Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2017, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 48-59.doi: 10.11978/2016060CSTR: 32234.14.2016060
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Genetic types and elemental occurrence phases of ferromanganese nodules in the northern South China Sea
Yi ZHONG1,2( ), Zhong CHEN1(
), Zhong CHEN1( ), Aibin MO1,2, Yun LUO1,2, Gang LI1, Xufeng ZHENG1
), Aibin MO1,2, Yun LUO1,2, Gang LI1, Xufeng ZHENG1
- 1. Key Laboratory of Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2016-06-23Revised:2016-09-01Online:2017-03-20Published:2017-04-06 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation (41376057, 41676056, 41306047)
CLC Number:
- P736
Cite this article
Yi ZHONG, Zhong CHEN, Aibin MO, Yun LUO, Gang LI, Xufeng ZHENG. Genetic types and elemental occurrence phases of ferromanganese nodules in the northern South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(2): 48-59.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
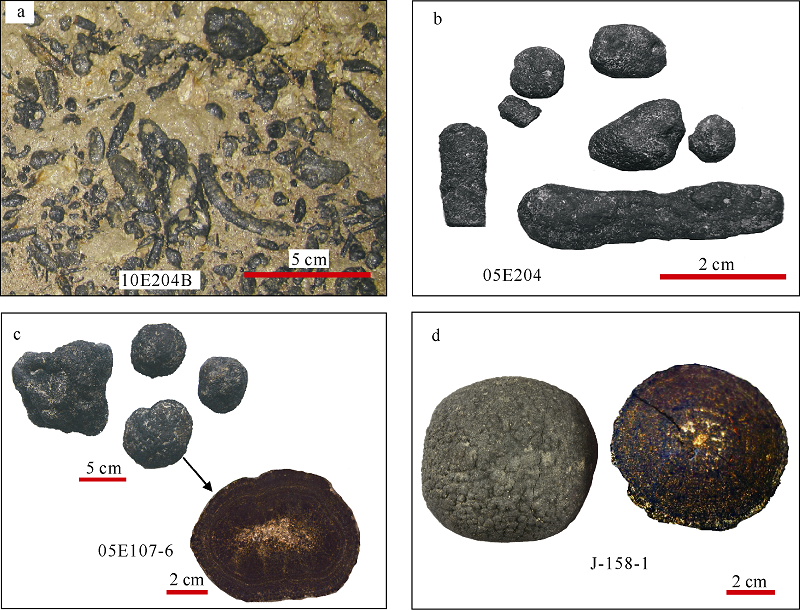
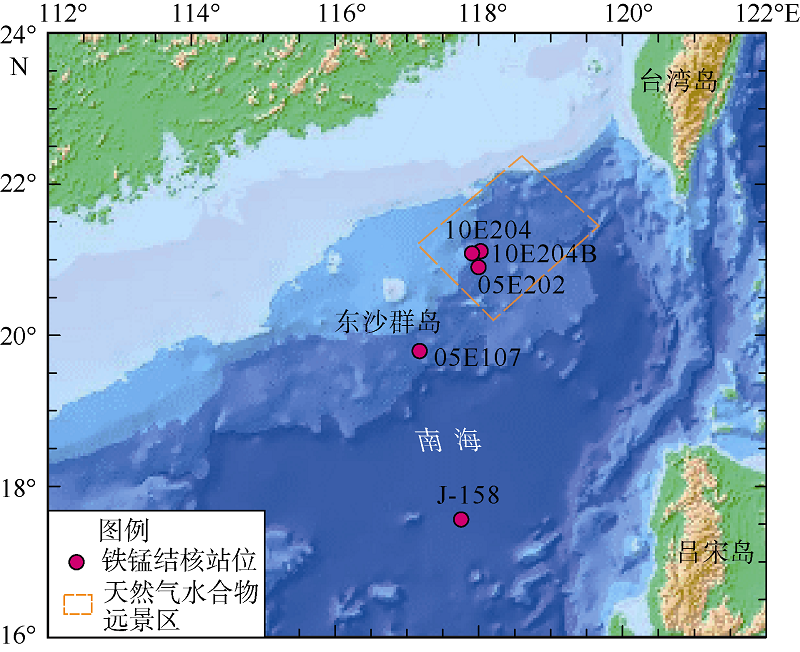
Tab. 1
Location and morphology of Fe-Mn nodules"
| 海区 | 站位 | 东经 | 北纬 | 水深/m | 样品号 | 形貌特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
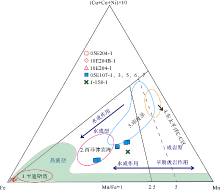
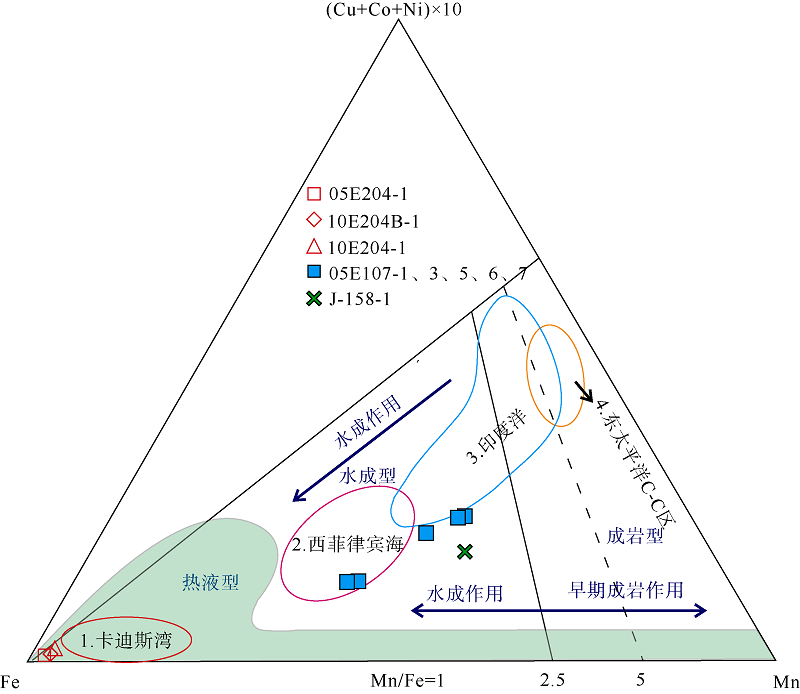
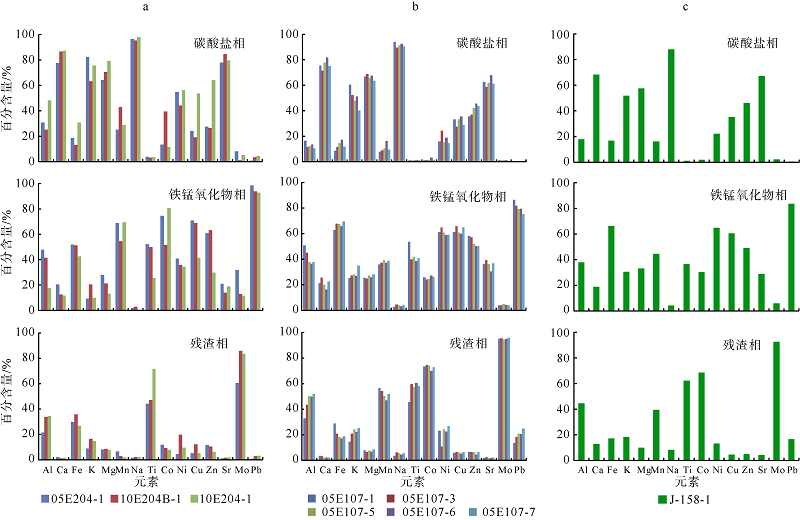
| 上陆坡 | 05E204 | 117°57′5.22″ | 20°59′7.8″ | 1370 | 05E204-1 | 球状, 直径约2cm |
| 10E204 | 117°59′12.504″ | 21°0′21.618″ | 1785 | 10E204-1 | 长条状 | |
| 10E204B | 117°57′18.852″ | 21°0′9.774″ | 1331 | 10E204B-1 | 棒状 | |
| 下陆坡 | 05E107 | 117°09′31.68″ | 19°46′25.8″ | 2255 | 05E107-1 | 球状, 直径3cm |
| 05E107-3 | 菜花状, 核心杂质多 | |||||
| 05E107-5 | 不规则块状 | |||||
| 05E107-6 | 椭球状, 半径5~8cm | |||||
| 05E107-7 | 扁球状, 直径约7cm | |||||
| 深海盆 | J-158 | 117°45′12.36″ | 17°33′41.76″ | 3570 | J-158-1 | 球状, 表层光滑 |
Tab. 2
REE geochemical characteristics in different phases of Fe-Mn nodules from the northern South China Sea"
| 参数 | 碳酸盐相 | 铁锰氧化物相 | 残渣相 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上陆坡 | 下陆坡 | 海盆 | 上陆坡 | 下陆坡 | 海盆 | 上陆坡 | 下陆坡 | 海盆 | ||
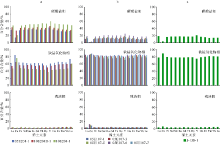
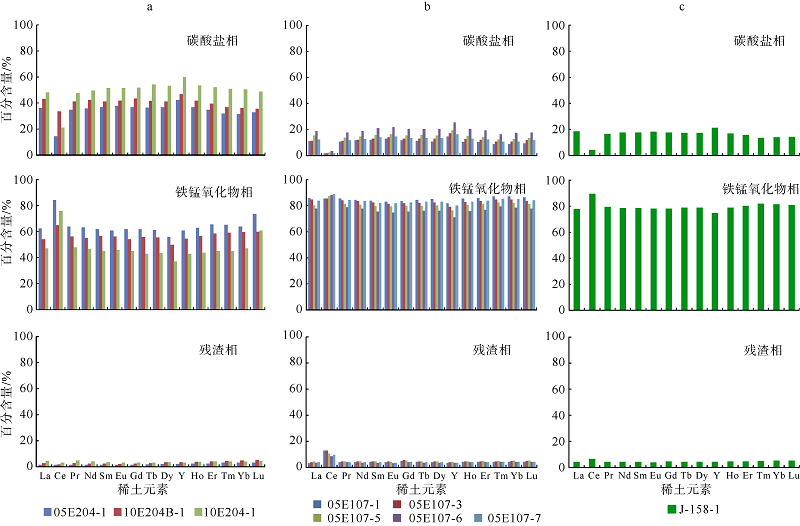
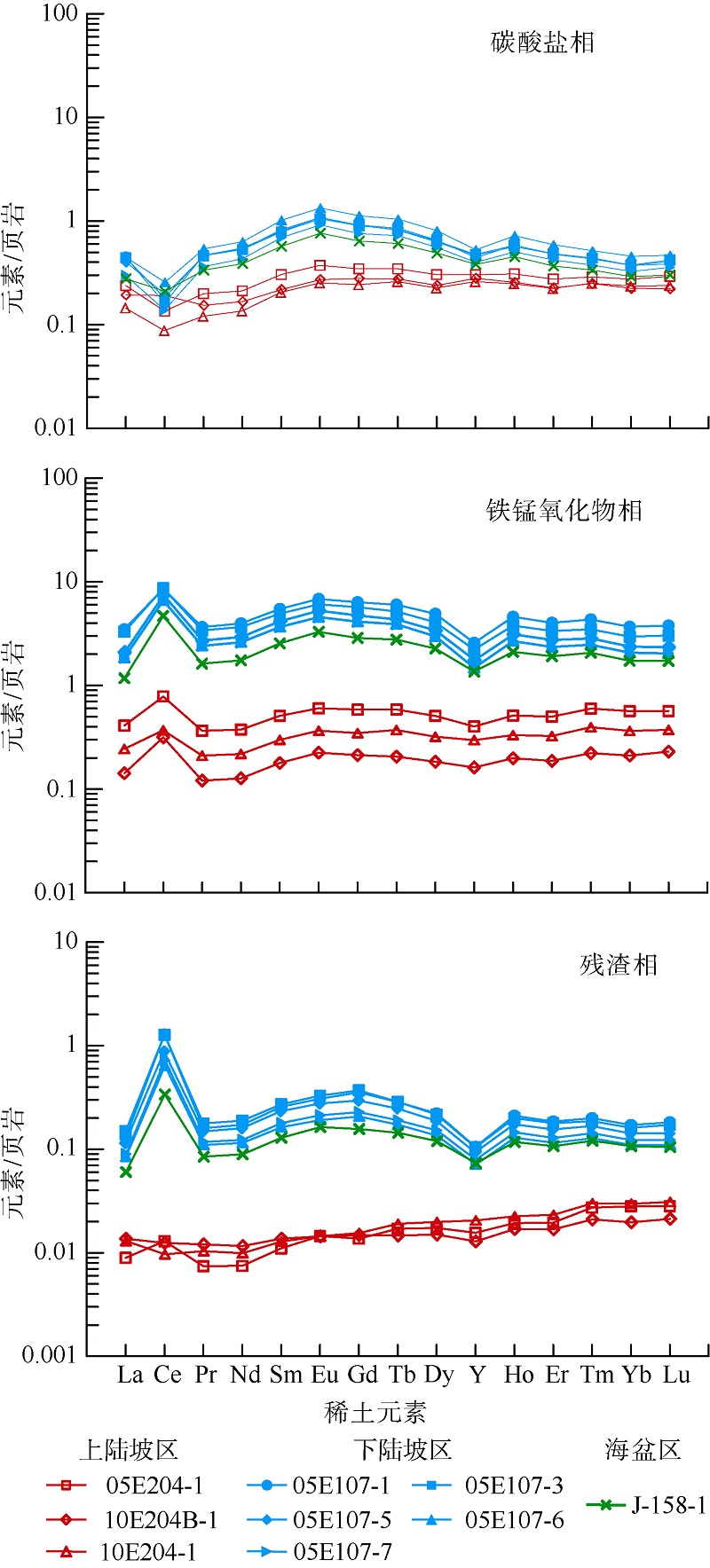
| ΣREE | 23.69~36.25 | 53.83~84.48 | 55.67 | 40.68~106.90 | 783.42~884.61 | 605.55 | 2.10~2.39 | 62.82~86.32 | 36.07 | |
