Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 45-52.doi: 10.11978/2020124CSTR: 32234.14.2020124
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Diversity and anti-bacteria activity of the gorgonian derived fungi from Weizhou Island of Guangxi Province*
LU Chunju1( ), LU Meilin1, LIU Xinming1, LIU Yonghong1,2, GAO Chenghai1, XU Xinya1(
), LU Meilin1, LIU Xinming1, LIU Yonghong1,2, GAO Chenghai1, XU Xinya1( )
)
- 1. Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
2. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2020-10-30Revised:2021-01-27Online:2021-09-10Published:2021-01-25 -
Contact:XU Xinya E-mail:2250562004@qq.com;xyxu@gxtcmu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42066006);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41606186);Guangxi Natural Science Foundation(AD19245116);Development Program of High level Talent Team under Qihuang Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine(2018006);Special Fund for Bagui Scholars of Guangxi(05019055);Initial Scientific Research Foundation of Introduced Doctors in 2019 of GXUCM(2018BS039);Scientific Research Foundation of Institute of Marine Drugs, GUCM(2018ZD005);Guangxi First-class Discipline: Chinese Materia Medica(Scientific Research of Guangxi Education Department)([2018] No. 12)
CLC Number:
- P735.51
Cite this article
LU Chunju, LU Meilin, LIU Xinming, LIU Yonghong, GAO Chenghai, XU Xinya. Diversity and anti-bacteria activity of the gorgonian derived fungi from Weizhou Island of Guangxi Province*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 45-52.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
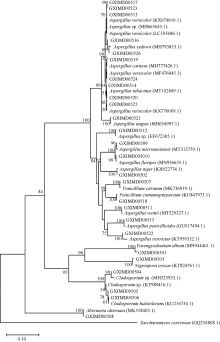
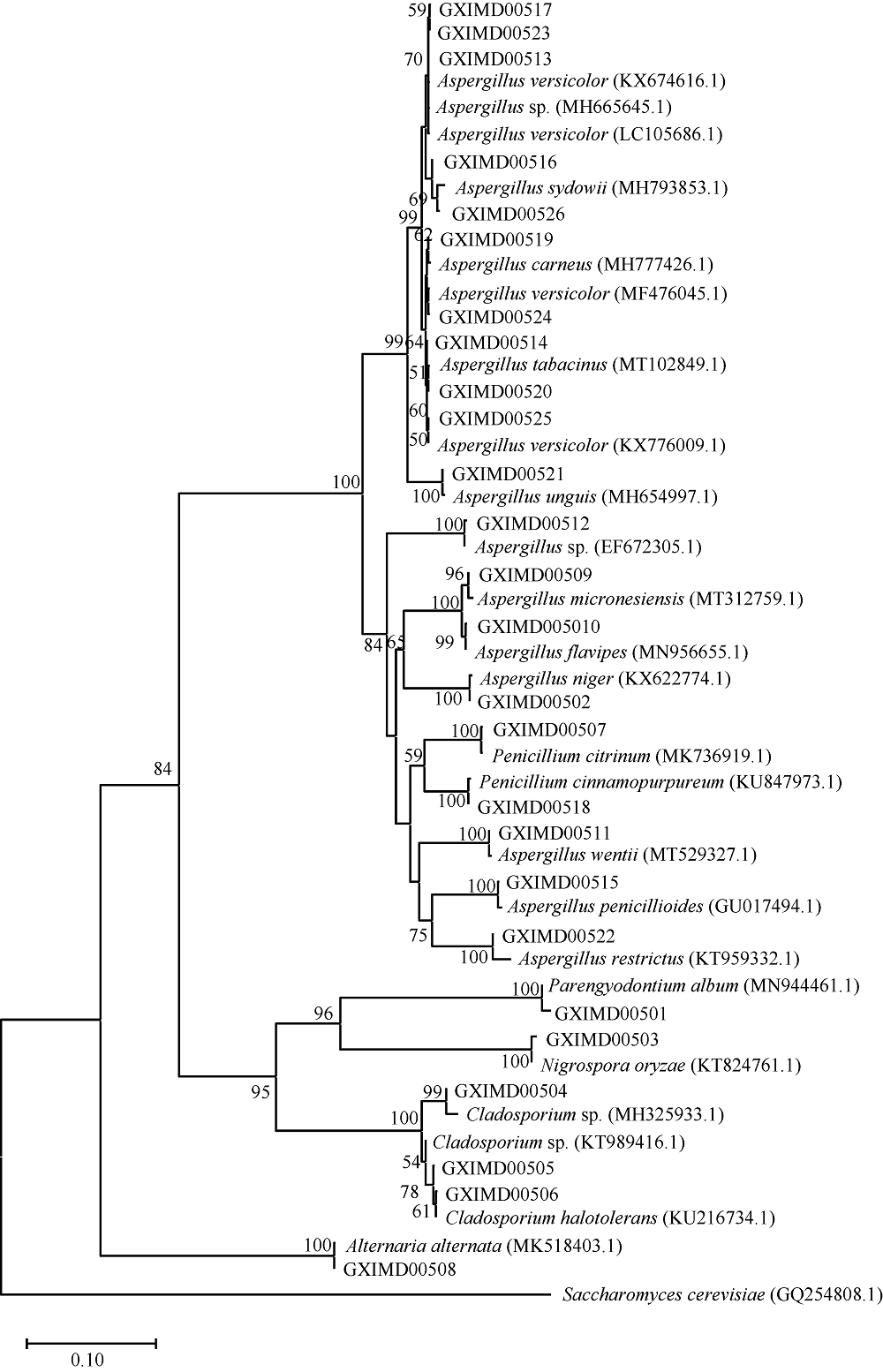
Tab. 1
Identification of fungal strains isolated from gorgonians based on DNA analysis of the ITS region"
| 菌株编号 | GenBan登录号 | 序列长度/bp | 最相近菌株(BLAST) | 相似度/% | GenBan登录号 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GXIMD00501 | MT672589 | 533 | Parengyodontium album | 100 | MN944461.1 |
| GXIMD00502 | MT672603 | 535 | Aspergillus niger | 100 | KX622774.1 |
| GXIMD00503 | MT672604 | 516 | Nigrospora oryzae | 100 | KT824761.1 |
| GXIMD00504 | MT672605 | 508 | Cladosporium sp. | 99.80 | MH325933 |
| GXIMD00505 | MT707929 | 515 | Cladosporium sp. | 99.61 | KT989416.1 |
| GXIMD00506 | MT672606 | 511 | Cladosporium halotolerans | 100 | KU216734.1 |
| GXIMD00507 | MT672611 | 512 | Penicillium citrinum | 100 | MK736919.1 |
| GXIMD00508 | MT672612 | 515 | Alternaria alternata | 100 | MK518403.1 |
| GXIMD00509 | MT672613 | 541 | Aspergillus micronesiensis | 99.82 | MT312759.1 |
| GXIMD00510 | MT672614 | 557 | Aspergillus flavipes | 99.64 | MN956655.1 |
| GXIMD00511 | MT672615 | 530 | Aspergillus wentii | 100 | MH855236.1 |
