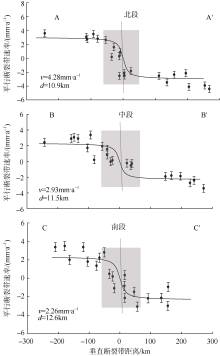
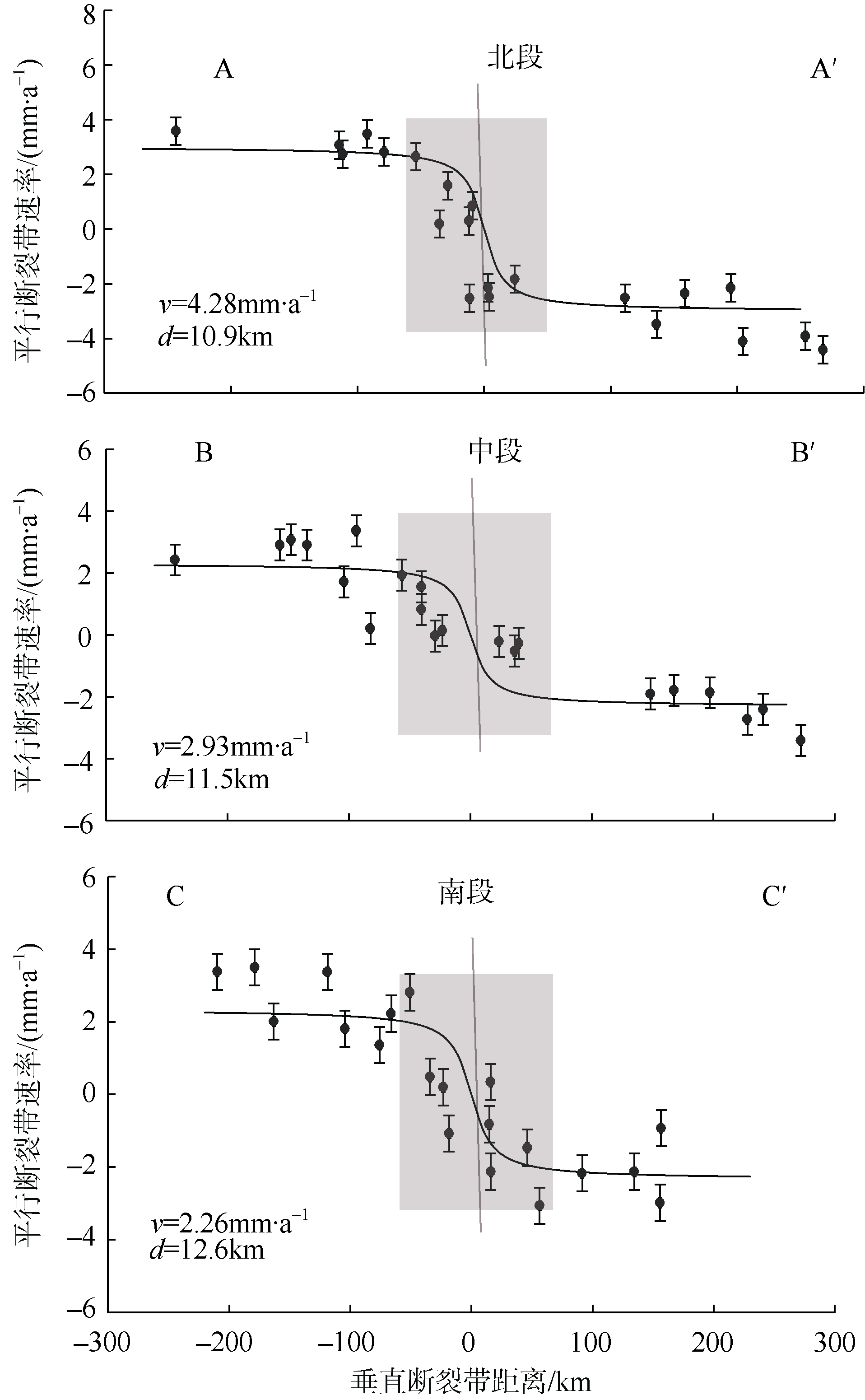
