热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 107-115.doi: 10.11978/2023047CSTR: 32234.14.2023047
广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征
耿婉璐1,2( ), 邢永泽2(
), 邢永泽2( ), 张秋丰1,2(
), 张秋丰1,2( ), 管卫兵1
), 管卫兵1
- 1.上海海洋大学海洋生态与环境学院, 上海 201306
2.自然资源部第四海洋研究所, 自然资源部热带海洋生态系统与生物资源重点实验室, 广西 北海 536015
-
收稿日期:2023-04-12修回日期:2023-05-25出版日期:2024-01-10发布日期:2024-01-19 -
作者简介:耿婉璐(1997—), 女, 河南省许昌市人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事湿地生态修复研究。email: genggengwanlu@163.com
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42141016); 自然资源部第四海洋研究所基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(202005)
Structural characteristics of macrobenthic communities at intertidal zone for mangrove in Beihai, Guangxi
GENG Wanlu1,2( ), XING Yongze2(
), XING Yongze2( ), ZHANG Qiufeng1,2(
), ZHANG Qiufeng1,2( ), GUAN Weibing1
), GUAN Weibing1
- 1. College of Marine Ecology and Environment, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
2. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Ecosystem and Bioresource, Fourth Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, Beihai 536015, China
-
Received:2023-04-12Revised:2023-05-25Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-19 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42141016); Scientific Research Fund of the Fourth Institute of Oceanography,MNR(202005)
摘要:
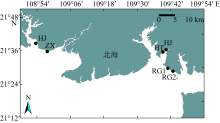
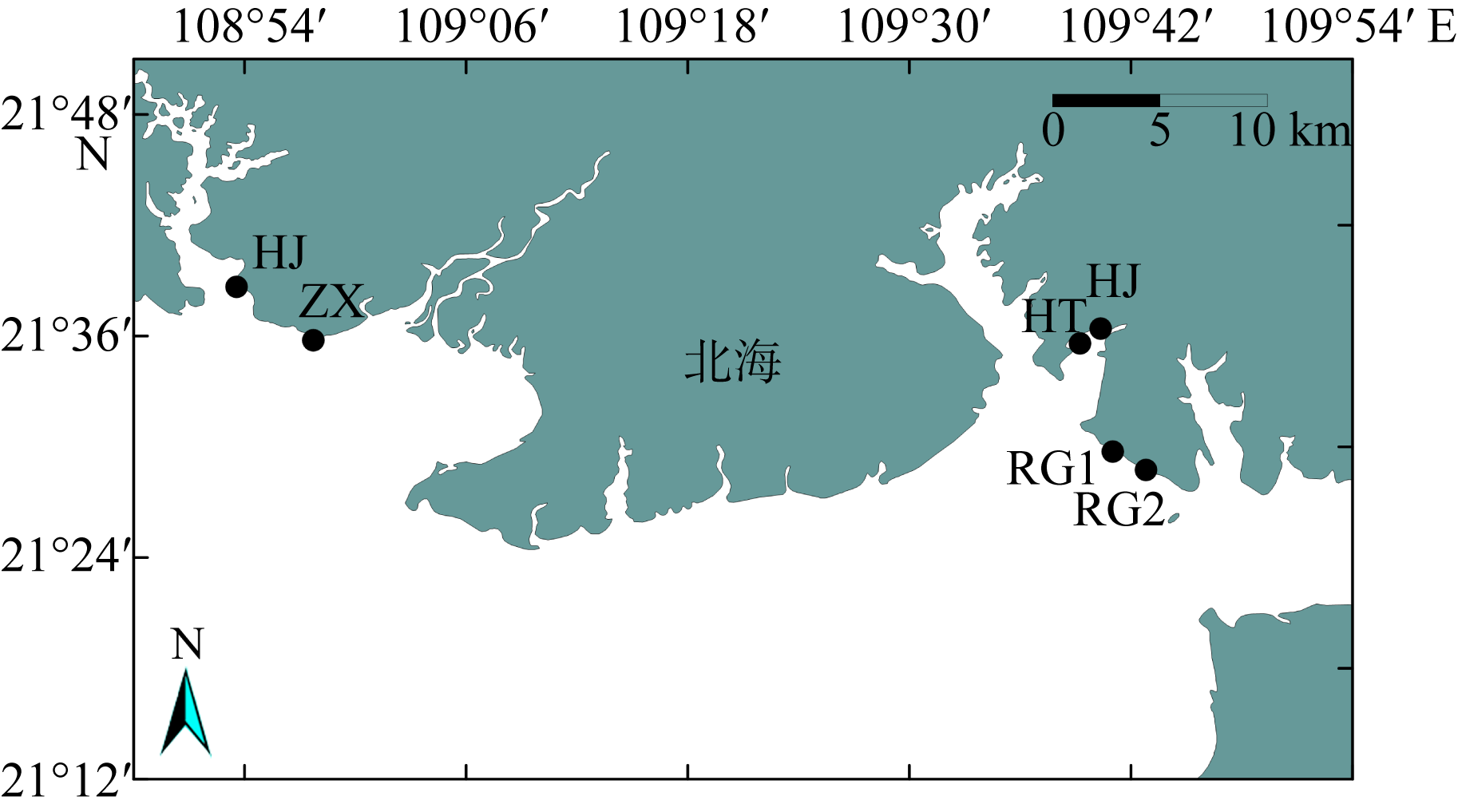
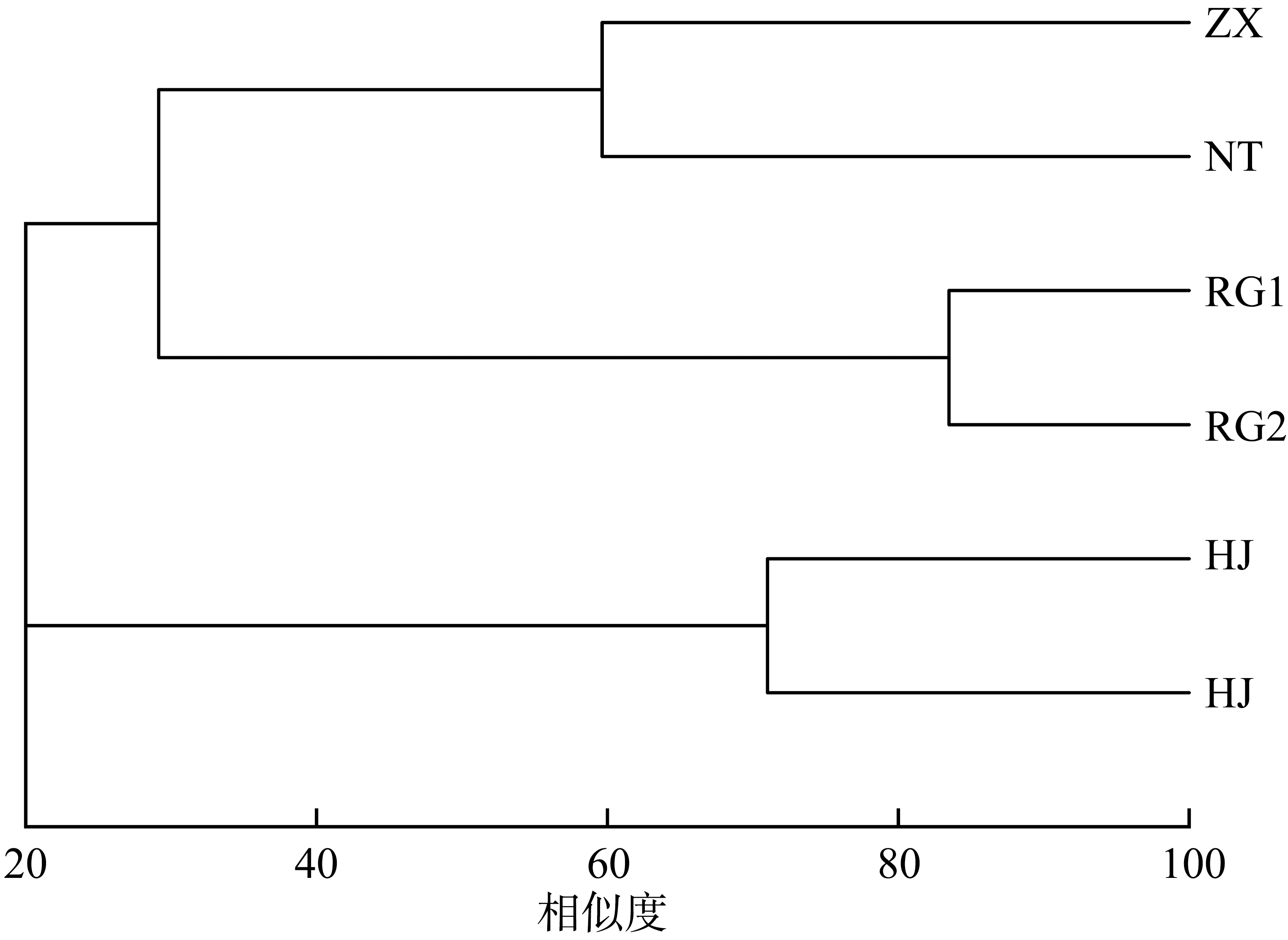
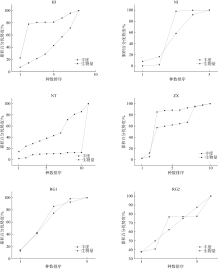
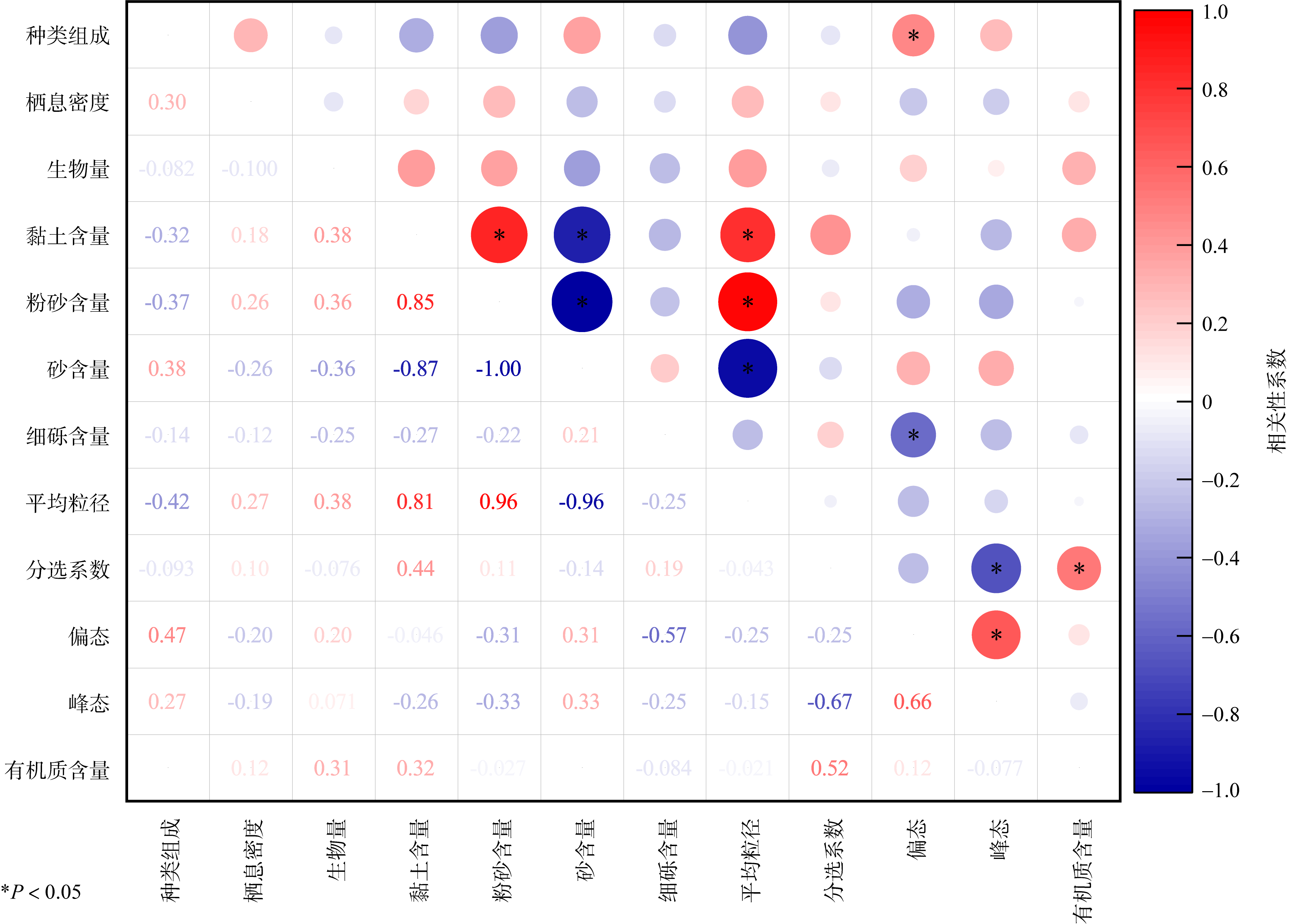
为了解广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落特征, 本文首次在北海市选择了2条光滩断面、2条有少量互花米草分布的断面和2条被互花米草覆盖的断面开展生态调查, 调查了大型底栖动物的群落结构特征, 并分析了其与环境因子之间的关系。结果表明, 调查区域大型底栖动物共29种, 不同生境的软体动物生物量、节肢动物栖息密度及蟹洞数量差异显著(P< 0.05), 大型底栖动物的种类组成与沉积物的偏态显著正相关(P< 0.05)。光滩样地黄金村HJ群落结构稳定, 其余样地大型底栖动物的群落结构均不稳定。互花米草的生长会对大型底栖动物群落结构产生影响。
引用本文
耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115.
GENG Wanlu, XING Yongze, ZHANG Qiufeng, GUAN Weibing. Structural characteristics of macrobenthic communities at intertidal zone for mangrove in Beihai, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 107-115.
