Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 1-11.doi: 10.11978/2021111CSTR: 32234.14.2021111
• Special Column: Mangrove Forest • Next Articles
Characteristics of water quality and their eutrophication assessment on the mangrove ecosystems along the Guangdong coast
INYANG Aniefiok Ini1,2,3,4,5( ), ZHOU Yueyue1,2,3,4,5, WANG Youshao1,2,3,5(
), ZHOU Yueyue1,2,3,4,5, WANG Youshao1,2,3,5( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Daya Bay Marine Biology Research Station, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen 518121, China
3. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
5. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
-
Received:2021-08-28Revised:2022-10-19Online:2022-11-10Published:2021-10-20 -
Contact:WANG Youshao E-mail:yswang@scsio.ac.cn;aniefiokinyang@yahoo.com -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Plan(2017FY100700);National Natural Science Foundation of China(U1901211);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41876126);International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences(133244KYSB20180012);Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0305);Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA23050200)
CLC Number:
- X52
Cite this article
INYANG Aniefiok Ini, ZHOU Yueyue, WANG Youshao. Characteristics of water quality and their eutrophication assessment on the mangrove ecosystems along the Guangdong coast[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 1-11.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

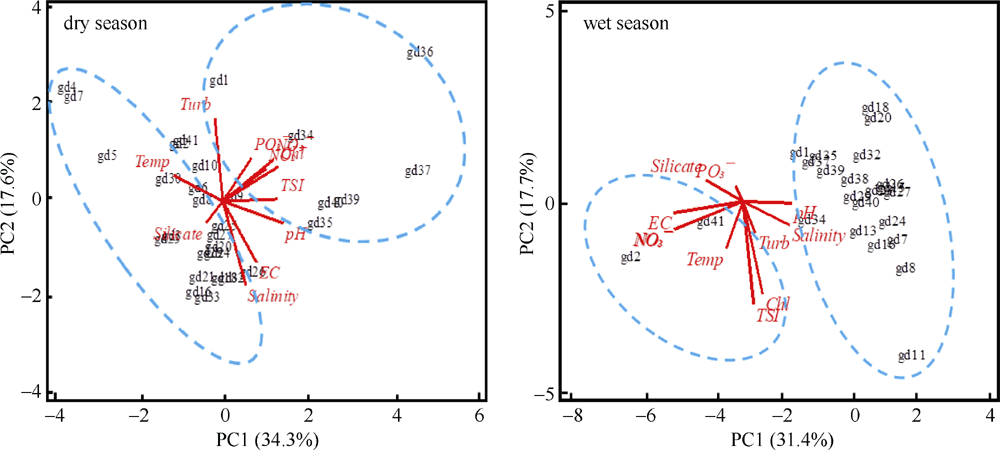
Fig. 2
Algal bloom on the floor of mangrove forest (Avicennia marina) around Peninsula and mid part of the Guangdong coast exposed during low tide. (a) Long term severe environmental pollution result in the mangrove plant death; (b) A. marina bed covered with algal bloom due to the long term nutrient enrichment"

Tab. 1
Spatiotemporal variation and T-test evaluation of environmental parameters during dry season (n = 30) and wet season (n = 23) in the mangroves"
| variables | season | minimum | maximum | mean | STD | T-test | dry vs wet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | dry | 7.23 | 8.63 | 7.95 | 0.338 | not sign. | P<0.05 |
| wet | 7.47 | 8.71 | 8.04 | 0.393 | |||
| temperature/℃ | dry | 13.33 | 29.79 | 20.37 | 3.946 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 23.76 | 34.49 | 30.09 | 2.447 | |||
| EC/ (µS·cm-1) | dry | 10.87 | 90.52 | 33.21 | 14.76 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 1338 | 9702 | 3745 | 1966 | |||
