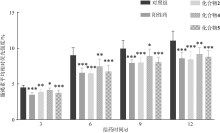
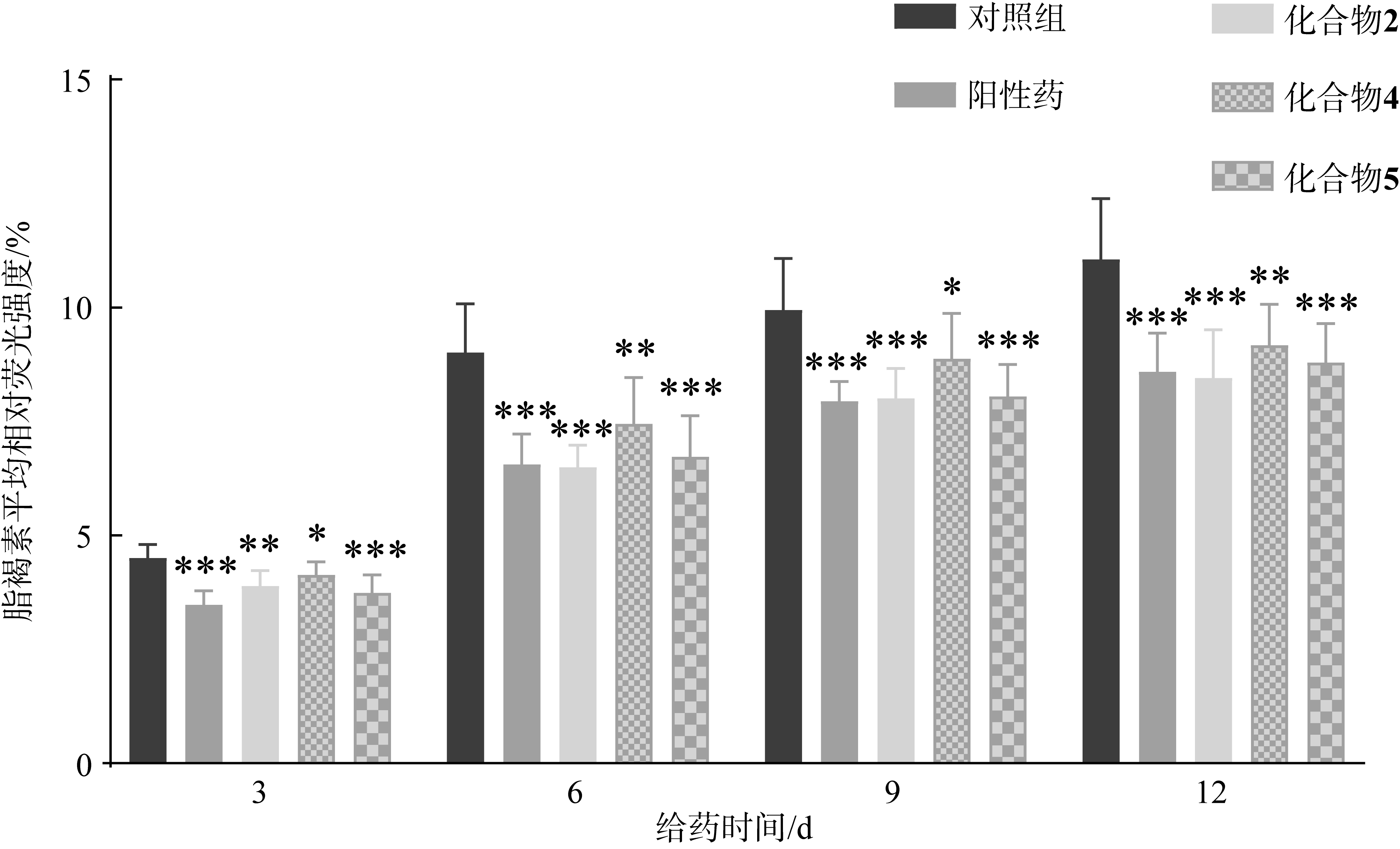
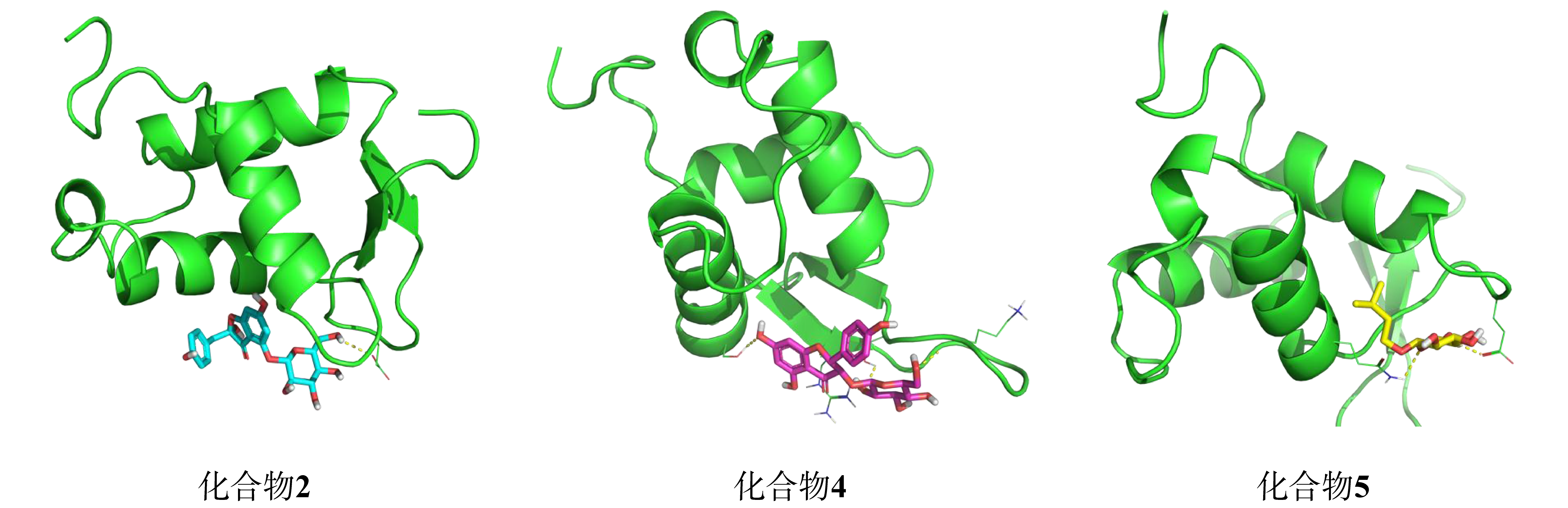
| [1] |
曹雷雷, 田海妍, 王友绍, 等, 2015. 红树植物无瓣海桑果实的化学成分研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(1): 77-82.
|
|
CAO LEILEI, TIAN HAIYAN, WANG YOUSHAO, et al, 2015. Chemical constituents in the fruits of mangrove plant Sonneratia apetala Buch. Ham[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 34(1): 77-82 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
韩敏敏, 李蜜, 刘昕明, 等, 2020. Khai岛和Pathiu岛珊瑚礁沉积物细菌多样性及细菌粗提物延缓秀丽隐杆线虫衰老活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(5): 19-29.
doi: 10.11978/2019126
|
|
HAN MINMIN, LI MI, LIU XINMING, et al, 2020. Studies on bacterial diversity in coral reef sediments in Khai Island and Pathiu Island and bacterial crude extract retards aging activity of Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(5): 19-29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
纪卿飞, 林文翰, 李军, 等, 2005. 中国红树林植物——无瓣海桑的化学成分研究Ⅱ[J]. 中国中药杂志, 30(16): 1258-1260.
|
|
JI QINGFEI, LIN WENHAN, LI JUN, et al, 2005. Chemical investingation of Chinese mangrove Sonneratia apetala Ⅱ[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 30(16): 1258-1260 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
