热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 91-107.doi: 10.11978/2025051CSTR: 32234.14.2025051
网采镜检与全息粒子成像综合分析贻贝养殖区浮游植物群落特征
杨天炜1( ), 林军1,2,3,4(
), 林军1,2,3,4( ), 焦俊鹏1, 吴越1
), 焦俊鹏1, 吴越1
- 1
上海海洋大学海洋科学与生态环境学院
2上海海洋大学海洋牧场工程技术研究中心
3船舶与海洋工程特种装备和动力系统国家工程研究中心
4上海海洋大学自然资源部海洋生态监测与修复技术重点实验室
-
收稿日期:2025-04-04修回日期:2025-05-23出版日期:2025-11-10发布日期:2025-12-03 -
通讯作者:林军。email: jlin@shou.edu.cn -
作者简介:杨天炜(2000—), 男, 浙江省衢州市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋生态及渔业碳汇研究。email: m220501216@st.shou.edu.cn
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42376207); 国家重点研发计划项目(2023YFD2401902)
Integrated analysis of phytoplankton community structure in mussel aquaculture areas using net sampling with microscopy and LISST Holo2
YANG Tianwei1( ), LIN Jun1,2,3,4(
), LIN Jun1,2,3,4( ), JIAO Junpeng1, WU Yue1
), JIAO Junpeng1, WU Yue1
- 1
College of Oceanography and Ecological Science ,Shanghai Ocean University
2Marine Ranching Engineering Technology Research Center ,Shanghai Ocean University
