Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2018, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 81-88.doi: 10.11978/2017122CSTR: 32234.14.2017122
Special Issue: 南海专题
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Optimization of temperature and time of acoustic physics parameters of seafloor sediment in the South China Sea
Yun LUO1,2( ), Zhengyu HOU1, Yuhang TIAN1,2, Antao XU1,2, Zhong CHEN1(
), Zhengyu HOU1, Yuhang TIAN1,2, Antao XU1,2, Zhong CHEN1( )
)
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2017-11-12Revised:2017-12-18Online:2018-07-20Published:2018-07-16 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation (41376057, 41676056);National Science and Technology Support Program (2014BAB14B01)
CLC Number:
- P736.211
Cite this article
Yun LUO, Zhengyu HOU, Yuhang TIAN, Antao XU, Zhong CHEN. Optimization of temperature and time of acoustic physics parameters of seafloor sediment in the South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 81-88.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
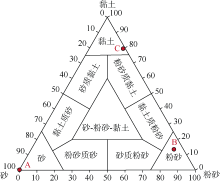
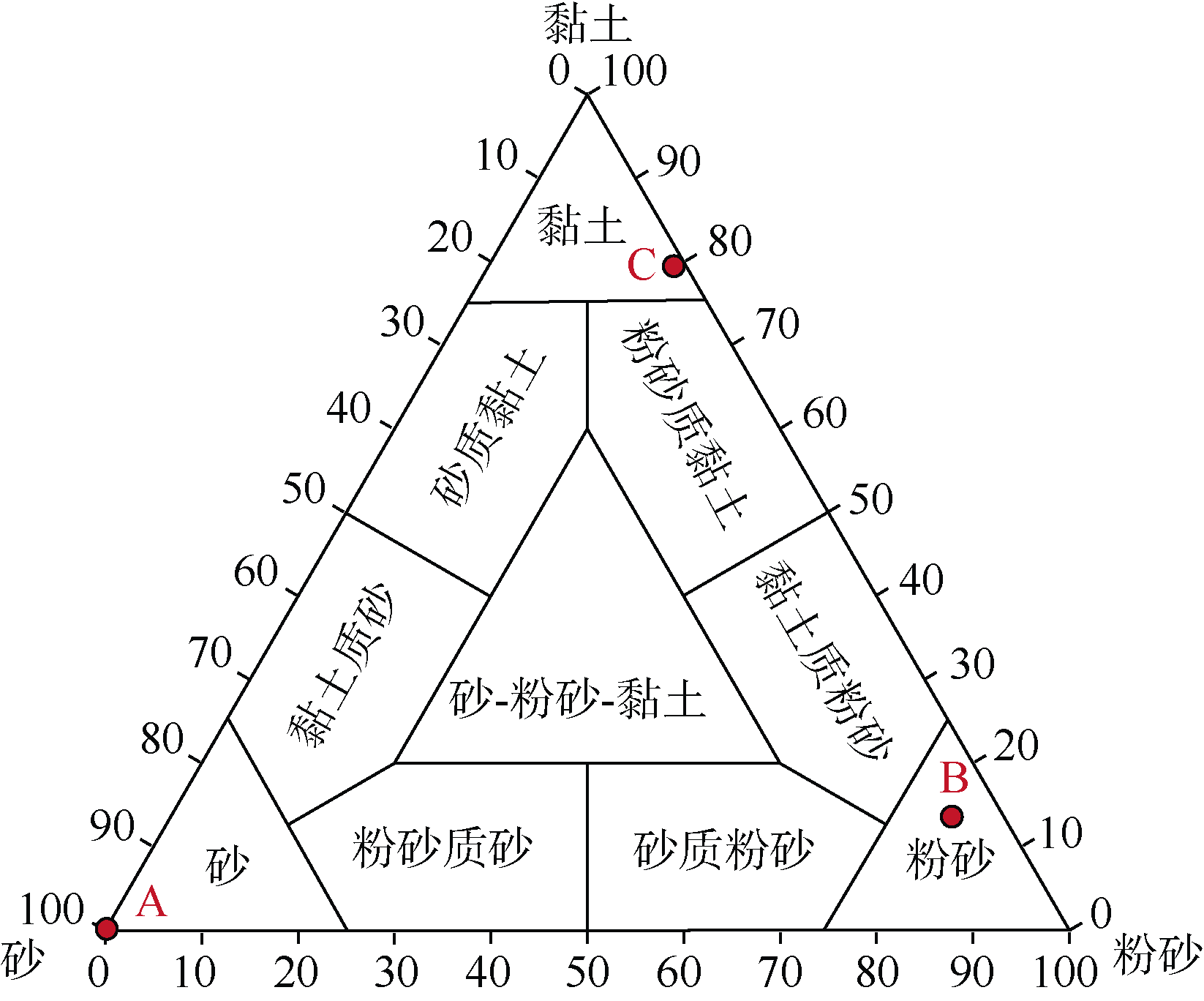
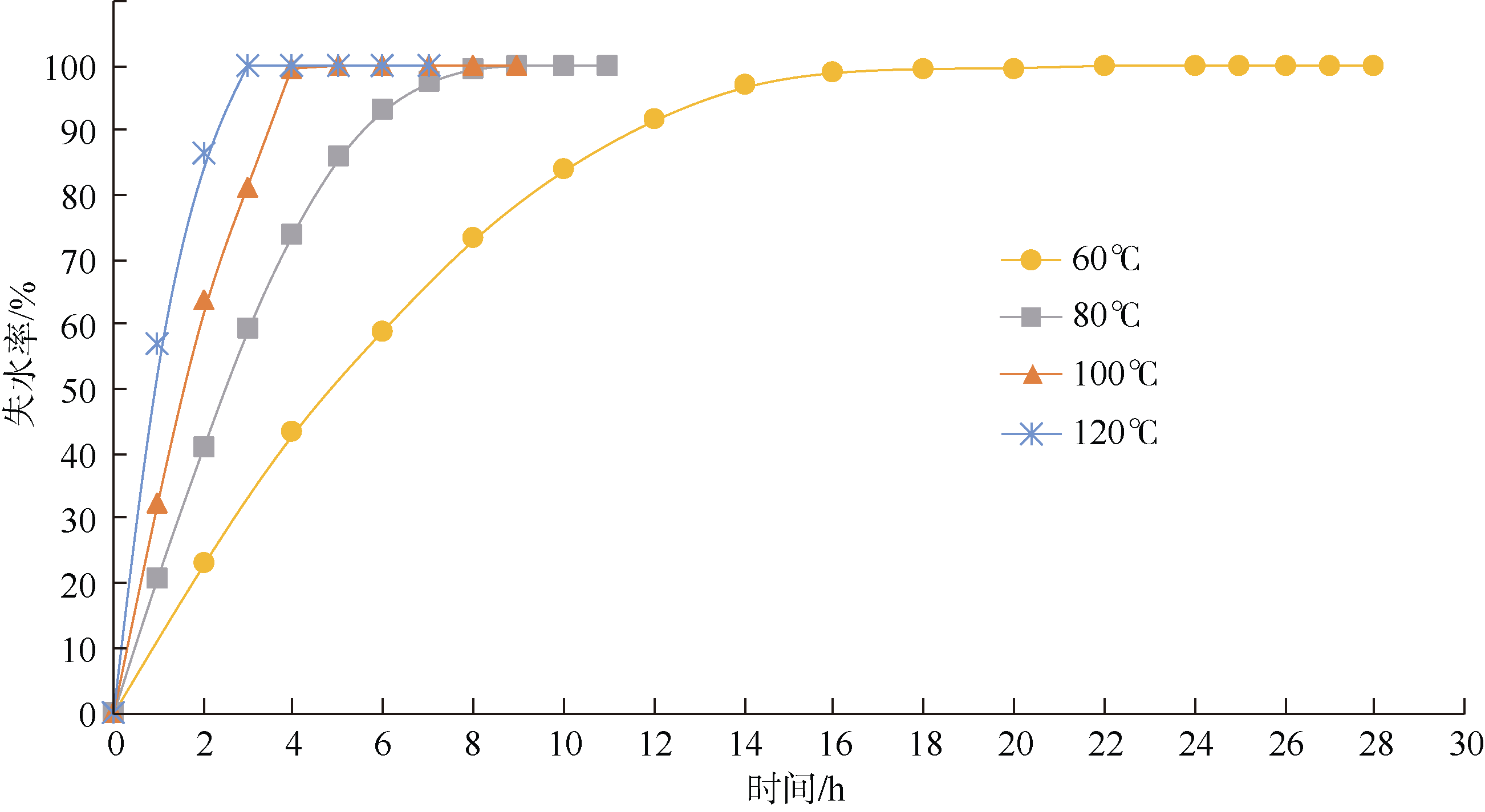
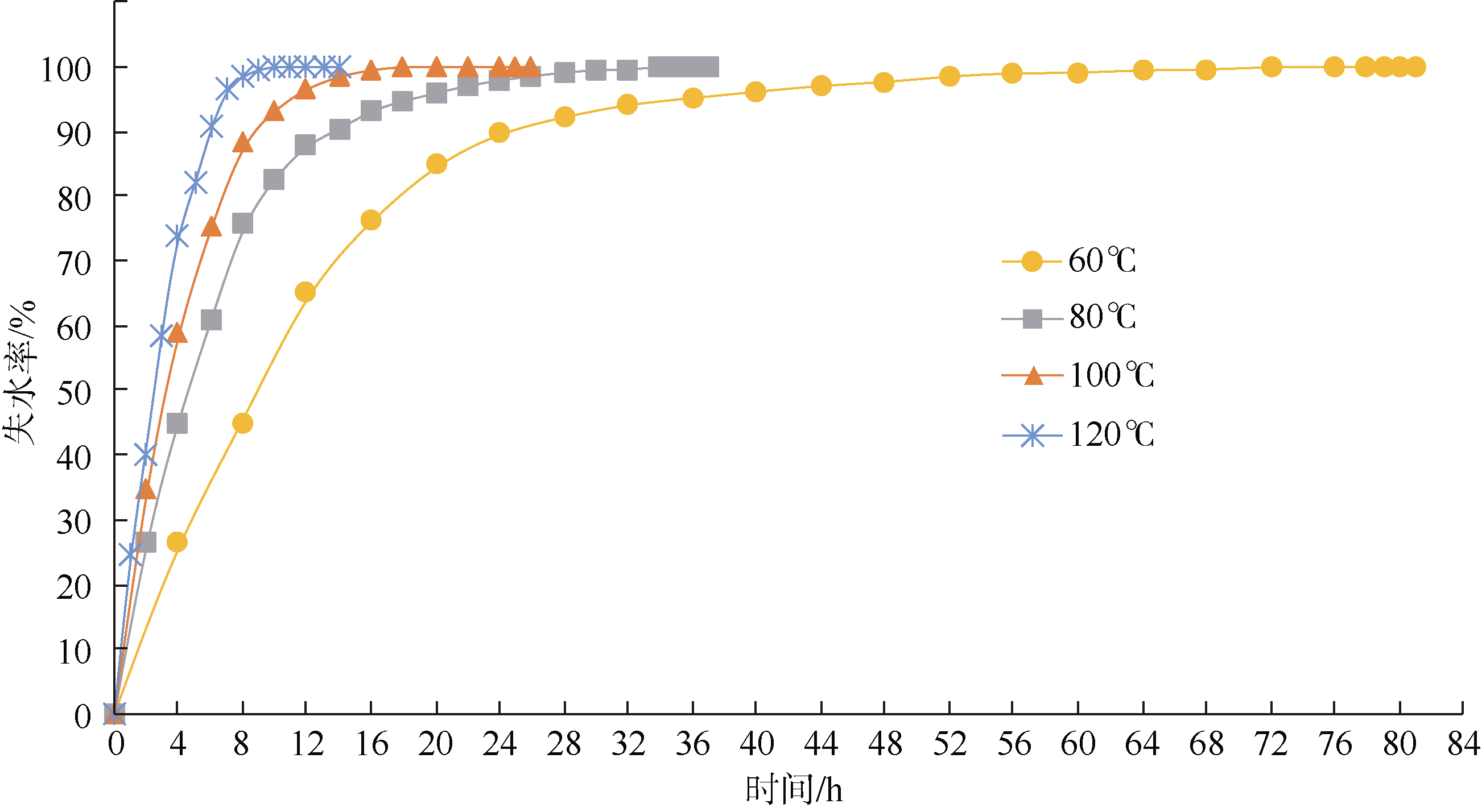
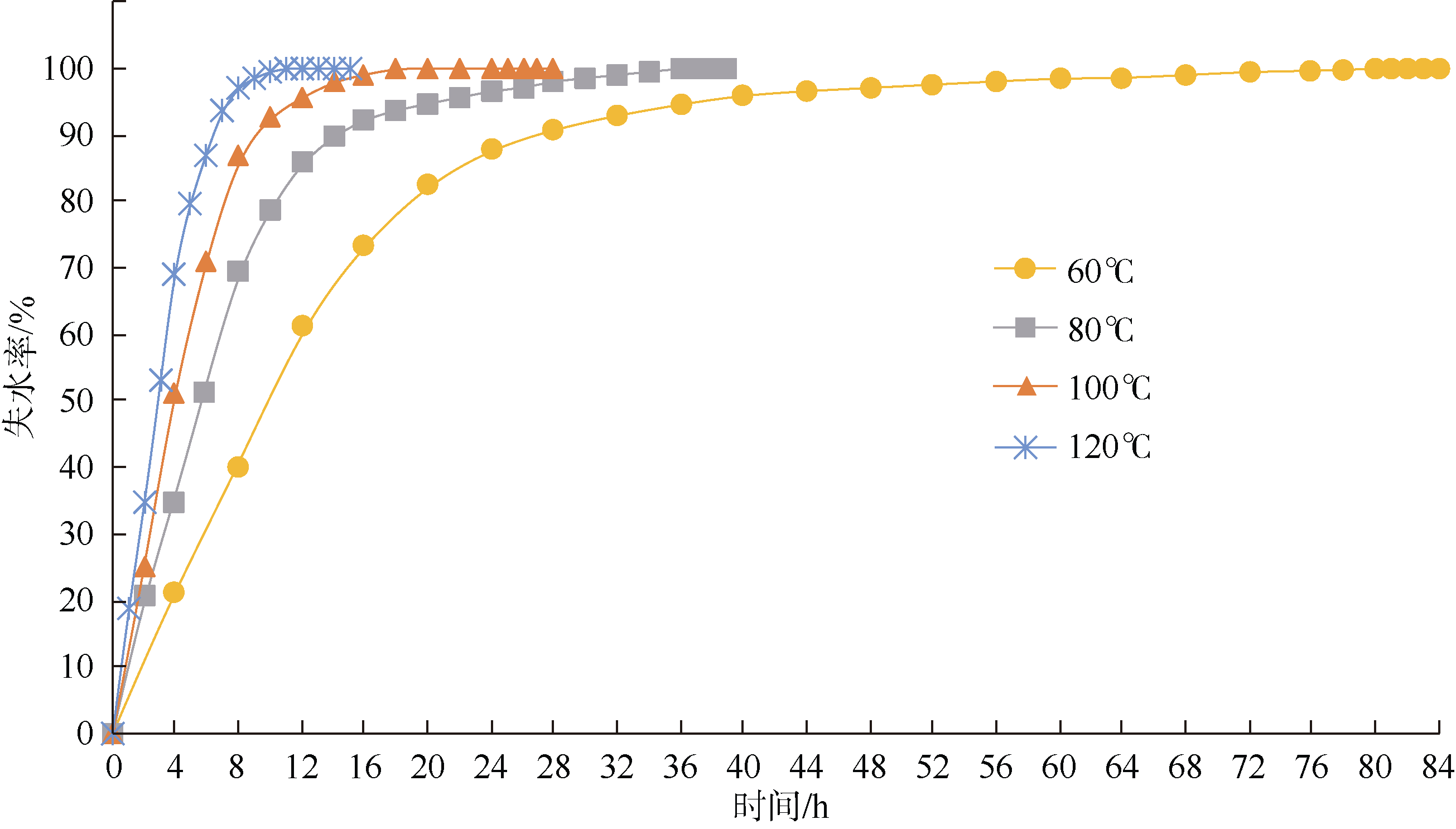
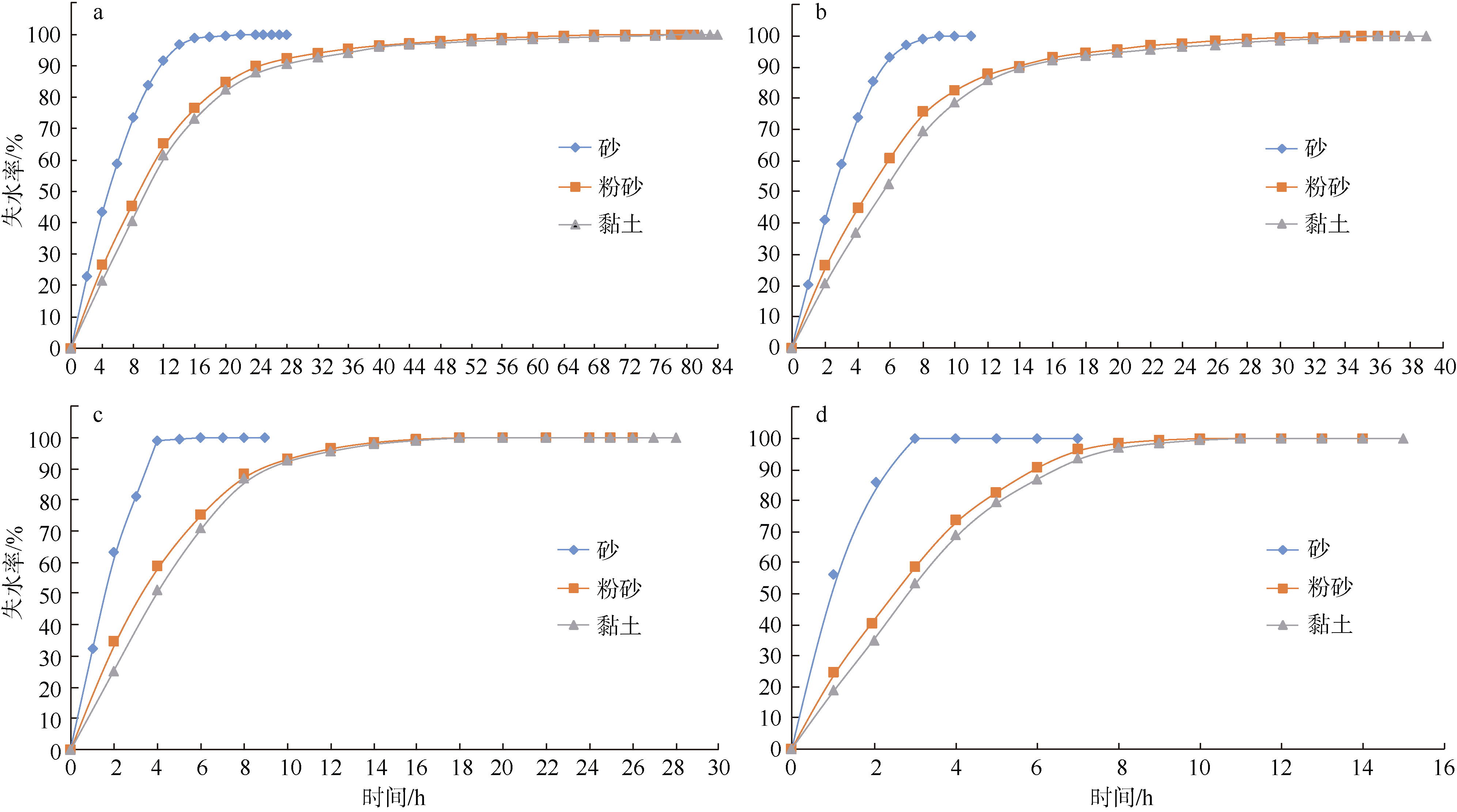
Tab. 1
Determination of physical parameters of sediments"
| 沉积物类型 | 湿密度/(g•cm-3) | 干密度/(g•cm-3) | 含水率/% | 比重 | 孔隙度 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂 | 本文 | 2.04 | 1.58 | 29.5 | 2.64 | 0.403 |
| 南海a | 1.68~2.02 | 1.12~1.64 | 19.3~54.8 | - | 0.362~0.800 | |
| 粉砂 | 本文 | 1.48 | 0.64 | 132.3 | 2.69 | 0.762 |
| 南海b | 1.33~1.67 | 0.55~1.02 | 61.4~156.0 | - | 0.607~0.868 | |
| 黏土 | 本文 | 1.41 | 0.52 | 170.1 | 2.72 | 0.808 |
| 南海 | - | - | - | - | - | |
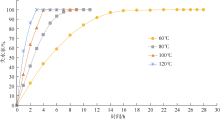
Tab. 2
