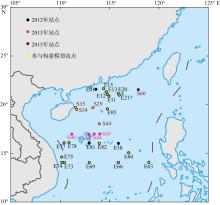
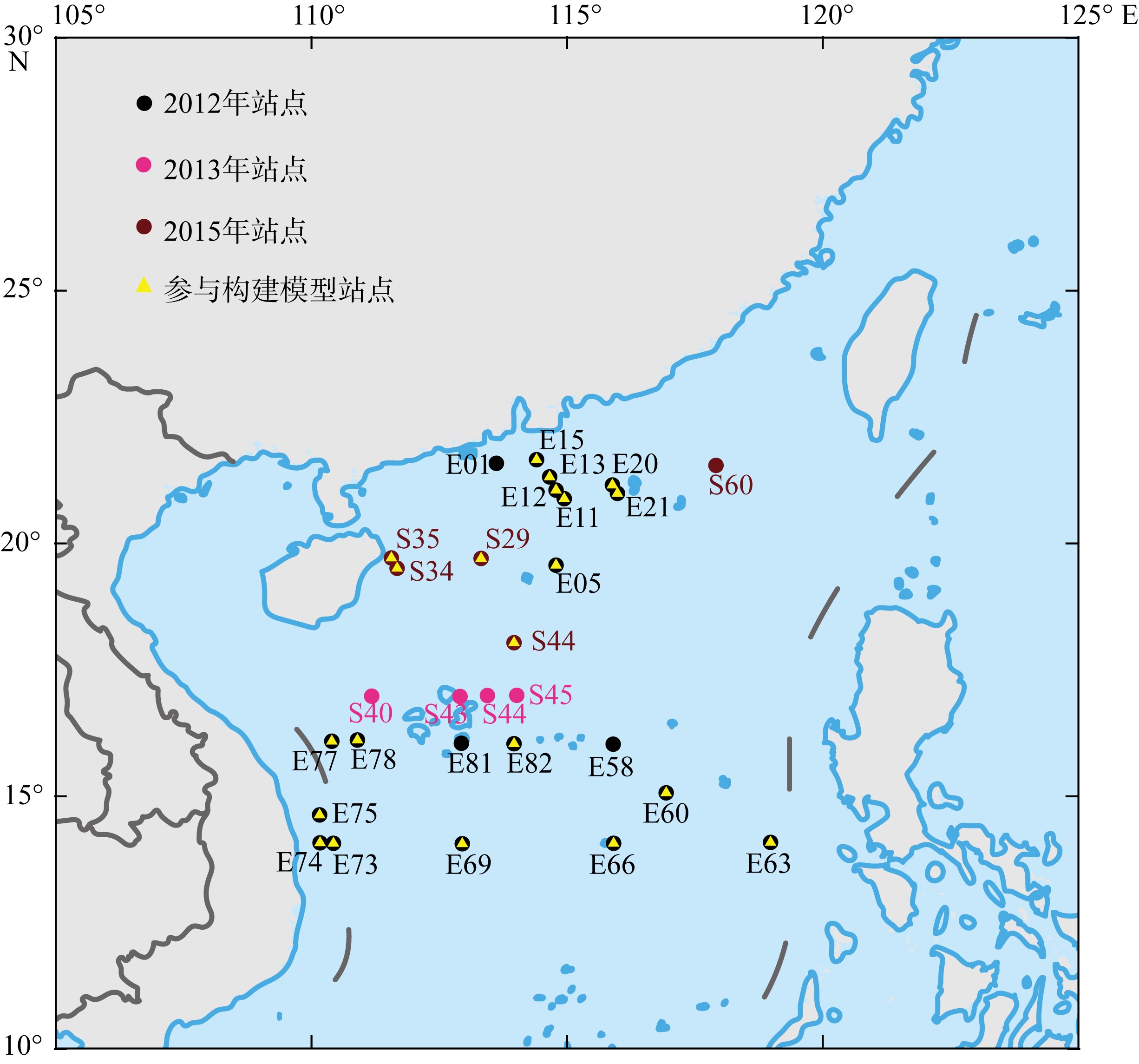
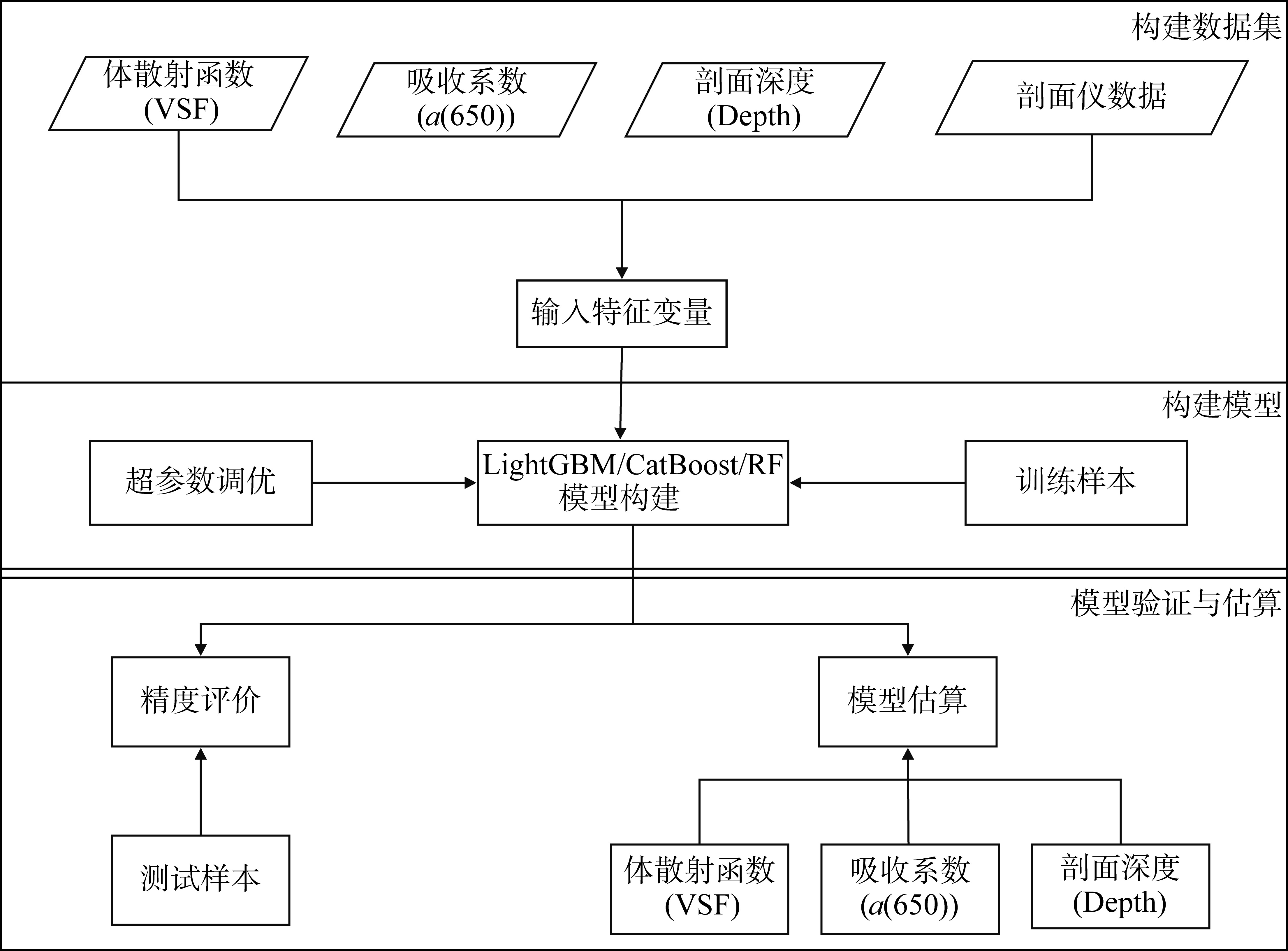
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 86-95.doi: 10.11978/2022146CSTR: 32234.14.2022146
• Marine Physics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Studying on diffuse attenuation coefficient in the South China Sea based on volume scattering function and absorption coefficient*
ZHANG Xianqing1,2( ), LI Cai1,3(
), LI Cai1,3( ), Zhou Wen1,3, LIU Cong1, XU Zhantang1,3, CAO Wenxi1,3, YANG Yuezhong1,3
), Zhou Wen1,3, LIU Cong1, XU Zhantang1,3, CAO Wenxi1,3, YANG Yuezhong1,3
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory, Guangzhou 511458, China
-
Received:2022-06-27Revised:2022-08-12Online:2023-05-10Published:2022-08-24 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976181); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976172); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976170); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou City China(201707020023); Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0305); Open Project Program of the State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography(LTOZZ1602)
Cite this article
