Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 161-170.doi: 10.11978/2022240CSTR: 32234.14.2022240
• Exploitation of Marine Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on the steroids from the coculture of soft coral-associated fungi Aspergillus sp. EGF7-0-1 and EGF15-0-3
SITU Meixia1( ), LEI Zufa1, YANG Qianru2, DENG Shengyi1, WU Kejian2, CHEN Honghao2, WEI Xia1,3, FAN Hao1, ZHANG Wei2(
), LEI Zufa1, YANG Qianru2, DENG Shengyi1, WU Kejian2, CHEN Honghao2, WEI Xia1,3, FAN Hao1, ZHANG Wei2( ), ZHANG Cuixian1(
), ZHANG Cuixian1( )
)
- 1. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
2. The Middle School Attached to Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
3. Pharmaceutical college, Guangxi Medicinal University, Nanning 530021, China
-
Received:2022-11-08Revised:2022-12-06Online:2023-09-10Published:2022-12-08 -
Supported by:Special fund of Guangdong Provincial Department of Natural Resources for Promoting High-quality Economic Development (Marine Economic Development)(GDNRC[2021]48); Special fund of Guangdong Provincial Department of Natural Resources for Promoting High-quality Economic Development (Marine Economic Development)(GDNRC[2020]039); National Natural Science Foundation of China(82273845); National Natural Science Foundation of China(81741160); Guangzhou Youth Science and Technology Education Project(KP市2022027)
Cite this article
SITU Meixia, LEI Zufa, YANG Qianru, DENG Shengyi, WU Kejian, CHEN Honghao, WEI Xia, FAN Hao, ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Cuixian. Research on the steroids from the coculture of soft coral-associated fungi Aspergillus sp. EGF7-0-1 and EGF15-0-3[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 161-170.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Instruments and reagents used in the experiment"
| 仪器/试剂 | 型号/规格 | 品牌 |
|---|---|---|
| 高分辨液质联用仪 | Triple TOFTM 5600+ | 美国 AB SCIEX公司 |
| 核磁共振波谱仪 | 400 MHz AVANCE Ⅲ型 | 德国Bruker公司 |
| 高效液相色谱 | QuikSep半制备型 | 北京慧德易科技有限公司 |
| 自动旋光仪 | MCP 500 | 安东帕公司 |
| 紫外透射反射仪 | WFH-201B | 上海精科实业有限公司 |