| ΣLREE | 19.55~31.09 | 44.38~70.58 | 47.33 | 37.16~97.33 | 730.18~832.62 | 560.31 | 1.77~2.10 | 60.22~82.73 | 33.85 | |
| ΣHREE | 4.14~5.41 | 9.45~13.90 | 8.33 | 3.52~9.57 | 53.24~61.10 | 45.23 | 0.29~0.38 | 2.60~3.60 | 2.22 | |
| ΣLREE/ΣHREE | 4.72~7.14 | 4.70~5.22 | 5.68 | 8.33~10.54 | 12.55~13.72 | 12.60 | 4.71~7.29 | 23.01~23.36 | 14.98 | |
| Ce/Ce* | 0.62~1.10 | 0.35~0.52 | 0.68 | 1.63~2.40 | 2.40~3.10 | 3.35 | 0.83~1.59 | 6.59~8.88 | 4.66 | |
| Eu/Eu* | 1.09~1.15 | 1.25~1.27 | 1.26 | 1.10~1.15 | 1.14~1.18 | 1.21 | 0.05~0.06 | 0.74~1.28 | 0.57 | |
| YN/HoN | 0.98~1.09 | 0.73~0.83 | 0.85 | 0.79~0.90 | 0.55~0.60 | 0.65 | 0.76~0.91 | 0.50~0.55 | 0.63 | |
| 1 | 鲍根德, 李全兴, 1991. 南海铁锰结核(壳)的元素地球化学研究[J]. 热带海洋, 10(3): 44-50. |
| BAO GENDE, LI QUANXING, 1991. Geochemistry of elements in ferromanganese nodules (crusts) from the South China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 10(3): 44-50 (in Chinese). | |
| 2 | 鲍根德, 李全兴, 1993. 南海铁锰结核(壳)的稀土元素地球化学[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 10(3): 304-313. |
| BAO GENDE, LI QUANXING, 1993. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in ferromanganese nodules (crusts) from the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnlogy, 10(3): 304-313 (in Chinese). | |
| 3 | 陈忠, 杨慧宁, 颜文, 等, 2006. 中国海域固体矿产资源分布及其区划——砂矿资源和铁锰(微)结核—结壳[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 26(5): 101-108. |
| CHEN ZHONG, YANG HUINING, YAN WEN, et al, 2006. Distributions and divisions of mineral resources in the sea areas of China: placer deposit and ferromanganese nodule/crust[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 26(5): 101-108 (in Chinese). | |
| 4 | 黄永样, 杨慧宁, 匡耀求, 等, 1997. 海底沉积物类型及其地球化学环境对多金属结核形成与分布的控制作用[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. |
| 5 | 赖来仁, 1995. 中国南海锰结核的成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 9(4): 293-298. |
| LAI LAIREN, 1995. The causative mechanism of polymetallic nodules from South China Sea[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 9(4): 293-298 (in Chinese). | |
| 6 | 李康, 曾志刚, 殷学博, 等, 2009. 东太平洋海隆13°N和赤道附近表层沉积物中的元素赋存状态[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 29(3): 53-60. |
| LI KANG, ZENG ZHIGANG, YIN XUEBO, et al, 2009. Mode of element occurrence in surface sediments from East Pacific Rise near 13°N and the equator[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 29(3): 53-60 (in Chinese ). | |