| GXIMD00512 | MT672616 | 540 | Aspergillus sp. | 99.81 | EF672305.1 |
| GXIMD00513 | MT672617 | 518 | Aspergillus sp. | 100 | MH665645.1 |
| GXIMD00514 | MT672618 | 518 | Aspergillus sp. | 100 | MK431431.1 |
| GXIMD00515 | MT672619 | 575 | Aspergillus penicillioides | 99.83 | GU017494.1 |
| GXIMD00516 | MT672620 | 502 | Aspergillus sydowii | 100 | MH793853.1 |
| GXIMD00518 | MT672622 | 509 | Penicillium cinnamopurpureum | 100 | KU847973.1 |
| GXIMD00519 | MT672623 | 513 | Aspergillus carneus | 99.81 | MH777426.1 |
| GXIMD00520 | MT672624 | 508 | Aspergillus tabacinus | 100 | MT635280.1 |
| GXIMD00521 | MT672625 | 519 | Aspergillus unguis | 100 | MH654997.1 |
| GXIMD00522 | MT672626 | 519 | Aspergillus restrictus | 100 | KT959332.1 |
| GXIMD00517 | MT672621 | 540 | Aspergillus versicolor | 99.81 | LC105686.1 |
| GXIMD00523 | MT742624 | 519 | Aspergillus versicolor | 100 | KX674616.1 |
| GXIMD00524 | MT742625 | 514 | Aspergillus versicolor | 99.81 | MF476045.1 |
| GXIMD00525 | MT742626 | 532 | Aspergillus versicolor | 100 | KX776009.1 |
| GXIMD00526 | MT742624 | 517 | Aspergillus versicolor | 99.81 | MN310533.1 |
Tab. 3
Antibacterial activities of ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extracts from fermentation broth of the gorgonian-derived fungal strains"
| 菌株 | 抑制率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 表皮葡萄球菌 | 无乳链球菌 | 海豚链球菌 | |
| Penicillium citrinum GXIMD00507 | 77.44 | 78.35 | 86.36 |
| Alternaria alternata GXIMD00508 | 63.64 | - | - |
| Aspergillus micronesiensis GXIMD00509 | 70.99 | 58.77 | 68.24 |
| Aspergillus flavipes GXIMD005010 | 57.60 | - | - |
| Aspergillus wentii GXIMD00511 | 76.90 | 69.33 | 81.22 |
| Aspergillus sydowii GXIMD00516 | 62.96 | - | 67.22 |
| Aspergillus versicolor GXIMD00517 | 58.42 | 62.05 | 80.02 |
| Penicillium cinnamopurpureum GXIMD00518 | 86.48 | 79.81 | 85.52 |
| Aspergillus carneus GXIMD00519 | 59.25 | - | 76.38 |
| Aspergillus tabacinus GXIMD00520 | 58.56 | - | 65.50 |
| Aspergillus unguis GXIMD00521 | 88.17 | 80.57 | 86.19 |
| 青霉素 | 91.44 | 73.93 | 84.93 |
Tab. 4
Anti-biofilm activities of EtOAc extracts from fermentation broth of the gorgonian-derived fungal strains"
| 菌株 | 耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌 | 表皮葡萄球菌 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC50/(μg•mL-1) | EC50/(μg•mL-1) | MIC50/(μg•mL-1) | EC50/(μg•mL-1) | ||
| Penicillium citrinum GXIMD00507 | >200 | - | >200 | 150.6 | |
| Aspergillus micronesiensis GXIMD00509 | >200 | - | >200 | 154.8 | |
| Aspergillus wentii GXIMD00511 | >200 | - | >200 | 40.3 | |
| Penicillium cinnamopurpureum GXIMD00518 | >200 | 105.4 | >200 | 102.9 | |
| Aspergillus carneus GXIMD00519 | >200 | 117.4 | >200 | 105.0 | |
| Aspergillus tabacinus GXIMD00520 | >200 | - | >200 | 66.3 | |
