热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 155-164.doi: 10.11978/2025013CSTR: 32234.14.2025013
深圳不同红树林群落生物量和碳储量
粟春青( ), 高育慧, 罗炘武, 韩梦梦, 宫彦章, 郑卫国(
), 高育慧, 罗炘武, 韩梦梦, 宫彦章, 郑卫国( )
)
广东文科绿色科技股份有限公司 ,广东省园林景观与生态恢复工程技术研究中心
-
收稿日期:2025-01-22修回日期:2025-03-06出版日期:2025-11-10发布日期:2025-12-03 -
通讯作者:郑卫国(1983—), 男, 山东省济宁市人, 硕士, 高级工程师, 主要从事植物引种与繁育、森林培育、生态修复研究。email: 57959061@qq.com -
作者简介:粟春青(1996—), 女, 广西贺州市人, 硕士, 工程师, 研究方向为园林植物景观与生态修复。email:1656702264@qq.com
-
基金资助:深圳市科技计划项目(KCXFZ202002011006491)
Forest biomass and carbon storage of different mangrove communities in Shenzhen, China
SU Chunqing( ), GAO Yuhui, LUO Xinwu, HAN Mengmeng, GONG Yanzhang, ZHENG Weiguo(
), GAO Yuhui, LUO Xinwu, HAN Mengmeng, GONG Yanzhang, ZHENG Weiguo( )
)
Guangdong Wenke Green Technology Corp. ,Ltd., Guangdong Landscape and Ecological Restoration Engineering Technology Research Center
-
Received:2025-01-22Revised:2025-03-06Online:2025-11-10Published:2025-12-03 -
Contact:ZHENG Weiguo. email: 57959061@qq.com -
Supported by:Shenzhen Municipal Science and Technology Plan Project(KCXFZ202002011006491)
摘要:
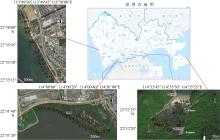
探究不同海岸条件下深圳红树林的群落特征及碳积累功能, 对深圳宝安西湾红树林、大鹏鹿咀山庄红树林、福田红树林国家级自然保护区3个红树林湿地的主要红树群落进行植物生长指标、土壤有机碳与植株碳含量测定, 对不同群落的生物量与土壤碳密度进行了对比研究。结果表明: 秋茄、海桑、无瓣海桑是深圳3个样点红树林群落的建群种、优势种或伴生种; 3个样点以西湾红树林的秋茄和海桑+无瓣海桑群落的植被碳密度最高, 分别为88.03和233.56t·hm-2; 福田红树林保护区具有最高的土壤有机碳密度(63.10g·kg-1)和土壤碳密度(134.65t·hm-2), 但其土壤含水量与土壤容重均显著低于其余2个样点; 大鹏鹿咀山庄红树林群落物种组成最丰富, 土壤容重最大, 而群落株高、胸径及生物量均较小; 不同红树群落均以无瓣海桑群落的树高、胸径与植被碳密度最高, 但其土壤有机碳含量、土壤碳密度均最小, 福田自然秋茄林的土壤有机碳含量高于其余乡土与外来红树林; 9种红树植物茎、叶、果的有机碳含量均以秋茄最高, 以老鼠簕最低, 不同器官碳含量中, 秋茄、木榄均以果实含量最高, 其余红树植物以茎、叶的有机碳较大。
中图分类号:
- S718.54
引用本文
粟春青, 高育慧, 罗炘武, 韩梦梦, 宫彦章, 郑卫国. 深圳不同红树林群落生物量和碳储量[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(6): 155-164.
SU Chunqing, GAO Yuhui, LUO Xinwu, HAN Mengmeng, GONG Yanzhang, ZHENG Weiguo. Forest biomass and carbon storage of different mangrove communities in Shenzhen, China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(6): 155-164.
