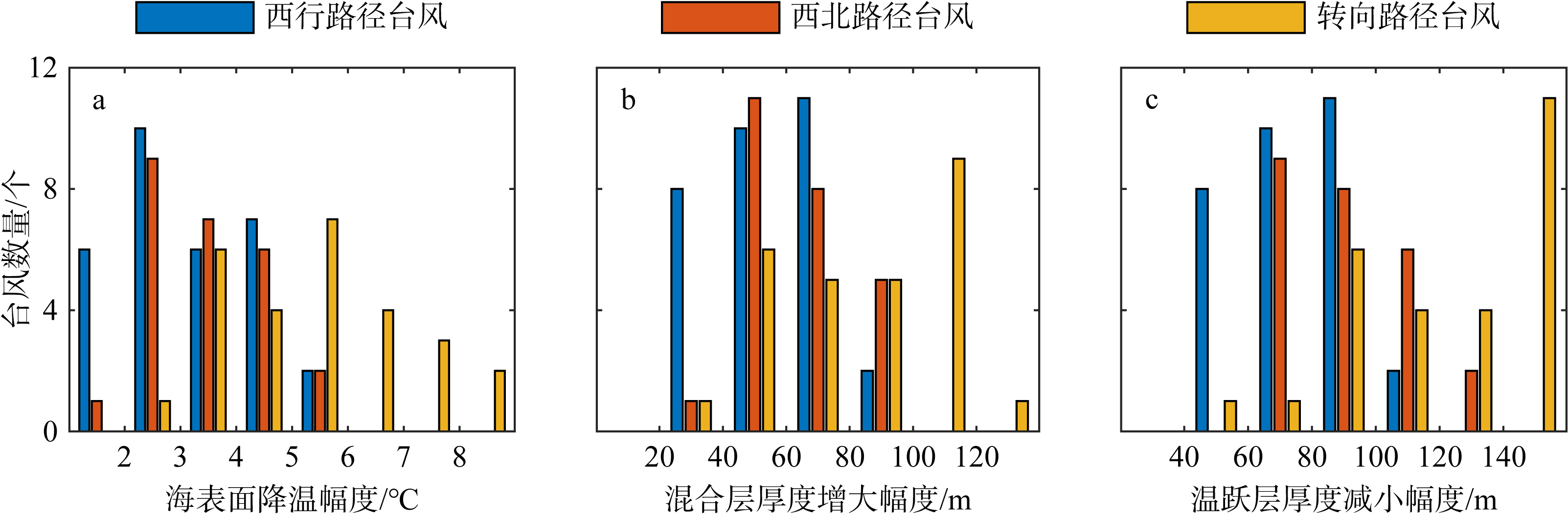
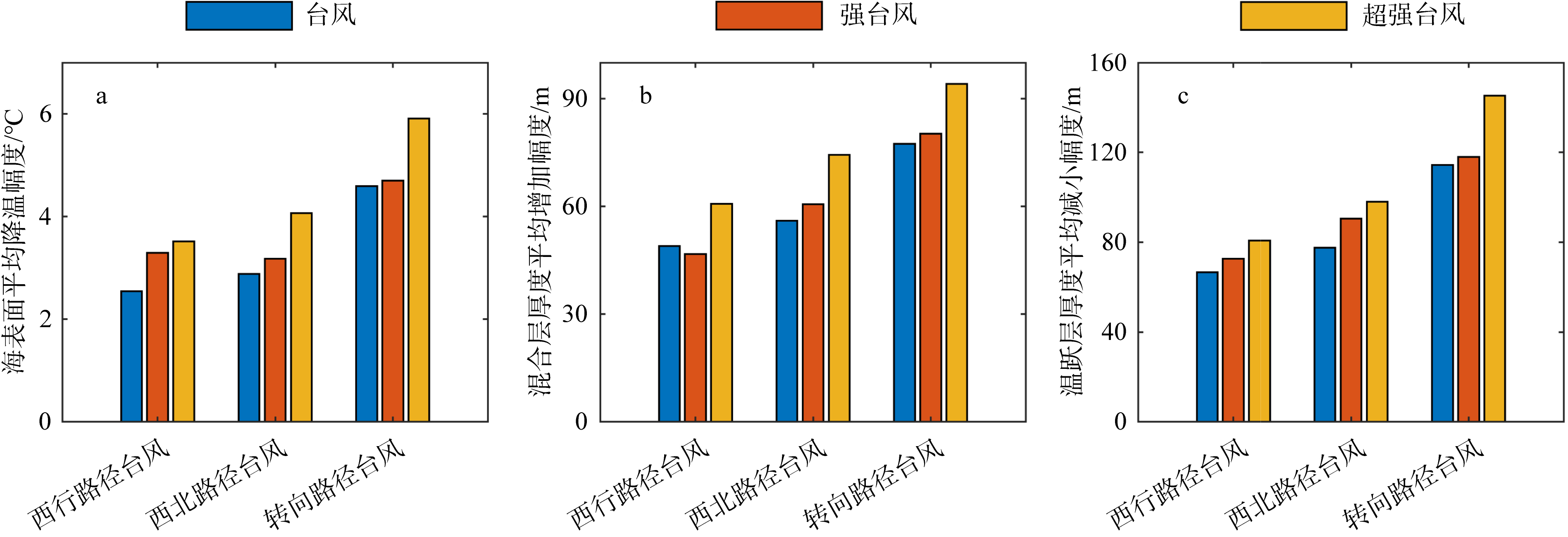
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 17-31.doi: 10.11978/2023141CSTR: 32234.14.2023141
• Marine Meteorology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China
SUN Zeming1( ), HAN Shuzong1,2(
), HAN Shuzong1,2( ), WANG Mingjie1, SU Hanxiang1
), WANG Mingjie1, SU Hanxiang1
- 1. Collage of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
2. College of Marine Science and Technology, Hainan Tropical Ocean University, Sanya 572022, China
-
Received:2023-10-04Revised:2023-12-07Online:2024-09-10Published:2024-10-10 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program(2022YFC3104000); Jiangsu Province Marine Science and Technology Innovation Project(JSZRHYKJ202304)
Cite this article
SUN Zeming, HAN Shuzong, WANG Mingjie, SU Hanxiang. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 17-31.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Spatiotemporal ranges of two optimal interpolated sea surface temperature data sets and corresponding sensors used"
| 传感器 | 空间范围 | 时间范围 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MW | TMI, AMSR-E, AMSR2, WindSat, GMI | 在2002-06-01之前: 40°S—40°N 在2002-06-01之后: 全球 | 1998-01-01 至今 |
