Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2018, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 72-89.doi: 10.11978/2017023CSTR: 32234.14.2017023
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
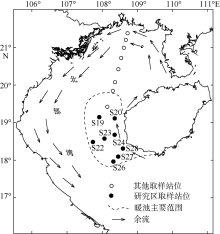
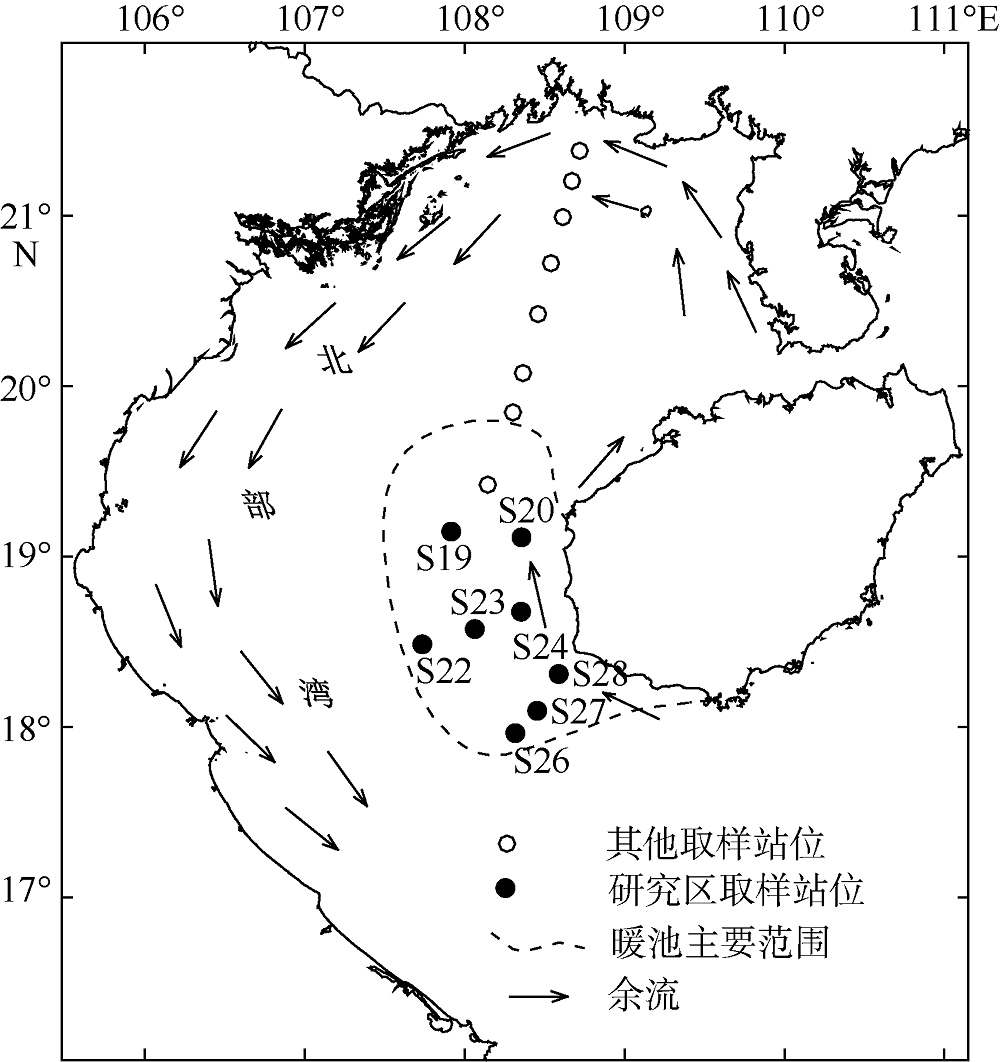
The primary sedimentary characteristics of Warm Pool in Beibu Gulf and its environmental indication*
Xiangqing HUANG( ), Zhen’ang CUI, Kai LIANG, Huayang GAN, Zhen XIA, Zhenhai HUO(
), Zhen’ang CUI, Kai LIANG, Huayang GAN, Zhen XIA, Zhenhai HUO( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Marine Mineral Resources, Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, Ministry of Land and Resources, Guangzhou 510760, China
-
Received:2017-03-01Revised:2017-09-05Online:2018-01-20Published:2018-02-02 -
Supported by:China Geological Survey Program (1212010914027)
CLC Number:
- P736.21
Cite this article
Xiangqing HUANG, Zhen’ang CUI, Kai LIANG, Huayang GAN, Zhen XIA, Zhenhai HUO. The primary sedimentary characteristics of Warm Pool in Beibu Gulf and its environmental indication*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(1): 72-89.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
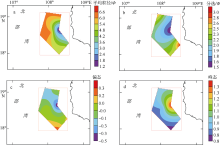
Tab. 1
Granularity statistics in bottom sediments of the study area and sub-division of Beibu Gulf"
| 各组分百分率 | 参数 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砾石 | 砂 | 粉砂 | 黏土 | 平均粒径/Φ | 分选/Φ | 偏态 | 峰态 | |
| 范围 | 5.3~14.6 | 3.5~85.4 | 0~71.5 | 0~31.2 | 1.1~6.9 | 1.5~3.0 | -0.4~0.3 | 0.8~1.4 |
| 平均值 | 10.4 | 34.5 | 46.0 | 17.8 | 5.1 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 变异系数 | 0.45 | 0.80 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.23 | 4.90 | 0.18 |
| 北部 | 11.2 | 38.8 | 43.9 | 15.1 | 4.9 | 2.1 | 0.1 | 1.3 |
| 中部 | 0.0 | 40.9 | 41.1 | 18.0 | 5.3 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 0.9 |
| 研究区东部 | 6.7 | 48.7 | 33.9 | 10.7 | 3.9 | 2.1 | -0.1 | 1.1 |
| 研究区西部 | 0.0 | 26.0 | 51.0 | 23.0 | 6.0 | 2.4 | 0.0 | 0.9 |
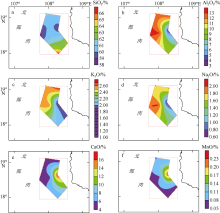
Tab. 2
Concentration statistics of macro-geochemical elements in bottom sediments of the study area and sub-division of Beibu Gulf"
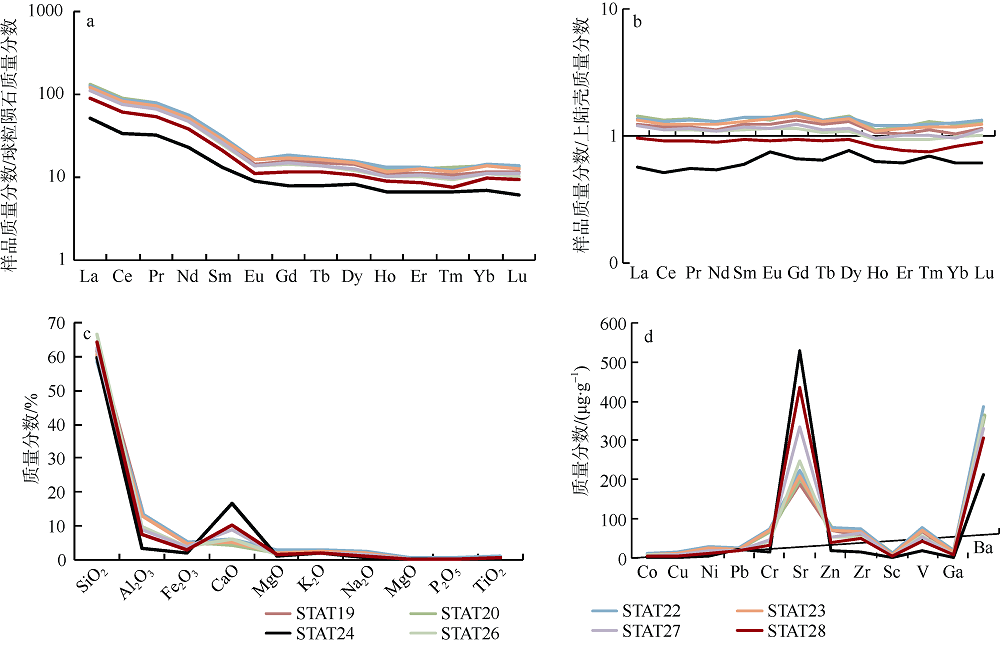
| 质量分数/% | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | P2O5 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 58.52~66.61 | 3.44~13.31 | 1.76~4.96 | 4.15~16.55 | 1.09~2.26 | 1.84~2.71 | 0.66~2.01 | 0.053~0.227 | 0.070~0.102 | 0.17~0.61 |
| 平均值 | 61.65 | 10.16 | 3.93 | 7.52 | 1.77 | 2.27 | 1.49 | 0.091 | 0.091 | 0.49 |
| 变异系数 | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.56 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.66 | 0.15 | 0.28 |
| 北部 | 66.64 | 10.67 | 4.72 | 3.06 | 1.94 | 1.87 | 1.67 | 0.065 | 0.081 | 0.49 |
| 中部 | 66.51 | 10.54 | 5.07 | 3.35 | 1.84 | 2.26 | 1.60 | 0.064 | 0.083 | 0.50 |
| 研究区东部 | 61.29 | 7.97 | 3.15 | 10.23 | 1.50 | 2.17 | 1.20 | 0.122 | 0.078 | 0.41 |
| 研究区西部 | 62.18 | 11.79 | 4.49 | 5.31 | 1.98 | 2.37 | 1.65 | 0.069 | 0.093 | 0.55 |
Tab. 3
Concentration statistics of micro-geochemical elements in bottom sediments of the study area and sub-division of Beibu Gulf"
| 质量分数/(μg•g-1) | Co | Cu | Ni | Pb | Cr | Sr | Zn | Zr | Sc | V | Ga | Ba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 3.48~ 12.25 | 3.75~ 14.70 | 6.04~ 32.10 | 20.0~ 30.3 | 17.1~ 75.10 | 190~ 530 | 20.71~ 78.70 | 15.52~ 74.15 | 2.83~ 12.20 | 18.51~ 77.74 | 2.71~ 17.75 | 152~ 325 |