The sound velocity prediction deviation of critical time and total drying at 80℃"
| 沉积物 类型 | 失水率/% | 含水率 偏差/% | 孔隙度 偏差/% | 公式(1)偏差/% | 公式(2)偏差/% | 公式(3)偏差/% | 公式(4)偏差/% | 公式(5)偏差/% | 公式(6)偏差/% | 公式(7)偏差/% | 公式(8)偏差/% | 公式(9)偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂 | 99.12 | 1.02 | 0.97 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.18 |
| 粉砂 | 99.29 | 2.34 | 0.55 | -1.74 | -0.02 | 0.07 | 0.00 | -0.02 | 0.04 | -0.07 | -0.04 | 0.13 |
| 黏土 | 99.30 | -0.55 | -0.12 | 0.68 | 0.02 | -0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.02 | -0.02 |
| 1 | 陈泓君, 彭学超, 朱本铎, 等, 2014. 南海1∶100万海南岛幅海洋区域地质调查与编图成果综述[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(6): 83-96. |
| CHEN HONGJUN, PENG XUECHAO, ZHU BENDUO, et al, 2014. A brief review of 1: 1000000 marine geological survey and mapping results of the Hainan sheet in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 34(6): 83-96 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 2 | 国家质量技术监督局, 中华人民共和国建设部, 1999. GB/T 50123-1999 土工试验方法标准[2007版][S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社 (in Chinese). |
| 3 | 洪刚, 吴百海, 邹大鹏, 2011. 温度对海底沉积物声学特性影响实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(6): 70-73. |
| HONG GANG, WU BAIHAI, ZOU DAPENG, 2011. Experimental study on acoustic characteristics of seafloor sediment on effects of temperature[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(6): 70-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 4 | 侯正瑜, 郭常升, 王景强, 2013. 南沙海域深水区表层沉积物声速与孔隙度相关关系[J]. 海洋科学, 37(7): 77-82. |
| HOU ZHENGYU, GUO CHANGSHENG, WANG JINGQIANG, 2013. Surface sediments acoustic velocity and porosity correlation in Nansha sea area abyssal region[J]. Marine Sciences, 37(7): 77-82 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 5 | 李亮, 陈忠, 刘建国, 等, 2014. 南海北部表层沉积物类型及沉积环境区划[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(1): 54-61. |
