Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2017, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 25-34.doi: 10.11978/2016047CSTR: 32234.14.2016047
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
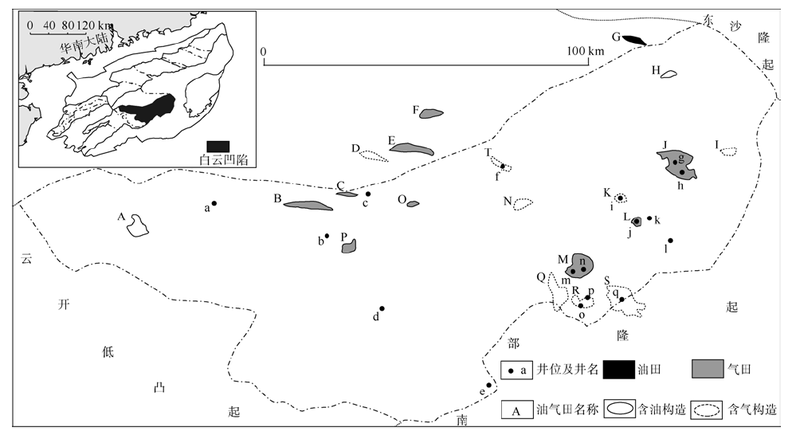
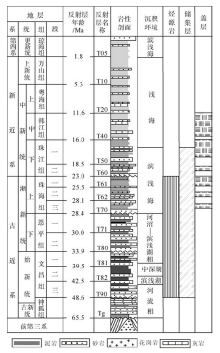
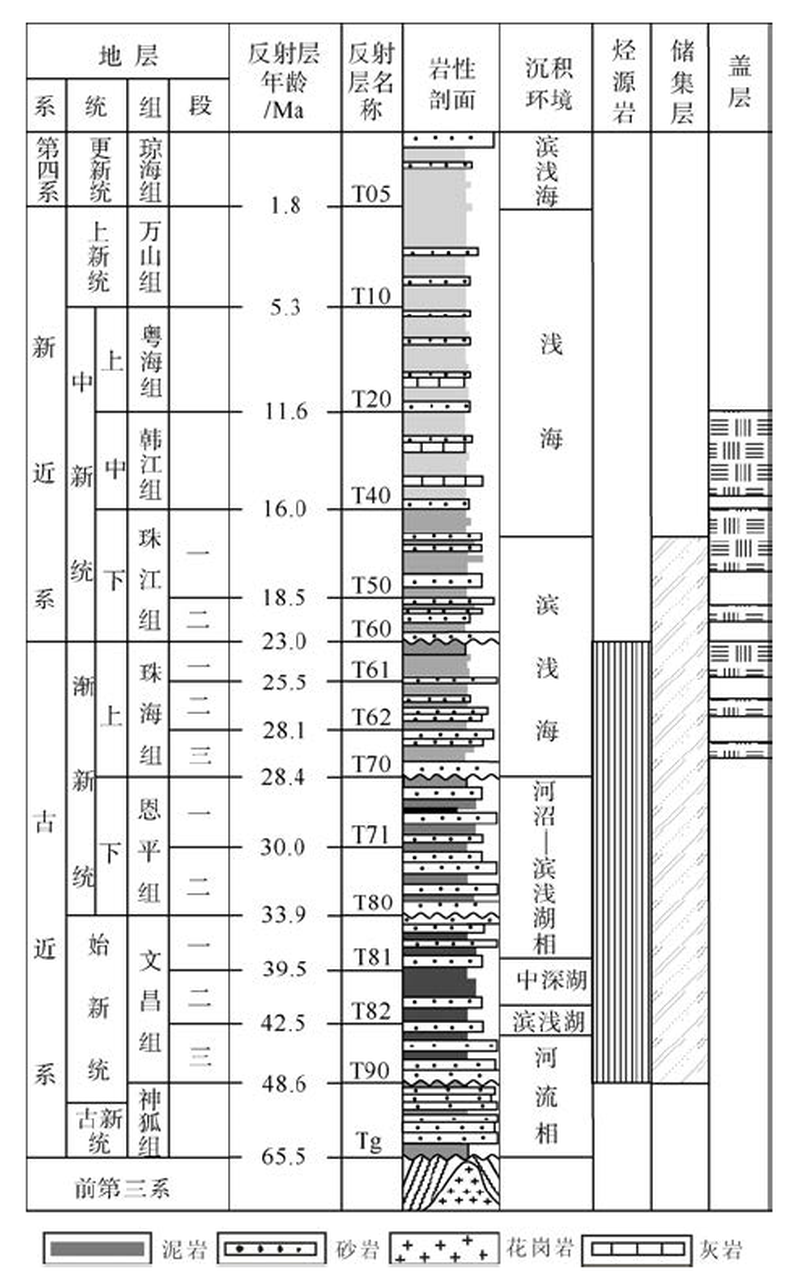
Thermal evolution of source rock and prediction of petroleum resources potential in Baiyun Depression, deep-water area of the northern South China Sea
Ke WANG( ), Gongcheng ZHANG, Haizhang YANG, Zhigang TONG, Shuchun YANG
), Gongcheng ZHANG, Haizhang YANG, Zhigang TONG, Shuchun YANG
- China National Offshore Oil Corporation Research Institute, Beijing 100028, China
-
Received:2016-05-06Revised:2016-06-08Online:2017-01-18Published:2017-01-19 -
Supported by:National Science and Technology Major Projects “Key Techniques in the Deep Ocean Oil and Gas Exploration” (2008ZX05025、2011ZX05025)
Cite this article
Ke WANG, Gongcheng ZHANG, Haizhang YANG, Zhigang TONG, Shuchun YANG. Thermal evolution of source rock and prediction of petroleum resources potential in Baiyun Depression, deep-water area of the northern South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 25-34.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
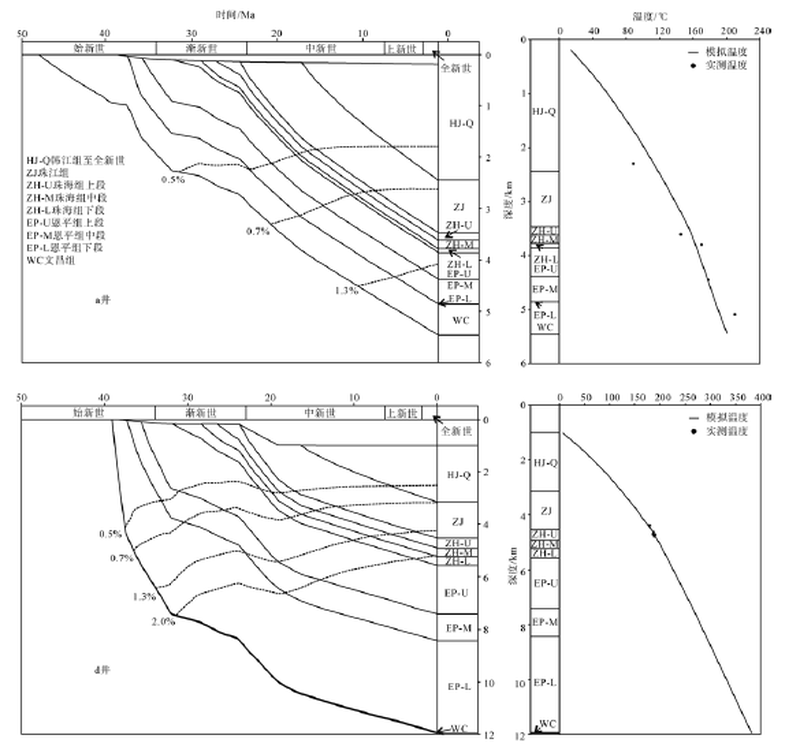
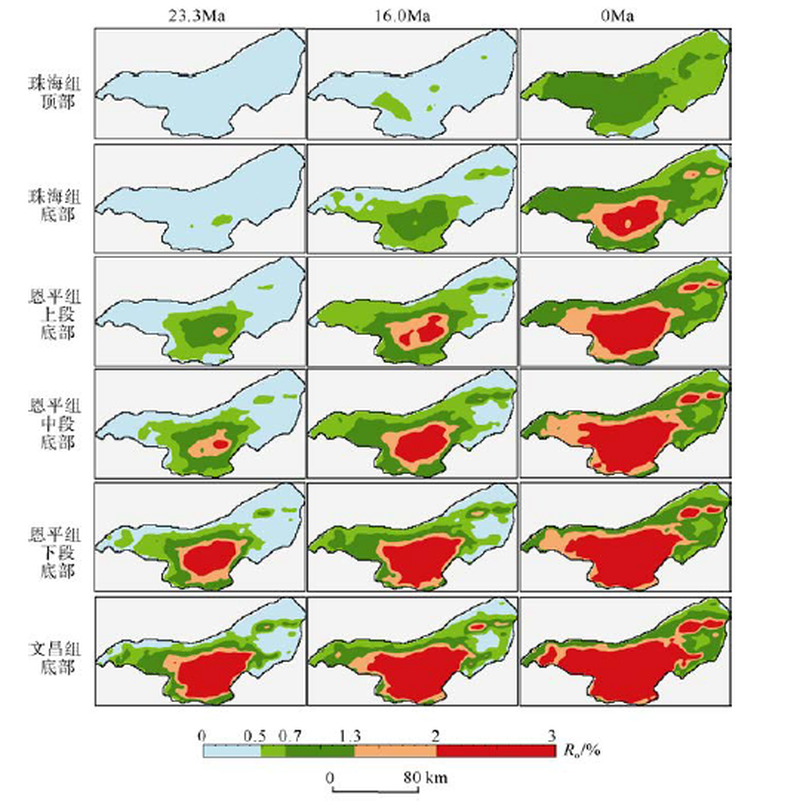
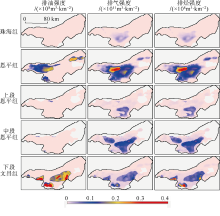
Tab. 2
Statistics of maturity evolution of the Baiyun Sag"
| 井号 | 演化时间/Ma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低成熟(Ro=0.5%) | 成熟(Ro=0.7%) | 高成熟(Ro=1.3%) | 过成熟(Ro=2.0%) | ||
| d | 恩平组 | 33.2 | 30.5 | 22.9 | 18.5 |
| 文昌组 | 37.4 | 36.4 | 33.8 | 31.4 | |
| c | 恩平组 | 20.3 | 10.4 | / | / |
| 文昌组 | 23.0 | 12.5 | / | / | |
| e | 恩平组 | 30.3 | 26.7 | 7.1 | / |
| 文昌组 | 36.5 | 29.4 | 19.1 | 2.9 | |
| g | 恩平组 | 9.1 | / | / | / |
| 文昌组 | 10.4 | / | / | / | |
| a | 恩平组 | 22.8 | 16.7 | 5.2 | / |
| 文昌组 | 31.1 | 20.2 | 9.6 | / | |
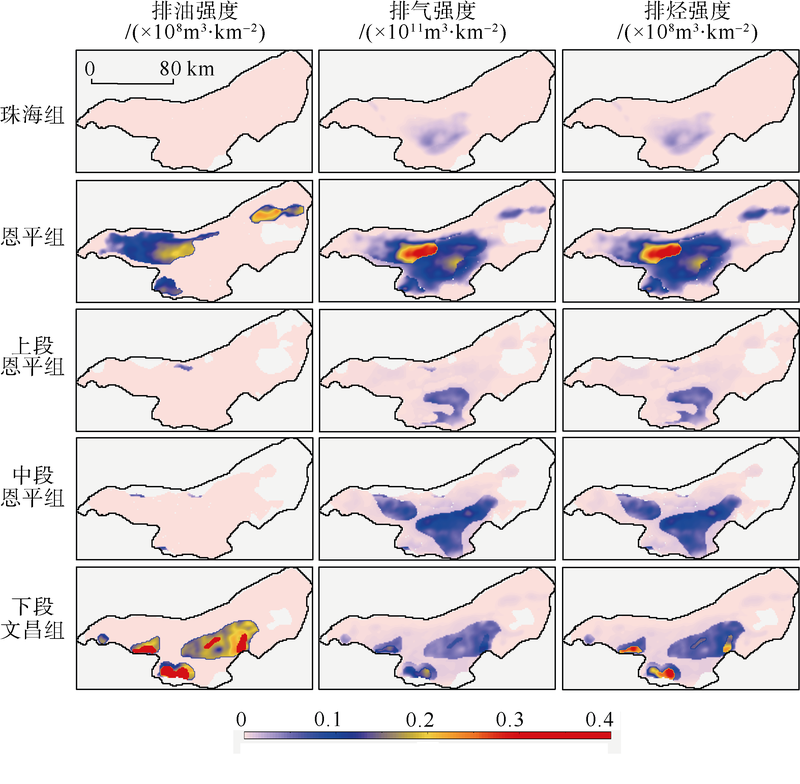
Tab. 3
Statistical expulsion quantity of source rock of the Baiyun Sag"
| 凹陷 | 层位 | 油/(×108m3) | 气/(×1011m3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P10 | P50 | P90 | P10 | P50 | P90 | ||