| 平均值 | 9.66 | 10.83 | 22.94 | 23.65 | 55.08 | 297 | 59.97 | 57.92 | 9.05 | 59.13 | 13.15 | 273 |
| 变异系数 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.19 |
| 北部 | 11.03 | 15.96 | 32.16 | 25.54 | 66.14 | 139 | 66.56 | 62.63 | 10.3 | 63.68 | 15.28 | 210 |
| 中部 | 11.83 | 15.29 | 29.57 | 24.87 | 68.57 | 139 | 67.33 | 59.83 | 10.31 | 64.30 | 15.6 | 261 |
| 研究区东部 | 7.49 | 8.01 | 16.38 | 22.73 | 40.93 | 390 | 46.33 | 45.87 | 7.00 | 45.53 | 9.80 | 233 |
| 研究区西部 | 11.45 | 12.99 | 27.97 | 25.18 | 65.57 | 221 | 70.53 | 63.15 | 10.61 | 69.57 | 15.82 | 306 |
Tab. 4
Concentration statistics of rare earth elements (REEs) in bottom sediments of the study area and sub-division of Beibu Gulf"
| 质量分数 /(μg•g-1) | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 16.84 ~42.71 | 32.86 ~85.01 | 3.89 ~9.60 | 14.14 ~34.07 | 2.67 ~6.31 | 0.66 ~1.21 | 2.51 ~5.89 | 0.41 ~0.86 | 2.65 ~4.99 | 0.52 ~0.95 | 1.41 ~2.73 | 0.22 ~0.43 | 1.34 ~2.72 | 0.19 ~0.42 |
| 平均值 | 34.63 | 69.43 | 7.82 | 27.74 | 5.14 | 1.02 | 4.66 | 0.71 | 4.11 | 0.78 | 2.26 | 0.34 | 2.21 | 0.34 |
| 变异系数 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
| 北部 | 35.53 | 70.58 | 7.72 | 28.47 | 5.21 | 0.93 | 4.60 | 0.73 | 4.25 | 0.78 | 2.31 | 0.34 | 2.27 | 0.35 |
| 中部 | 37.2 | 72.30 | 8.20 | 30.2 | 5.49 | 1.01 | 4.81 | 0.74 | 4.22 | 0.77 | 2.23 | 0.33 | 2.27 | 0.36 |
| 研究区东部 | 29.49 | 58.95 | 6.69 | 23.78 | 4.40 | 0.88 | 4.00 | 0.62 | 3.63 | 0.68 | 1.97 | 0.30 | 1.95 | 0.31 |
| 研究区西部 | 37.62 | 75.88 | 8.56 | 30.11 | 5.61 | 1.10 | 5.04 | 0.77 | 4.40 | 0.85 | 2.41 | 0.36 | 2.37 | 0.37 |
Tab. 5
Ratio statistics of geochemical elements in bottom sediments of the study area and sub-division of Beibu Gulf"
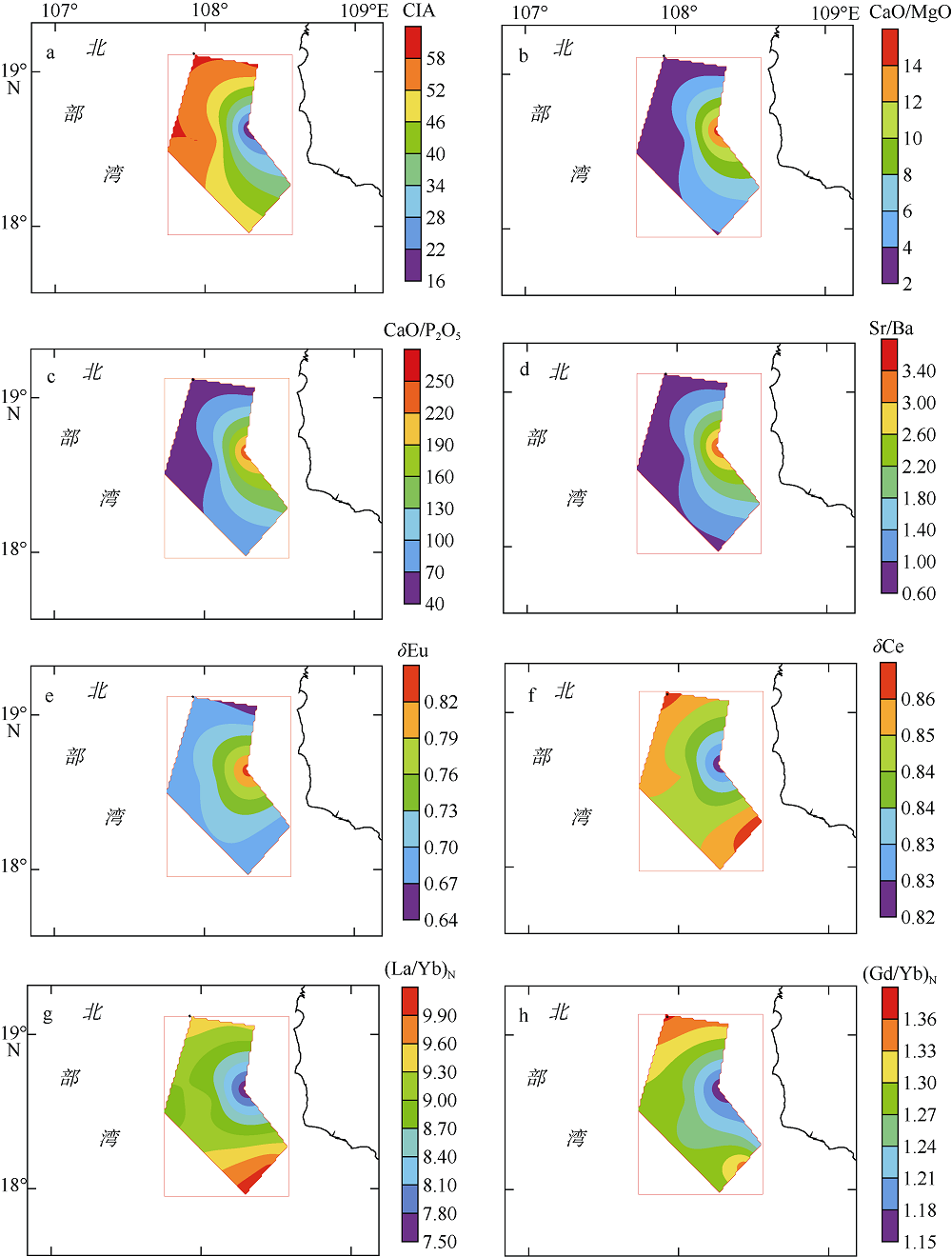
| 质量分数/(μg•g-1) | CIA | CaO/MgO | CaO/P2O5 | Sr/Ba | δEu | δCe | (La/Yb)N | (Gd/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 15.28~60.35 | 2.08~15.23 | 43.71~247.01 | 0.64~3.49 | 0.64~0.84 | 0.82~0.86 | 7.46~10.07 | 1.15~1.37 | 3.94~4.47 |
| 平均值 | 47.33 | 5.05 | 93.30 | 1.26 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 9.23 | 1.28 | 4.20 |
| 变异系数 | 0.33 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| 北部 | 61.13 | 1.74 | 40.74 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 0.85 | 9.33 | 1.25 | 4.26 |
| 中部 | 57.22 | 1.96 | 47.60 | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.84 | 9.96 | 1.32 | 4.23 |
| 研究区东部 | 37.06 | 8.11 | 143.20 | 1.98 | 0.73 | 0.83 | 8.75 | 1.22 | 4.16 |
| 研究区西部 | 55.61 | 2.78 | 57.75 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 9.47 | 1.30 | 4.20 |
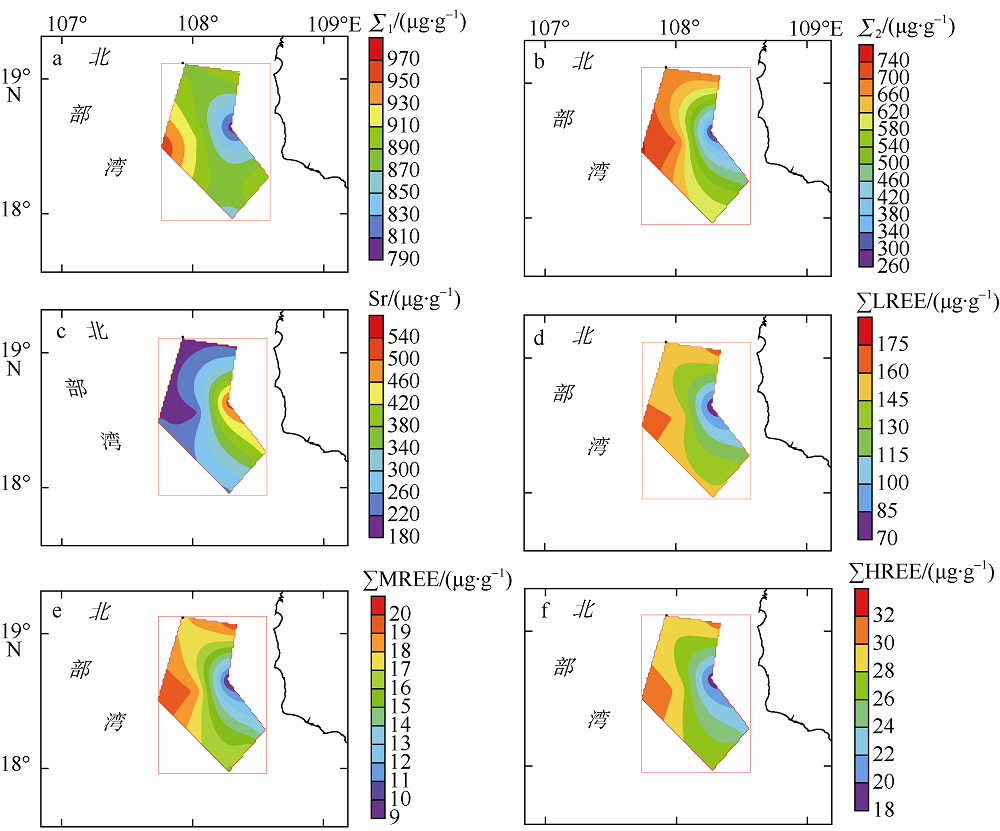
Fig. 5
Distributions of main micro-geochemical elements and REEs in bottom sediments of the study area. (a) ∑1 (sum of micro-geochemical elements); (b) ∑2 (sum of micro-geochemical elements except Sr); (c) Sr; (d) ∑LREE (sum of light rare earth elements); (e) ∑MREE (sum of middle rare earth elements); (f) ∑HREE (sum of heavy rare earth elements)"
Tab. 6
Dominant species of foraminifera and diatom in bottom sediments of the study area"
| 类型 | 站位 | 优 势 种 | 含量/% | 均方差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有孔虫 | S19 | B. nodosaris - T. foliace - H. praecineta - P. schroeteriana | 56.86 | 0.01 |
| S20 | S. orbis - Q. seminula - T. conica - P. schroeteriana | 73.58 | 0.10 | |
| S22 | T. foliace - H. praecineta - P. schroeteriana - E. advenum | 64.40 | 0.07 | |
| S23 | H. mantaensis - T. foliace - Q. seminula - Florilus decorus | 61.03 | 0.06 | |
