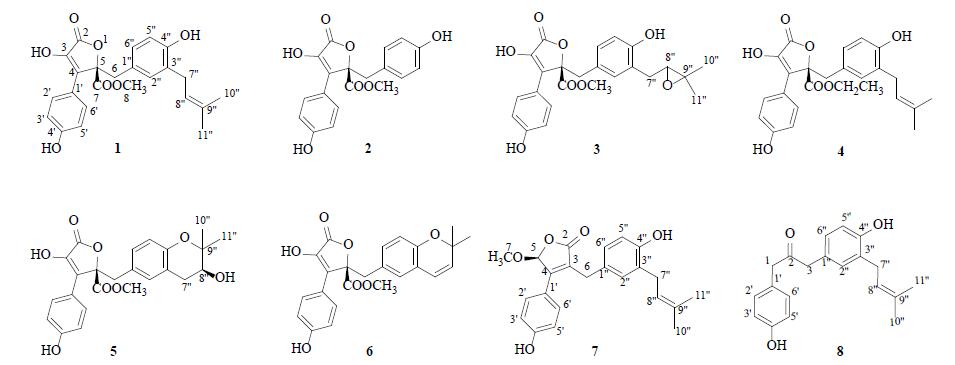
| [1] |
陈传兵, 胡金姗, 于鑫, 等, 2022. 深海放线菌Actinomadura cremea中的生物碱类化合物[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 61(3): 28-34.
|
|
CHEN CHUANBING, HU JINSHAN, YU XIN, et al, 2022. The alkolides from deep sea actinomycete Actinomadura cremea[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 61(3): 28-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
巩婷, 董世豪, 朱平, 2014. 海洋真菌杂色曲霉F62丁内酯类化合物研究[J]. 菌物学报, 33(3): 706-712.
|
|
GONG TING, DONG SHIHAO, ZHU PING, 2014. Butyrolactone derivatives isolated from the marine fungus Aspergillus versicolor F62[J]. Mycosystema, 33(3): 706-712 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
胡翥, 王浩文, 安林坤, 2016. 酪氨酰-DNA磷酸二酯酶: 潜在的肿瘤治疗靶点[J]. 药学学报, 51(2): 215-225.
|
|
HU ZHU, WANG HAOWEN, AN LINKUN, 2016. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterases: potential targets for cancer treatment[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 51(2): 215-225 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
黎咏怡, 蔡金旋, 方越, 等, 2022. 南海软珊瑚共附生真菌Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3中色酮、蒽醌及其二聚体类化合物[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 61(4): 70-78.
|
|
LI YONGYI, CAI JINXUAN, FANG YUE, et al, 2022. Xanthones, anthraquinone and their dimers from soft coral-associated symbiotic and epiphytic fungus Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 61(4): 70-78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
司徒美霞, 雷祖发, 杨倩茹, 等, 2023. 海洋本草软珊瑚共附生曲霉属真菌EGF7-0-1和EGF15-0-3共培养中甾体类成分研究Ⅱ[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 161-170.
|
|
SITU MEIXIA, LEI ZUFA, YANG QIANRU, et al, 2023. Research on the steroids from the coculture of soft coral-associated fungi Aspergillus sp. EGF7-0-1 and EGF15-0-3[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42(5): 161-170 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
BAO JIE, LI XIUXIU, HE FEI, et al, 2020. Asperbutenolide A, an unusual aromatic butenolide dimer with diverse bioactivities from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCAU011[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 61(32): 152193.
|
| [7] |
BAO JIE, LI XIUXIU, ZHU KONGKAI, et al, 2021. Bioactive aromatic butenolides from a mangrove sediment originated fungal species, Aspergillus terreus SCAU011[J]. Fitoterapia, 150: 104856.
|
| [8] |
CHATTERJEE S, SAHOO R, NANDA S, 2021. Recent reports on the synthesis of γ-butenolide, γ-alkylidenebutenolide frameworks, and related natural products[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 19(34): 7298-7332.
|
| [9] |
CHEN MINQI, LIANG JINYUE, WANG YUAN, et al, 2022. A new benzaldehyde from the coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus C23-3 and its anti-inflammatory effects via suppression of MAPK signaling pathway in RAW264. 7 cells[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science B, 23(3): 230-240.
|
| [10] |
CHENG YIJIA, CHEN NANNAN, LI JING, et al, 2021. Antimicrobial chlorinated carbazole alkaloids from the sponge-associated actinomycete Streptomyces diacarni LHW51701[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 39(5): 1188-1192.
|
| [11] |
DAVIS A R, 1991. Alkaloids and ascidian chemical defense: evidence for the ecological role of natural products from Eudistoma olivaceum[J]. Marine Biology, 111(3): 375-379.