表1
不同样地土壤理化因子"
| 样地类型 | 样地名称 | 有机质/% | 黏土/% | 粉砂/% | 砂/% | 细砾/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 光滩 | HJ | 0.47±0.05a | 1.42±0.21ab | 28.56±3.48bc | 69.83±3.60ab | 0.19±0.11 |
| NJ | 0.47±0.03a | 2.41±0.21b | 37.91±3.90c | 59.68±4.10a | - | |
| 平均值 | 0.48±0.09 | 1.92±0.01* | 33.23±0.15* | 64.76±0.18 | 0.10±0.039 | |
| 少量互花米草 | ZX | 1.88±0.12ab | 2.18±0.09b | 29.95±0.64bc | 67.56±0.64ab | 0.31±0.18 |
| NT | 3.08±0.45b | 1.97±0.06ab | 26.21±0.63abc | 71.82±0.61abc | - | |
| 平均值 | 2.48±0.12* | 2.08±0.01b | 28.08±0.01 | 69.69±0.01 | 0.16±0.06 | |
| 互花米草 | RG1 | 0.77±0.22a | 1.23±0.36a | 17.88±1.71ab | 80.75±2.02bc | 0.14±0.08 |
| RG2 | 1.35±0.33a | 0.90±0.15a | 15.19±0.29a | 83.83±0.37c | 0.08±0.04 | |
| 平均值 | 1.06±0.38 | 1.07±0.08 | 16.54±0.50 | 82.29±0.59* | 0.11±0.01 |
表4
不同样地大型底栖动物生物量"
| 样地类型 | 样地名称 | 生物量/(g·m−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软体动物 | 节肢动物 | 其他动物 | 合计 | ||
| 光滩 | HJ | 182.83 | 0 | 0.64 | 183.47 |
| NJ | 176.16 | 2.45 | 2.35 | 180.96 | |
| 平均值 | 179.49±3.34a | 1.23±1.23a | 1.49±0.86a | 182.23±1.26a | |
| 少量互花米草 | ZX | 318.51 | 10.19 | 5.6 | 334.29 |
| NT | 793.07 | 38.61 | 19.68 | 851.36 | |
| 平均值 | 555.79±237.28b | 24.4±14.21a | 12.64±7.04a | 592.83±258.54b | |
| 互花米草 | RG1 | 693.87 | 66.83 | 0 | 760.69 |
| RG2 | 703.95 | 3.79 | 5.49 | 713.23 | |
| 平均值 | 698.91±5.04b | 35.31±31.52a | 2.75±2.75a | 736.96±23.73b | |
表5
不同样地大型底栖动物栖息密度"
| 样地类型 | 样地名称 | 栖息密度/(ind.·m−2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软体动物 | 节肢动物 | 其他动物 | 合计 | 蟹洞 | ||
| 光滩 | HJ | 70 | 0 | 6 | 76 | 304 |
| NJ | 54 | 6 | 6 | 66 | 1008 | |
| 平均值 | 62±8a | 3±3a | 6a | 71±5a | 656±352a | |
| 少量互花米草 | ZX | 214 | 6 | 6 | 226 | 1158 |
| NT | 32 | 27 | 54 | 113 | 2603 | |
| 平均值 | 123±91a | 17±11ab | 30±24a | 169±57b | 1880±723b | |
| 互花米草 | RG1 | 43 | 32 | 0 | 75 | 587 |
| RG2 | 6 | 22 | 16 | 44 | 358 | |
| 平均值 | 25±19a | 27±5b | 8±8a | 59±16a | 472±115a | |
| [1] |
鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析(第三版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 25-38.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
蔡永久, 龚志军, 秦伯强, 2010. 太湖大型底栖动物群落结构及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 18(1): 50-59.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.050 |
|
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.050 |
|
| [3] |
冯建祥, 黄茜, 陈卉, 等, 2018. 互花米草入侵对盐沼和红树林滨海湿地底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(3): 943-951.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
黄雅琴, 王建军, 何雪宝, 等, 2020. 三沙湾互花米草(Spartina alterniflora) 入侵对大型底栖动物群落结构的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(3): 506-519.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
纪莹璐, 蒲思潮, 陶卉卉, 等, 2022. 丁字湾盐沼湿地不同植被生境大型底栖动物群落结构研究[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 53(3): 412-420.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
赖廷和, 何斌源, 黄中坚, 等, 2019. 防城河口湾潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(2): 67-77.
doi: 10.11978/2018058 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2018058 |
|
| [7] |
刘士龙, 秦旭东, 王广军, 等, 2019. 2017 年夏季北海市冯家江入海口红树林潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构及多样性[J]. 湿地科学, 17(3): 352-358.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
陆琳莹, 邵学新, 杨慧, 等, 2020. 浙江滨海湿地互花米草生长性状对土壤化学因子的响应[J]. 林业科学研究, 33(5): 177-183.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
马克平, 1994. 生物群落多样性的测度方法Ⅰα多样性的测度方法(上)[J]. 生物多样性, 1994(3): 162-168.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
马文刚, 夏景全, 魏一凡, 等, 2022. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场近岛区底表大型底栖动物群落结构及评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(3): 135-146.
