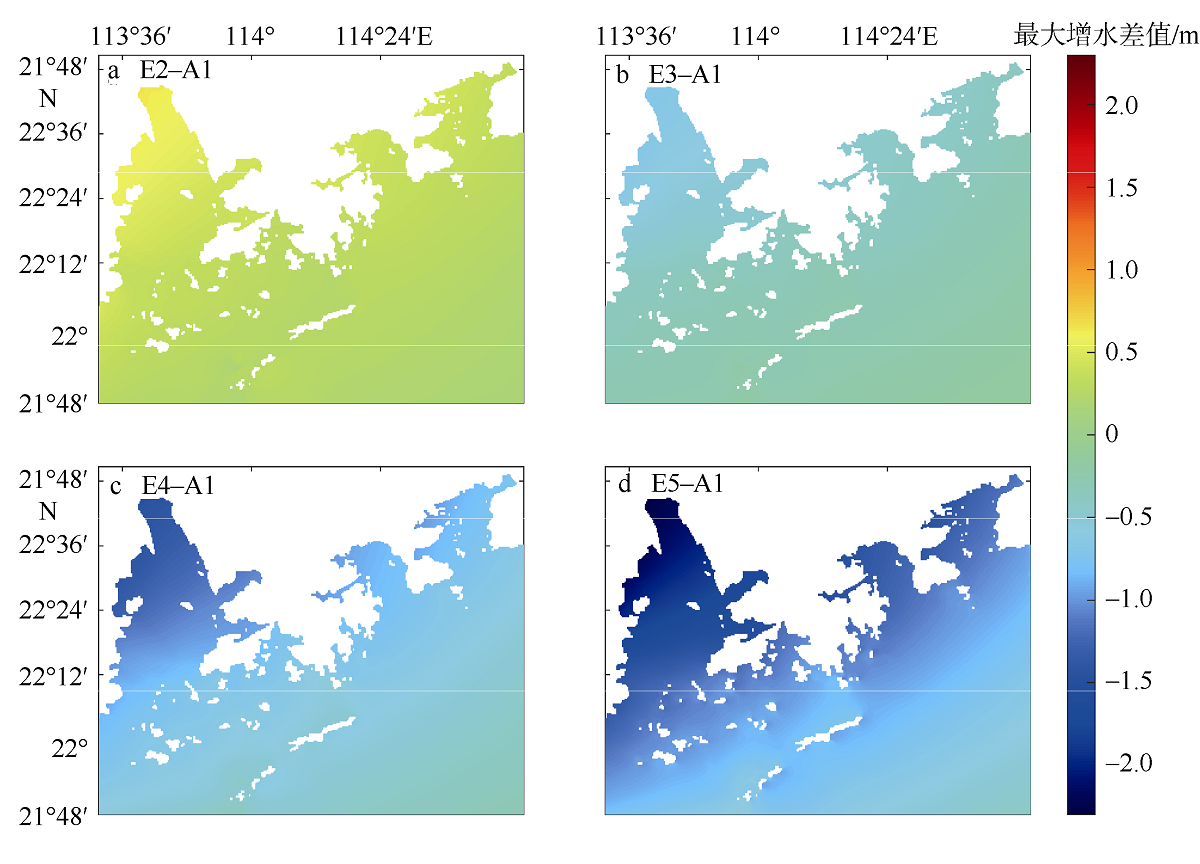
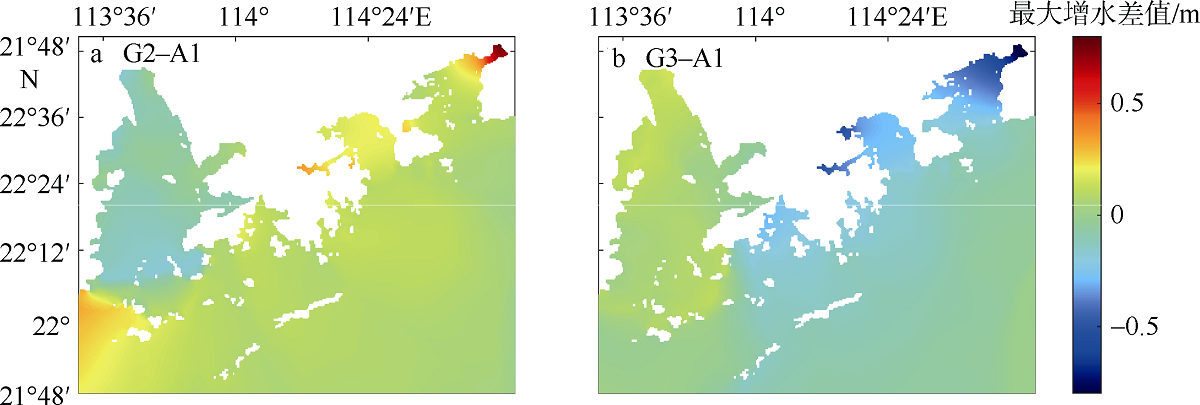
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 91-100.doi: 10.11978/2021124CSTR: 32234.14.2021124
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
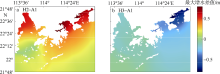
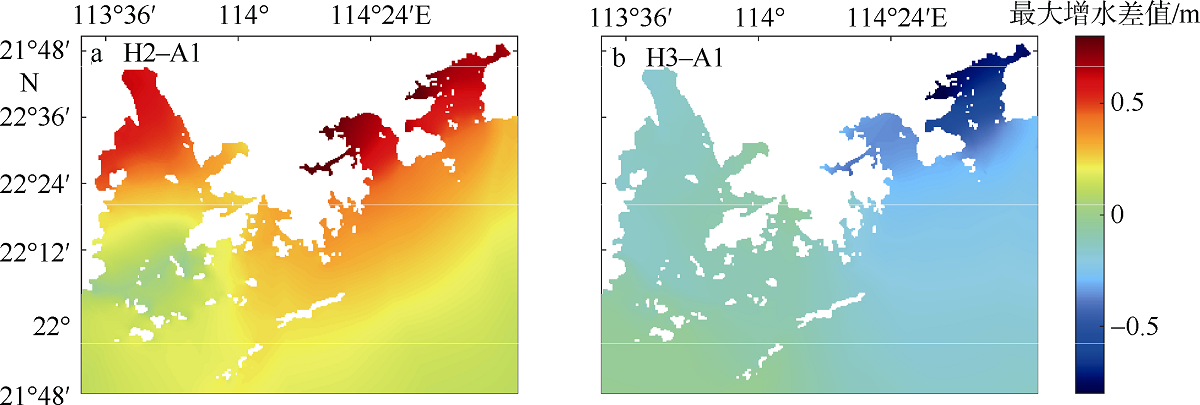
Analysis on the influencing factors of storm surges near Shenzhen
DENG Guotong1( ), LIU Mincong2, XING Jiuxing1, SHENG Jinyu1,3, ZHOU Kai2, CHEN Shengli1(
), LIU Mincong2, XING Jiuxing1, SHENG Jinyu1,3, ZHOU Kai2, CHEN Shengli1( )
)
- 1. Institute for Ocean Engineering (Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University), Shenzhen 518055, China
2. Shenzhen Marine Monitoring & Forecasting Center, Shenzhen 518034, China
3. Department of Oceanography (Dalhousie University), Halifax B3H 4R2, Canada
-
Received:2021-09-15Revised:2021-10-30Published:2021-11-03 -
Contact:CHEN Shengli E-mail:dgt18@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn;shenglichen@sz.tsinghua.edu.cn -
Supported by:Shenzhen Peacock Plan(KQJSCX20170720174016789)
CLC Number:
- P731.23
Cite this article
DENG Guotong, LIU Mincong, XING Jiuxing, SHENG Jinyu, ZHOU Kai, CHEN Shengli. Analysis on the influencing factors of storm surges near Shenzhen[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 91-100.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | 陈波, 陈宪云, 董德信, 等, 2015. 登陆北部湾北部台风对广西近岸水位变化的影响分析[J]. 广西科学, 22(3): 245-249, 254. |
| CHEN BO, CHEN XIANYUN, DONG DEXIN, et al, 2015. Analysis of the influence of water level change in Guangxi nearshore caused by typhoon landed in the north of Beibu Gulf[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 22(3): 245-249, 254. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 冯士筰, 1982. 风暴潮导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | 毛献忠, 姜茜, 2012. 深圳香港海域可能最高潮位和浪高计算分析[J]. 海洋工程, 30(2): 129-135. |