|
| [12] |
FAN HAO, SHI ZHIMIAN, LEI YANHU, et al, 2022a. Rare carbon-bridged citrinin dimers from the starfish-derived symbiotic fungus Penicillium sp. GGF16-1-2[J]. Marine Drugs, 20(7): 443.
|
| [13] |
FAN HAO, WEI XIA, SITU MEIXIA, et al, 2022b. γ-Aromatic butenolides of microbial source - a review of their structures, biological activities and biosynthesis[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 19(6): e202200208.
|
| [14] |
FAN HAO, WANG LI, ZHANG ZEKUN, et al, 2023. Bioactive Aspergteroids G-J from soft-coral-associated symbiotic and epiphytic fungus Aspergillus terreus EGF7-0-1[J]. Bioengineering, 10(7): 805.
|
| [15] |
HOSOE T, IIZUKA T, KOMAI S, et al, 2005. 4-Benzyl-3-phenyl-5H-furan-2-one, a vasodilator isolated from Malbranchea filamentosa IFM 41300[J]. Phytochemistry, 66(23): 2776-2779.
|
| [16] |
HU DEXUAN, TANG WENLIN, ZHANG YU, et al, 2021. Synthesis of methoxy-, methylenedioxy-, hydroxy-, and halo-substituted benzophenanthridinone derivatives as DNA topoisomerase IB (TOP1) and tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1) inhibitors and their biological activity for drug-resistant cancer[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 64(11): 7617-7629.
|
| [17] |
LAEV S S, SALAKHUTDINOV N F, LAVRIK O I, 2016. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase inhibitors: progress and potential[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 24(21): 5017-5027.
|
| [18] |
LIU MENGTING, ZHOU QUN, WANG JIANPING, et al, 2018. Anti-inflammatory butenolide derivatives from the coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus and structure revisions of aspernolides D and G, butyrolactone VI and 4', 8''-diacetoxy butyrolactone VI[J]. RSC Advances, 8(23): 13040-13047.
|
| [19] |
PAL A, BANIK B K, 2020. Facile synthesis of highly funtionalized butyrolactones through an unprecedented base-catalyzed condensation[J]. Heterocyclic Letters, 10(4): 537-542.
|
| [20] |
PENG QINGYUN, CHEN WEIHAO, LIN XIUPING, et al, 2022. Butenolides from the coral-derived fungus Aspergillius terreus SCSIO41404[J]. Marine Drugs, 20(3): 212.
|
| [21] |
QI CHANGXING, GAO WEIXI, WANG JIANPING, et al, 2018. Terrusnolides A-D, new butenolides with anti-inflammatory activities from an endophytic Aspergillus from Tripterygium wilfordii[J]. Fitoterapia, 130: 134-139.
|
| [22] |
SAN-MARTÍN A, ROVIROSA J, VACA I, et al, 2011. New butyrolactone from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp[J]. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 56(1): 625-627.
|
| [23] |
SHEN SIYU, TONG YURU, LUO YUNFENG, et al, 2022. Biosynthesis, total synthesis, and pharmacological activities of aryltetralin-type lignan podophyllotoxin and its derivatives[J]. Natural Product Reports, 39(9): 1856-1875.
|
| [24] |
SUN YATING, LIU JINGTANG, LI LEI, et al, 2018. New butenolide derivatives from the marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 28(3): 315-318.
|
| [25] |
WANG JUNFENG, LU ZHENYU, LIU PEIPEI, et al, 2012. Cytotoxic polyphenols from the fungus Penicillium expansum 091 006 endogenous with the mangrove plant Excoecaria agallocha[J]. Planta Medica, 78(17): 1861-1866.
|
| [26] |
WEI XIA, WANG FANGTING, SITU MEIXIA, et al, 2022. Pyranodipyran derivatives with tyrosyl DNA phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitory activities and fluorescent properties from Aspergillus sp. EGF 15-0-3[J]. Marine Drugs, 20(3): 211.
|
| [27] |
YE YANQING, XIA CONGFANG, YANG JUANXIA, et al, 2014. Butyrolactones derivatives from the fermentation products of an endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 35(10): 3059-3062.
|
| [28] |
ZHANG YUANYUAN, ZHANG YI, YAO YUANBEI, et al, 2018. Butyrolactone-I from coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus attenuates neuro-inflammatory response via suppression of NF-κB pathway in BV-2 cells[J]. Marine Drugs, 16(6): 202.
|
 ), ZHAO Lining2(
), ZHAO Lining2( ), CHEN Xinqi1, HE Jiahong1, FAN Hao1, CHEN Leyi1, ZHANG Cuixian1(
), CHEN Xinqi1, HE Jiahong1, FAN Hao1, CHEN Leyi1, ZHANG Cuixian1( ), HE Xixin1(
), HE Xixin1( )
)