洋叶绿素α时空分布及对季风变动响应的研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
刘慧杰, 张虎山, 2012. 海洋石油污染及治理措施[J]. 广州环境科学, 27(4): 35-38.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
刘江宜, 窦世权, 牟德刚, 2020. 海岛资源环境承载能力评价研究——以广西涠洲岛为例[J]. 中国渔业经济, 38(6): 109-120.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
刘敬合, 黎广钊, 农华琼, 1991. 涠洲岛地貌与第四纪地质特征[J]. 广西科学院学报, 7(1): 27-36.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
龙雅婷, 余克服, 王瑞, 等, 2022. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁的发育过程及其与气候的对应关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 42(1): 184-193.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王文欢, 余克服, 王英辉, 2016. 北部湾涠洲岛珊瑚礁的研究历史、现状与特色[J]. 热带地理, 36(1): 72-79.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002806 |
|
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002806 |
|
| [13] |
魏浩天, 刘刚, 韩孝辉, 等, 2020. 珊瑚礁对热液流体的地球化学记录——来自南海西沙永兴岛珊瑚礁稀土元素的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 40(4): 78-95.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
韦蔓新, 黎广钊, 何本茂, 等, 2013. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁生态区各种形态磷含量的季节变化及其影响因素[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 32(2): 258-265.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
吴敏兰, 2014. 北部湾北部海域营养盐的分布特征及其对生态系统的影响研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
周强, 姜允斌, 郝记华, 等, 2021. 磷的生物地球化学循环研究进展[J]. 高校地质学报, 27(2): 183-199.
|
|
doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2020002 |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.07.014 pmid: 21820683 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.11.028 pmid: 15737355 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1149345 pmid: 18276889 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
pmid: 17815626 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
pmid: 16794077 |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
pmid: 21141658 |
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
pmid: 17256993 |
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
doi: S0025-326X(18)30691-X pmid: 30509822 |
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [1] | 周志乾, 连喜平, 谭烨辉. 南海磷虾科长螯磷虾属Stylocheiron——新纪录种的形态特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 66-71. |
| [2] | 黎洁丽, 邹立功, 杨宇峰, 王庆. 基于形态和环境DNA宏条形码技术的广西涠洲岛马尾藻场浮游动物群落结构及其粪便碳通量[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 104-120. |
| [3] | 王超, 屈科, 王旭, 高榕泽, 王傲宇. 人工生态礁体群对非平整岛礁孤立波水动力特性影响的试验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(2): 30-38. |
| [4] | 周志乾, 连喜平, 谭烨辉. 南海细足磷虾属Hansarsia的分类学研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(2): 100-114. |
| [5] | 谢宏宇, 刘永, 李纯厚, 赵金发, 孙金辉, 沈建忠, 石娟, 王腾. 西沙群岛浪花礁珊瑚礁鱼类种类组成与演替[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 114-128. |
| [6] | 黄良民, 林强, 谭烨辉, 黄小平, 周林滨, 黄晖. 热带海洋特色生态系统恢复重构与保护思考*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 1-12. |
| [7] | 王佳熹, 卢护木, 齐鑫, 高程海, 刘永宏, 罗小卫. 涠洲岛鹿角珊瑚共附生真菌Arachniotus ruber GXIMD 02510的次级代谢产物及抑菌活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 174-180. |
| [8] | 莫丹杨, 宁志铭, 杨斌, 夏荣林, 刘志金. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁区沉积物硝酸盐异化还原过程对温度变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [9] | 李黛, 王旭东, 贾子策, 冯东. 深海极端环境黑碳的地球化学特征及其环境意义*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 20-32. |
| [10] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [11] | 贾男, 周天成, 胡思敏, 张琛, 黄晖, 刘胜. 南沙群岛海域珊瑚礁区三种寄居蟹的摄食差异比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 109-121. |
| [12] | 彭尔曼, 姚宇, 李壮志, 许从昊. 波流共同作用下珊瑚礁海岸水动力特性数值模拟研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 187-194. |
| [13] | 黄晖, 袁翔城, 宋严, 李颖心, 周伟华, 龙爱民. 珊瑚礁生态系统固碳过程及储碳机制研究进展*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 13-21. |
| [14] | 黄晖, 俞晓磊, 黄林韬, 江雷. 珊瑚礁生态学研究现状和展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 3-12. |
| [15] | 高洁, 余克服, 许慎栋, 黄学勇, 陈飚, 王永刚. 西沙群岛永乐环礁礁外坡沉积物中有机碳的含量与来源分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
|
||