3National Engineering Research Center for Special Equipment and Power Systems of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering
4Key Laboratory of Marine Ecological Monitoring and Restoration Technology ,Ministry of Natural Resources, Shanghai Ocean University
-
Received:2025-04-04Revised:2025-05-23Online:2025-11-10Published:2025-12-03 -
Contact:LIN Jun. email: jlin@shou.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42376207); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2023YFD2401902)
摘要:
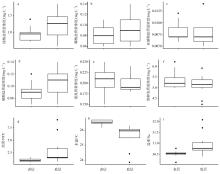
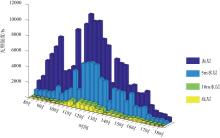
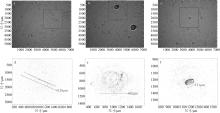
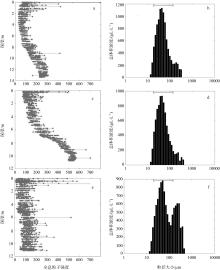
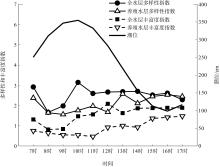
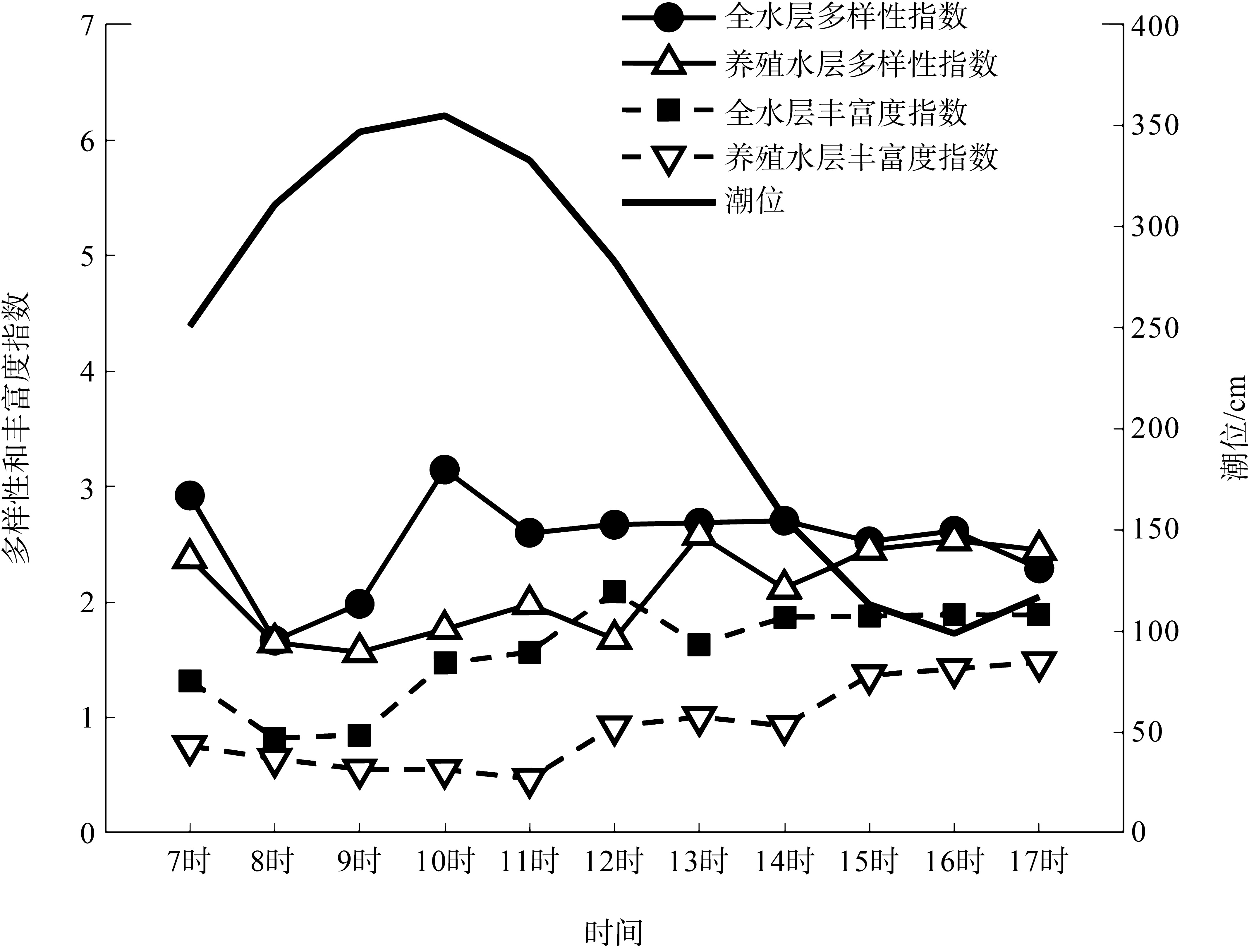
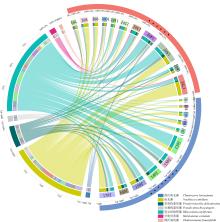
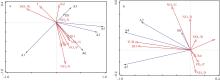
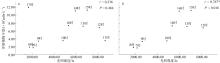
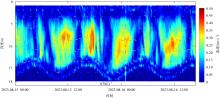
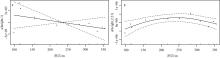