| 白云凹陷 | 珠海组 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67.0 | 34.4 | 13.4 |
| 恩平组上段 | 35.9 | 24.5 | 14.5 | 613.6 | 533.0 | 458.6 | |
| 恩平组中段 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 74.1 | 67.7 | 61.6 | |
| 恩平组下段 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 245.7 | 229.6 | 212.8 | |
| 恩平组 | 36.5 | 24.8 | 14.7 | 933.4 | 830.2 | 733.0 | |
| 文昌组 | 85.4 | 77.1 | 69.5 | 188.4 | 176.7 | 165.4 | |
Tab. 5
Statistical clustering coefficient of other oil & gas fields"
| 油气田 名称 | 聚集系数 /% | 油气田 名称 | 聚集系数/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | 石油 | 15.62 | N | 石油 | / |
| 天然气 | / | 天然气 | 5.13 | ||
| E | 石油 | 5.65 | C | 石油 | 0.45 |
| 天然气 | 2.43 | 天然气 | 0.23 | ||
| J | 石油 | 0.48 | Q | 石油 | / |
| 天然气 | 2.48 | 天然气 | 1.51 | ||
| B | 石油 | 0.37 | T | 石油 | / |
| 天然气 | 0.30 | 天然气 | 1.79 | ||
| P | 石油 | 0.14 | D | 石油 | / |
| 天然气 | 0.20 | 天然气 | 0.10 | ||
| O | 石油 | / | M | 石油 | / |
| 天然气 | 2.45 | 天然气 | 1.70 | ||
| I | 石油 | 0.92 | |||
| 天然气 | 8.52 | ||||
| [1] | 崔莎莎, 何家雄, 陈胜红, 等, 2009. 珠江口盆地发育演化特征及其油气成藏地质条件[J]. 天然气地球科学, 20(3): 384-391. |
| CUI SHASHA, HE JIAXIONG, CHEN SHENGHONG, et al, 2009. Development characteristics of Pearl River Mouth Basin and its geological conditions for oil and gas accumulation[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 20(3): 384-391 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 冯志强, 曾维军, 1982. 珠江口盆地的构造演化与南海之形成[J]. 地质学报, 56(3): 212-222. |
| FENG ZHIQIANG, ZENG WEIJUN, 1982. Tectonic evolution of Zhujiangkou (Pearl- River-Mouth) Basin and origin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 56(3): 212-222 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 金之钧, 张金川, 1999. 油气资源评价技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 66-71. |
| [4] | 金之钧, 张金川, 2002. 油气资源评价方法的基本原则[J]. 石油学报, 23(1): 19-23. |
| JIN ZHIJUN, ZHANG JINCHUAN, 2002. Fundamental principles for petroleum resources assessments[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 23(1): 19-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 梁建设, 王琪, 郝乐伟, 等, 2011. 成岩相分析方法在南海北部深水区储层预测的应用——以珠江口盆地白云凹陷为例[J]. 沉积学报, 29(3): 503-511. |