| TDS /(mg·L-1) | dry | 0.098 | 21.61 | 14.67 | 5.957 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 2.042 | 18.14 | 10.44 | 5.892 | |||
| turbidity /FTU | dry | 5.6 | 395 | 82.91 | 94.67 | not sign. | P<0.05 |
| wet | 9.2 | 204 | 59.261 | 41.23 | |||
| salinity/‰ | dry | 5.11 | 27.31 | 18.78 | 7.019 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 2.15 | 22.82 | 12.67 | 7.538 | |||
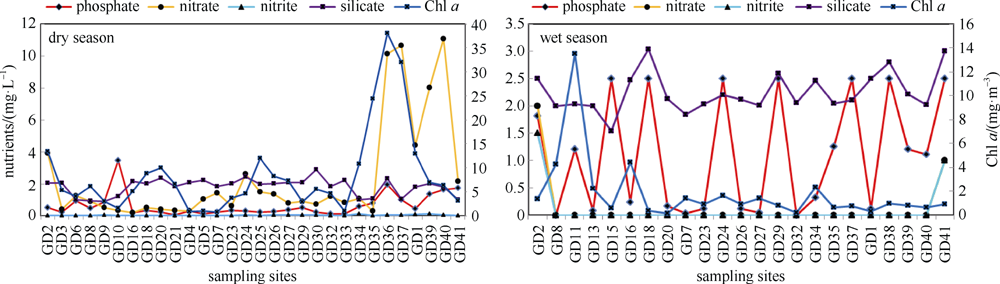
| nitrate /(mg·L-1) | dry | 3.5 | 127.2 | 50.923 | 40.76 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 0 | 2.0 | 0.13 | 0.458 | |||
| nitrite/ (mg·L-1) | dry | 0.6 | 12.0 | 3.59 | 2.59 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 0 | 1.5 | 0.109 | 0.368 | |||
| phosphate/ (mg·L-1) | dry | 0.13 | 34.5 | 9.45 | 8.35 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 0 | 2.5 | 0.997 | 1.042 | |||
| silicate /( mg·L-1) | dry | 0.884 | 2.882 | 1.814 | 0.533 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 1.54 | 3.04 | 2.25 | 0.368 | |||
| Chl a/ (mg·m-3) | dry | 0.752 | 38.084 | 8.38 | 8.778 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 0.137 | 13.526 | 1.804 | 2.794 | |||
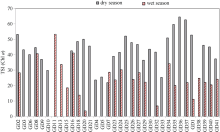
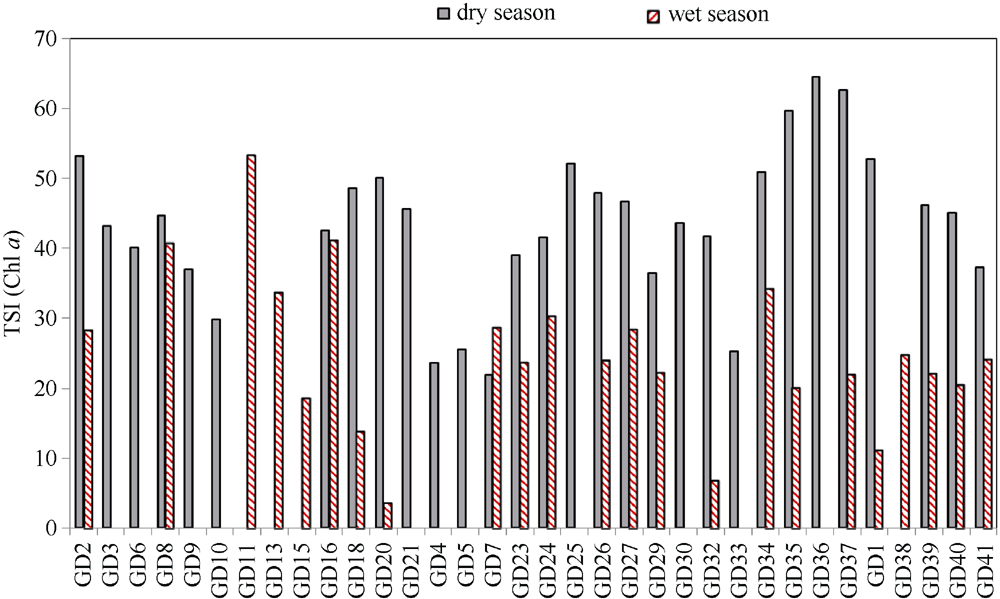
| TSI | dry | 21.9 | 64.53 | 43.312 | 10.76 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 3.65 | 53.27 | 25.11 | 11.17 | |||
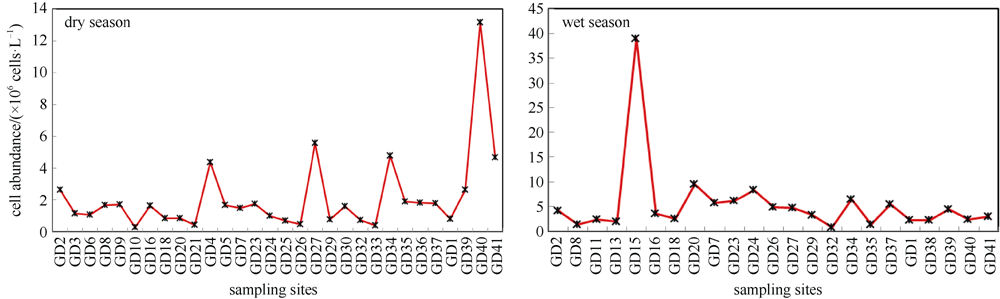
| algal density (cells·L-1) | dry | 558 | 23703 | 3881 | 4493 | sign. | P<0.01 |
| wet | 1395 | 70144 | 9826 | 13757 |
Tab. 2
Pearson correlation coefficient of environmental parameters in the mangroves during the wet season (n = 23) and dry season (n = 30)"
| pH | temperature | EC | TDS | turbidity | salinity | nitrate | nitrite | phosphate | silicate | Chl a | TSI (Chl a) | algal density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dry season | pH | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| temperature | -0.602** | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| EC | 0.439* | -0.336 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| TDS | 0.443* | -0.259 | 0.361* | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| turbidity | -0.122 | 0.299 | -0.358* | -0.349 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| salinity | 0.458** | -0.263 | 0.342 | 0.959** | -0.361* | 1.000 | ||||||||
| nitrate | 0.431* | -0.264 | 0.413* | -0.090 | 0.179 | -0.119 | 1.000 | |||||||
| nitrite | 0.512** | -0.331 | -0.013 | -0.019 | 0.077 | -0.022 | 0.505** | 1.000 | ||||||
| phosphate | 0.204 | -0.397* | 0.077 | -0.180 | 0.042 | -0.243 | 0.420* | 0.154 | 1.000 | |||||
| silicate | -0.206 | 0.300 | 0.133 | -0.006 | 0.181 | 0.110 | -0.012 | -0.063 | -0.355 | 1.000 | ||||