| MAO XIANZHONG, JIANG QIAN, 2012. Possible maximum storm water level and wave height in Shenzhen and Hong Kong waters[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 30(2): 129-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 隋广军, 唐丹玲, 2015. 台风灾害评估与应急管理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| SUI GUANGJUN, TANG DANLING, 2015. Typhoon disaster assessment and emergency management[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 魏巍, 2009. 深圳市台风风场数值模拟与危险性分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学. |
| 2009. Typhoon wind hazard analysis of Shenzhen based on wind-field model numerical simulation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 夏丽花, 邬惠明, 刘铭, 等, 2014. 热带气旋影响福建沿海风暴潮特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(3): 40-45. |
| XIA LIHUA, WU HUIMING, LIU MING, et al, 2014. Characteristic analysis of storm surges along Fujian coast associated with tropical cyclones[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 33(3): 40-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 张文舟, 胡建宇, 商少平, 等, 2004. 福建沿海风暴潮特征的分析[J]. 海洋通报, 23(3): 12-19. |
| ZHANG WENZHOU, HU JIANYU, SHANG SHAOPING, et al, 2004. On the characteristics of storm surges along Fujian coast[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 23(3): 12-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 赵长进, 葛建忠, 丁平兴, 2015. 长江口及其邻近海区无结构网格风暴潮预报系统的研制与分析[J]. 海洋科学进展, 33(2): 182-194. |
| ZHAO CHANGJIN, GE JIANZHONG, DING PINGXING, 2015. An unstructured numerical model for storm surge in the Changjiang estuary and its application[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 33(2): 182-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | BRETSCHNEIDER C L, 1972. A non-dimensional stationary hurricane wave model[C]// Offshore Technology Conference. Houston, Texas: OneOetro: OTC-1517-MS. |
| [10] |
EGBERT G D, EROFEEVA S Y, 2002. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 19(2): 183-204.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2002)019<0183:EIMOBO>2.0.CO;2 |
| [11] |
HOLLAND G J, 1980. An analytic model of the wind and pressure profiles in hurricanes[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 108(8): 1212-1218.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<1212:AAMOTW>2.0.CO;2 |