doi: 10.11978/2021125 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2021125 |
|
| [11] |
仇乐, 刘金娥, 陈建琴, 等, 2010. 互花米草扩张对江苏海滨湿地大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 34(8): 50-55.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
任海庆, 袁兴中, 刘红, 等, 2015. 环境因子对河流底栖无脊椎动物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 35(10): 3148-3156.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
沈永明, 王艳芳, 陈寿军, 等, 2013. 互花米草盐沼湿地大型底栖动物时空分布特征[J]. 地理研究, 32(4): 638-644.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
谢志发, 何文珊, 刘文亮, 等, 2008. 不同发育时间的互花米草盐沼对大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 27(1): 63-67.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
杨泽华, 童春富, 陆健健, 2007. 盐沼植物对大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 27(11): 4387-4393.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
袁涛萍, 李恒翔, 李路, 等, 2017. 夏季大亚湾大型底栖动物群落结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(1): 41-47.
doi: 10.11978/2016040 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2016040 |
|
| [17] |
赵彩云, 李俊生, 宫璐, 等, 2014. 广西北海市滨海湿地互花米草入侵对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 湿地科学, 12(6): 733-739.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
赵永强, 曾江宁, 陈全震, 等, 2009. 不同互花米草(Spartina alterniflora Loisel)密度生境中大型底栖动物群落格局[J]. 自然资源学报, 24(4): 630-639.
doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2009.04.009 |
|
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.09.003 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.3354/meps073231 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/0006-3207(96)00017-1 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(01)02358-8 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1442-9993.2000.01016.x |
| [26] |
doi: 10.3354/meps226077 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1007/s10750-022-04877-x |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2007.05.004 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1188528 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1007/s10530-007-9097-x |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1111/aec.2007.32.issue-7 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00392515 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113796 |
| [1] | 饶义勇, 赵美榕, 旷泽行, 黄洪辉, 谭萼辉. 浮筏式牡蛎养殖对大型底栖动物群落功能结构的影响——以大鹏澳为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 69-83. |
| [2] | 吴鸿博, 罗锋, 陈治澎, 朱飞, 曾靖伟, 张弛, 李瑞杰. 红树林生态重建效果预测研究新模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 86-97. |
| [3] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [4] | 郑法, 黄福林, 陈泽恒, 丁伟品. 基于LUCC和景观格局变化的广西山口红树林湿地动态研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 165-173. |
| [5] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [6] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [7] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [8] | 周治刚, 岳文, 李辉权, 林阳阳. 树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 108-120. |
| [9] | 申键, 简焯锴, 欧阳雪敏, 艾彬. 结合潮位校正的雷州半岛红树林湿地动态变迁遥感监测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 137-153. |
| [10] | 孙婷婷, 郝雯瑾, 徐鹏臻, 叶丽靖, 董志军. 海水酸化对海月水母螅状体共附生微生物的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 111-119. |
| [11] | 董俊德, 黄小芳, 龙爱民, 王友绍, 凌娟, 杨清松. 红树林固氮微生物及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 1-11. |
| [12] | 张兰兰, 程夏雯, 向荣, 邱卓雅, 常虎. 2019年春季孟加拉湾中部放射虫群落结构垂向变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [13] | 梁寒峭, 陈文凤, 范益铠, 朱子冬, 马国需, 陈德力, 田婧. 红树林来源曲霉属和木霉属内生真菌次生代谢产物及活性研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 12-24. |
| [14] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [15] | 张程飞, 任广波, 吴培强, 胡亚斌, 马毅, 阎宇, 张菁锐. 基于高分光学与全极化SAR的海南八门湾红树林种间分类方法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 153-168. |
|
||