| Chl a | 0.530** | -0.303 | 0.093 | 0.185 | 0.273 | 0.182 | 0.601** | 0.359* | 0.213 | -0.095 | 1.000 | |||
| TSI (Chl a) | 0.513** | -0.318 | 0.231 | 0.266 | -0.119 | 0.273 | 0.469** | 0.399* | 0.062 | -0.105 | 0.838** | 1.000 | ||
| algal density | 0.267 | -0.055 | 0.108 | -0.055 | -0.071 | -0.099 | 0.379* | 0.498** | 0.141 | 0.099 | -0.077 | -0.062 | 1.000 | |
| wet season | pH | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| temperature | -0.237 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| EC | -0.576** | 0.206 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| TDS | 0.534** | 0.111 | -0.466* | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| turbidity | 0.0851 | 0.135 | -0.125 | 0.078 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| salinity | 0.527** | 0.104 | -0.457* | 1.000** | 0.0701 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| nitrate | -0.321 | 0.228 | 0.733** | -0.308 | -0.085 | -0.310 | 1.000 | |||||||
| nitrite | -0.323 | 0.240 | 0.725** | -0.325 | -0.074 | -0.327 | 0.992** | 1.000 | ||||||
| phosphate | -0.031 | -0.097 | 0.044 | 0.031 | 0.134 | 0.035 | 0.075 | 0.045 | 1.000 | |||||
| silicate | -0.097 | -0.213 | 0.317 | -0.276 | -0.055 | -0.273 | 0.340 | 0.381 | 0.208 | 1.000 | ||||
| Chl a | 0.140 | 0.006 | -0.156 | 0.140 | 0.110 | 0.135 | -0.063 | -0.068 | -0.076 | -0.133 | 1.000 | |||
| TSI (Chl a) | 0.064 | 0.159 | -0.019 | 0.193 | 0.178 | 0.192 | 0.049 | 0.044 | -0.074 | -0.098 | 0.799** | 1.000 | ||
| algal density | 0.194 | 0.065 | -0.042 | 0.245 | -0.021 | 0.250 | -0.067 | -0.073 | 0.305 | -0.444* | -0.144 | -0.153 | 1.000 |
| [1] | DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION OF GUANGDONG PROVINCE, 2016. 2015 Report on the state of Guangdong Provincial environment[R]. Guangzhou: Department of Environmental Protection of Guangdong Province. |
| 广东省环境保护厅, 2016. 2015《广东省环境状况报告》[R]. 广州: 广东省环境保护厅. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | GEEDICKE I, OLDELAND J, LEISHMAN M R, 2018. Urban stormwater run-off promotes compression of saltmarshes by freshwater plants and mangrove forests[J]. Science of the Total Environment,637-638: 137-144. |
| [3] | HELCOM, 2015. Guidelines concerning phytoplankton species composition, abundance and biomass[M]//HELCOM. Manual for marine monitoring in the COMBINE programme of HELCOM. Helsinki: HELCOM. |
| [4] |
HOU ZHAOJIANG, JIANG YUAN, LIU QI, et al, 2018. Impacts of environmental variables on a phytoplankton community: a case study of the tributaries of a subtropical river, Southern China[J]. Water, 10(2): 152.