| S24 | T. conica - Q. seminula - B. nodosaris - P. schroeteriana - S. orbis - T. foliace | 60.48 | 0.01 | |
| S26 | P. schroeteriana - H. praecineta - Q. seminula - H. mantaensis - T. foliace | 56.91 | 0.01 | |
| S27 | P. schroeteriana - P. lateralis - H. praecineta - T. foliace - H. mantaensis | 52.88 | 0.03 | |
| S28 | Hanzawaia concentrina - A. madagascariensis - P. schroeteriana - H. mantaensis - Q. seminula | 50.10 | 0.01 | |
| 硅藻 | S19 | Actinocyclus ehrenbergi - C. striata - S. fluminensis | 33.90 | 0.003 |
| S20 | C. striata - M. sulcata | 53.62 | 0.002 | |
| S22 | C. striata | 52.63 | 0.003 | |
| S23 | C. striata - S. fluminensis - N. fasciculata | 54.29 | 0.06 | |
| S24 | S. fluminensis - N. fasciculate - C. lorenziana | 42.00 | 0.03 | |
| S28 | C. lorenziana - C. striata | 34.62 | 0.08 |
Tab. 7
Environmental indicators by foraminifera and diatom in bottom sediments of the study area and sub-division of Beibu Gulf"
| 质量分数 | 有孔虫 | 硅藻 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浮游种/底栖种 | 温跃层种/混合层种 | 冷水种/暖水种 | 热性种/广温种 | 咸水种/半咸水种 | 浮游种/底栖种 | |
| 比值范围 | 0~0.91 | 0~0.36 | 0~0.37 | 0~0.49 | 0~2.20 | 0~0.33 |
| 北部 | 0.00 | — | — | 0.12 | 0.10 | — |
| 中部 | 0.02 | — | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.12 | — |
| 研究区东部 | 0.02 | — | 0.11 | 0.24 | 1.00 | 0.05 |
| 研究区西部 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.14 |
Tab. 8
Biodiversity index of foraminifera and diatom in bottom sediments of the study area and sub-division of Beibu Gulf"
| H' | 有孔虫 | 硅藻 | 有孔虫和硅藻 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浮游 | 底栖 | 浮游 | 底栖 | 总浮游 | 总底栖 | ∑H' | |
| 范围 | 0~0.90 | 1.06~2.52 | 0~0.69 | 1.07~2.33 | 0~0.90 | 2.12~4.59 | 2.13~5.47 |
| 北部 | — | 1.58 | 0.00 | 1.33 | 0.00 | 2.91 | 2.91 |
| 中部 | 0.00 | 2.07 | — | 1.52 | 0.00 | 3.59 | 3.59 |
| 研究区东部 | 0.00 | 2.10 | 0.21 | 1.92 | 0.21 | 4.02 | 4.23 |
| 研究区西部 | 0.27 | 2.21 | 0.46 | 1.66 | 0.73 | 3.87 | 4.60 |
| [1] | 蔡俊军, 卢振权, 何家雄, 等, 2014. 祁连山冻土区天然气水合物伴生碳酸盐岩的地球化学特征[J]. 新能源, 34(2): 143-153. |
| CAI JUNJUN, LU ZHENQUAN, HE JIAXIONG, et al, 2014. Geochemical behaviors of carbonates associated with gas hydrate in the Qilian Mountain permafrost[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(2): 143-153 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 蔡立哲, 马丽, 高阳, 等, 2002. 海洋底栖动物多样性指数污染程度评价标准的分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 41(5): 641-646. |
| CAI LIZHE, MA LI, GAO YANG, et al, 2002. Analysis on assessing criterion for polluted situation using species diversity index of marine macrofauna[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 41(5): 641-646 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 曹知勉, 戴民汉, 2008. 海洋钙离子非保守行为及海洋钙问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 23(1): 8-16. |
| CAO ZHIMIAN, DAI MINHAN, 2008. Non-conservative calcium in the sea and oceanic calcium problems[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 23(1): 8-16 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 车秀芬, 张京红, 黄海静, 等, 2014. 海南岛气候区划研究[J]. 热带农业科学, 34(6): 60-65, 70. |
| CHE XIUFEN, ZHANG JINGHONG, HUANG HAIJING, et al, 2014. Climate regionalization in Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 34(6): 60-65, 70 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 陈建徽, 陈发虎, 张家武, 等, 2008. 中国西北干旱区小冰期的湿度变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 63(1): 23-33. |
