Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 152-160.doi: 10.11978/2022015CSTR: 32234.14.2022015
• Exploitation of Marine Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
Physicochemical analysis and evaluation of the antithrombotic activity of different molecular weights of heparin from clam Coelomactra antiquata
CHEN Guanlan1( ), CHEN Jianping1, LI Rui1, JIA Xuejing1, LIU Xiaofei1, SONG Bingbing1, ZHONG Saiyi1,2,3(
), CHEN Jianping1, LI Rui1, JIA Xuejing1, LIU Xiaofei1, SONG Bingbing1, ZHONG Saiyi1,2,3( )
)
- 1. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Aquatic Product Processing and Safety, Guangdong Province Engineering Laboratory for Marine Biological Products, Guangdong Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center of Seafood (College of Food Science and Technology, Guangdong Ocean University), Zhanjiang 524008, China
2. Shenzhen Research Institute, Guangdong Ocean University, Shenzhen 518108, China
3. Collaborative Innovation Center of Seafood Deep Processing, Dalian Polytechnic University, Dalian 116034, China
-
Received:2022-01-26Revised:2022-03-29Online:2023-01-10Published:2022-03-25 -
Contact:ZHONG Saiyi. email:zsylxc@126.com -
Supported by:Guangdong Key Area Research and Development Program Project(2020B1111030004); National Key Research and Development Program Key Special Project(2019YFD0902005); Shenzhen Science and Technology Program Project(PT202001-17); Zhanjiang Science and Technology Program Project(2019A01015); Guangdong Province High School Science and Technology Innovation Team Project(2021KCXTD021); Shenzhen Science and Technology Program Project(JCYJ2017081818111335796)
Cite this article
CHEN Guanlan, CHEN Jianping, LI Rui, JIA Xuejing, LIU Xiaofei, SONG Bingbing, ZHONG Saiyi. Physicochemical analysis and evaluation of the antithrombotic activity of different molecular weights of heparin from clam Coelomactra antiquata[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 152-160.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 3
The changes of mice body weight before and after the experiment (n=12)"
| 组别 | W0/g | W7/g |
|---|---|---|
| B | 25.3±3.4 | 32.8±2.5* |
| M | 23.8±3.0 | 32.9±2.6* |
| Y | 24.6±2.5 | 34.6±3.5* |
| G2L | 24.6±3.5 | 33.4±1.9* |
| G2M | 25.6±3.1 | 34.0±2.6* |
| G2H | 24.5±2.9 | 33.6±1.9* |
| DG1L | 24.0±3.0 | 34.8±2.2* |
| DG1M | 23.6±2.2 | 35.6±2.7* |
| DG1H | 24.4±3.3 | 33.0±2.4* |
| DG2L | 24.4±3.5 | 33.6±3.0* |
| DG2M | 23.9±3.8 | 32.1±1.8* |
| DG2H | 23.9±3.2 | 31.6±3.4* |
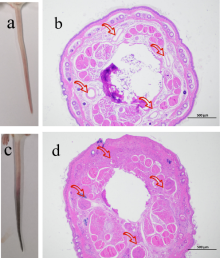
Fig. 4
Photographs of black tails of mice in the blank control group (a) and the histopathological findings of their tails (HE staining, ×40) (b), and photographs of black tails of mice in the model control group (c) and the histopathological findings of their tails (HE staining, ×40) (d) 48h after carrageenan treatment"

Tab. 4
Blacktail ratio of mice in different treatment groups at 24h, 48h after carrageenan treatment"
| 组别 | 黑尾比率/% | |
|---|---|---|
| 24h | 48h | |
| B | 0±0 | 0±0 |
| M | 52.03±5.46## | 57.73±8.89## |
| Y | 28.92±0.56** | 33.01±1.61** |
| G2L | 48.67±2.78 | 45.39±4.43 |
| G2M | 35.01±1.41** | 33.32±2.09** |
| G2H | 31.30±3.23** | 30.83±4.34** |
| DG1L | 46.91±5.27 | 45.05±3.88 |
| DG1M | 36.96±3.19* | 34.31±1.68** |
| DG1H | 19.94±5.26** | 18.70±2.82** |
| DG2L | 47.82±5.67 | 49.16±4.71 |
| DG2M | 47.30±4.70 | 47.25±6.61 |
| DG2H | 43.95±6.54 | 45.00±5.42 |
| [1] |
陈观兰, 陈菁, 陈建平, 等, 2021. 不同分子质量海蚌肝素结构表征及抗凝血与纤溶活性的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 47(17): 119-125.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
侯萍, 马军, 陈燕, 等, 2018. 几种海藻粗多糖的理化性质及结构特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(2): 55-62.
doi: 10.11978/2017049 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2017049 |
|
| [3] |
李赛丽, 张海珠, 李杨, 等, 2018. 喙尾琵琶甲粗提物对角叉菜胶致大鼠非细菌性前列腺炎的治疗作用[J]. 中药材, 41(6): 1454-1458.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
凌沛学, 何兆雄, 姬胜利, 2015. 肝素[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社:264- 271.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
刘海韵, 王维民, 谌素华, 等, 2020. 马尾藻岩藻聚糖分离纯化及其对小鼠黑尾血栓的效果[J]. 食品科学, 41(9): 91-97.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
温扬敏, 罗彩林, 陈文标, 等, 2010. 西施舌的体外抗氧化和溶菌酶活性研究[J]. 中国热带医学, 10(12): 1511-1512.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
温扬敏, 杨维群, 陈长明, 等, 2013. 西施舌多糖对人食管癌EC-9706细胞增殖及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 34(21): 357-360.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
温扬敏, 万端静, 谢永华, 等, 2015. 西施舌对糖尿病小鼠血脂及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 西部中医药, 28(10): 19-21.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
肖素军, 吴培赛, 贺娟, 等, 2018. 猕猴桃根多糖对角叉菜胶致小鼠尾部血栓形成的影响[J]. 广西医学, 40(12): 1336-1339.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
严尚隆, 潘创, 杨贤庆, 等, 2021. 长松藻多糖降解、结构表征及降血糖活性测定[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 47(18): 119-126.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
杨东达, 2020. 海参内脏多糖的分离、结构鉴定、免疫活性及其应用研究[D]. 福建: 华侨大学.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
杨维群, 温扬敏, 林文东, 等, 2015. 西施舌多糖对人食管鳞癌裸鼠移植瘤作用的研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 27(8): 1402-1406.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
曾凡珂, 潘蕾蔓, 张祎, 等, 2022. 荸荠皮多糖的理化性质及抗氧化活性[J]. 现代食品科技, 38(3): 82-88, 81.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
郑必胜, 伍磊, 周林, 等, 2021. 硫酸酯化裂褶多糖的制备及其抗凝血活性[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 49(11): 9-18.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
周艳霞, 普兴宏, 戚彦飞, 等, 2021. 桑生地黄汤对代谢综合征大鼠体重、血糖、血脂的影响[J]. 内蒙古中医药, 40(7): 145-147.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
pmid: 4050621 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.3390/md20010050 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1002/jbt.2015.29.issue-5 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.031 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30514-1 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1042/bj0840106 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.3390/md18010006 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules24244630 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000592 pmid: 29738376 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules22050749 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.161 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.3390/md13052770 pmid: 25955754 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.3390/ph9030037 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.3390/ph9030038 |
| [31] |
pmid: 4066664 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12070607 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2016.03.008 |
| No related articles found! |
|
||