| LIANG JIANSHE, WANG QI, HAO LEWEI, et al, 2011. Application of diagenetic facies analysis to reservoir prediction in deep water area of the Northern South China Sea: a case study from Baiyun Sag, Zhujiangkou Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 29(3): 503-511 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 彭大均, 陈长民, 庞雄, 等, 2004. 南海珠江口盆地深水扇系统的发现[J]. 石油学报, 25(5): 17-23. |
| PENG DAJUN, CHEN CHANGMIN, PANG XIONG, 2004. Discovery of deep-water fan system in South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 25(5): 17-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 7.邵磊, 孟晓捷, 张功成, 等, 2013. 白云凹陷断裂特征对构造与沉积的控制作用[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 41(9): 1435-1441. |
| SHAO LEI, MENG XIAOJIE, ZHANG GONGCHENG, et al, 2013. Feature of faults system and its influence on tectonic and sedimentary history of Baiyun Sag[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 41(9): 1435-1441 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 盛秀杰, 金之钧, 鄢琦, 等, 2013. 成藏体系油气资源评价中的统计方法体系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 34(6): 827-833, 854. |
| SHENG XIUJIE, JIN ZHIJUN, YAN QI, et al, 2013. Statistical method series for the resource assessment of petroleum accumulation system[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 34(6): 827-833, 854 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 石广仁, 2009. 盆地模拟技术30年回顾与展望[J]. 石油工业计算机应用,(1): 3-6., 2009. |
| SHI GUANGRENReview and outlook for the 30th anniversary of basin modeling techniques[J]. Computer Applications of Petroleum, (1): 3-6 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 田作基, 吴义平, 王兆明, 等, 2014. 全球常规油气资源评价及潜力分析[J]. 地学前缘, 21(3): 10-17. |
| TIAN ZUOJI, WU YIPING, WANG ZHAOMING, et al, 2014. Global conventional oil & gas resource assessment and its potential[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(3): 10-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 王善书, 1982. 珠江口盆地地质构造的基本特征[J]. 石油学报, 3(增刊): 1-13. |
| WANG SHANSHU, 1982. Basic geological structural features of the basin at the Mouth of Pearl River[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 3(S): 1-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 王琪, 郝乐伟, 陈国俊, 等, 2010. 白云凹陷珠海组砂岩中碳酸盐胶结物的形成机理[J]. 石油学报, 31(4): 553-558. |
