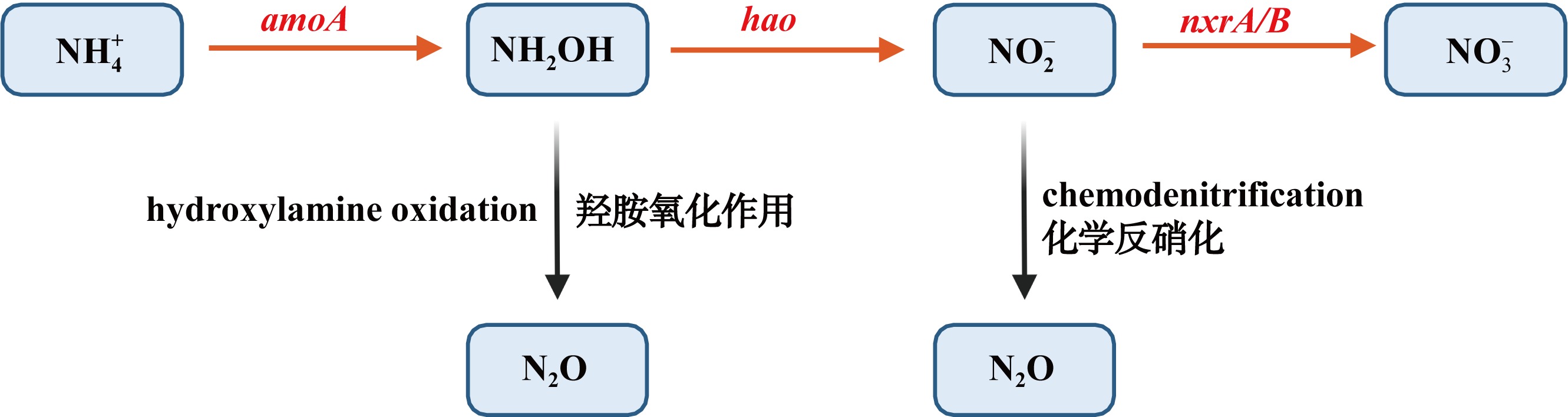
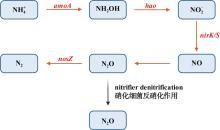
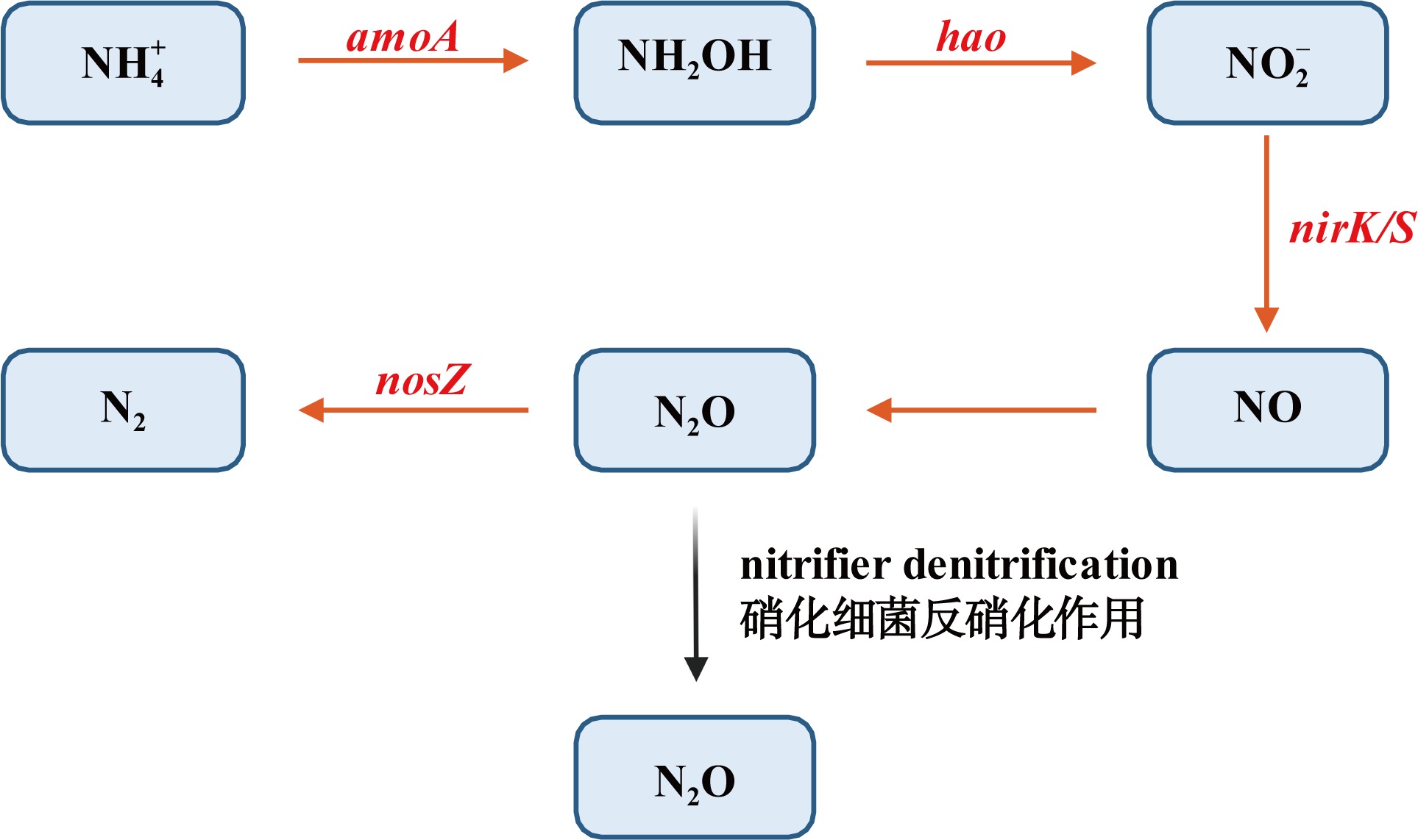
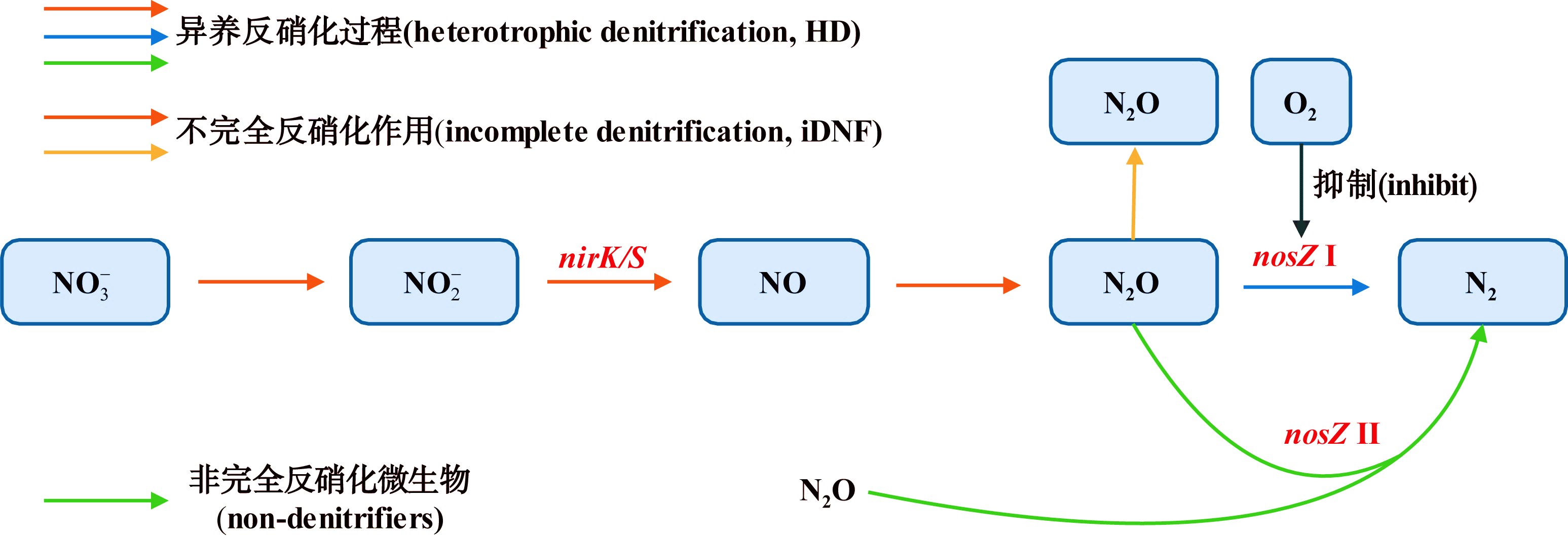
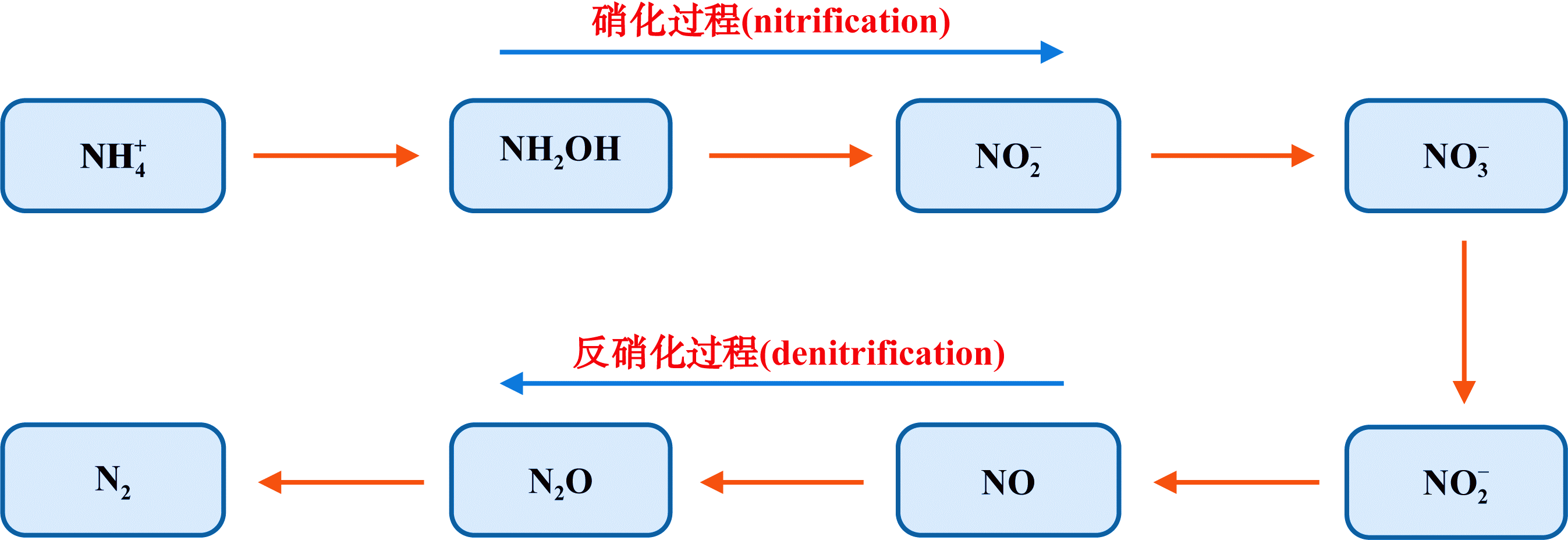
| [1] |
陈玲, 白洁, 赵阳国, 等, 2016. 分离于河口区芦苇湿地1株好氧反硝化菌的鉴定及其反硝化特性[J]. 微生物学报, 56(8): 1314-1325.
|
|
CHEN LING, BAI JIE, ZHAO YANGGUO, et al, 2016. Identification and denitrification characteristics of an aerobic denitrifier in estuary Phragmites wetland[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 56(8): 1314-1325 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
丁吾举, 陆菲雨, 赵博, 等, 2024. 氮周期供给时潜流带沉积物硝化、反硝化动力学[J]. 地球科学, 49(10): 3712-3722.
|
|
DING WUJU, LU FEIYU, ZHAO BO, et al, 2024. Kinetics of nitrification and denitrification in hyporheic zone sediment with periodical supply of nitrogen[J]. Earth Science, 49(10): 3712-3722 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
