Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 77-85.doi: 10.11978/2024241CSTR: 32234.14.2024241
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
MaxEnt model predicting potential distribution of Trichiurus japonicus in the coastal waters of China under global climate change
FENG Zhanquan( ), SU Maoliang, DU Yuanyuan, ZHONG Youling, ZHANG Junbin(
), SU Maoliang, DU Yuanyuan, ZHONG Youling, ZHANG Junbin( )
)
- Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Marine Bioresource & Eco-Environmental Science, College of Life Sciences and Oceanography, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
-
Received:2024-12-28Revised:2025-03-18Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-10-14 -
Contact:ZHANG Junbin -
Supported by:Sustainable Development Program of Shenzhen(2023N066); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976108)
CLC Number:
- P735.121
Cite this article
FENG Zhanquan, SU Maoliang, DU Yuanyuan, ZHONG Youling, ZHANG Junbin. MaxEnt model predicting potential distribution of Trichiurus japonicus in the coastal waters of China under global climate change[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 77-85.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Environmental variables from Bio-ORACLE"
| 因子序号 | 环境因子 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| bio_1 | 底层海流方向bot current direction | ° |
| bio_2 | 底层海流速度bot current velocity | m·s-1 |
| bio_3 | 底层溶解氧bot dissolved oxygen | mmol·m-3 |
| bio_4 | 底层初级生产力bot primary productivity | mmol·m-3 |
| bio_5 | 底层盐度bot salinity | ‰ |
| bio_6 | 底层温度bot temperature | ℃ |
| bio_7 | 表层叶绿素surf chlorophyll | mg·m-3 |
| bio_8 | 表层海流方向surf current direction | ° |
| bio_9 | 表层海流速度surf current velocity | m·s-1 |
| bio_10 | 表层溶解氧surf dissolved oxygen | mmol·m-3 |
| bio_11 | 表层初级生产力surf primary productivity | mmol·m-3 |
| bio_12 | 表层盐度surf salinity | ‰ |
| bio_13 | 表层温度surf temperature | ℃ |
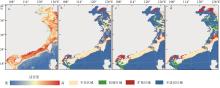
Fig. 4
Predicted suitable habitat distribution of T. japonicus in coastal waters of China under different SSPs. (a) Current distribution of suitable habitats for T. japonicus; (b), (c), and (d) represent predicted changes in future suitable habitat distribution under the SSP1-1.9, SSP2-4.5, and SSP5-8.5, respectively"

Tab. 2
Classification of distribution probability grades for T. japonicus suitable habitats in coastal waters of China"
| 区域 | 现在/% | SSP1-1.9/% | SSP2-4.5/% | SSP5-8.5/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不适宜区(0~MPT) | 16.03 | 19.58 | 22.17 | 10.79 |
| 边缘适生区(MPT~10P) | 52.10 | 48.00 | 45.85 | 56.07 |
| 低适生区(10P~0.5) | 19.90 | 18.99 | 18.25 | 19.63 |
| 中适生区(0.5~0.75) | 11.47 | 12.76 | 12.98 | 12.22 |
| 高适生区(0.75~1) | 0.49 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 1.29 |
| [1] |
曹睿星, 官文江, 高峰, 等, 2023. 基于最大熵和栖息地指数模型预测东、黄海日本鲭渔场分布[J]. 海洋学报, 45(9): 72-81.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
杜萍, 陈全震, 李尚鲁, 等, 2020. 东海带鱼资源变动及其栖息地驱动因子研究进展[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 40(1): 126-132.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
刘星雨, 2022. 气候变化对中国近海主要经济鱼类潜在适宜生境影响的研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
马腾龙, 万亿, 吴萍娟, 等, 2024. 环境因素对浮游植物生长及群落结构的影响[J]. 环境保护前沿, (3): 459-466.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
齐国君, 陈婷, 高燕, 等, 2015. 基于Maxent的大洋臀纹粉蚧和南洋臀纹粉蚧在中国的适生区分析[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 37(2): 219-223.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
孙述好, 黄紫薇, 胡男, 等, 2024. 大麻哈鱼幼鱼对温度、盐度、pH及溶解氧耐受性的研究[J]. 黑龙江水产, 43(2): 140-143.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
武晓宇, 董世魁, 刘世梁, 等, 2018. 基于MaxEnt模型的三江源区草地濒危保护植物热点区识别[J]. 生物多样性, 26(2): 138-148.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017188 |
|
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017188 |
|
| [8] |
张曼, 2022. 北部湾带鱼资源状况研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
张曼, 王雪辉, 蔡研聪, 等, 2022. 北部湾带鱼空间聚散变化特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 29(11): 1647-1658.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
张鹏, 2020. 阿曼湾海域带鱼生物学特性、矢耳石形态和微化学研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
张旭, 张佳, 王婕, 等, 2023. 温度和光照周期对硬头鳟幼鱼生长、生理及行为的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 38(2): 251-258.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aaw1620 pmid: 31624208 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aau1758 pmid: 30819962 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1061967 pmid: 11567137 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747 pmid: 7063747 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18300-3 pmid: 32917860 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1239352 pmid: 24031017 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-3058-8 pmid: 27610324 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2010.02783.x pmid: 21078088 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61008-3 pmid: 38702432 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [1] | WANG Zihan, ZENG Cong, JIANG Ziyu, CAO Ling. Conservation gap analysis of threatened fish in the East China Sea and adjacent sea areas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 66-86. |
| [2] | WANG Youshao. Impacts, challenges and opportunities of global climate change on mangrove ecosystems [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 1-14. |
|
||