doi: 10.3390/w10020152 |
| [5] | INYANG A I, DAN M U, SUNDAY K E, 2018. Seasonal and spatial variations of physicochemical properties of eastern Obolo coastal water, Niger Delta-Nigeria[J]. Journal of Marine Biology & Oceanography, 7(1): 1000188. |
| [6] |
INYANG A I, WANG YOUSHAO, 2020. Phytoplankton diversity and community responses to physicochemical variables in mangrove zones of Guangzhou Province, China[J]. Ecotoxicology, 29(6): 650-668.
doi: 10.1007/s10646-020-02209-0 pmid: 32350642 |
| [7] |
JHA D K, VINITHKUMAR N V, SAHU B K, et al, 2015. Multivariate and geo-spatial approach for seawater quality of Chidiyatappu Bay, south Andaman Islands, India[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 96(1-2): 463-470.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.004 pmid: 25972234 |
| [8] |
JIANG ZHIBING, LIAO YIBO, LIU JINGJING, et al, 2013. Effects of fish farming on phytoplankton community under the thermal stress caused by a power plant in a eutrophic, semi-enclosed bay: Induce toxic dinoflagellate (Prorocentrum minimum) blooms in cold seasons[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1-2): 315-324.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.07.006 pmid: 24070454 |
| [9] |
LIU J Y, 2013. Status of marine biodiversity of the China Seas[J]. PLoS One, 8(1): e50719.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050719 |
| [10] |
MACDONNELL C P, ZHANG LI, GRIFFITHS L, et al, 2017. Nutrient concentrations in tidal creeks as indicators of the water quality role of mangrove wetlands in Southwest Florida[J]. Ecological Indicators, 80: 316-326.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.05.043 |
| [11] | MANJU M N, RESMI P, GIREESH KUMAR T R, et al, 2012. Assessment of water quality parameters in mangrove ecosystems along Kerala coast: a statistical approach[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 6(4): 893-902. |
| [12] | MIYITTAH M K, TULASHIE S K, TSYAWO F W, et al, 2020. Assessment of surface water quality status of the Aby lagoon system in the western Region of Ghana[J]. Heliyon, 6(7): e4466. |
| [13] |
MORRIS J T, SUNDARESHWAR P V, NIETCH C T, et al, 2002. Responses of coastal wetlands to rising sea level[J]. Ecology, 83(10): 2869-2877.
doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[2869:ROCWTR]2.0.CO;2 |
| [14] |
MUKATE S, WAGH V, PANASKAR D, et al, 2019. Development of new integrated water quality index (IWQI) model to evaluate the drinking suitability of water[J]. Ecological Indicators, 101: 348-354.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.01.034 |
| [15] |
PAWAR P R, 2013. Monitoring of impact of anthropogenic inputs on water quality of mangrove ecosystem of Uran, Navi Mumbai, west coast of India[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 75(1-2): 291-300.
doi: S0025-326X(13)00351-2 pmid: 23856298 |
| [16] |
QU HONGJUAN, KROEZE C, 2010. Past and future trends in nutrients export by rivers to the coastal waters of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 408(9): 2075-2086.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.12.015 |
| [17] | RAHAMAN S M B, GOLDER J, RAHAMAN M S, et al, 2013. Spatial and temporal variations in phytoplankton abundance and species diversity in the Sundarbans mangrove forest of Bangladesh[J]. Journal of Marine Science: Research & Development, 3(2): 1000126. |
| [18] |
RAO K, PRIYA N, RAMANATHAN A L, 2018. Impact of seasonality on the nutrient concentrations in Gautami- Godavari estuarine mangrove complex, Andhra Pradesh, India[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 129(1): 329-335.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.02.052 |
| [19] |
REIS C R G, NARDOTO G B, OLIVEIRA R S, 2017. Global overview on nitrogen dynamics in mangroves and consequences of increasing nitrogen availability for these systems[J]. Plant and Soil, 410(1-2): 1-19.
doi: 10.1007/s11104-016-3123-7 |
| [20] |
SAMARA F, SOLOVIEVA N, GHALAYINI T, et al, 2020. Assessment of the environmental status of the mangrove ecosystem in the United Arab emirates[J]. Water, 12(6): 1623.