| 7 | 梁宏锋, 姚德, 刘新波, 等, 1991. 南海尖峰海山多金属结壳地球化学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 11(4): 49-58. |
| LIANG HONGFENG, YAO DE, LIU XINBO, et al, 1991. Geochemistry of polymetallic crust from Jianfeng seamount, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 11(4): 49-58 (in Chinese ). | |
| 8 | 梁美桃, 陈绍谋, 吴必豪, 等, 1988. 南海海盆和陆坡锰结核的特征及地球化学的初步研究[J]. 热带海洋, 7(3): 10-18. |
| LIANG MEITAO, CHEN SHAOMOU, WU BIHAO, et al, 1988. A preliminary study on characteristics and geochemistry of manganese nodules from the basin and continental slope of the South China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 7(3): 10-18 (in Chinese). | |
| 9 | 林振宏, 季福武, 张富元, 等, 2003. 南海东北陆坡区铁锰结核的特征和成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 23(1): 7-12. |
| LIN ZHENHONG, JI FUWU, ZHANG FUYUAN, et al, 2003. Characteristics and origin of ferromanganese nodules from the northeastern continental slope of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 23(1): 7-12 (in Chinese). | |
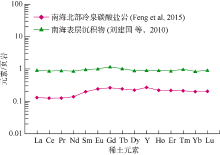
| 10 | 刘建国, 陈忠, 颜文, 等, 2010. 南海表层沉积物中细粒组分的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 35(4): 563-571. |
| LIU JIANGUO, CHEN ZHONG, YAN WEN, et al, 2010. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in the fine-grained fraction of surface sediment from South China Sea[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 35(4): 563-571 (in Chinese). | |
| 11 | 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等, 1984. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| 12 | 陆红峰, 刘坚, 陈芳, 等, 2005. 南海台西南区碳酸盐岩矿物学和稳定同位素组成特征——天然气水合物存在的主要证据之一[J]. 地学前缘, 12(3): 268-276. |
| LU HONGFENG, LIU JIAN, CHEN FANG, et al, 2005. Mineralogy and stable isotopic composition of authigenic carbonates in bottom sediments in the offshore area of southwest Taiwan, South China Sea: Evidence for gas hydrates occurrence[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(3): 268-276 (in Chinese). | |
| 13 | 王贤觉, 陈毓蔚, 吴明清, 1984. 铁锰结核的稀土和微量元素地球化学及其成因[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 15(6): 501-514. |
| WANG XIANJUE, CHEN YUWEI, WU MINGQING, 1984. Geochemistry of RE and trace elements in ferromanganese nodules and their genesis[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 15(6): 501-514 (in Chinese). | |
| 14 | 王勇军, 陈木宏, 陆钧, 等, 2007. 南海表层沉积物中钙质超微化石分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(5): 26-34. |