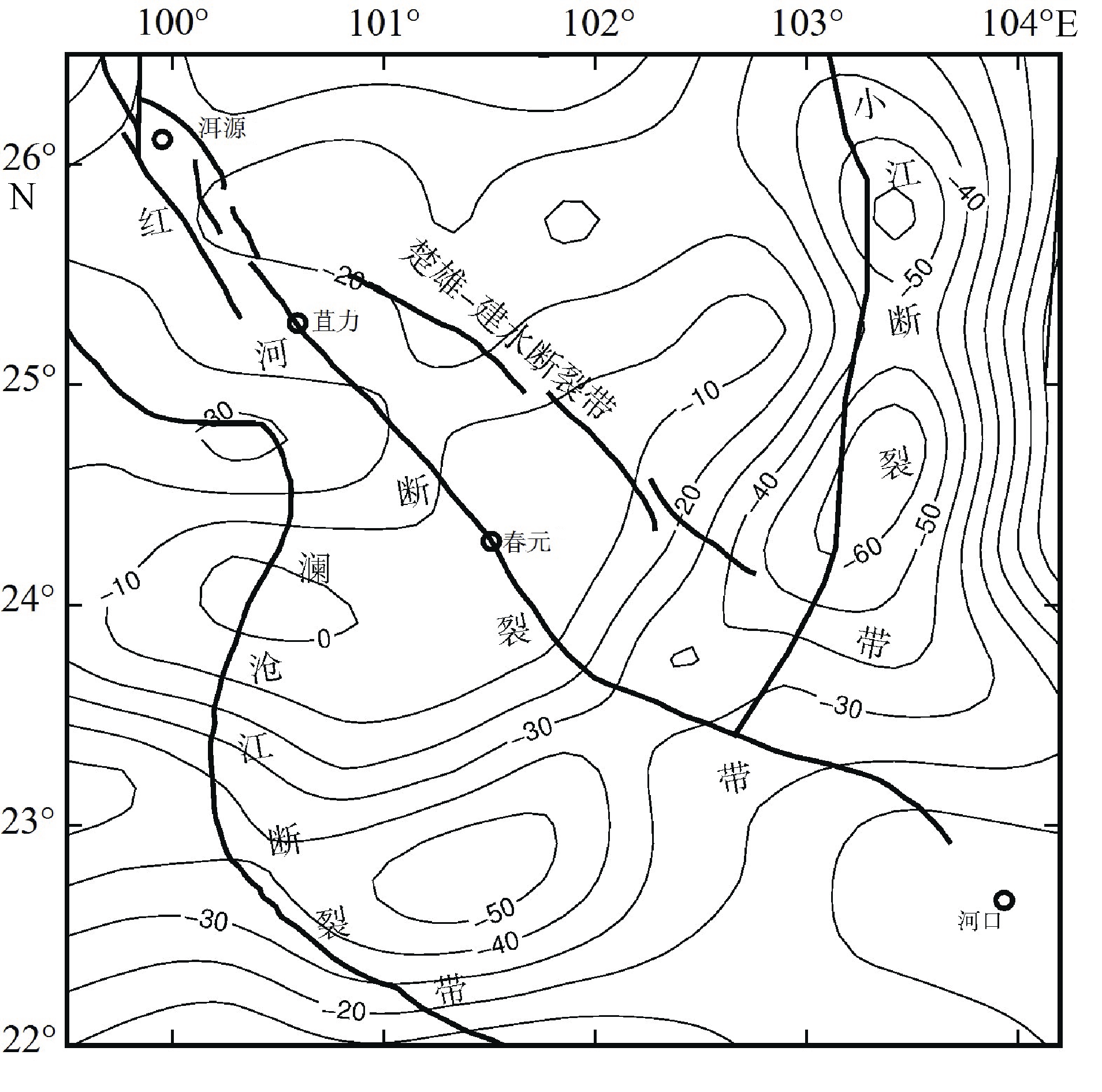
| 1 |
白志明, 王椿镛, 2003. 云南地区上部地壳结构和地震构造环境的层析成像研究[J]. 地震学报, 35(2): 117-127.