| MW_IR | MW: TMI, AMSR-E, AMSR2,WindSat, GMI IR: MODIS-Terra, MODIS-Aqua, VIIRS-NPP, VIIRS-N20 | 全球 | 2002-06-01 至今 |
Fig. 2
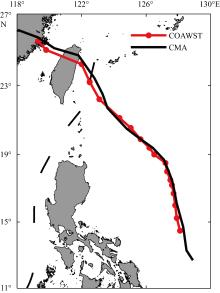
Temperature profile comparison of Argo and COAWST coupling models near the typhoon path before and after the passage of No. 1709 typhoon “Nesat”. The dashed blue line in the figure (a) is the 169th profile data of No. 2902656 Argo, the solid red line is the temperature profile of COAWST simulation results, and the dashed blue line in the figure (b) is the 170th profile data of No. 2902656 Argo, the solid red line is the temperature profile of COAWST simulation results"
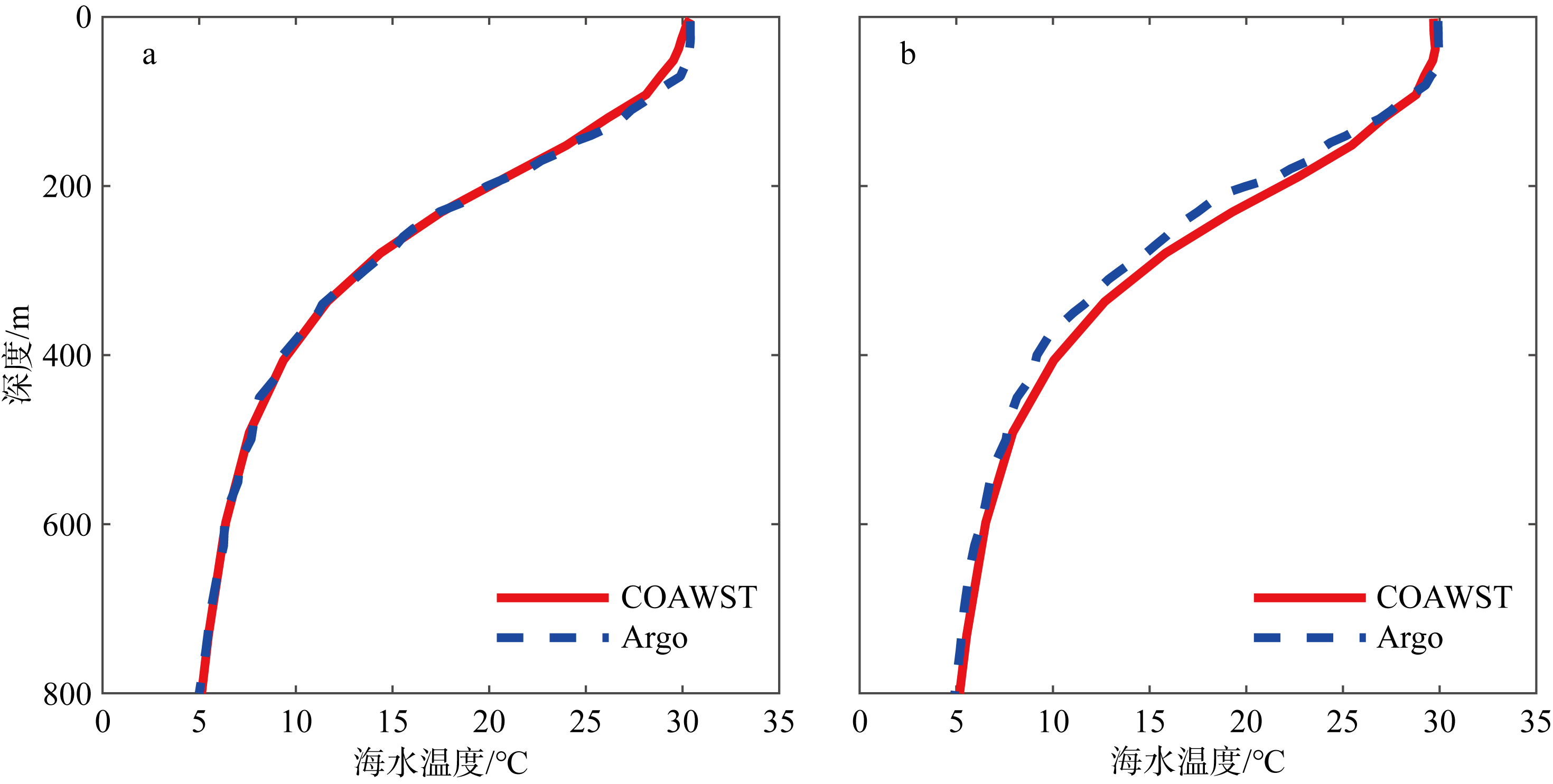
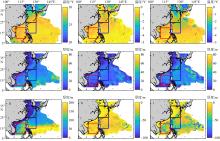
Fig. 6
Temporal and spatial characteristics of the variation amplitude of SST, MLT and TT induced by typhoon samples. (a) The average SST before the typhoon; (b) the average reduction of SST during typhoon transit; (c) the average reduction of SST within 7 days after the passage of the typhoon; (d) average MLT before the typhoon; (e) the average increase of MLT during typhoon transit; (f) the average increase in MLT