| WANG YONGJUN, CHEN MUHONG, LU JUN, et al, 2007. Distribution of calcareous nannofossils in surface sediments of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 26(5): 26-34 (in Chinese). | |
| 15 | 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华, 1989. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| 16 | 张兰兰, 陈木宏, 陈忠, 等, 2010. 南海表层沉积物中的碳酸钙含量分布及其影响因素[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 35(6): 891-898. |
| ZHANG LANLAN, CHEN MUHONG, CHEN ZHONG, et al, 2010. Distribution of calcium carbonate and its controlling factors in surface sediments of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(6): 891-898 (in Chinese). | |
| 17 | 张振国, 方念乔, 杜远生, 等, 2008. 南海西北陆缘多金属结核地球化学及其与大洋结核的对比[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 28(4): 51-56. |
| ZHANG ZHENGUO, FANG NIANQIAO, DU YUANSHENG, et al, 2008. Comparison between northwestern continental margin of the South China Sea and other oceans of geochemical characteristics of polymetallic nodules[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 28(4): 51-56 (in Chinese). | |
| 18 | 周怀阳, 2015. 深海海底铁锰结核的秘密[J]. 自然杂志, 37(6): 397-404. |
| ZHOU HUAIYANG, 2015. Metallogenetic mystery of deep sea ferromanganese nodules[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 37(6): 397-404 (in Chinese). | |
| 19 | ABOUCHAMI W, GALER S J G, KOSCHINSKY A, 1999. Pb and Nd isotopes in NE Atlantic Fe-Mn crusts: proxies for trace metal paleosources and paleocean circulation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(10): 1489-1505. |
| 20 | ALBARÈDE F, SIMONETTI A, VERVOORT J D, et al, 1998. A Hf-Nd isotopic correlation in ferromanganese nodules[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 25(20): 3895-3898. |
| 21 | BATURIN G N, 2010. Element composition of ferromanganese concretions in the Black Sea[J]. Oceanology, 50(1): 83-92. |
| 22 | BATURIN G N, DUBINCHUK V T, 2009. Composition of ferromanganese nodules from Riga Bay (Baltic Sea)[J]. Oceanology, 49(1): 111-120. |
| 23 | BATURIN G N, DOBRETSOVA I G, DUBINCHUK V T, 2014. Hydrothermal manganese mineralization in the Peterbourgskoye ore field (North Atlantic)[J]. Oceanology, 54(2): 222-230. |
| 24 | BOGDANOV Y A, GURVICH E G, BOGDANOVA O Y, et al, 1995. Ferromanganese nodules of the Kara Sea[J]. Oceanology, 34(5): 722-732. |