| LI LIANG, CHEN ZHONG, LIU JIANGUO, et al, 2014. Distribution of surface sediment types and sedimentary environment divisions in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 33(1): 54-61 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 6 | 林学辉, 辛文彩, 徐磊, 2015. 海洋沉积物含水率对部分碱金属及碱土金属元素含量的影响及意义[J]. 海洋科学, 39(12): 106-111. |
| LIN XUEHUI, XIN WENCAI, XU LEI, 2015. Effect of water content on certain alkali and alkali-earth elements in marine sediments[J]. Marine Sciences, 39(12): 106-111 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 7 | 卢博, 1994. 海底浅层沉积物声速与物理性质[J]. 科学通报, 39(5): 435-437 (in Chinese). |
| 8 | 卢博, 梁元博, 1994. 中国东南沿海海洋沉积物物理参数与声速的统计相关[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 24(5): 556-560. |
| LU BO, LIANG YUANBO, 1995. Statistical correlation of physical parameters with sound velocity in marine sediments of South and East China Seas[J]. Science in China (Series B), 38(5): 613-618 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 9 | 卢博, 1995. 用声速Cp和Cs判别沉积物性质[J]. 台湾海峡, 14(2): 118-123. |
| LU BO, 1995. Judging sediment property from sound velocity Cp and Cs[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 14(2): 118-123 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 10 | 卢博, 李赶先, 黄韶健, 等, 2005. 中国黄海、东海和南海北部海底浅层沉积物声学物理性质之比较[J]. 海洋技术, 24(2): 28-33. |
| LU BO, LI GANXIAN, HUANG SHAOJIAN, et al, 2005. The Comparing of seabed sediment acoustic-physical properties in the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea and northern the South China Sea[J]. Ocean Technology, 24(2): 28-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 11 | 卢博, 李赶先, 孙东怀, 等, 2006a. 中国东南近海海底沉积物声学物理性质及其相关关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 25(2): 12-17. |