江林芸, 2023. 无瓣海桑枝叶降尿酸活性部位的筛选及其机制研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学: 1-62.
|
|
JIANG LINYUN, 2023. Isolation of hypouricemic fraction of Sonneratia apetala leaves and branches and its mechanisms investigation[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine: 1-62 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
李家怡, 易湘茜, 杜正彩, 等, 2019. 无瓣海桑果实提取物对D-半乳糖致衰老小鼠抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 21(4): 647-651.
|
|
LI JIAYI, YI XIANGXI, DU ZHENGCAI, et al, 2019. Effect of the extracts of Sonneratia apetala fruit on antioxidative ability in aging mice induced by D-galactose[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 21(4): 647-651 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
李军, 姜华, 路西明, 等, 2021. 山茱萸果核化学成分研究[J]. 中国药学杂志, 56(15): 1210-1214.
doi: 10.11669/cpj.2021.15.004
|
|
LI JUN, JIANG HUA, LU XIMING, et al, 2021. Constituents from the seeds of Cornus offcinalis Sieb. et Zucc[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 56(15): 1210-1214 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
林海生, 宋文东, 吴婕, 等, 2009. 无瓣海桑叶子和果实中脂肪酸成分的检测分析[J]. 福建分析测试, 18(3): 5-9.