| Aspergillus versicolor GXIMD00525 | >200 | - | >200 | 155.0 | |
| 青霉素 | 6.67 | - | - | - | |
| [1] | 方燕, 潘丽霞, 易湘茜, 等, 2012. 柳珊瑚Anthogorgia caerulea相关可培养细菌抗污活性筛选[J]. 广西科学, 19(3):253-256. |
| FANG YAN, PAN LIXIA, YI XIANGXI, et al, 2012. Antifouling activity of culturable bacteria associated with the gorgonian Anthogorgia caerulea[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 19(3):253-256 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 傅奇, 林俊杰, 庄峙厦, 等, 2020. 一株海洋来源蛋白酶产生菌Parengyodontium album HX2019006的鉴定及其发酵条件研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 46(10):185-190. |
| FU QI, LIN JUNJIE, ZHUANG ZHIXIA, et al, 2020. Identification of the marine protease-producing fungus Parengyodontium album HX2019006 and the optimization of its fermentation conditions[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 46(10):185-190 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 黄峰, 王玮韧, 饶鑫, 等, 2019. 热带珊瑚岛植物种植对土壤改良及其微生物群落形成的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(17):6227-6237. |
| HUANG FENG, WANG WEIREN, RAO XIN, et al, 2019. Soil improvements and microbial community development following establishment of plant communities in a tropical coral island[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(17):6227-6237 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 黄艳冰, 蒋晓东, 刘威, 等, 2018. 叶状蔷薇珊瑚来源真菌Parengyodontium album SCSIO 40430次级代谢产物研究[J]. 微生物学通报, 45(9):1881-1888. |
| HUANG YANBING, JIANG XIAODONG, LIU WEI, et al, 2018. Chromanones from Montipora foliosa-derived Parengyodontium album SCSIO 40430[J]. Microbiology China, 45(9):1881-1888 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 罗晓雯, 李莉, 朱永肖, 等, 2018. 鱼类海豚链球菌病研究进展[J]. 水产科学, 37(6):847-854. |
| LUO XIAOWEN, LI LI, ZHU YONGXIAO, et al, 2018. Research progress on diseases caused by pathogen Streptococcus iniae in fishes: a review[J]. Fisheries Science, 37(6):847-854 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 苏友禄, 刘婵, 邓益琴, 等, 2019. 罗非鱼无乳链球菌病的研究进展[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 34(5):757-766. |
| SU YOULU, LIU CHAN, DENG YIQIN, et al, 2019. Research on Streptococcus agalactiae disease in tilapia: a review[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 34(5):757-766 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 王文欢, 余克服, 王英辉, 2016. 北部湾涠洲岛珊瑚礁的研究历史、现状与特色[J]. 热带地理, 36(1):72-79. |
| WANG WENHUAN, YU KEFU, WANG YINGHUI, 2016. A Review on the research of coral reefs in the Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf[J]. Tropical Geography, 36(1):72-79 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 王亚楠, 2012. 中国南海柳珊瑚共附生微生物多样性与抗菌作用研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 1-267. |