| WANG QI, HAO LEWEI, CHEN GUOJUN, et al, 2010. Forming mechanism of carbonate cements in siliciclastic sandstone of Zhuhai formation in Baiyun Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 31(4): 553-558 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 杨通佑, 范尚炯, 陈元千, 等, 1990. 石油及天然气储量计算方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 20-100. |
| [14] | 张功成, 杨海长, 陈莹, 等, 2014. 白云凹陷——珠江口盆地深水区一个巨大的富生气凹陷[J]. 天然气工业, 34(11): 11-25. |
| ZHANG GONGCHENG, YANG HAIZHANG, CHEN YING, et al, 2014. The Baiyun Sag: a giant rich gas-generation sag in the deepwater area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(11): 11-25 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 张林晔, 李政, 孔样星, 等, 2014. 成熟探区油气资源评价方法研究——以渤海湾盆地牛庄洼陷为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 25(4): 477-489. |
| ZHANG LINHUA, LI ZHENG, KONG YANGXING, et al, 2014. Study on evaluation method of petroleum resources in mature exploration area: Taking Niuzhuang Sag of Bohaiwan Basin as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(4): 477-489 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 赵柳生, 1988. 珠江口盆地油气藏形成条件及油气富集规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 15(1): 1-9. |
| ZHAO LIUSHENG, 1988. The condition on formation of oil (gas) field and oil (gas) accumulation in Zhujiangkou Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 15(1): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [17] | 周总瑛, 唐跃刚, 2004. 我国油气资源评价现状与存在问题[J]. 新疆石油地质, 25(5): 554-556. |
| ZHOU ZONGYING, TANG YUEGANG, et al, 2004. Current situation and problems in China's oil and gas resources assessment[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 25(5): 554-556 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 周总瑛, 白森舒, 何宏, 2005. 成因法与统计法油气资源评价对比分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 27(1): 67-73. |