within 7 days after the typhoon’s passage; (g) average TT before the typhoon; (h) the average reduction of TT during typhoon transit; (i) average reduction of TT within 7 days after the typhoon’s passage. The black box area is the main impact area of the turning typhoon. The area in blue box is the main affected area of the northwestward typhoon. The area in the red box is the main impact area of the westward typhoon. The blank area in the figure is the area not affected by the typhoon samples"

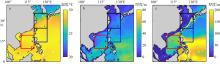
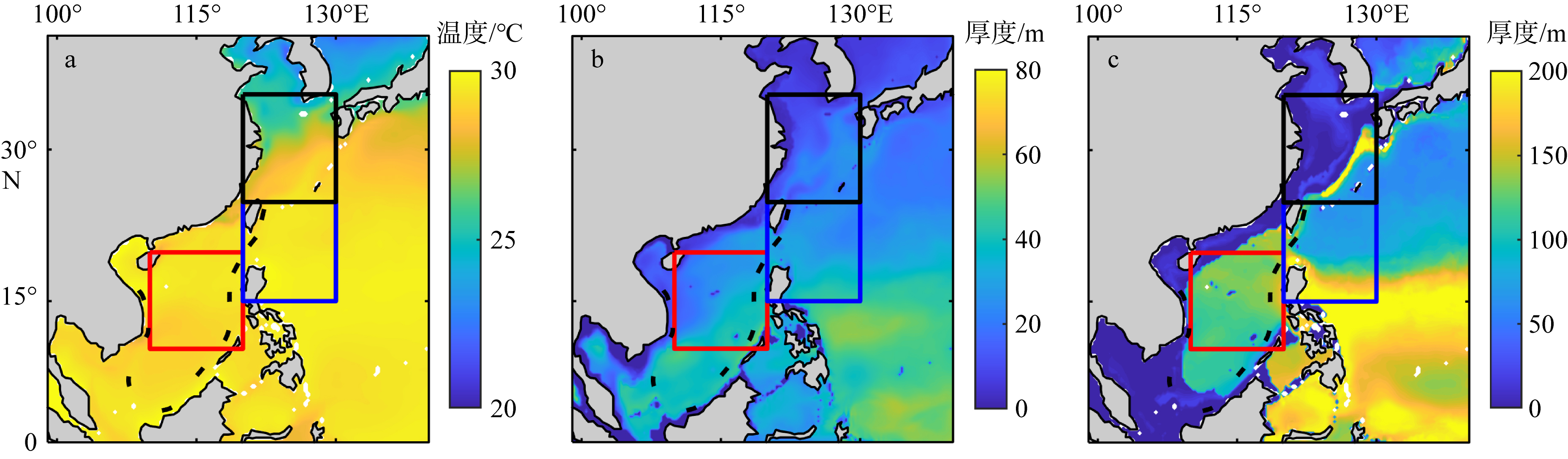
Fig. 7
The average SST (a), MLT (b) and TT (c) from July to September in the mean affect area from 2001 to 2020 (https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/GLOBAL_REANALYSIS_PHY_001_031/), the red, blue and black boxes in the figure show the main affect area of the westward typhoon, the northwestward typhoon and the turning typhoon respectively"
Tab. 8
Background field information of the main affect areas of each type of typhoon"
| 主要影响区域内SST平均值/℃ | 主要影响区域内MLT平均值/m | 主要影响区域内TT平均值/m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过境前2d平均 | 7—9月平均 | 过境前2d平均 | 7—9月平均 | 过境前2d平均 | 7—9月平均 | |