| 超净工作台 | SW-CJ-1FD | 苏州净化设备厂 |
| 立式压力蒸汽灭菌器 | LS-100H | 江阴滨江医疗设备有限公司 |
| 电子天平 | PWN224ZH | 奥豪斯仪器(常州)有限制造公司 |
| 旋转蒸发器 | XHRE-2000A | 上海宵汉实业发展有限公司 |
| 低温冷却液循环泵 | XHDLSB-5/25 | 上海宵汉实业发展有限公司 |
| 色谱柱a: Luna 分析柱 | 4.6mm×100mm, 5μm | 美国Phenomenex公司 |
| 色谱柱b: YMC-Pack ODS-A半制备柱 | 10mm×250mm, 5μm | 日本YMC Co.,Ltd.公司 |
| 色谱柱c: H& EC18半制备柱 | 10mm×250mm, 5μm | 北京慧德易科技有限公司 |
| 常规柱层析硅胶 | 200~300目、300~400目 | 青岛海洋化工厂 |
| Sephadex LH-20 | YILIMART 500G | 瑞典 cytiva公司 |
| C-18反相色谱填料 | YMC*GEL ODS-A-HG | 日本 YMC公司 |
| 乙酸乙酯、石油醚、甲醇、乙腈、二氯甲烷、 三氯甲烷和正丁醇 | 分析纯 | 广东光华科技股份有限公司 |
| 氘代氯仿 | 25G | 美国剑桥CIT公司 |
| 葡萄糖 | 分析纯 | 天津致远化学试剂有限公司 |
| 技术琼脂粉 | 分析纯 | 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司 |
| 土豆、大米、海盐 | 购于市场 |
Tab. 2
1H NMR Data of 1~10 in CDCl3"
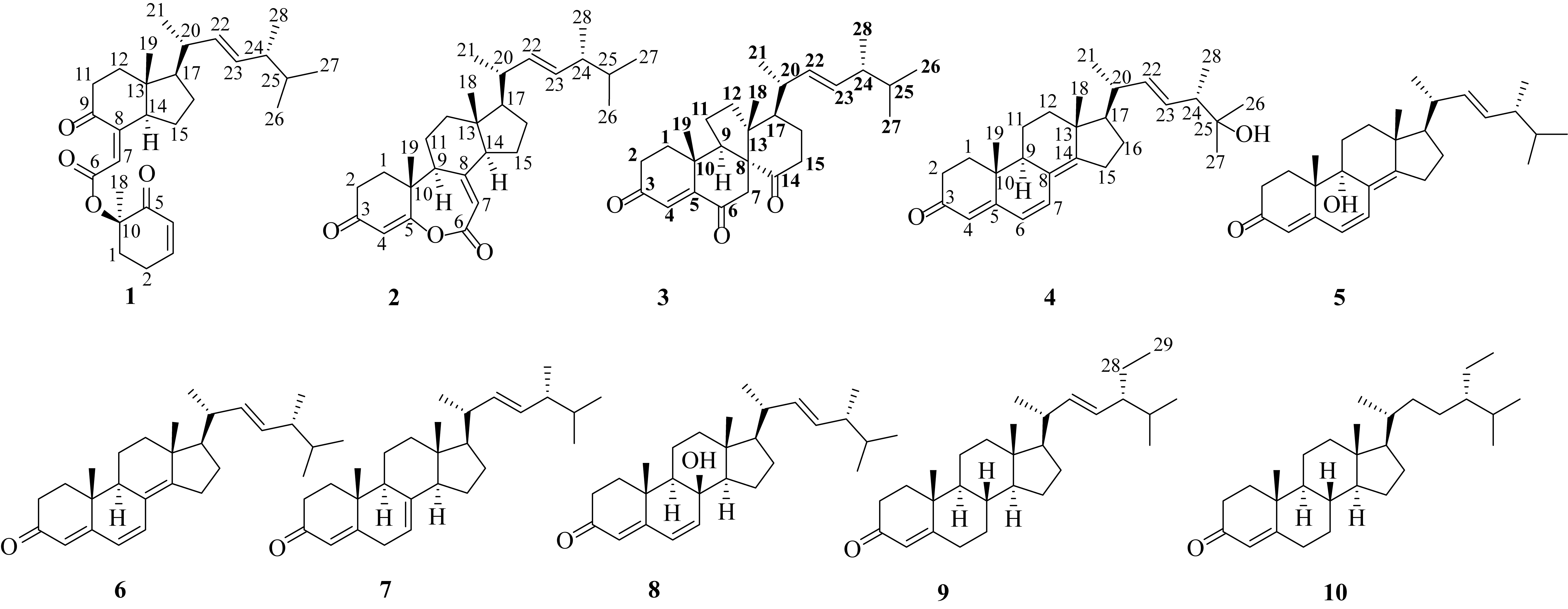
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 6.03, d, 10.1 | 5.74, s | 6.36, s | 5.74, s | 5.88, s |
| 6 | 6.04, d, 9.5 | 6.12, d, 9.6 | |||
| 7 | 5.64, d, 2.4 | 5.72, s | 2.65, dd, 16.9, 1.5 | 6.60, d, 9.5 | 6.49, d, 9.6 |
| 9 | 2.81, t, 9.1 | ||||
| 18 | 0.87, s | 0.63, s | 0.98, s | 0.96, s | 0.96, s |
| 19 | 1.47, s | 1.23, s | 1.26, s | 0.99, s | 1.11, s |
| 21 | 1.02, d, 6.6 | 1.02, d, 6.6 | 1.09, d, 7.1 | 1.08, d, 6.7 | 1.08, d, 6.7 |
| 22 | 5.14, dd, 15.3, 8.4 | 5.14, dd, 15.3, 8.4 | 5.24, dd, 15.2, 6.0 | 5.34, dd, 15.2, 7.6 | 5.20, dd, 15.3, 7.9 |
| 23 | 5.26, dd, 15.3, 7.7 | 5.25, dd, 15.2, 7.6 | 5.28, d, 15.2, 6.1 | 5.39, dd, 15.2, 7.8 | 5.27, dd, 15.3, 7.2 |
| 26 | 0.84, d, 6.8 | 0.82, d, 6.8 | 0.81, d, 6.8 | 1.14, s | 0.83, d, 6.8 |
| 27 | 0.82, d, 6.8 | 0.82, d, 6.8 | 0.83, d, 6.8 | 1.17, s | 0.85, d, 6.8 |
| 28 | 0.91, d, 6.8 | 0.91, d, 6.8 | 0.91, d, 6.8 | 1.01, d, 6.7 | 0.93, d, 6.9 |
| No. | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 4 | 5.73, s | 5.79, d, 2.0 | 5.72, s | 5.72, s | 5.71, s |
| 6 | 6.03, d, 9.5 | 6.09, d, 9.6 | |||
| 7 | 6.61, d, 9.5 | 6.16, d, 9.6 | |||
| 18 | 0.96, s | 0.60, s | 1.02, s | 0.73, s | 0.70, s |
| 19 | 0.99, s | 1.17, s | 1.32, s | 1.18, s | 1.17, s |
| 21 | 1.06, d, 6.7 | 1.03, d, 6.6 | 0.99, d, 6.6 | 1.02, d, 6.6 | .91, d, 6.5 |