ZHANG Xianqing, LI Cai, Zhou Wen, LIU Cong, XU Zhantang, CAO Wenxi, YANG Yuezhong. Studying on diffuse attenuation coefficient in the South China Sea based on volume scattering function and absorption coefficient*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 86-95.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 2
The hyperparameters results of CatBoost/LightGBM/RF"
| CatBoost | LightGBM | RF |
|---|---|---|
| n_estimators =800 | learning rate = 0.008,max_depth = 2,num_leaves= 10, min_data_in_leaf=18, min_sum_hessian_in_leaf =0.001, feature_fraction=0.3,bagging_fraction=0.8,reg_alpha=0.001,reg_lambda=0.03 | n_estimators=300 max_features=6 |
| [1] |
曹渝昆, 朱萌, 2019. 基于主成分分析和LightGBM的风电场发电功率超短期预测[J]. 上海电力学院学报, 35(6): 562-566.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
宫鹏, 王德兴, 袁红春, 等, 2021. 基于LightGBM的南太平洋长鳍金枪鱼渔场预报模型研究[J]. 水产科学, 40(5): 762-767.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
卢雪梅, 苏华, 2020. 基于OLCI数据的福建近海悬浮物浓度遥感反演[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(8): 2819-2827.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
徐磊, 吴鹏, 徐明生, 等, 2021. 基于卷积神经网络与LightGBM的短期风电功率预测方法[J]. 水电能源科学, 39(2): 209-212+199.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
张天一, 苏华, 杨欣, 等, 2020. 基于LightGBM的全球海洋次表层温盐遥感预测[J]. 遥感学报, 24(10): 1255-1269.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
赵文静, 曹文熙, 胡水波, 等, 2018. MODIS-Aqua漫射衰减产品Kd(490)在南海海域的精度对比[J]. 光学精密工程, 26(1): 14-24.