表2
不同红树的异速生长方程"
| 红树树种 | 异速生长方程 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 秋茄Kandelia obovata | WAGB=0.0341(D2H)1.03; WBGB =0.0483(D2H)0.834 | Clough et al, |
| 木榄Bruguiera gymnorrhiza | WAGB=0.186D2.31; WBGB=0.4697D1.5541 | Clough et al, |
| 桐花树Aegiceras corniculata | WTGB=0.251ρD2.46 | Howard et al, |
| 海桑Sonneratia caseolaris | WTGB=0.251ρD2.46 | Howard et al, |
| 无瓣海桑Sonneratia apetala | WAGB=0.280(D2H)0.693; WBGB=0.038(D2H)0.759 | Ren et al, |
| 拉关木Laguncularia racemosa | WTGB=0.251ρD2.46 | Howard et al, |
| 白骨壤Avicennia marina | lgWAGB=2.113lgD−0.511 lgWBGB=1.171lgD+0.106 | Comley et al, |
| 红海榄Rhizophora stylosa | WAGB =0.2206D2.4292 WBGB=0.261D1.86 | Tamai et al, |
| 海漆Excoecaria agallocha | WAGB=0.1029D2.46 WBGB=0.08928D2.22 | Komiyama et al, |
表3
深圳3个样点调查样方红树林主要群落参数特征"
| 样点 | 群落类型 | 样方号 | 样方数 | 每100m2 平均株数 | 平均树 高/m | 平均胸 径/cm | 平均间 距/m | 树种组成 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 宝安西湾红树林 | 秋茄 | A1—A4, A11—A15 | 9 | 30 | 6.29 | 12.73 | 1.83 | 多为秋茄纯林, 个别样方伴生有海桑 |
| 海桑+无瓣海桑 | A5—A10 | 6 | 22 | 7.96 | 22.98 | 2.00 | 以海桑、无瓣海桑为优势种, 个别样方伴生有秋茄 | |
| 大鹏鹿咀山庄红树林 | 无瓣海桑 | B1、B2、B6 | 3 | 38 | 2.96 | 5.46 | 1.59 | 以无瓣海桑为优势种, 伴生种海漆, 多见木榄、白骨壤、秋茄、红海榄、桐花树等幼苗 |
| 红海榄 | B5、B7 | 2 | 39 | 1.85 | 3.41 | 1.58 | 以红海榄为优势种, 伴生种秋茄、无瓣海桑 | |
| 海漆 | B3、B8 | 2 | 30 | 2.95 | 5.11 | 1.78 | 以海漆为优势种, 伴生种秋茄、桐花树、拉关木 | |
| 拉关木 | B4 | 1 | 37 | 4.12 | 4.44 | 1.62 | 以拉关木为优势种, 伴生种秋茄、海漆 | |
| 福田红树林保护区 | 秋茄 | C1—C11, C14—C18 | 16 | 41 | 5.42 | 10.29 | 1.48 | 以秋茄占绝对优势种, 伴生种木榄、桐花树, 林下老鼠簕、木榄、卤蕨幼苗密布 |
| 海桑+无瓣海桑 | C12—C13 | 2 | 19 | 8.46 | 20.34 | 2.14 | 以海桑为优势种, 伴生种无瓣海桑, 林下老鼠簕密布 |
表5
深圳3个样点红树林群落的土壤有机碳与碳密度"
| 样点 | 群落/均值 | 含水量/% | 容重/(g·cm-3) | 土壤有机碳/(g·kg-1) | 土壤有机碳密度/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西湾红树林 | 秋茄 | 85.74 | 1.40 | 16.91 | 39.16 |
| 海桑+无瓣海桑 | 89.71 | 1.32 | 15.73 | 38.73 | |
| 地区均值 | 87.59±3.92a | 1.36±0.09a | 16.40±4.58b | 38.94±9.78b | |
| 大鹏鹿咀山庄红树林 | 无瓣海桑 | 84.66 | 1.36 | 17.01 | 44.63 |
| 红海榄 | 78.9 | 1.33 | 27.52 | 72.46 | |
| 海漆 | 76.9 | 1.34 | 23.52 | 64.41 | |
| 拉关木 | 76.5 | 1.68 | 25.92 | 86.92 | |
| 地区均值 | 80.26±4.91b | 1.39±0.17a | 22.38±3.82b | 61.82±22.77b | |
| 福田红树林保护区 | 秋茄 | 74.55 | 1.02 | 64.80 | 139.42 |
| 海桑+无瓣海桑 | 81.15 | 1.21 | 26.24 | 63.67 | |
| 地区均值 | 74.96±6.10c | 1.04±0.13b | 63.10±23.75a | 134.65±49.96a |
表6
深圳3个样点红树林植株有机碳含量"
| 样点 | 序号 | 有机碳含量/(g·kg-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 树种 | 叶 | 茎 | 果 | 花托 | 平均值 | ||
| 宝安西湾红树林 | 1 | 秋茄 | 398.90±7.38B | 379.37±5.58B | 446.32±17.42 | 463.06±11.39 | 421.91±36.99B |
| 2 | 无瓣海桑 | 373.79±12.78A | 437.95±10.06A | 404.48±15.53 | - | 405.41±29.98A | |
| 大鹏鹿咀山庄红树林 | 1 | 秋茄 | 387.39±7.17Bb | 417.19±14.33Aa | - | - | 402.29±19.21Ba |
| 2 | 无瓣海桑 | 379.26±9.77Abc | 379.26±12.41Bbc | 387.39±13.27 | - | 381.97±12.04Bb | |
| 3 | 红海榄 | 363.01±11.81c | 360.30±8.13cde | - | - | 361.66±9.75cd | |
| 4 | 海漆 | 414.48±16.48a | 387.39±10.84b | - | - | 400.94±19.38a | |
| 5 | 桐花树 | 390.10±12.41b | 371.14±7.16bcd | - | - | 380.62±13.79b | |
| 6 | 木榄 | 360.30±8.13cd | 365.72±9.77cd | 403.65±11.06 | - | 376.56±22.46bc | |
| 7 | 拉关木 | 330.50±9.77e | 344.05±8.13e | - | - | 337.28±10.94e | |
| 8 | 白骨壤 | 341.34±11.81de | 352.17±10.84de | - | - | 346.76±11.75de | |
| 福田红树林保护区 | 1 | 秋茄 | 446.32±8.37Aa | 432.37±10.06Aa | 482.58±14.76a | - | 453.76±24.52Aa |
| 2 | 无瓣海桑 | 393.32±8.37Ab | 362.63±12.78Bbc | - | - | 377.98±19.39Bc | |
| 3 | 海桑 | 446.32±15.53a | 373.79±12.16b | 404.48±5.85b | - | 408.20±33.15b | |