| 25 | BURTON K W, LEE D C, CHRISTENSEN J N, et al, 1999. Actual timing of neodymium isotopic variations recorded by Fe-Mn crusts in the western North Atlantic[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 171(1): 149-156. |
| 26 | CHRISTENSEN J N, HALLIDAY A N, GODFREY L V, et al, 1997. Climate and ocean dynamics and the lead isotopic records in Pacific ferromanganese crusts[J]. Science, 277(5328): 913-918. |
| 27 | CRONAN D S, 1997. Some controls on the geochemical variability of manganese nodules with particular reference to the tropical South Pacific[M]//NICHOLSON K, HEIN J R, BÜHN B, et al. Manganese mineralization: Geochemistry and mineralogy of terrestrial and marine deposits. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 119(1): 139-151. |
| 28 | DYMOND J, LYLE M, FINNEY B, et al, 1984. Ferromanganese nodules from MANOP Sites H, S, and R—Control of mineralogical and chemical composition by multiple accretionary processes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48(5): 931-949. |
| 29 | FENG DONG, CHENG MING, KIEL S, et al, 2015. Using Bathymodiolus tissue stable carbon, nitrogen and sulfur isotopes to infer biogeochemical process at a cold seep in the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1(104): 52-59. |
| 30 | FRANK M, REYNOLDS B C, O'NINONS R K, 1999. Nd and Pb isotopes in Atlantic and Pacific water masses before and after closure of the Panama gateway[J]. Geology, 27(12): 1147-1150. |
| 31 | GONZÁLEZ F J, SOMOZA L, LUNAR R, et al, 2007. Fe-Mn nodules associated with hydrocarbon seeps: A new discovery in the Gulf of Cadiz (eastern central Atlantic)[J]. Episodes, 30(3): 187-196. |
| 32 | GONZÁLEZ F J, SOMOZA L, LEÓN R, et al, 2012. Ferromanganese nodules and micro-hardgrounds associated with the Cadiz Contourite Channel (NE Atlantic): palaeoenvironmental records of fluid venting and bottom currents[J]. Chemical Geology, 310-311: 56-78. |
| 33 | HAN XIQIU, JIN XIANGLONG, YANG SHUFENG, et al, 2003. Rhythmic growth of Pacific ferromanganese nodules and their Milankovitch climatic origin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 211(1/2): 143-157. |
| 34 | HE LIANGBIAO, 1991. Geochemical characteristics of Fe-Mn nodules and crusts from the Mariana ridge and the west Philippine Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 36(14): 1190-1193. |