|
|
doi: 10.3788/OPE. |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2016.10.007 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.3390/jmse8080558 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.1989.34.8.1389 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1117/12.958262 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1002/jgrd.v122.13 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1071/MF9810517 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1364/AO.33.003276 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2003)20<563:ANMFTM>2.0.CO;2 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1002/lno.v63.6 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.3390/s120404514 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1364/AO.36.008710 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.3390/rs13040709 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.1978.23.2.0260 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(87)90005-7 |
| [33] |
pmid: 16826267 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.1961.6.4.0451 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1007/s00343-008-0323-x |
| [1] | QI Huandong, ZHU Cheng, LI Xuchun, JING Xindi, SONG Derui. Rule set and multilayer perceptron based quality control method for Argo temperature data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 190-202. |
| [2] | LI Cai, LIU Cong, ZHANG Xianqing, CHEN Fei, XIAO Zhihui, YANG Zeming, ZHENG Yuanning, ZHOU Wen, XU Zhantang. Development and Application of the Multiangle Volume Scattering and Attenuation Meter (VSAM)* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 1-11. |
| [3] | ZHAO Hongwuyi, ZHOU Wen, ZENG Kai, DENG Lin, LIAO Jianzu, CAO Wenxi. A study of the regional size-fractionated primary production algorithm based on phytoplankton absorption coefficient and photosynthetically active radiation in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 43-55. |
| [4] | Guifen WANG, Wenlong XU, Wen ZHOU, Zhantang XU, Wenxi CAO. Retrieving phytoplankton size class from hyperspectral particulate absorption data measured by the ship-based underway flow-through system [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(5): 50-61. |
| [5] | Wenjing ZHAO, Wenxi CAO, shuibo HU, Guifen WANG, Zhenyu LIU, Min XU. The spectral characteristics of phytoplankton absorption coefficient and assessment of MODIS-Aqua products in typical sea areas of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 35-44. |
| [6] | ZHOU Hong-li, ZHU Jian-hua, Li Tong-ji. Spectral properties of colored dissolved organic matter in Chinese offshore waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(1): 23-29. |
| [7] | LI Cai, CAO Wen-xi, KE Tian-cun, ZHOU Wen, YANG Yue-zhong, LU Gui-xin, GUO Chao-ying, WANG Gui-fen, SUN Zhao-hua. Progress in measurement techniques of volume scattering function of the ocean [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 65-72. |
| [8] | HU Shui-bo, CAO Wen-xi, LIN Jun-fang, YANG Yue-zhong, WANG Gui-fen, ZHOU wen. Spectral absorption properties of colored dissolved organic matter along 6°N transect of tropical eastern Indian Ocean [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(4): 13-21. |
| [9] | WANG Lin, ZHAO Dong-zhi, YANG Jian-hong, JIANG Ling-ling,,LIU Yong-jian. Total absorption characteristics of alga Amphidinium carerae Hulburt in growth and decay periods [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(2): 88-93. |
| [10] | ZHOU Hong-li, ZHU Jian-hua, LI Tong-ji, WANG Xiao-yong. Optical properties of de-pigmented particles offshore of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(6): 57-61. |
| [11] | WANG Gui-fen,CAO Wen-xi,YANG Yue-zhong,ZHOU Wen,LIANG Shao-jun,. Variations of absorption coefficient of seawater in the Pearl River Estuary and a hyperspectral retrieval model for an algal bloom [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(2): 52-58. |
| [12] | WANG Wen-qi,DONG Qiang,SHANG Shao-ling,WU Jing-yu,LEE Zhong-ping. An evaluation of two semi-analytical ocean color algorithms for waters off South China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(5): 35-42. |
|
||