| 西行路径台风 | 28.49 | 29.28 | 24.08 | 29.01 | 106.05 | 118.02 |
| 西北路径台风 | 29.21 | 29.56 | 25.74 | 27.51 | 100.27 | 114.98 |
| 转向路径台风 | 27.25 | 27.54 | 13.46 | 14.59 | 21.14 | 38.95 |
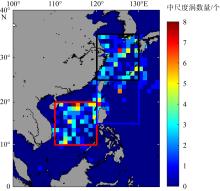
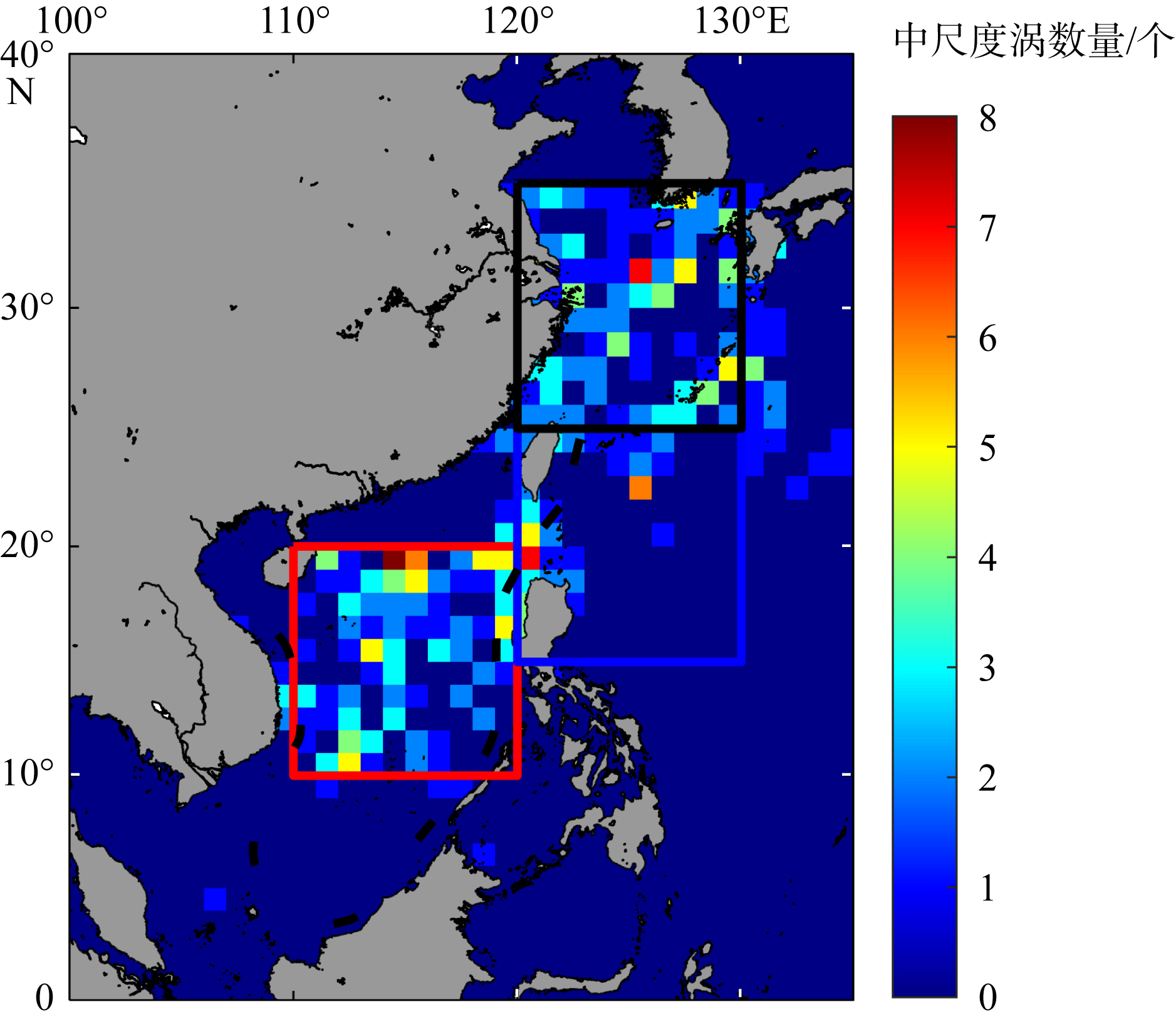
Fig. 8
The number of mesoscale cold vortices from July to September in the mean affect area from 2002 to 2021, using AVISO altimetry data (https://data.aviso.altimetry.fr/aviso-gateway/data/META3.1exp_DT/META3.1exp_DT_twosat/), the red, blue and black boxes in the figure show the main affect area of the westward typhoon, the northwestward typhoon and the turning typhoon respectively"
| [1] |
顾润源, 朱官忠, 李振海, 等, 1993. 影响我国的不同路径台风的对比分析[J]. 山东气象, 13(2): 1-5, 15 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
韩玉康, 龚立新, 2017. 南海温跃层对台风过程响应的数值模拟研究[J]. 海洋信息, (4): 12-21 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
刘增宏, 许建平, 朱伯康, 等, 2006. 利用Argo资料研究2001—2004年期间西北太平洋海洋上层对热带气旋的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 25(1): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
孙凡, 于非, 司广成, 等, 2021. 台风过境对黄海冷水团及其环流结构的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 52(5): 1125-1136.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
徐文玲, 苏洁, 2007. 台风对西北太平洋海表温度的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 37(S2): 17-22.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
杨晓霞, 唐丹玲, 2010. 台风引起南海海表面降温的位置变化特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(4): 26-31.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.04.026 |
|
| [7] |
叶家成, 杜新观, 余锦华, 2019. 影响中国大陆热带气旋路径分类及其特征研究[J]. 气象科学, 39(3): 304-311.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
郑颖青, 余锦华, 吴启树, 等, 2013. K-均值聚类法用于西北太平洋热带气旋路径分类[J]. 热带气象学报, 29(4): 607-615.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 国家标准化管理委员会, 2006. GB/T 19201-2006 热带气旋等级[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
GENERAL ADMINISTRATION OF QUALITY SUPERVISION, INSPECTION AND QUARANTINE OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA, NATIONAL STANDARDIZATION ADMINISTRATION, 2006. GB/T 19201-2006 Grade of tropical cyclones[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
|
| [10] |
周磊, 陈大可, 雷小途, 等, 2019. 海洋与台风相互作用研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 64(1): 60-72.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
pmid: 10797004 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
|
||