|
|
BAI ZHIMING, WANG CHUNYONG, 2003. Tomographic investigation of the upper crustal structure and seismotectonic environments in Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 25(2): 117-127 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 2 |
丁开华, 许才军, 邹蓉, 等, 2013. 利用GPS分析川滇地区活动地块运动与应变模型[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 38(7): 822-827.
|
|
DING KAIHUA, XU CAIJUN, ZOU RONG, et al, 2013. Crustal movement and strain model of active blocks analyzed by GPS in Sichuan-Yunnan region[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 38(7): 822-827 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 3 |
李西, 冉勇康, 陈立春, 等, 2016. 红河断裂带南段全新世地震活动证据[J]. 地震地质, 38(3): 596-604.
|
|
LI XI, RAN YONGKANG, CHEN LICHUN, et al, 2016. The holocene seismic evidence on southern segment of the red River Fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(3): 596-604 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 4 |
刘耀辉, 李金平, 王刘伟, 2015. 红河断裂带闭锁程度和滑动亏损分布特征研究[J]. 测绘工程, 24(8): 20-22, 26.
|
|
LIU YAOHUI, LI JINPING, WANG LIUWEI, 2015. Inversion study on locking and slip deficit of red River fault zone[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 24(8): 20-22, 26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 5 |
吕江宁, 沈正康, 王敏, 2003. 川滇地区现代地壳运动速度场和活动块体模型研究[J]. 地震地质, 25(4): 543-554.
|
|
LYU JIANGNING, SHEN ZHENGKANG, WANG MIN, 2003. Contemporary crustal deformaction and active tectonic block model of the Sichuan-Yunnan region, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 25(4): 543-554 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 6 |
宋剑, 杨少敏, 王伟, 等, 2016. 安宁河—则木河—小江断裂带闭锁特征研究[J]. 大地测量学与地球动力学, 36(6): 490-494.
|
|
SONG JIAN, YANG SHAOMIN, WANG WEI, et al, 2016. Study on the locking characteristics of Anninghe-Zemuhe- Xiaojiang fault zone[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 36(6): 490-494 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 7 |
王阎昭, 王恩宁, 沈正康, 等, 2008. 基于GPS资料约束反演川滇地区主要断裂现今活动速率[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 38(5): 582-597.
|
|
WANG YANZHAO, WANG ENNING, SHEN ZHENGKANG, et al, 2008. GPS-constrained inversion of present-day slip rates along major faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan region, China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(9): 1267-1283 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 8 |
魏文薪, 2012. 川滇块体东边界主要断裂带运动特性及动力学机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
WEI WENXIN, 2012. Study on mechanisms and characteristics of major faults in the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 9 |
闻学泽, 杜方, 龙锋, 等, 2011. 小江和曲江—石屏两断裂带系统的构造动力学与强震序列的关联性[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 41(5): 713-724.
|
|
WEN XUEZE, DU FANG, LONG FENG, et al, 2011. Tectonic dynamics and correlation of major earthquake sequences of the Xiaojiang and Qujiang-Shiping fault systems, Yunnan[J]. Science China Earth Science, 54(10): 1563-1575 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 10 |
向宏发, 万景林, 韩竹军, 等, 2006. 红河断裂带大型右旋走滑运动发生时代的地质分析与FT测年[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 36(11): 977-987.
|
|
XIANG HONGFA, WAN JINGLIN, HAN ZHUJUN, et al, 2006. Geological analysis and FT dating of the large-scale right-lateral strike-slip movement of the Red River Fault zone[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 50(3): 331-342 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 11 |
向宏发, 虢顺民, 张晚霞, 等, 2007. 红河断裂带南段中新世以来大型右旋位错量的定量研究[J]. 地震地质, 29(1): 34-50.
|
|
XIANG HONGFA, GUO SHUNMIN, ZHANG WANXIA, et al, 2007. Quantitative study on the large scale dextral strike-slip offset in the southern segment of the red river fault since Miocene[J]. Seismology and Geology, 29(1): 34-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 12 |
徐锡伟, 程佳, 许冲, 等, 2014. 青藏高原块体运动模型与地震活动主体地区讨论: 鲁甸和景谷地震的启示[J]. 地震地质, 36(4): 1116-1134.