| 35 | HEIN J R, MIZELL K, KOSCHINSKY A, et al, 2013. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: comparison with land-based resources[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 51: 1-14. |
| 36 | HU YU, FENG DONG, PECKMANN J, et al, 2014. New insights into cerium anomalies and mechanisms of trace metal enrichment in authigenic carbonate from hydrocarbon seeps[J]. Chemical Geology, 381: 55-66. |
| 37 | HUI GEGE, LI SANZHONG, GUO LINGLI, et al, 2016. Source and accumulation of gas hydrate in the northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 69: 127-145. |
| 38 | KENNETT J P, WATKINS N D, 1975. Deep-sea erosion and manganese nodule development in the Southeast Indian Ocean[J]. Science, 188(4192): 1011-1013. |
| 39 | KOSCHINSKY A, HEIN J R, 2003. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: solid-phase associations and seawater speciation[J]. Marine Geology, 198(3/4): 331-351. |
| 40 | MILLIMAN J D, FARNSWORTH K L, 2011. River discharge to the coastal ocean: a global synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| 41 | MUKHOPADHYAY R, IYER S D, GHOSH A K, 2003. The Indian Ocean Nodule Field: petrotectonic evolution and ferromanganese deposits[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 60(1/2): 67-130. |
| 42 | NICHOLSON K, HEIN J R, BUHN B, et al, 1997. Manganese mineralization: geochemistry and mineralogy of terrestrial and marine deposits[M]. London: The Geological Society. |
| 43 | PRAKASH L S, RAY D, PAROPKARI A L, et al, 2012. Distribution of REEs and yttrium among major geochemical phases of marine Fe-Mn-oxides: Comparative study between hydrogenous and hydrothermal deposits[J]. Chemical Geology, 312-313: 127-137. |
| 44 | RONA P A, 2008. The changing vision of marine minerals[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 33(3/4): 618-666. |
| 45 | TONG HONGPENG, FENG DONG, CHENG HAI, et al, 2013. Authigenic carbonates from seeps on the northern continental slope of the South China Sea: New insights into fluid sources and geochronology[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 43: 260-271. |
| 46 | USUI A, GRAHAM I J, DITCHBURN R G, et al, 2007. Growth history and formation environments of ferromanganese deposits on the Philippine Sea Plate, northwest Pacific Ocean[J]. Island Arc, 16(3): 420-430. |