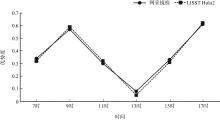
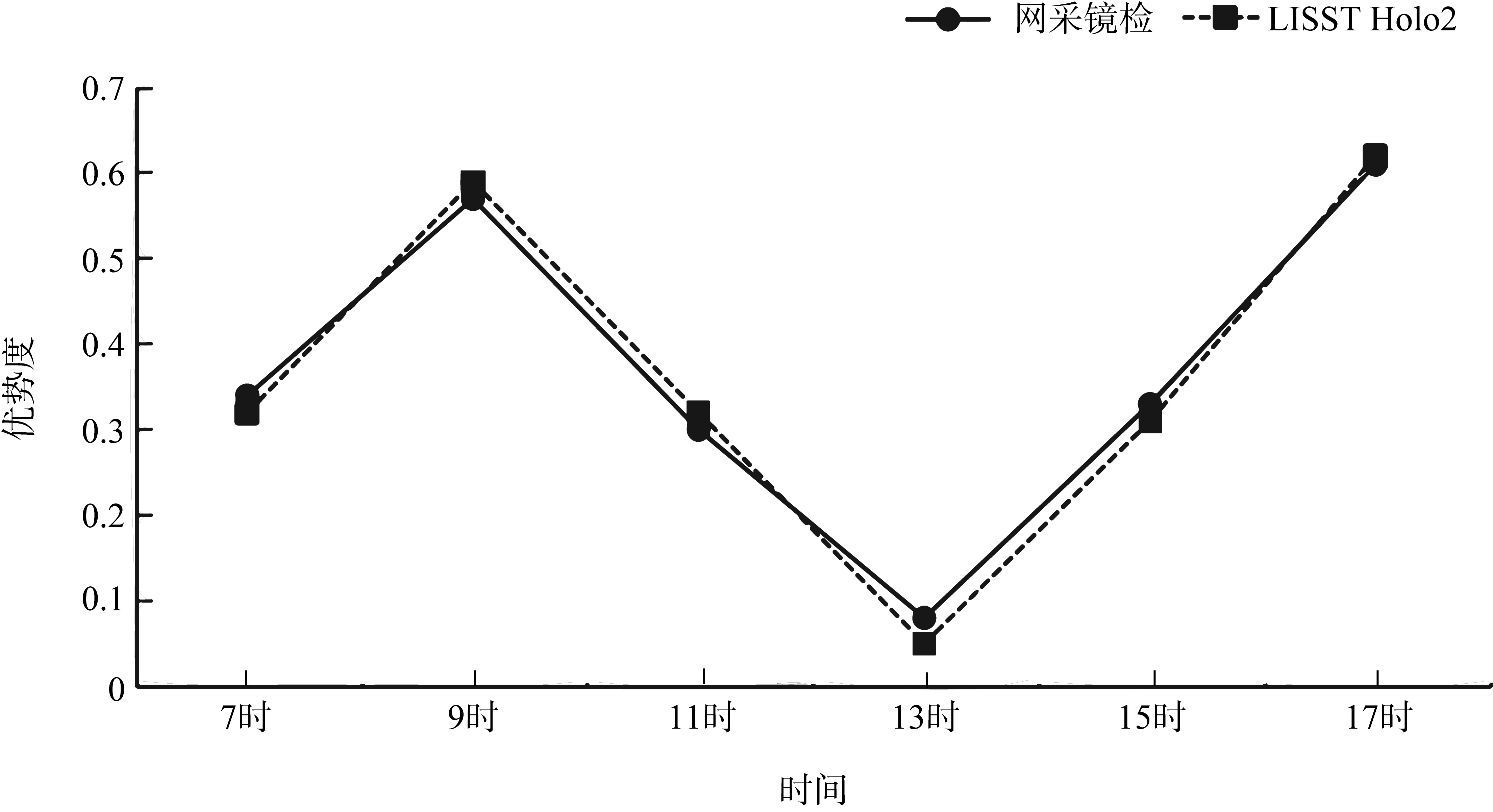
本文基于2023年8月期间在浙江省枸杞岛贻贝浮筏式养殖场利用网采镜检以及水下数字全息粒子成像系统(LISST Holo2)进行调查获得的浮游植物实测数据, 对网采和粒子影像数据进行综合比较研究, 并分析其群落结构晨昏动态变化及影响因子。调查期间共鉴定出5门38属75种浮游植物, 其中夜光藻(Noctiluca scintillans)和笔尖形根管藻(Rhizosolenia styliformis)等为主要优势种, 且养殖区正处于夜光藻赤潮暴发阶段。养殖水层浮游植物种类与丰度低于全水层, 但其共现网络复杂度更高, 群落稳定性及种间互作更强。潮汐对全水层浮游植物分布影响显著[广义相加模型(generalized additive models, GAM)解释量57.4%], 而养殖水层丰度变化主要受光照主导(P=0.016)。LISST Holo2共鉴定出3门34属浮游植物, 占网采镜检鉴定结果的89.4%, 在大粒径藻类(如夜光藻)监测中与传统网采镜检结果高度一致(优势度曲线R²>0.8)。LISST Holo2观测与传统采样相比, 解决了其样品保存和处理繁琐, 数据获取滞后以及难以测量浮游植物粒径大小等问题, 本研究验证其在大粒径藻类监测中的可靠性, 有助于未来海洋生态系统监测与保护的研究。
中图分类号:
- Q948.8
引用本文
杨天炜, 林军, 焦俊鹏, 吴越. 网采镜检与全息粒子成像综合分析贻贝养殖区浮游植物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(6): 91-107.
YANG Tianwei, LIN Jun, JIAO Junpeng, WU Yue. Integrated analysis of phytoplankton community structure in mussel aquaculture areas using net sampling with microscopy and LISST Holo2[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(6): 91-107.