| 22 | 5.26, dd, 15.2,7.1 | 5.16, dd, 15.2, 7.7 | 5.12, dd, 15.3, 8.2 | 5.15, dd, 15.2, 8.5 | |
| 23 | 5.20, dd, 15.2,7.8 | 5.23, dd, 15.2, 6.9 | 5.22, dd, 15.3, 7.6 | 5.02, dd, 15.2, 8.5 | |
| 26 | 0.83, d, 6.8 | 0.82, d, 6.5 | 0.82, d, 6.8 | 0.84, d, 6.3 | 0.83, d, 6.8 |
| 27 | 0.85, d, 6.8 | 0.84, d, 6.5 | 0.83, d, 6.8 | 0.79, d, 6.3 | 0.82, d, 6.8 |
| 28 | 0.93, d, 6.9 | 0.91, d, 6.5 | 0.91, d, 6.8 | ||
| 29 | 0.80, t, 7.3 | 0.84, t, 7.3 |
Tab. 3
13C NMR Data of 1~10 in CDCl3"
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32.1, t | 33.9, t | 39.0, t | 34.1, t | 27.6, t | 34.3, t | 33.2, t | 35.2, t | 35.7, t | 35.7, t |
| 2 | 24.8, t | 33.2, t | 34.5, t | 34.1, t | 34.0, t | 34.3, t | 34.3, t | 33.8, t | 34.0, t | 32.1, t |
| 3 | 148.8, d | 198.4, s | 199.3, s | 199.7, s | 199.5, s | 199.7, t | 199.6, s | 199.9, s | 199.7, s | 199.8, s |
| 4 | 128.1, d | 114.7, d | 126.7, d | 123.2, d | 126.4, d | 123.1, d | 122.8, d | 125.3, d | 123.8, d | 123.7, d |
| 5 | 195.8, s | 173.9, s | 156.2, s | 124.7, s | 161.4, s | 124.6, s | 169.2, s | 163.5, s | 171.7, s | 171.9, s |
| 6 | 164.3, d | 162.4, s | 200.2, s | 124.7, d | 124.8, d | 124.6, d | 33.2, t | 128.2, d | 33.0, t | 33.0, t |
| 7 | 117.5, d | 113.3, d | 41.0, t | 134.1, d | 130.9, d | 134.2, d | 115.7, d | 139.4, d | 32.0, t | 33.9, t |
| 8 | 156.2, s | 159.5, s | 62.3, s | 164.5, s | 126.7, s | 164.5, s | 139.7, s | 71.9, s | 35.6, d | 35.6, d |
| 9 | 204.6, s | 47.2, d | 49.5, d | 44.5, d | 72.6, s | 44.5, d | 45.9, d | 53.3, d | 53.8, d | 53.8, d |
| 10 | 81.2, s | 40.4, s | 36.1, s | 36.9, s | 42.4, s | 36.9, s | 38.2, s | 36.3, s | 38.6, s | 38.7, s |
| 11 | 39.0, t | 25.4, t | 25.3, t | 19.0, t | 25.5, t | 19.1, t | 22.1, t | 18.0, t | 21.0, t | 21.0, t |
| 12 | 38.0, t | 39.1, t | 38.5, t | 35.6, t | 32.1, t | 35.7, t | 39.1, t | 40.9, t | 39.5, t | 39.4, t |
| 13 | 46.5, s | 47.0, s | 54.1, s | 44.2, s | 44.6, s | 44.1, s | 43.5, s | 44.2, s | 42.3, s | 42.5, s |
| 14 | 57.9, d | 58.1, d | 215.0, s | 155.7, s | 158.3, s | 156.3, s | 55.1, d | 57.2, d | 56.0, d | 56.0, d |