| LU BO, LI GANXIAN, SUN DONGHUAI, et al, 2006. Acoustic-physical properties of seafloor sediments from nearshore southeast China and their correlations[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 25(2): 12-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 12 | 卢博, 李赶先, 黄韶健, 2006b. 在轴向应力-应变下海底沉积物声速及其变化[J]. 海洋学报, 28(2): 93-100. |
| LU BO, LI GANXIAN, HUANG SHAOJIAN, 2006. The sound velocity variation in seafloor sediments on its axial stress-strain course[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 28(2): 93-100 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 13 | 卢博, 李赶先, 黄韶健, 2007. 用声学三参数判别海底沉积物性质[J]. 声学技术, 26(1): 6-14. |
| LU BO, LI GANXIAN, HUANG SHAOJIAN, 2007. Discrimination of seafloor sediment properties from sound velocity waveform and amplitude[J]. Technical Acoustics, 26(1): 6-14 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 14 | 潘国富, 2003. 南海北部海底浅部沉积物声学特性研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学: 1-107. |
| PAN GUOFU, 2003. Research on the acoustic characteristics of seabed sediments in the northern South China Sea[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University: 1-107 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 15 | 邱燕, 钟和贤, 刘坚, 2008. 南海中南部表层沉积物类型、分布与水动力条件[J]. 南海地质研究, (1): 1-13. |
| QIU YAN, ZHONG HEXIAN, LIU JIAN, 2008. Type, distribution and hydrodynamic condition of seafloor sediments in the middle and southern parts of South China Sea[J]. Geological Research of South China, (1): 1-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 16 | 唐永禄, 1998. 海底沉积物孔隙度与声速的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 20(6): 39-43. |
| TANG YONGLU, 1998. The relationship between porosity of sea bed sediment and sound velocity[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 20(6): 39-43 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 17 | 田雨杭, 2016. 琼东南海域沉积物声学特征及粒度模式反演声学特性研究[D]. 广州: 中国科学院南海海洋研究所: 1-69. |