|
|
LIN HAISHENG, SONG WENDONG, WU JIE, et al, 2009. Analysis of fatty acids constituents in the leaves and gains of Sonneratia apetala[J]. Fujian Analysis & Testing, 18(3): 5-9 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
刘晶晶, 2020. 无瓣海桑果实多糖的初步表征、抗肝损伤作用及机制研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学: 1-64.
|
|
LIU JINGJING, 2020. Preliminary characterization, hepatoprotective effect and potentail mechanisms of Sonneratia apetala fruit polysaccharides against acetaminophen induced liver injury[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinses Medicine: 1-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
刘希达, 韩娜, 刘志惠, 等, 2021. 覆盆子抗氧化和α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性成分研究[J]. 中草药, 52(17): 5226-5232.
|
|
LIU XIDA, HAN NA, LIU ZHIHUI, et al, 2021. Active components of antioxidation and α-glucosidase inhibitory from Rubi fructus[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 52(17): 5226-5232 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
陆远, 张研, 王莹, 等, 2024. 金银花化学成分及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中成药, 46(8): 2638-2644.
|
|
LU YUAN, ZHANG YAN, WANG YING, et al, 2024. Chemical constituents from Lonicera japonica and their antioxidant activities[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 46(8): 2638-2644 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
时志春, 赵媛, 夏琳, 等, 2021. 苹果树皮化学成分研究[J]. 中药材, 44(10): 2326-2331.
|
|
SHI ZHICHUN, ZHAO YUAN, XIA LIN, et al, 2021. Chemical constituents of Malus pumila bark[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 44(10): 2326-2331 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
叶磊, 冯丽萍, 黄李璐, 等, 2024. 木芙蓉花的化学成分研究(Ⅱ)[J]. 中药材, 47(1): 91-95.
|
|
YE LEI, FENG LIPING, HUANG LILU, et al, 2024. Chemical constituents from the flowers of Hibiscus mutabilis(Ⅱ)[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 47(1): 91-95 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
易湘茜, 李家怡, 高程海, 等, 2017. 无瓣海桑果实乙醇提取物及其不同极性萃取物抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技, 38(19): 27-30.
|
|
YI XIANGXI, LI JIAYI, GAO CHENGHAI, et al, 2017. Antioxidant activity of alcohol extract and different polar parts of Sonneratia apetala fruits[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 38(19): 27-30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
易湘茜, 李家怡, 杜正彩, 等, 2019. 无瓣海桑果实提取物对衰老小鼠学习记忆能力的影响及其机制研究[J]. 广西植物, 39(11): 1534-1540.
|
|
YI XIANGXI, LI JIAYI, DU ZHENGCAI, et al, 2019. Effects and mechanisms of Sonneratia apetala fruit extracts on learning and memory abilities in aging mice[J]. Guihaia, 39(11): 1534-1540 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
朱华, 戴忠华, 2017. 中国壮药图鉴(上)[M]. 南宁: 广西科学技术出版社:763 (in Chinese).
|
| [16] |
BASSOLINO L, PETRONI K, POLITO A, et al, 2022. Does plant breeding for antioxidant-rich foods have an impact on human health?[J]. Antioxidants, 11(4): 794.
|
| [17] |
JIANG SHU, JIANG CUIPING, CAO PEI, et al, 2022. Sonneradon A extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by modulating mitochondrial and IIS signaling pathways[J]. Marine Drugs, 20(1): 59.
|
| [18] |
RODRIGUEZ-COLMAN M J, DANSEN T B, BURGERING B M T, 2024. FOXO transcription factors as mediators of stress adaptation[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 25(1): 46-64.
|
| [19] |
SHEFA A A, BAISHAKHI F S, ISLAM S, et al, 2014. Phytochemical and pharmacological evaluation of fruits of Sonneratia apetala[J]. Global Journal of Medical Research, 14(3): 1-6.
|
| [20] |
WANG XINRUI, ZHANG CHANGLONG, PENG YAJIE, et al, 2018. Chemical constituents, antioxidant and gastrointestinal transit accelerating activities of dried fruit of Crataegus dahurica[J]. Food Chemistry, 246: 41-47.
|
| [21] |
YI XIANGXI, JIANG SHU, QIN MEI, et al, 2020. Compounds from the fruits of mangrove Sonneratia apetala: isolation, molecular docking and antiaging effects using a Caenorhabditis elegans model[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry, 99: 103813.
|
 ), XIA Jialang1,2, BAI Meng1,2, LI Yueyao1,2, WEI Jinhua1,2, LIU Kai1,2, GAO Chenghai1,2(
), XIA Jialang1,2, BAI Meng1,2, LI Yueyao1,2, WEI Jinhua1,2, LIU Kai1,2, GAO Chenghai1,2( ), YI Xiangxi1,2(
), YI Xiangxi1,2( )
)