| 47 | VERLAAN P A, CRONAN D S, MORGAN C L, 2004. A comparative analysis of compositional variations in and between marine ferromanganese nodules and crusts in the South Pacific and their environmental controls[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 63(3): 125-158. |
| 48 | WEGORZEWSKI A V, KUHN T, 2014. The influence of suboxic diagenesis on the formation of manganese nodules in the Clarion Clipperton nodule belt of the Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Geology, 357: 123-138. |
| 49 | WEN X, DE CARLO E H, LI Y H, 1997. Interelement relationships in ferromanganese crusts from the central Pacific ocean: Their implications for crust genesis[J]. Marine Geology, 136(3/4): 277-297. |
| 50 | YAN QUANSHU, CASTILLO P, SHI XUEFA, et al, 2015. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of volcanic rocks from Daimao Seamount (South China Sea) and their tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 218-219: 117-126. |
| 51 | YANG TAO, JIANG SHAOYONG, YANG JINGHONG, et al, 2008. Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and its carbon isotopic composition in sediment pore waters from the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 64(2): 303-310. |
| 52 | YAO BOCHU, ZENG WEIJUN, HAYES D E, et al, 1994. The geological memoir of South China Sea surveyed jointly by China and USA[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press: 1204. |
| 53 | YAO YUNGCHANG, CHEN JUCHIN, HUH CHIHAN, et al, 2014. Geochemistry and Origin of Layers in Single Manganese Nodule from the Philippine Sea and Manganese Nodules from Offshore Minami-Torishima, Western Pacific[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 88(6): 1835-1845. |
| 54 | ZHANG ZHENGUO, DU YUANSHENG, WU CHANGHANG, et al, 2013. Growth of a polymetallic nodule from the northwestern continental margin of the South China Sea and its response to changes in the paleoceanographical environment of the Late Cenozoic[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 56(3): 453-463. |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [3] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [4] | ZHAO Minghui, YUAN Ye, ZHANG Jiazheng, ZHANG Cuimei, GAO Jinwei, WANG Qiang, SUN Zhen, CHENG Jinhui. New developments on the rift-breakup of the continent-ocean transition zone in the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [5] | YANG Yikai, ZENG Lili. Spatiotemporal characteristics of mesoscale eddies with transport capability of saline Kuroshio water in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 75-85. |