| TIAN YUHANG, 2016. Research on the acoustic properties and the inversion of geoacoustic parameters using the grain size of surface sediments Southeast off Hainan Island[D]. Guangzhou: South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, CAS: 1-69 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 18 | 田雨杭, 陈忠, 刘吉睿, 等, 2016. 琼东南外海海底沉积物粒度组分对孔隙度、声速的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 35(3): 48-54. |
| TIAN YUHANG, CHEN ZHONG, LIU JIRUI, et al, 2016. Influence of the grain size on the porosity and acoustic velocity of offshore surface sediments in the Southeastern Hainan island[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 35(3): 48-54 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 19 | 肖晓, 石要红, 冯秀丽, 等, 2016. 北部湾表层沉积物粒度分布规律及沉积动力分区[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 46(5): 83-89. |
| XIAO XIAO, SHI YAOHONG, FENG XIULI, et al, 2016. Surface sediment characteristics and dynamics in Beibu gulf[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 46(5): 83-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 20 | 张富元, 章伟艳, 张德玉, 等, 2004. 南海东部海域表层沉积物类型的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 26(5): 94-105. |
| ZHANG FUYUAN, ZHANG WEIYAN, ZHANG DEYU, et al, 2004. Research on surface sediment types and distributions from the eastern South China Sea, China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 26(5): 94-105 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 21 | 中国地质调查局广州海洋地质调查局, 2015. 海底沉积物类型图(南海地质地球物理图系)[M]. 广州: 中国航海图书出版社(in Chinese). |
| 22 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2008. GB 12763.8-2007 海洋调查规范第8部分: 海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社 (in Chinese). |
| 23 | 周志愚, 杜继川, 赵广存, 等, 1983. 南海、黄海海底声速垂直分布的测量结果[J]. 海洋学报, 5(5): 543-552 (in Chinese). |