| CHEN JIANHUI, CHEN FAHU, ZHANG JIAWU, et al, 2008. Humidity variability in the arid northwest China during LIA derived from different proxy records[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 63(1): 23-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 陈清, 樊隽轩, MELCHIN M J, 2012. 古生物多样性统计方法及其适用性分析[J]. 古生物学报, 51(4): 445-462. |
| CHEN QING, FAN JUNXUAN, MELCHIN M J, 2012. Methods for paleobiodiversity measurement and case studies of their applicability[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 51(4): 445-462 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 崔振昂, 林进清, 甘华阳, 等, 2015. 南海北部湾东部海域表层沉积物地球化学特征[J]. 海洋科学, 39(7): 103-111. |
| CUI ZHEN’ANG, LIN JINQING, GAN HUAYANG, et al, 2015. Geochemical characteristics of the surface sediments in the eastern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 39(7): 103-111 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 戴明, 李纯厚, 张汉华, 等, 2007. 海南岛以南海域浮游植物群落特征研究[J]. 生物多样性, 15(1): 23-30. |
| DAI MING, LI CHUNHOU, ZHANG HANHUA, et al, 2007. Characteristics of the phytoplankton community in the southern waters of Hainan Island[J]. Biodiversity Science, 15(1): 23-30 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 窦衍光, 李军, 李炎, 2012. 北部湾东部海域表层沉积物稀土元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 地球化学, 41(2): 147-157. |
| DOU YANGUANG, LI JUN, LI YAN, 2012. Rare earth element compositions and provenance implication of surface sediments in the eastern Beibu Gulf[J]. Geochimica, 41(2): 147-157 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 方念乔, 刘豪, 李琦, 等, 2013. 南海新生代碳酸盐沉积与区域构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 20(5): 227-234. |
| FANG NIANQIAO, LIU HAO, LI QI, et al, 2013. The pattern of carbonate sedimentation and its relation to the evolution of the South China Sea in Cenozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(5): 227-234 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 付淑清, 朱照宇, 欧阳婷萍, 等, 2010. 南海南部陆坡晚第四纪沉积物稀土元素及环境意义[J]. 热带地理, 30(1): 24-29. |
| FU SHUQING, ZHU ZHAOYU, OUYANG TINGPING, et al, 2010. Sedimentary records of rare earth elements from southern South China Sea continental slope and its paleoclimatic implications during late Quaternary[J]. Tropical Geography, 30(1): 25-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 高劲松, 陈波, 何小英, 等, 2014. 海南岛西岸上升流与暖池的数值研究[J]. 广西科学, 21(4): 331-337. |
| GAO JINSONG, CHEN BO, HE XIAOYING, et al, 2014. Numerical study on the upwelling and warm pool off the western coast of Hainan Island[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 21(4): 331-337 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 高劲松, 陈波, 侍茂崇, 2015. 北部湾夏季环流结构及生成机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 45(1): 99-112. |
| GAO JINSONG, CHEN BO, SI MAOCHONG, 2015. Summer circulation structure and formation mechanism in the Beibu Gulf[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 58(2): 286-299. | |
| [14] | 高亚辉, 梁君荣, 陈长平, 等, 2011. 海洋硅藻多样性与生态作用研究[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 50(2): 455-464. |
| GAO YAHUI, LIANG JUNRONG, CHEN CHANGPING, et al, 2011. Studies on biodiversity and ecological importance of marine diatoms[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 50(2): 455-464 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 广州海洋地质调查局, 2013. 北部湾广西近岸海洋地质环境与地质灾害调查报告[R]. 广州: 广州海洋地质调查局. |
| GUANGZHOU MARINE GEOLOGICAL SURVEY, 2013. Investigation report on the near-shore marine geological environment and geological hazards along Guangxi coast, China[R]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey (in Chinese). | |