| WANG YANAN, 2012. Study on diversity of gorgonian-derived symbiotic microorganisms from South China Sea and antimicrobial mechanism[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China: 1-267 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 杨小梅, 李菲, 胡丽琴, 等, 2014. 柳珊瑚Anthogorgia caerulea相关可培养共生放线菌多样性及其生物毒活性研究[J]. 广西科学院学报, 30(4):248-252. |
| YANG XIAOMEI, LI FEI, HU LIQIN, et al, 2014. Diversity and biotoxicity of culturable actinomycetes associated with the gorgonian Anthogorgia caerulea[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 30(4):248-252 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 张青, 雷呈祥, 赵旭, 2003. 表皮葡萄球菌生物膜形成分子机制的研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 43(5):681-685. |
| ZHANG QING, LEI CHENGXIANG, ZHAO XU, 2003. Progress on molecular mechanism of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 43(5):681-685 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 张行, 李新圃, 杨峰, 等, 2020. 无乳链球菌研究进展[J]. 中国兽医学报, 40(4):864-872. |
| ZHANG XING, LI XINPU, YANG FENG, et al, 2020. Research progress of Streptococcus agalactiae[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 40(4):864-872 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 赵美霞, 余克服, 张乔民, 2006. 珊瑚礁区的生物多样性及其生态功能[J]. 生态学报, 26(1):186-194. |
| ZHAO MEIXIA, YU KEFU, ZHANG QIAOMIN, 2006. Review on coral reefs biodiversity and ecological function[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(1):186-194 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2020. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 37(2):175-223.
doi: 10.1039/C9NP00069K |
| [14] |
DING WEI, ZHANG WEIPENG, WANG RUOJUN, et al, 2019. Distribution, diversity and functional dissociation of the mac genes in marine biofilms[J]. Biofouling, 35(2):230-243.
doi: 10.1080/08927014.2019.1593384 |
| [15] |
JIN YECHENG, CHEN QIAN, LI XIANG, et al, 2014. Astragali Radix protects myocardium from ischemia injury by modulating energy metabolism[J]. International Journal of Cardiology, 176(3):1312-1315.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.07.154 |
| [16] |
KONG FANDONG, HUANG XIAOLONG, MA QINGYUN, et al, 2018. Helvolic acid derivatives with antibacterial activities against Streptococcus agalactiae from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus HNMF0047[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 81(8):1869-1876.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00382 |
| [17] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, LI M, et al, 2018. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35(6):1547-1549.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096 |
| [18] |
LIU SEN, WANG HAIBO, SU MINGZHI, et al, 2017. New metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii J05B-7F-4[J]. Natural Product Research, 31(14):1682-1686.