| [12] |
IRISH J L, RESIO D T, RATCLIFF J J, 2008. The influence of storm size on hurricane surge[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(9): 2003-2013.
doi: 10.1175/2008JPO3727.1 |
| [13] |
JELESNIANSKI C P, 1966. Numerical computations of storm surges without bottom stress[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 94(6): 379-394.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1966)094<0379:NCOSSW>2.3.CO;2 |
| [14] |
LARGE W G, POND P, 1981. Open ocean momentum flux measurements in moderate to strong winds[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 11(3): 324-336.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1981)011<0324:OOMFMI>2.0.CO;2 |
| [15] | LI MING, ZHONG LIEJUN, BOICOURT W C, et al, 2006. Hurricane-induced storm surges, currents and destratification in a semi-enclosed bay[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(2): L02604. |
| [16] |
LU XIAOQIN, YU HUI, YING MING, et al, 2021. Western north pacific tropical cyclone database created by the china meteorological administration[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 38(4): 690-699.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0211-7 |
| [17] | REGO J L, LI CHUNYAN, 2009. On the importance of the forward speed of hurricanes in storm surge forecasting: a numerical study[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(7): L07609. |
| [18] |
SEBASTIAN A, PROFT J, DIETRICH J C, et al, 2014. Characterizing hurricane storm surge behavior in Galveston Bay using the SWAN + ADCIRC model[J]. Coastal Engineering, 88: 171-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2014.03.002 |
| [19] | WANG ZHILI, LU YONGJUN, GENG YANFANG, 2010. Derivation of parametric tropical cyclone models for storm surge modeling[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 24(2): 245-254. |
| [20] |
WEISBERG R H, ZHENG LIANYUAN, 2006. Hurricane storm surge simulations for Tampa Bay[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 29(6): 899-913.