| [16] | 广州海洋地质调查局, 2014. 南海北部湾全新世环境演变及人类活动影响研究成果报告[R]. 广州: 广州海洋地质调查局. |
| GUANGZHOU MARINE GEOLOGICAL SURVEY, 2014. Investigation report on the Holocene environmental evolution and anthropogenic impact of Beibu Gulf, China[R]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey (in Chinese). | |
| [17] | 侯光良, 方修琦, 2011. 中国全新世气温变化特征[J]. 地理科学进展, 30(9): 1075-1080. |
| HOU GUANGLIANG, FANG XIUQI, 2011. Characteristics of Holocene temperature change in China[J]. Progress in Geography, 30(9): 1075-1080 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 黄以琛, 李炎, 邵浩, 等, 2008. 北部湾夏冬季海表温度、叶绿素和浊度的分布特征及调控因素[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 47(6): 856-863. |
| HUANG YICHEN, LI YAN, SHAO HAO, et al, 2008. Seasonal variations of sea surface temperature, chlorophyll-a and turbidity in Beibu Gulf, MODIS imagery study[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 47(6): 856-863 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [19] | 黄镇国, 张伟强, 2007. 中国热带西部的小冰期[J]. 热带地理, 27(6): 489-492. |
| HUANG ZHENGGUO, ZHANG WEIQIANG, 2007. The little ice age in the west part of tropical China[J]. Tropical Geography, 27(6): 489-492 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [20] | 李保华, 孔晓敏, 王晓燕, 2010. 北部湾中部海域底质沉积物中的有孔虫[J]. 微体古生物学报, 27(2): 99-108. |
| LI BAOHUA, KONG XIAOMIN, WANG XIAOYAN, 2010. Foraminifera in surface sediments of the Tonkin Gulf, northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 27(2): 99-108 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [21] | 李春园, 孙蕾, 葛璇, 等, 2013. 南海北部表层沉积物碳酸盐含量和δ18O及δ13C的空间与粒径分布特征及其控制因素[J]. 海洋学报, 35(3): 246-254. |
| LI CHUNYUAN, SUN LEI, GE XUAN, et al, 2013. Spatial and grain size distribution of carbonates content δ18O and δ13C in surface sediments from the northern South China Sea and their controlling factors[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(3): 246-254 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [22] | 李家熙, 吴功建, 1999. 中国生态环境地球化学图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| LI JIAXI, WU JIANGONG, 1999. Atlas of Chinese ecological environmental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese). | |
| [23] | 李森, 孙武, 李凡, 等, 2005. 海南岛西部热带沙漠化土地特征与成因[J]. 地理学报, 60(3): 433-444. |
| LI SEN, SUN WU, LI FAN, et al, 2005. Study on the characteristics and the cause of sandy desertified land in the west of Hainan Island[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 60(3): 433-444 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [24] | 李学杰, 陈芳, 刘坚, 等, 2004. 南海西部表层沉积物碳酸盐分布特征及其溶解作用[J]. 地球化学, 33(3): 254-260. |
| LI XUEJIE, CHEN FANG, LIU JIAN, et al, 2004. Distribution and its dissolution of carbonate in seafloor surface sediment in the western South China Sea[J]. Geochimica, 33(3): 254-260 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [25] | 侍茂崇, 2014. 北部湾环流研究述评[J]. 广西科学, 21(4): 313-324. |
| SHI MAOCHONG, 2014. Study comments on circulation in Beibu Gulf[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 21(4): 313-324 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [26] | 孙湘平, 2006. 中国近海区域海洋[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. |
| SUN XIANGPING, 2006. Zhongguo Jinhai Quyu Haiyang[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press (in Chinese). | |
| [27] | 童国榜, 陈亮, 龙江平, 等, 2012. 北部湾东部表层孢粉沉积特征及其沉积动力环境[J]. 科学通报, 57(9): 743-752. |