表2
浮游植物优势种的优势度"
| 编号 | 优势种 | 优势度 | 粒径大小 | 形态特征 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 贻贝养殖层 | 全水层 | ||||
| A1 | 中肋骨条藻(Skeletonema costatum) | / | 0.04 | 直径6~22μm | 单个细胞近似球形, 链长2~8个细胞 |
| A2 | 笔尖形根管藻(Rhizosolenia styliformis) | 0.35 | 0.36 | 直径5~15μm,长200~500μm | 细胞呈长圆柱形, 末端尖锐 |
| A3 | 洛氏角毛藻(Chaetoceros lorenzianus) | / | 0.04 | 长约20~50μm, 宽约10~30μm | 细胞呈圆柱形或椭圆形通常形成短链, 由 2~6个细胞组成 |
| A4 | 尖刺伪菱形藻(Pseudo-nitzschia pungens) | 0.03 | / | 宽2~5μm, 长70~130μm | 细长针形 |
| A5 | 柔软伪菱形藻(Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima) | 0.06 | 0.05 | 宽1.5~3μm, 长30~80μm | 较尖刺伪菱形藻更纤细 |
| A6 | 佛氏海线藻(Thalassionema frauenfeldii | / | 0.02 | 宽2~5μm, 长20~60μm | 线状或短棒状, 常形成星形群体 |
| B1 | 夜光藻(Noctiluca scintillans) | 0.31 | 0.29 | 直径200~2000μm | 球形或肾形 |
| [1] |
毕远溥, 董婧, 蒋双, 等, 2002. 小窑湾双壳贝类筏式养殖对海域环境的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 8(3): 270-275.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈丹丹, 庞巧珠, 涂志刚, 等, 2021. 后水湾深水网箱养殖区浮游植物群落季节变化及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 40(1): 73-80.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈奕帆, 王君玥, 王英豪, 等, 2024. 典型赤潮生物夜光藻研究进展[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 39(6): 1075-1086.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
代鲁平, 李超伦, 王世伟, 等, 2016. 基于ZooScan图像技术的南黄海夏季浮游动物群落结构分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(4): 764-773.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
段晓萌, 秦华伟, 马浩阳, 等, 2023. 黄河口及莱州湾海域磷的时空分布及浮游生物对低磷胁迫的响应[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 53(11): 87-98.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
凡仁福, 魏皓, 赵亮, 2015. 高生产力区LISST-100和OBS对悬浮颗粒物测量的比较研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 33(4): 492-500.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
关莹莹, 林军, 焦俊鹏, 等, 2022. 高滤食压力下贻贝筏式养殖场及周边海域浮游植物群落特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 41(4): 543-553.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
关莹莹, 2021. 规模化贻贝养殖海域浮游植物群落结构及其环境影响因子研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
霍笑康, 王永刚, 周灵同, 等, 2024. 结合生态网络解析白洋淀浮游生物生态位和种间联结性特征[J]. 环境科学, 45(9): 5298-5307.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
焦念志, 杨燕辉,
|
| [11] |
李红飞, 林森杰, 2019. 南海浮游植物生态学研究进展[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 58(1): 1-10.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
李立群, 王艳, 王彪, 等, 2024. 2009—2021年夏季长江口海域浮游生物群落结构时空分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 37(2): 233-245.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
李斯远, 2022. 厚壳贻贝的摄食选择偏好及其食物识别机制研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
梁文钊, 唐丹玲, 2017. 南海西部夏季表层浮游植物粒径结构分布特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(4): 93-101.
doi: 10.11978/2016104 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2016104 |
|
| [15] |
陆斗定, 张志道, 朱根海, 等, 1994. 浙江近海夜光藻的分布及其生态学特点[J]. 东海海洋, 12(3): 62-69.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
施玉珍, 张才学, 张际标, 等, 2017. 水东湾海域浮游植物潮汐分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 37(18): 5981-5992.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
孙晓霞, 郭术津, 刘梦坛, 等, 2021. 印太交汇区浮游植物和浮游动物生态学研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 52(2): 323-331.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
孙东, 赵冬至, 文世勇, 等, 2010. 夜光藻赤潮与环境因子关系的模糊分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 29(1): 70-75.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
宋书群, 孙军, 俞志明, 2009. 长江口及其邻近水域叶绿素a的垂直格局及成因初析[J]. 植物生态学报, 33(2): 369-379.
doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2009.02.015 |
|
doi: 10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2009.02.015 |
|
| [20] |
唐启升, 蒋增杰, 毛玉泽, 2022. 渔业碳汇与碳汇渔业定义及其相关问题的辨析[J]. 渔业科学进展, 43(5): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
唐紫琦, 宋敏杰, 王馨, 等, 2024. 2022年南黄海绿潮分布与浮游生物群落关系初探[J]. 海洋科学, 48(3): 26-41.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
谭益国, 钟威, 林军, 等, 2024. 浮筏式贻贝养殖设施阻流效应的数值模拟[J/OL]. 水产学报: 1-13. (2024-02-19) [2025-04-04]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1283.S.20240207.1550.002.html
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
陶宗娅, 邹琦, 1999. 植物光合作用光抑制分子机理及其光保护机制[J]. 西南农业学报, 12(S2): 9-18.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
王旭, 赵旭, 章守宇, 等, 2015. 枸杞岛贻贝养殖水域碳氮磷分布格局[J]. 水产学报, 39(11): 1650-1664.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
吴晓凡, 汪振华, 章守宇, 等, 2024. 大规模筏式贻贝养殖区浮游植物群落结构昼夜变化特征[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 33(5): 1211-1222.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
温英, 林军, 杨冠林, 等, 2022. 贻贝浮筏养殖设施水动力效应及附生海藻碎屑输运的数值模拟[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 31(6): 1549-1561.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
徐亚军, 赵亮, 原野, 2016. 基于声学仪器与粒径分析仪研究东海浮游动物昼夜垂直迁移过程[J]. 海洋学报, 38(8): 123-130.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
徐兆礼, 高文烨, 2004. 东海赤潮高发区夜光藻数量分布与环境关系的研究[C]// 中国水产学会. 中国水产学会第五届青年学术年会摘要集, 上海: 中国水产学会: 135.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
杨冠林, 2022. 典型贻贝浮筏式养殖海域物理—生态—贝类生长耦合数值模型的构建及应用[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
岳新利, 张梦柯, 谷利德, 等, 2023. 福建平潭外海域夜光藻赤潮期营养元素和溶解态痕量金属动态与响应[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 62(3): 375-384.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
赵文, 2005. 水生生物学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [32] |
周曦杰, 2014. 枸杞岛典型生境螺贝类代表种—角蝾螺、紫贻贝摄食生态初步研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.3800/pbr.8.9 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1038/334340a0 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1007/s12601-015-0008-2 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170343 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(94)00105-I |
| [40] |
doi: 10.3354/meps062283 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.973155 |
| [1] | 于蓁, 郭祥瑞, 刘雪睿, 孙浩, 张燕英. 山东沿海三种海草根际真核生物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(5): 86-96. |
| [2] | 冯战权, 苏冒亮, 杜媛媛, 钟友凌, 张俊彬. 基于MaxEnt模型分析全球气候变化对中国沿海带鱼潜在分布的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(5): 77-85. |
| [3] | 孙佳宁, 王玉清, 章守宇, 王凯. 绿华岛海域海藻场大型底栖生物群落结构及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(4): 119-135. |
| [4] | 代丽, 潘铧康, 刘励阳, 何健, 赵科, 祁剑飞, 张真, 苏培, 冯丹青. 环境因子对污损生物沙筛贝(Mytilopsis sallei)幼体附着变态的影响研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 121-129. |
| [5] | 周志希, 唐汇娟, 柯志新, 刘甲星, 周伟华. 基于形态学和高通量测序的春季南澳海域浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 53-65. |
| [6] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [7] | 马文刚, 夏景全, 魏一凡, 尹洪洋, 覃乐政, 刘相波, 胡雪晴, 许强, 李秀保, 王爱民. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场近岛区底表大型底栖动物群落结构及评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [8] | 向晨晖, 刘甲星, 柯志新, 周林滨, 谭烨辉. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构和种类组成对淡澳河河口水加富的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 49-60. |
| [9] | 黄建中, 魏宇衡, 顾志峰, 吴川良, 许强, 王爱民, 李秀保. 海南西岛珊瑚群落变化及其影响因素 *[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6): 103-113. |
| [10] | 何思璇,何斌源. 防城河口湾鱼类群落结构及其与环境因子关系研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(5): 86-97. |
| [11] | 雷新明, 黄晖, 练健生, 张浴阳, 杨剑辉. [已撤稿] 三亚珊瑚礁珊瑚藻种类及其空间特征与环境因子的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(3): 79-88. |
| [12] | 毋浩亮, 胡松. 环境因子对南海土台风“蝴蝶”与“银河”强度的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(3): 26-34. |
| [13] | 崔磊, 吕颂辉, 董悦镭, 郜星晨, 李丽, 刘丰华, 岑竞仪. 围填海工程对淇澳岛附近水域环境因子与生物群落的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(2): 96-105. |
| [14] | 吴风霞, 黄洪辉, 黄建荣, 刘华雪. 春季白沙湾浮游纤毛虫群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(3): 79-86. |
| [15] | 刘俏, 龙丽娟. 环境因子对慢原甲藻(Prorocentrum rhathymum)生长的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(3): 93-100. |
|
||