| 4 | 桐花树 | 398.90±5.58b | 367.19±9.78b | - | - | 383.05±18.77bc | |
| 5 | 木榄 | 343.11±7.38c | 345.90±10.05c | 401.69±13.95b | - | 363.57±30.11c | |
| 6 | 老鼠簕 | 304.06±12.16d | 267.79±8.37d | - | - | 285.92±21.95d | |
| [1] |
曹庆先, 2010. 北部湾沿海红树林生物量和碳贮量的遥感估算[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈瑶瑶, 张雅松, 娄铎, 等, 2019. 广东英罗湾不同潮位红树林-滩涂系统碳密度差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(6): 1134-1140.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.06.008 |
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈毅青, 陈宗铸, 陈小花, 等, 2020. 石梅湾3种植物叶片与其群落凋落物C, N, P生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 林业资源管理 (4): 66-73.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈顺洋, 安文硕, 陈彬, 等, 2021. 红树林生态修复固碳效果的主要影响因素分析[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 40(1): 34-42.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
樊月, 潘云龙, 陈志为, 等, 2019. 四种红树植物根茎叶的碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(4): 1041-1048.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
高天伦, 2018. 广东省雷州附城主要红树林群落碳储量及其影响因子[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
郭梦晴, 杨颖, 许叶, 等, 2020. 高州油茶人工林碳储量分布特征[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 41(3): 86-92.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
广东省市场监督管理局, 2024. 滨海湿地生态系统固碳量评估技术规程: DB44/T 2504—2024[S]. 广州: 广东省市场监督管理局.
|
| [9] |
胡懿凯, 2019. 淇澳岛不同恢复类型红树林碳密度和固碳速率比较研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
胡柳柳, 谭敏, 罗琴, 等, 2024. 基于WorldView-3遥感影像的福田红树林碳储量年际变化[J]. 广西植物, 44(8): 1403-1414.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
姜生秀, 赵鹏, 张俊年, 等, 2024. 祁连山典型植被土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 林草资源研究 (2): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
李海生, 董华杰, 张彩婵, 等, 2019. 深圳鹿咀红树林资源现状及保护[J]. 安徽农业科学, 47(20): 110-112.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
李艺蝉, 2021. 红树植物木质部结构特征及其对环境因子的响应[D]. 南宁: 广西大学.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
毛子龙, 杨小毛, 赵振业, 等, 2012. 深圳福田秋茄红树林生态系统碳循环的初步研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(7): 1189-1199.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906(2012)07-1189-11 |
|
|
|
| [15] |
彭聪姣, 钱家炜, 郭旭东, 等, 2016. 深圳福田红树林植被碳储量和净初级生产力[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(7): 2059-2065.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201607.029 |
|
|
|
| [16] |
彭逸生, 庄雪茵, 赵丽丽, 等, 2023. 树种选择和滩地高程对红树林修复早期系统碳储量的影响[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版)(中英文), (2): 37-46.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
邱瑾, 戴洪涛, 邢永泽, 等, 2023. 广西山口不同演替阶段红树植物叶茎根的生态化学计量特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(3): 149-157.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
覃国铭, 张靖凡, 周金戈, 等, 2023. 广东省红树林土壤碳储量及固碳潜力研究[J]. 热带地理, 43(1): 23-30.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003606 |
|
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003606 |
|
| [19] |
孙学超, 黄展鹏, 张琼锐, 等, 2022. 珠海淇澳岛人工次生无瓣海桑纯林的植被碳储量变化[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 54(4): 89-100.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
温远光, 1999. 广西英罗港5种红树植物群落的生物量和生产力[J]. 广西科学, 6(2): 142-147.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
徐芳, 2020. 基于Sentinel-2的红树林提取及碳储量估算研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
颜葵, 2015. 海南东寨港红树林湿地碳储量及固碳价值评估[D]. 海口: 海南师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