| TONG GUOBANG, CHEN LIANG, LONG JIANGPING, et al, 2012. Surface pollen distribution patterns in Beibu Gulf and corresponding sediment dynamics environment[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(8): 902-911. | |
| [28] | 王红梅, 吴晓萍, 邱轩, 等, 2013. 微生物成因的碳酸盐矿物研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 40(1): 180-189. |
| WANG HONGMEI, WU XIAOPING, QIU XUAN, et al, 2013. Microbially induced carbonate precipitation: a review[J]. Microbiology China, 40(1): 180-189 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [29] | 王丽荣, 赵焕庭, 2008. 我国南海珊瑚礁区现代沉积底栖有孔虫的生态特征研究综述[J]. 热带地理, 28(4): 346-350. |
| WANG LIRONG, ZHAO HUANTING, 2008. A review of the studies in China on the ecological characteristics of modern sedimental benthic foraminifera of coral reef in South China Sea[J]. Tropical Geography, 28(4): 346-350 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [30] | 许冬, 初凤友, 杨海丽, 等, 2012. 北部湾现代沉积速率[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 32(6): 17-26. |
| XU DONG, CHU FENGYOU, YANG HAILI, et al, 2012. Modern sedimentation rates in the Beibu Gulf[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 32(6): 17-26 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [31] | 许冬, 李家彪, 初凤友, 等, 2013. 北部湾东部沉积物结构和碳酸盐含量变化对末次海侵和环流作用的响应[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 38(S1): 70-82. |
| XU DONG, LI JIABIAO, CHU FENGYOU, et al, 2013. The response of sedimentary records in eastern Beibu Gulf to the last Postglacial transgression and circulation[J]. Earth Science — Journal of China University of Geosciences, 38(1): 70-82 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [32] | 杨作升, 范德江, 郭志刚, 等, 2002. 东海陆架北部泥质区表层沉积物碳酸盐粒级分布与物源分析[J]. 沉积学报, 20(1): 1-6. |
| YANG ZUOSHENG, FAN DEJIANG, GUO ZHIGANG, et al, 2002. Distribution of the carbonate clast size and the provenance analyses of the surface sediments in the northern East China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 20(1): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [33] | 殷建军, 覃嘉铭, 林玉石, 2013. 石笋记录年际、年代际极端天气/气候事件研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 32(2): 203-210. |
| YIN JIANJUN, QIN JIAMING, LIN YUSHI, 2013. Research progress on the interannual-interdecadal extreme weather event recorded by stalagmites[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 32(2): 203-210 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [34] | 张金鹏, 朱本铎, 陈炽新, 等, 2013. 南海西北部表层沉积硅藻的分布特征与环境分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 29(11): 8-13. |
| ZHANG JINPENG, ZHU BENDUO, CHEN CHIXIN, et al, 2013. Distribution pattern of diatom in surface sediments of the northwestern South China Sea and its environmental implications[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 29(11): 8-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [35] | 张萍, 缴建华, 孙万胜, 等, 2016. 渤海湾天津近岸海域大型底栖动物群落结构及次级生产力的初步研究[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 31(3): 324-330. |
| ZHANG PING, JIAO JIANHUA, SUN WANSHENG, et al, 2016. Community structure and secondary production of macrobenthos in Tianjin coastal seawaters in Bohai Bay[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 31(3): 324-330 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [36] | 张娴, 邵晓华, 王涛, 2013. 中国小冰期气候研究综述[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 5(4): 317-325. |