| [6] | ZENG Yigang, JING Zhiyou, HUANG Xiaolong, ZHENG Ruixi. Analysis of the dynamic characteristics of the east Guangdong shelf front in the northern South China Sea in summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 136-145. |
| [7] | MA Mengzhen, LI Qian, WU Zhengchao, CHEN Yinchao, YU Jiancheng. Underwater glider observation of oxygen minimum zone in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
| [8] | WANG Renzheng, SHAN Zhengduo, MENG Siyu, GONG Xiang. Interannual variation of subsurface chlorophyll maximum in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 63-75. |
| [9] | WANG Jian, CHEN Chuqun, ZHOU Weihua, LI Xiangfu, WU Jie, YE Haibin, TANG Shilin. Estimating the spatial distribution of heterotrophic bacteria abundance in the Northern South China Sea using remote sensing* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 53-62. |
| [10] | Chan SHU, Bingxu GENG, Weiwei FANG, Peng XIU. Parameter analysis and optimization using genetic algorithm in a marine ecosystem model of the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 98-106. |
| [11] | YANG Wei, DONG Yuan, ZU Tingting, LIU Changjian, XIU Peng. Distribution of Chlorophyll-a and its influencing factors in the northern South China Sea in summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(6): 9-20. |
| [12] | ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, CHEN Tianran. Micro-bioerosion in Porites corals in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(6): 74-79. |
| [13] | Xia WANG,Wendong FANG,Rongyu CHEN. Intra-seasonal variability of sea level anomalies and their propagation features in the northern South China Sea from 25 years of satellite altimetry data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 1-12. |
| [14] | Yandan HUANG, Jiexin XU, Junliang LIU, Zhiwu CHEN, Shuqun CAI. A study of near-inertial oscillations in the northern South China Sea based on in-situ observations during the passage of Typhoon Kalmaegi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 16-25. |
| [15] | Zeting XU, Shiyu LI, Jiatang HU, Siying WANG, Bin WANG, Mingxian GUO, Bingxu GENG. Summer phytoplankton responses to upwelling and river plume in northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 92-103. |
|
||