| ZHOU ZONGYING, BAI SENSHU, HE XIONG, 2005. Comparison of genetic and statistical methods for petroleum resource assessment[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 27(1): 67-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [1] | ZHAO Zhongxian, SUN Zhen, MAO Yunhua, ZHANG Huodai. Heterogeneous extension and pulsed tectonic subsidence in the northern South China Sea margin* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 96-115. |
| [2] | Hao YI, Zhe WEI, Xuefei YI, Zhaoming CHEN, Jianyao WU. Seismic data depth correction of strata beneath the carbonate in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 97-104. |
| [3] | Weibiao ZHANG, Hui ZHONG, Jie ZHENG, Yijun XIA, Qingwen ZOU. The influence factors and development tendency of proved reserves in the eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(3): 94-101. |
| [4] | JIANG Ning, QUAN Zhizheng, PENG Guangrong, ZHANG Qinglin, LEI Yongchang, XU Yingjing, CHENG Weihua. Research on sedimentary facies based on seismic sedimentology: A case study of Paleogene Strata of Panyu 4 Sag in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(4): 102-111. |
| [5] | YANG Dong-sheng, ZHAO Zhi-gang, YANG Hai-zhang, JI Mo, TONG Zhong-fei. Application of integration of processing and interpretation techniques of Jinghai Sag in the deep water area of Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(5): 75-82. |
| [6] | XIE Hui, ZHOU Di, CHEN Guang-hao, LI Peng-chun, PANG Xiong, LI Yuan-ping, ZHAO Mei-song. Uncertainty and parameterization in backstripping of basin subsidence analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(5): 50-59. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jiang-yang, SUN Zhen, ZHANG Su-fang. Analysis of Mesozoic tectonic deformation in the Chaoshan Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(5): 41-49. |
| [8] | WU Bao-zhen, SHI Xiao-bin, YANG Xiao-qiu, SHI Hong-cai, JIANG Hai-yan, YANG Jun. Analysis on lithospheric strength of the Baiyun Sag and its surrounding area in the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 62-68. |
| [9] | ZHAO Zhong-xian,ZHOU Di,LIAO Jie,. Tertiary Paleogeography and Depositional Evolution in the Pearl River Mouth Basin of the Northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(6): 52-60. |
|
||