|
|
XU XIWEI, CHEN JIA, XU CHONG, et al, 2014. Discussion on block kinematic model and future themed areas for earthquake occurrence in the tibetan plateau: Inspiration from the Ludian and Jinggu earthquakes[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(4): 1116-1134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 13 |
许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等, 2011. 印度—亚洲碰撞大地构造[J]. 地质学报, 85(1): 1-33.
|
|
XU ZHIQIN, YANG JINGSUI, LI HAIBING, et al, 2011. On the tectonics of the India-Asia collision[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(1): 1-33 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 14 |
薛志照, 1986. 唐山地震震源深度分布与地壳结构的关系[J]. 地震地质, 8(3): 69-78.
|
|
XUE ZHIZHAO, 1986. The relationship between focal depth and crustal structure for Tangshan earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 8(3): 69-78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 15 |
岳彩亚, 党亚民, 杨强, 等, 2017. 川滇地区次级地块及其主要断裂带现今活动研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 37(2): 176-181.
|
|
YUE CAIYA, DANG YAMIN, YANG QIANG, et al, 2017. Analysis of the current activity in Sichuan-Yunnan region and its sub blocks of main faults[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 37(2): 176-181 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 16 |
张建国, 汪良谋, 徐煜坚, 等, 1993. 红河断裂深部震源环境介质力学性质分析[J]. 地震地质, 15(2): 131-137.
|
|
ZHANG JIANGUO, WANG LIANGMOU, XU YUJIAN, et al, 1993. Analysis of mechanics property of the medium under the deep seismic source environment along Red River Fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 15(2): 131-137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 17 |
张培震, 王敏, 甘卫军, 等, 2003. GPS观测的活动断裂滑动速率及其对现今大陆动力作用的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 81-92.
|
|
ZHANG PEIZHEN, WANG MIN, GAN WEIJUN, et al, 2003. Slip rates along major active faults from GPS measurements and constraints on contemporary continental tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 81-92 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 18 |
张希, 江在森, 王双绪, 等, 2005. 川滇地区地壳水平运动的弹性块体边界负位错模型与强震地点预测[J]. 地震研究, 28(2): 119-124.
|
|
ZHANG XI, JIANG ZAISEN, WANG SHUANGXU, et al, 2005. Negative dislocation model of elastic block boundary of horizontal crustal movement and the prediction of strong earthquake position in Sichuan-Yunnan area[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 28(2): 119-124 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 19 |
虢顺民, 张靖, 李祥根, 等, 1984. 云南红河断裂带北段断裂位错与地震重复发生的时间间隔[J]. 地震地质, 6(1): 1-12.
|
|
GUO SHUNMIN, ZHANG JING, LI XIANGGEN, et al, 1984. Fault displacement and recurrence intervals of earthquakes at the northern segment of the Honghe fault zone, Yunnan Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 6(1): 1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 20 |
虢顺民, 计凤桔, 向宏发, 等, 2001. 红河活动断裂带[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 120-124 (in Chinese).
|
| 21 |
ALLEN C R, HAN Y, SIEH K E, et al, 1984. Red River and associated faults, Yunnan Province, China: quaternary geology, slip rates, and seismic hazard[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 95(6): 686-700.
|
| 22 |
GAN W J, ZHANG P Z, SHEN Z K, et al, 2007. Present-day crustal motion within the Tibetan Plateau inferred from GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112: 1-14.
|
| 23 |
LOVELESS J P, MEADE B J, 2011. Partitioning of localized and diffuse deformation in the Tibetan Plateau from joint inversions of geologic and geodetic observations[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 303(1-2): 11-24.
|
| 24 |
MCCAFFREY R, 2002. Crustal block rotation and plate coupling[C]//Plate Boundary Zones, AGU Geodynamics Series, 30: 101-122.
|
 ), Jinping LI1,2(
), Jinping LI1,2( )
)