Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 154-166.doi: 10.11978/2023045CSTR: 32234.14.2023045
• Exploitation of Marine Resources • Previous Articles
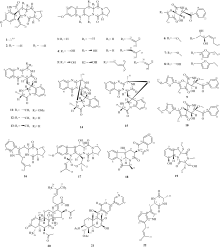
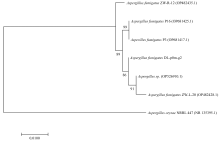
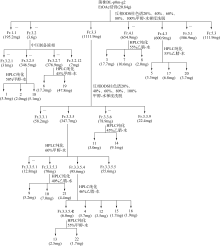
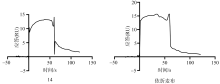
Study on the chemical constituents and pharmacological activity of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus DL-p0m-g2 in the Beibu Gulf
FENG Ting( ), SUN Jian, WANG Yufei, PAN Weibin, QIN Xucan, QIN Bingyun, ZHOU Liman, WANG Cong, WANG Pei, KONG Fandong(
), SUN Jian, WANG Yufei, PAN Weibin, QIN Xucan, QIN Bingyun, ZHOU Liman, WANG Cong, WANG Pei, KONG Fandong( )
)
- School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Key Laboratory of Chemistry and Engineering of Forest Products, State Ethnic Affairs Commission, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Chemistry and Engineering of Forest Products, Guangxi Collaborative Innovation Center for Chemistry and Engineering of Forest Products, Key Laboratory of Universities in Guangxi for Excavation and Development of Ancient Ethnomedicinal Recipes, Guangxi Minzu University, Nanning 530006, China
-
Received:2023-04-08Revised:2023-04-18Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-19 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province(2021GXNSFBA075036); Specific Research Project of Guangxi for Research Bases and Talents(AD22035018); National Natural Science Foundation of China(82104034); Xiangsi Lake Youth Innovation Team Project of Guangxi Minzu University(2021RSCXSHQN01); 2021 University-Level Scientific Research Projects of Guangxi Minzu University(2021 MDKJ003)
Cite this article
FENG Ting, SUN Jian, WANG Yufei, PAN Weibin, QIN Xucan, QIN Bingyun, ZHOU Liman, WANG Cong, WANG Pei, KONG Fandong. Study on the chemical constituents and pharmacological activity of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus DL-p0m-g2 in the Beibu Gulf[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 154-166.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
陈雷, 赵旻, 叶烨, 等, 2017. 藏菖蒲烟曲霉的化学成分[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 23(5): 918-923.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
高谕康, 邱子言, 宋永清, 等, 2020. 一株海洋曲霉MDCW-15中的新烟曲霉素[J]. 中草药, 51(24): 6137-6141.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
郭思雨, 邹庭光, 朱静琳, 等, 2020. 海南东寨港红树林内生真菌Aspergillus fumigatus SAS10吡喃酮类代谢产物[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 59(4): 19-23.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
李基兴, 杨斌, 刘永宏, 等, 2020. 越前水母共附生真菌Aspergillus fumigatus sp.次级代谢产物研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 32(1): 81-86.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
罗明和, 黄洪波, 卢来春, 等, 2015. 海洋真菌Eurotium amstelodami SCSIO 151二酮哌嗪吲哚生物碱类次生代谢产物的研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 27(1): 50-54.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
钱诗筠, 刘涛, 华会明, 等, 2020. 海洋真菌Aspergillus fumigatus YK-7次级代谢产物的研究[J]. 化学与生物工程, 37(3): 25-28+41.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
任虹, 曹学丽, 王巧娥, 等, 2011. 真菌萨氏曲霉D2-6抗肿瘤活性代谢产物[J]. 中国药学杂志, 46(8): 569-575.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
王聪, 高谕康, 雷福厚, 等, 2019. 一株海洋青霉中的新二萜糖酯[J]. 中草药, 50(11): 2518-2523.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
王聪, 王立平, 范杰, 等, 2017. 深海链霉菌Streptomyces malaysiensis OUCMDZ-2167来源的细胞毒性产物[J]. 有机化学, 37(3): 658-666.
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201609021 |
|
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201609021 |
|
| [10] |
王庆琳, 陈水浩, 陈冬妮, 等, 2020. 中国南海海洋真菌资源及其活性次级代谢产物研究评述[J]. 生物资源, 42(5): 505-514.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
朱伟明, 王文玲, 王立平, 等, 2015. 珊瑚真菌 Aspergillus sp.OUCMDZ-3658 产生的生物碱[J]. 中国海洋药物, 34(6): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王亚楠, 高海, 丁健, 等, 2019. 红树林来源耐酸真菌 Aspergillus fumigatus OUCMDZ-5210 次生代谢产物的研究[J]. 中国海洋药物, 38(5): 47-53.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王宇, 李占林, 白皎, 等, 2017. 海洋真菌烟曲霉Aspergillus fumigatus YK-7中生物碱类代谢产物及其抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 52(15): 1308-1312.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
吴萌萌, 刘怡, 严馨, 等, 2021. 苦荞麸皮黄酮提取物及有效成分的抑菌活性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 40(11): 77-83.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
徐新亚, 杨宏, 宁小清, 等, 2020. 北部湾海洋微生物物种多样性与化学多样性研究进展[J]. 广西科学, 27(5): 433-450+461.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
张金新, 段园园, 毕洪凯, 等, 2023. 一株海洋真菌Aspergillus jensenii LW128的次级代谢产物及其抗菌活性研究[J]. 微生物学报, 63(1): 419-429.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
赵欢, 杨晨悦, 赵梓钧, 等, 2018. 藏药裂叶独活内生真菌Cosmospora stegonsporii发酵液中的二酮哌嗪类成分研究[J]. 中药材, 41(5): 1099-1102.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
赵文英, 张亚鹏, 朱天骄, 等, 2006. 海洋来源真菌A-f-11中吲哚二酮哌嗪类抗肿瘤活性成分的研究[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 31(12): 749-752+764.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03796 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1248/cpb.44.1843 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1021/ol062257t |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00150 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.3390/md14010018 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1021/jf300146n |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00014 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1080/10286020.2018.1488833 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285 pmid: 32162523 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1007/s12272-010-0401-4 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1021/np200740e |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1799363 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3390/md21020063 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01165 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1021/np50115a011 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1007/s10600-017-2243-5 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1021/jo100496f |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1739046 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00842 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00328 |
| [1] | YANG Bin, SALENDRA Limbadri, LIU Juan, LIU Yonghong. Alkaloids from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus SCSIO41214 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 195-201. |
| [2] | LU Chunju, LU Meilin, LIU Xinming, LIU Yonghong, GAO Chenghai, XU Xinya. Diversity and anti-bacteria activity of the gorgonian derived fungi from Weizhou Island of Guangxi Province* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 45-52. |
| [3] | CAO Lei-lei1, 2, TIAN Hai-yan2, WANG You -shao3, ZHOU Xue-feng1, JIANG Ren-wang2, LIU Yong-hong1. Chemical constituents in the fruits of mangrove plant Sonneratia apetala Buch. Ham. [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(1): 77-82. |
| [4] | CHAI Xing-yun,HU Jing,HUANG Hui,LEI Hui,CHEN Xian-qiang,LI Yun-qiu,SUN Jia. Pregnane steroids from a gorgonian Menella sp. in South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 127-130. |
| [5] | LI Yun-qiu,WANG Bin,YANG Bin,HUANG Ri-ming,LIU Yong-hong,ZOU Xiao-li. Study on the compounds of marine sponge Haliclona sp. [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 124-126. |
|
||