| 24 | 邹大鹏, 吴百海, 卢博, 2007. 海底沉积物声速经验方程的分析和研究[J]. 海洋学报, 29(4): 43-50. |
| ZOU DAPENG, WU BAIHAI, LU BO, 2007. Analysis and study on the sound velocity empirical equations of seafloor sediments[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 29(4): 43-50 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 25 | 邹大鹏, 吴百海, 卢博, 等, 2008. 海底沉积物物理参数的声学反演模式[J]. 海洋学报, 30(5): 17-22. |
| ZOU DAPENG, WU BAIHAI, LU BO, et al, 2008. Acoustic inversion models of physical parameters of seabed sediments[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 30(5): 17-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 26 | 邹大鹏, 卢博, 吴百海, 等, 2009. 基于同轴差距测量法的南海深水海底沉积物声衰减特性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 28(3): 35-39. |
| ZHOU DAPENG, LU BO, WU BAIHAI, et al, 2009. Acoustic attenuation characteristics of deep-water seafloor sediments from the South China Sea based on coaxial differential distance attenuation measurement method[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 28(3): 35-39 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 27 | 邹大鹏, 阎贫, 卢博, 2012. 基于海底表层沉积物声速特征的南海地声模型[J]. 海洋学报, 34(3): 80-86. |
| ZOU DAPENG, YAN PIN, LU BO, 2012. A geoacoustic model based on sound speed characteristic of seafloor surface sediments of the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(3): 80-86 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 28 | ANDERSON R E, 1974. Statistical correlation of physical properties and sound velocity in sediments[C]//HAMPTON L, ed. Physics of Sound in Marine Sediments. Boston, MA: Springer: 481-518. |
| 29 | BUCKINGHAM M J, 2005. Compressional and shear wave properties of marine sediments: Comparisons between theory and data[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 117(1): 137-152. |