| 15 | 21.9, t | 22.6, t | 38.1, t | 25.3, t | 25.7, t | 25.5, t | 23.0, t | 19.1, t | 24.3, t | 24.2, t |
| 16 | 29.1, t | 27.7, t | 23.3, t | 27.7, t | 27.8, t | 27.9, t | 28.2, t | 28.2, t | 28.9, t | 28.2, t |
| 17 | 55.3, d | 56.3, d | 49.5, d | 55.6, d | 55.7, d | 55.8, d | 55.9, d | 56.6, d | 55.9, d | 55.9, d |
| 18 | 12.1, q | 12.5, q | 17.2, q | 19.1, q | 17.9, q | 19.1, q | 12.3, s | 14.6, q | 12.2, q | 12.0, s |
| 19 | 21.9, q | 20.0, q | 24.2, q | 16.8, q | 20.9, q | 16.8, q | 21.4, q | 19.0, q | 17.4, q | 19.0, s |
| 20 | 40.1, d | 40.2, d | 37.4, d | 39.5, d | 39.3, d | 39.4, d | 40.6, d | 39.9, d | 40.5, d | 36.1, d |
| 21 | 21.0, q | 21.0, q | 23.8, q | 21.2, q | 21.3, q | 21.4, q | 21.2, q | 20.7, q | 19.0, q | 18.7, q |
| 22 | 134.6, d | 134.7, d | 132.5, d | 138.4, d | 134.9, d | 135.2, d | 135.6, d | 135.4, d | 138.1, d | 34.0, t |
| 23 | 132.9, d | 132.8, d | 135.3, d | 129.9, d | 132.9, d | 132.7, d | 132.4, d | 132.3, d | 129.5, d | 29.1, t |
| 24 | 42.8, d | 42.8, d | 43.4, d | 48.3, d | 43.0, d | 43.0, d | 42.9, d | 43.0, d | 51.2, d | 45.8, d |
| 25 | 33.0, d | 33.1, d | 33.2, d | 72.5, s | 33.2, d | 33.2, d | 33.0, d | 33.2, d | 31.9, d | 26.1, d |
| 26 | 19.7, q | 20.0, q | 19.8, q | 27.1, q | 19.8, q | 20.1, q | 20.1, q | 19.8, q | 21.2, q | 17.4, q |
| 27 | 20.0, q | 19.6, q | 20.2, q | 26.6, q | 20.1, q | 19.8, q | 19.8, q | 20.1, q | 21.1, q | 19.8, q |
| 28 | 17.6, q | 17.6, q | 17.1, q | 15.8, q | 17.8, q | 17.8, q | 17.7, q | 17.8, q | 25.4, t | 23.1, t |
| 29 | 12.3, q | 12.0, q |
| [1] |
蔡金旋, 冯冉奇, 韦霞, 等, 2022. 两株软珊瑚共附生曲霉属真菌 EGF7-0-1和EGF15-0-3共培养中杂萜类成分研究[J]. 中国海洋药物, 41(4): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
黎咏怡, 蔡金旋, 方越, 等, 2022. 南海软珊瑚共附生真菌 Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3中色酮、蒽醌及其二聚体类化合物[J]. 中山大学学报, (4): 70-78.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
刘炳新, 韦霞, 肖细姬, 等, 2021. 南海软珊瑚共附生真菌 Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3苯甲醛类化合物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(4): 63-69.