doi: 10.3390/w12061623 |
| [21] |
SONG XINGYU, HUANG LIANGMIN, ZHANG JIANLIN, et al, 2009. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Daya Bay, China: an in situ study of primary production and environmental impacts[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(9): 1310-1318.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.04.030 pmid: 19501846 |
| [22] | TJANDRAATMADJA G, DIAPER C, 2006. Sources of critical contaminants in domestic wastewater: a literature review[R]. Canberra: CSIRO: Water for a Healthy Country National Research Flagship: 5. |
| [23] | TORIMAN M E, ARFAN A, YUSOP Z, 2013. Assessment of mangrove water quality by multivariate statistical analysis in Suppa Coast, South Sulawesi, Indonesia[J]. World Applied Sciences Journal, 28(9): 1301-1310. |
| [24] | VALIELA I, KINNEY E L, CULBERTSON J, et al, 2009. Global losses of mangroves and salt marshes[M]//DUARTE C M. Global loss of coastal habitats: rates, causes and consequences. Bilbao: Fundaćon BBVA: 107-142. |
| [25] | WANG MINGCUI, LIU XUEQIN, ZHANG JIANHUI, 2002. Evaluate method and classification standard on lake eutrophication[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 18(5): 47-49. |
| [26] | WANG YOUSHAO, 2019. Molecular ecology of mangroves[M]. Beijing: Science Press. |
| 王友绍, 2019. 红树林分子生态学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | WANG YOUSHAO, SUN CUICI, WANG YUTU, et al, 2019. Ecological theory and technological innovations guide marine ecology research and protection in tropical and subtropical areas of China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of sciences, 34(1): 121-129. |
| 王友绍, 孙翠慈, 王玉图, 等, 2019. 生态学理论与技术创新引领我国热带、亚热带海洋生态研究与保护[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 24(1): 121-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | WANG YOUSHAO, GU JIDONG, 2021. Ecological responses, adaptation and mechanisms of mangrove wetland ecosystem to global climate change and anthropogenic activities[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 162: 105248. |
| [1] | AN Fan, JIANG Yue, WANG Yu, CAO Guangping, GAO Chenghai, LIU Yonghong, YI Xiangxi, BAI Meng. Studies on secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus GXIMD 03158 isolated from mangroves Acanthus ilicifolius L. [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 41-48. |
| [2] | WU Hongbo, LUO Feng, CHEN Zhipeng, ZHU Fei, ZENG Jingwei, ZHANG Chi, LI Ruijie. A novel pattern for predicting the effects of mangrove ecological reconstruction [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 86-97. |
| [3] | LIANG Hanqiao, CHEN Wenfeng, FAN Yikai, ZHU Zidong, MA Guoxu, CHEN Deli, TIAN Jing. Research progress on the secondary metabolites and activities of endophytic fungi of genus Aspergillus and Trichoderma from mangroves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 12-24. |
| [4] | WANG Youshao. Impacts, challenges and opportunities of global climate change on mangrove ecosystems [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 1-14. |
| [5] | ZHANG Liming, TAN Yehui, LI Jiajun, HUANG Xiaoping, LIU Jiaxing. Characteristics of the phytoplankton community and its response to Dan’ao River input in Daya Bay in summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [6] | Di DONG, Jisheng ZENG, Zheng WEI, Jinhui YAN. Integrating spaceborne optical and SAR imagery for monitoring mangroves and Spartina alterniflora in Zhangjiang Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 107-117. |
| [7] | Fuwu XIE, Xingyu SONG, Yehui TAN, Meiting TAN, Yadong HUANG, Huaxue LIU. Impact of simulated warming and nutrients input on plankton community metabolism in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 48-57. |
| [8] | Fuwu XIE, Huaxue LIU, Honghui HUANG, Xingyu SONG. Effects of thermal discharge and nutrients input on size structure of phytoplankton in Daya Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 55-64. |
| [9] | Chunhua QIU, Yongsheng CUI, Shiqi HU, Dan HUO. Seasonal variation of Guangdong coastal thermal front based on merged satellite data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(5): 16-23. |
| [10] | CHEN Jin, LU Ping, CHEN Zhong-ying, YAN Hui-hua, LI Lai-sheng. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus at Daya Bay in Huizhou during spring and summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 109-114. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yi-chun, PENG Peng-fei, HU Chao-qun, ZHONG Ming, CHEN Yan-feng, ZHAO Zhe, XIA Jian-jun. Analysis of nutritional value and observation of biological characteristics in microalga Amphora sp. as food for sea cucumber Stichopus horrens [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 59-64. |
| [12] | LUO Chuan-xiu,CHEN Mu-hong,LIU Jian-guo,ZHANG Lan-lan,XIANG Rong,LU Jun. Pollen distribution in marine surface sediments of Guangdong coast and southeast Hainan Island and its environmental significance [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(2): 55-61. |
|
||