| 30 | CHEN MINPEN, SHIEH Y T, CHYAN J M, 1988. Acoustic and physical properties of surface sediments in northern Taiwan strait[J]. Acta Oceanogrphica Taiwanica, 21: 92-118. |
| 31 | HAMILTON E L, 1980. Geoacoustic modeling of the sea-floor[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 68(5): 1313-1340. |
| 32 | HOU ZHENGYU, GUO CHENGSHENG, WANG JIANGQIANG, et al, 2015. Seafloor sediment study from South China Sea: Acoustic & physical property relationship[J]. Remote Sensing, 7(9): 11570-11585. |
| 33 | JACKSON D R, RICHARDSON M D, 2007. High-frequency seafloor acoustic[M]. New York: Springer: 1-512. |
| 34 | KAN GUANGMING, LIU BAOHUA, WANG JINGQIANG, et al, 2017. Sound speed dispersion characteristics of three types of shallow sediments in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, doi: 10.1080/1064119X.2017.1392659. |
| 35 | LU BO, LIU QIANG, LI GANXIAN, 2010. Grain and pore factors in acoustic response to seafloor sediments[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 28(2): 115-129. |
| 36 | ORSI T H, DUNN D A, 1990. Sound velocity and related physical properties of fine-grained abyssal sediments from the Brazil Basin (South Atlantic Ocean)[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 88(3): 1536-1542. |
| [1] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 3. data sharing service and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [2] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, HE Yunkai, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 1. data reorganization technology and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [3] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, XU Xiaolu, YUAN Li. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 2. data curation and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [4] | SUN Zeming, HAN Shuzong, WANG Mingjie, SU Hanxiang. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [5] | QI Huandong, ZHU Cheng, LI Xuchun, JING Xindi, SONG Derui. Rule set and multilayer perceptron based quality control method for Argo temperature data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 190-202. |
| [6] | LIN Guihuan, YAN Youfang, LIU Ying. Ocean stratification in the Indonesian-Australian basin and its influencing factors [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 57-67. |
| [7] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [8] | GAO Rongze, QU Ke, REN Xingyue, WANG Xu. Application of convolutional neural network methods in the evolution of hydrodynamic characteristics of tsunamis like-wave over fringing reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 68-75. |
| [9] | MO Danyang, NING Zhiming, YANG Bin, XIA Ronglin, LIU Zhijin. Response of dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in coral reef sediments of the Weizhou island to temperature changes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [10] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [11] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [12] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [13] | QIU Yan, JU Dong, HUANG Wenkai, WANG Yingmin, NIE Xin. Re-determination of the initiation time of the seafloor spreading of the Central Basin, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 154-165. |
| [14] | ZHAO Minghui, YUAN Ye, ZHANG Jiazheng, ZHANG Cuimei, GAO Jinwei, WANG Qiang, SUN Zhen, CHENG Jinhui. New developments on the rift-breakup of the continent-ocean transition zone in the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [15] | WENG Shaojia, CAI Jinhai, PANG Yunxi, LUO Rongzhen. Application of convolutional neural network to sea surface temperature prediction in the coastal waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 40-47. |
|
||