doi: 10.1007/BF02798649 |
| [21] |
WU ZHIYUAN, JIANG CHANGBO, CHEN JIE, et al, 2019. Three-dimensional temperature field change in the South China Sea during Typhoon Kai-Tak (1213) based on a fully coupled atmosphere-wave-ocean model[J]. Water, 11(1): 140.
doi: 10.3390/w11010140 |
| [22] |
YANG JIE, LI LINLIN, ZHAO KUIFENG, et al, 2019. A comparative study of Typhoon Hato (2017) and Typhoon Mangkhut (2018)-their impacts on coastal inundation in Macau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(12): 9590-9619.
doi: 10.1029/2019JC015249 |
| [23] |
YING MING, ZHANG WEI, YU HUI, et al, 2014. An overview of the China meteorological administration tropical cyclone database[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 31(2): 287-301.
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-12-00119.1 |
| [1] | HUANG Yuan, CEN Jingyi, LIANG Qianyan, LYU Songhui, WANG Jianyan. Study on the community structure of eukaryotic phytoplankton in the Shenzhen Bay based on high-throughput sequencing technology [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 21-33. |
| [2] | DING Yiting, DONG Dibo. Study on comprehensive risk assessment of storm surges for Fujian Province from the perspective of resilience [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 126-136. |
| [3] | ZHANG Zheran, HU Junyang, ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Penghui, XING Jiuxing, CHEN Shengli. Storm surge simulations of the coastal area of Shenzhen using different types of typhoon meteorological fields—a case study of Typhoon Mangkhut* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [4] | GAO Na, ZHAO Mingli, MA Yi, XU Wanming, ZHAN Haigang, CAI Shuqun. Effect of typhoon on storm surge in the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 32-42. |
| [5] | XU Jie, GUO Jibing, CHEN Zhiqiang, ZHU Zhihui, WANG Qin, TANG Yanling. Comparative study on the contribution of various influential factors and characteristics analysis of an extra-tropical storm surge caused by cold front in the Yangshan Port and its adjacent area [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 126-135. |
| [6] | SUN Fenglin. Disaster loss assessment of storm surge based on Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 75-81. |
| [7] | SHEN Qianying, JI Xiaomei, ZHANG Wei, XU Yanwen. Impact of estuarine storm surge barriers on spatiotemporal variation of tidal asymmetry in a delta* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 1-9. |
| [8] | WANG Yuanqi, YANG Yang, ZHOU Liang, WANG Yaping, GAO Shu. Interpreting the origin of coastal boulders on a coral reef flat at Xiaodonghai of Hainan Island based on storm wave energy analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 110-121. |
| [9] | Min ZHANG, Jun LUO, Jinlei HU, Xuezhi ZENG. Inundation risk assessment of storm surge along Lei Zhou coastal areas* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 1-12. |
| [10] | YIN Chengtuan, ZHANG Jinshan, XIONG Mengjie, XU Junhui. Trend analysis of typhoon and storm surge disaster on the South China Sea coast of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(1): 35-42. |
| [11] | Xiaoshan ZHUANG, Qingliu HUAN, Ying PENG, Jieliang WANG, Rensong PANG, Kai ZHOU. Spatial and temporal distribution of dissolved oxygen in the coastal waters of eastern Shenzhen [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(5): 98-105. |
| [12] | LUO Shihao, JING Zhiyou, QI Yiquan, XIE Qiang. Numerical study on sub-mesoscale processes in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(5): 10-19. |
| [13] | XIA Li-hua, WU Hui-ming, LIU Ming, LENG Dian-song, LI Ting-ting. Characteristic analysis of storm surges along Fujian coast associated with tropical cyclones [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(3): 40-45. |
| [14] | ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Jie-xiang, ZHANG Yu-bin, LU Dong-wei, DING Yu-jing, SUN Xing-li. Temporal and spatial distributions of bacterioplankton biomass and the influenced factors in Shenzhen Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 65-71. |
| [15] | WANG Kang-fa-sheng,YIN Zhan-e,YIN Jie. Analysis on typhoon-induced storm surge vulnerability of China’s coastal areas on rising sea level background [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(6): 31-36. |
|
||