doi: 10.1080/14786419.2017.1289205 |
| [19] |
MELANDER R J, BASAK A K, MELANDER C, 2020. Natural products as inspiration for the development of bacterial antibiofilm agents[J]. Natural Product Reports, 37(11):1454-1477.
doi: 10.1039/D0NP00022A |
| [20] |
QIN XIAOYAN, YANG KAILIN, WANG CHANGYUN, et al, 2014. Secondary metabolites of the zoanthid-derived Fungus Trichoderma sp. TA26-28 collected from the South China Sea[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 50(5):961-964.
doi: 10.1007/s10600-014-1134-2 |
| [21] |
REN YAXIN, LUO HUIYING, HUANG HUOQING, et al, 2020. Improving the catalytic performance of Proteinase K from Parengyodontium album for use in feather degradation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 154:1586-1595.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.043 |
| [22] |
VON SALM J L, WITOWSKI C G, FLEEMAN R M, et al, 2016. Darwinolide, a new Diterpene Scaffold that inhibits Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm from the Antarctic Sponge Dendrilla membranosa[J]. Organic Letters, 18(11):2596-2599.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b00979 |
| [23] |
TSANG C C, CHAN J F W, PONG W M, et al, 2016. Cutaneous hyalohyphomycosis due to Parengyodontium album gen. et comb. nov.[J]. Medical Mycology, 54(7):699-713.
doi: 10.1093/mmy/myw025 |
| [24] |
ZHANG YAPENG, ZHU TIANJIAO, FANG YUCHUN, et al, 2007. Carbonarones A and B, new bioactive γ-pyrone and α-pyridone derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus carbonarius[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 60(2):153-157.
doi: 10.1038/ja.2007.15 |
| [1] | FENG Ting, SUN Jian, WANG Yufei, PAN Weibin, QIN Xucan, QIN Bingyun, ZHOU Liman, WANG Cong, WANG Pei, KONG Fandong. Study on the chemical constituents and pharmacological activity of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus DL-p0m-g2 in the Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 154-166. |
| [2] | GUO Yunxue, CAI Xingsheng, GU Jiayu, WANG Xiaoxue. Effects of polar and lateral flagella on biofilm formation in marine Pseudoalteromonas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 126-135. |
| [3] | CHENG Xiawen, ZHANG Lanlan, QIU Zhuoya, XIANG Rong, CHANG Hu. Biodiversity, biogeography and seasonal variation of zooplankton Collodarians (Radiolaria) in surface waters from the northern Indian Ocean to the South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 97-112. |
| [4] | WANG Zihan, ZENG Cong, JIANG Ziyu, CAO Ling. Conservation gap analysis of threatened fish in the East China Sea and adjacent sea areas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 66-86. |
| [5] | ZHU Xinyuan, LIU Min, HUANG Ying, ZHAO Zhe. Effects of the ferric enterobactin receptor regulator VPA0148 on virulence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 93-101. |
| [6] | Xinming LEI,Hui HUANG,Jiansheng LIAN,Laurence J MCCOOK. The diversity and distribution of coralline algae in China: state of knowledge and research [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 30-40. |
| [7] | DU Jian-guo, LIU Zheng-hua, YU Xing-guang, XU Zhang-cheng, HU Wen-jia, CHEN Bin, MA Zhi-yuan, LIN Jin-lan. Fish species diversity and trophic level in the Jiulong Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(6): 76-82. |
| [8] | LI Hai-ping ,YAN Qing-pi ,XU Xiao-jin ,SU Yong-quan ,QIN Ying-xue . Establishment of in vitro biofilm model and characteristics of biofilm formation of Vibrio harveyi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(3): 99-104. |
| [9] | KE Zhi-xin,HUANG Liang-min,TAN Ye-hui,YIN Jian-qiang. Species composition and abundance of phytoplankton in the northern South China Sea in summer 2007 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 131-143. |
|
||