| ZHANG XIAN, SHAO XIAOHUA, WANG TAO, 2013. Regional climate characteristics in China during the Little Ice Age[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 5(4): 317-325 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [37] | 周秀骥, 赵平, 刘舸, 等, 2011. 中世纪暖期、小冰期与现代东亚夏季风环流和降水年代-百年尺度变化特征分析[J]. 科学通报, 56(25): 2060-2067. |
| ZHOU XIUJI, ZHAO PING, LIU GE, et al, 2011. Characteristics of decadal-centennial-scale changes in east Asian summer monsoon circulation and precipitation during the Medieval Warm Period and Little Ice Age and in the present day[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(28/29): 3003-3011. | |
| [38] | BAUER A, WANIEK J J, 2010. Modeling biological production in the central beibu gulf[R]. BEIBU Workshop, Guangzhou, China. |
| [39] | BELDE J, REUNING L, BACK S, 2017. Bottom currents and sediment waves on a shallow carbonate shelf, Northern Carnarvon Basin, Australia[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 138: 142-153. |
| [40] | ENDLER M, 2011. Composition, spatial distribution and dynamics of suspended particulate matter (SPM) in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea[R]. BEIBU Workshop, Warnemund, Germany. |
| [41] | KAI LIANG, BAUER A, BRUST J, 2011. Benthic foraminiferal distribution patterns in the Beibu Gulf[R]. BEIBU Workshop, Warnemund, Germany. |
| [42] | KUMAR P V H, JOSHI M, SANILKUMAR K V, et al, 2009. Growth and decay of the Arabian Sea mini warm pool during May 2000: observations and simulations[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 56(4): 528-540. |
| [43] | LI JIAXUN, WANG GUIHUA, XIE SHANGPING, et al, 2012. A winter warm pool southwest of Hainan Island due to the orographic wind wake[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C8): C08036. |
| [44] | LI JIAXUN, ZHANG REN, LING ZHENG, 2014. Effects of Cardamom Mountains on the formation of the winter warm pool in the gulf of Thailand[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 91: 211-219. |
| [45] | MARTIN J B, 2017. Carbonate minerals in the global carbon cycle[J]. Chemical Geology, 449(2017): 58-72. |
| [46] | NI Y, HARFF J, XIA Z, et al, 2016. Post-glacial mud depocentre in the southern Beibu Gulf: acoustic features and sedimentary environment evolution[M]//CLIFT P D, HARFF J, WU J, et al. River-Dominated Shelf Sediments of East Asian Seas. Geological Society. London: Special Publications: 429. |
| [47] | OSBORNE M C, DUNBAR R B, MUCCIARONE D A, et al, 2013. Regional calibration of coral-based climate reconstructions from Palau, West Pacific Warm Pool (WPWP)[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 386: 308-320. |
| [48] | PIOTROWSKI A M, BANAKAR V K, SCRIVNER A E, et al, 2009. Indian Ocean circulation and productivity during the last glacial cycle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 285(1/2): 179-189. |
| [49] | RADENAC M-H, MESSIÉ MO, LÉGER F, et al, 2013. A very oligotrophic zone observed from space in the equatorial Pacific warm pool[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 134: 224-233. |
| [50] | TSIARAS K P, KOURAFALOU V H, RAITSOS D E, et al, 2012. Inter-annual productivity variability in the North Aegean Sea: influence of thermohaline circulation during the Eastern Mediterranean Transient[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 96: 72-81. |
| [51] | WANIEK J J, 2010. Beibu Gulf and its importance for South China Sea[R]. BEIBU Workshop, Guangzhou, China. |
| [52] | ZHANG CHENGLONG, HUANG HUI, YE CHENG, 2013. Diurnal and seasonal variations of carbonate system parameters on Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 96: 65-74. |