doi: 10.11978/2020085 |
|
|
|
| [4] |
肖细姬, 邓芸, 谢路凤, 等, 2019. 柳珊瑚 Leptogorgia rigida中甾体类成分研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(4): 64-69.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1021/np070165m |
| [6] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms150610926 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0812 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2009.09.064 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1021/np000315s |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1002/jcb.27853 pmid: 30548286 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00180 pmid: 31999123 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1248/cpb.52.1005 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03724 pmid: 28121455 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03557 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1021/np980422a |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules191221378 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00170 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1038/s41429-019-0242-4 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03863 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1080/14786419.2016.1258559 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31551-4 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1021/np50071a019 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.05.068 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw035 pmid: 27576366 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1080/14786410701642706 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b00539 |
| [29] |
doi: S0039-128X(18)30015-1 pmid: 29360535 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1002/acn3.408 pmid: 28589168 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1007/s10600-015-1531-1 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03795 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1271/bbb.100918 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [1] | SUN Manman, ZENG Yanbo, XU Han, YAO Ligong, GUO Yuewei, SU Mingzhi. Chemical composition and antibacterial activities of the soft coral Lobophytum sp. from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 189-197. |
| [2] | GAO Yaxin, WANG Hao, DAI Haofu, XIA Zhihui, ZENG Yanbo. Cytotoxic steroids from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis collected off the Xisha [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 56-63. |
| [3] | FAN Hao, HE Jiahong, WEI Xia, CHEN Leyi, CHEN Xinqi, ZHANG Cuixain. Phenolic acids from soft coral-associated symbiotic and epiphytic fungi Aspergillus sp. EGF7-0-1 (Ⅱ) [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 171-177. |
| [4] | YU Qiang, DONG Xianxian, LI Changqing, ZHANG Xin, ZHAO Guoli, CHIN Yaoxian, WANG Peizheng. Physiological responses of two soft corals to herbicide acetochlor stress [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 133-145. |
| [5] | ZHANG Han, TAN Yanhong, YANG Bin, LIU Yonghong, LI Yunqiu. Study on the secondary metabolites from the South China Sea soft coral-derived fungus Acremonium sp. SCSIO41216 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 135-139. |
| [6] | LIU Bingxin, WEI Xia, XIAO Xiji, ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Cuixian. Research on benzaldehydes from the soft coral-associated symbiotic fungus Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 63-69. |
| [7] | Yubin JI,Zhe ZHANG,Weihao ZHANG,Hu WANG,Ying PAN,Wei JIANG. QSI activity-oriented isolation of metabolites from Fusarium solanum [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 98-103. |
| [8] | Yanhong TAN, Jixing LI, Xiuping LIN, Bin YANG, Yonghong LIU, Yunqiu LI. Study on the secondary metabolites from the South China Sea soft coral-derived fungus Eupenicillium sp. DX-SER3 (KC871024) [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 43-47. |
| [9] | CHAI Xing-yun,HU Jing,HUANG Hui,LEI Hui,CHEN Xian-qiang,LI Yun-qiu,SUN Jia. Pregnane steroids from a gorgonian Menella sp. in South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 127-130. |
| [10] | QI Xin,HUANG Hai,ZHOU Wen-yi,YIN Shao-wu,ZHANG Yong,LIU Xiao-chun,. Variations in sex steroid hormone level and changes in ultrastructure of related cells during the artificial maturation of spermary of Anguilla marmorata [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(6): 130-136. |
|
||