朱德煌, 2023. 深圳福田土著和外来红树物种叶片的化学计量特征[J]. 湿地科学, 21(5): 681-688.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
张子鸣, 王艺杰, 王莹, 等, 2023. 珠江口红树林湿地土壤碳的分布特征和影响因素研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(1): 297-306.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
张欢欢, 马胜中, 常晓红, 等, 2024. 红树林碳汇研究现状及未来对策[J/OL]. 地球化学:1-10. (2024-10-29) [2025-01-22]. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19700/j.0379-1726.2024.01.150
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
周丽丽, 李树斌, 王万萍, 等, 2020. 福建漳江口4种红树植物叶片碳氮磷化学计量及养分重吸收特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 26(3): 674-680.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
周元慧, 2020. 广西北部湾红树林生态系统的生态化学计量特征研究[D]. 南宁: 南宁师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
周治刚, 岳文, 李辉权, 等, 2024. 树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(2): 108-120.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
朱利永, 黄泓杰, 2019. 深圳市宝安区西海岸红树林恢复与重建研究[J]. 林业科技, 44(4): 59-62 (in Chinese).
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2024.102504 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/0378-1127(89)90034-0 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1071/BT04162 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1038/ngeo1123 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1017/S0266467405002476 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.11.037 pmid: 24374165 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.846556 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1007/BF02348582 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137142 |
| [1] | 王日明, 苏金恒, 戴志军, 吴天亮, 谢晓雯, 黄春梅, 李兴荣, 张尚宇. 钦州湾茅岭江河口红树林湿地动态变化过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(6): 143-154. |
| [2] | 谢小魁, 李兴荣, 王日明, 戴志军, 龚受基, 庞文鸿, 张尚宇. 北部湾茅尾海潮滩外来红树无瓣海桑时空演替[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(6): 132-142. |
| [3] | 胡鑫, 熊兰兰, 陈顺洋, 张黄琛, 邹易阳, 张吉超, 刘东熙, 何佳潞, 吴于琪, 朱振杰. 幼龄红树生物量模型及幼林红树林碳储量研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 187-199. |
| [4] | 田蜜, 钟才荣, 吕晓波, 方赞山, 黄丹慜. 东寨港不同退塘还林模式红树林群落特征比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 58-65. |
| [5] | 袁羽杰, 钟仕全, 蒋卫国, 初爱萍, 凌子燕. 基于环境减灾二号卫星的2023年铁山港红树林病虫害动态监测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 188-196. |
| [6] | 刘思妮, 白猛, 朱义广, 罗小卫, 高程海, 刘永宏, 徐新亚, 蒋晓东. 红树林来源链霉菌中2-羟基苯基噻唑啉衍生物及其生物合成基因簇分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(2): 64-72. |
| [7] | 吴雪, 赵鑫, 辜伟芳, 朱科桦, 葛振鸣. 浙南海岸带人工秋茄(Kandelia obovata)红树林与互花米草(Spartina alterniflora)盐沼土壤碳汇对比研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [8] | 黄良民, 林强, 谭烨辉, 黄小平, 周林滨, 黄晖. 热带海洋特色生态系统恢复重构与保护思考*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 1-12. |
| [9] | 吴鸿博, 罗锋, 陈治澎, 朱飞, 曾靖伟, 张弛, 李瑞杰. 红树林生态重建效果预测研究新模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 86-97. |
| [10] | 郑法, 黄福林, 陈泽恒, 丁伟品. 基于LUCC和景观格局变化的广西山口红树林湿地动态研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 165-173. |
| [11] | 黄圆, 岑竞仪, 梁芊艳, 吕颂辉, 王建艳. 基于高通量测序技术的深圳湾真核浮游植物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 21-33. |
| [12] | 周治刚, 岳文, 李辉权, 林阳阳. 树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 108-120. |
| [13] | 申键, 简焯锴, 欧阳雪敏, 艾彬. 结合潮位校正的雷州半岛红树林湿地动态变迁遥感监测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 137-153. |
| [14] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [15] | 张哲然, 胡俊洋, 周凯, 张鹏晖, 邢久星, 陈胜利. 不同类型台风气象场对深圳近海海域风暴潮模拟的比较研究—以台风“山竹”为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
|
||