| [1] | SUN Zeming, HAN Shuzong, WANG Mingjie, SU Hanxiang. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [2] | LU Tianmei, GUAN jiasong, QIN Shijing, LIU Yonghong, SU Zhiwei. Preliminary study on the culturable myxobacteria resources from the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi and their antibacterial activity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 158-168. |
| [3] | XU Yixiao, HE Xilin, ZHANG Teng, LAN Wenlu. Causative species of Phaeocystis blooms in Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 122-130. |
| [4] | Yanfeng WANG,Jing YU,Pimao CHEN,Jie YU,Zhunan LIU. Relationship between spatial-temporal distribution of light falling-net fishing ground and marine environments * [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 68-76. |
| [5] | ZHANG Kui, CHEN Zuozhi, WANG Yuezhong, SUN Dianrong, QIU Yongsong. Population structure of Priacanthus macracanthus in the Beibu Gulf, and parameters for its growth, mortality and maturity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(5): 20-28. |
| [6] | SUN Longqi, LIN Yuanshao, CHEN Lixiao, CAO Wenqing, ZHENG Lianming. Analysis of ecosystem structure and function in the northern Beibu Gulf Ⅶ: Nutrition structure and keystone species selection based on Ecopath with Ecosim [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(4): 51-62. |
| [7] | LI Zili, CAO Hongyan, JIA Chunyang. Observation of wind field in the Beibu Gulf during Typhnoon Usagi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(4): 31-34. |
| [8] | YANG Lu, CAO Wenqing, LIN Yuanshao, CHEN Yinghan, LIN Zhaojin, WANG Xuehui. Preliminary study on feeding habits and trophic niche of nine economic fish species in Beibu Gulf in summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(2): 66-75. |
| [9] | WANG Fu-jing, LIN Yuan-shao, CAO Wen-qing, ZHANG Wen-jing, ZHENG Lian-ming, YANG Wei-di, WANG Yu-jie. The relationship between nutrients and phytoplankton community structure in northern Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(6): 73-85. |
| [10] | TANG Bo, LONG Jiang-ping, JIN Lu, XU Dong, LI Tuan-jie. The contrast of heavy metals’ ecological risks in marine sediments between the Beibu Gulf and the Pearl River Delta [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(3): 75-81. |
| [11] | WANG Wen-jie, XU Jian. Salinity effect on Holocene Mg/Ca-temperature estimation from the Indo-Pacific warm-pool sediment samples [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 94-100. |
| [12] | LONG Chao, CHEN Xian-yun, CHEN Bo, HE Bi-juan, GAO Cheng-hai, WANG Yi-bing. Morphological and phylogenetic analysis of Prorocentrum triestinum isolated from the Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 66-71. |
| [13] | YU Ying, ZHANG Wu-chang, CAI Yu-ming, FENG Mei-ping, LI Hai-bo, XIAO Tian. Abundance and biomass of planktonic ciliates in the Beibu Gulf during summer 2009 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 60-65. |
| [14] | YU Yong-qiang,LI Chao,WANG Dong-xiao,LIU Hai-long. Numerical simulation of seasonal cycle in the warm pool and its sensitivity to surface heat flux and momentum forcing [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 1-10. |
| [15] | LI Heng-xiang,YAN Yan,HE Wei-hong,ZOU Xiao-li. An ecological study on fouling in the waters off the Bailong Peninsula in the Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(3): 108-113. |
|
||