洪义国, 胡耀豪, 刘晓晗, 等, 2020. 海洋N2O的排放及其关键微生物过程作用机制研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 60(9): 1852-1864.
|
|
HONG YIGUO, HU YAOHAO, LIU XIAOHAN, et al, 2020. N2O emission and related microbial mechanism in the ocean[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 60(9): 1852-1864 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
李冀, 朱莹, 张晓君, 2017. 非典型氧化亚氮还原酶基因nosZ Ⅱ研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 44(7): 1714-1719.
|
|
LI JI, ZHU YING, ZHANG XIAOJUN, 2017. Researches on the atypical nitrous oxide reductase[J]. Microbiology China, 44(7): 1714-1719 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
ABELL G C J, REVILL A T, SMITH C, et al, 2010. Archaeal ammonia oxidizers and nirS-type denitrifiers dominate sediment nitrifying and denitrifying populations in a subtropical macrotidal estuary[J]. The ISME Journal, 4(2): 286-300.
|
| [6] |
ADAMS C A, ANDREWS J E, JICKELLS T, 2012. Nitrous oxide and methane fluxes vs. carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous burial in new intertidal and saltmarsh sediments[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 434: 240-251.
|
| [7] |
ARÉVALO-MARTÍNEZ D L, KOCK A, LÖSCHER C R, et al, 2015. Massive nitrous oxide emissions from the tropical South Pacific Ocean[J]. Nature Geoscience, 8(7): 530-533.
|
| [8] |
BABBIN A R, BIANCHI D, JAYAKUMAR A, et al, 2015. Nitrogen cycling. Rapid nitrous oxide cycling in the suboxic ocean[J]. Science, 348(6239): 1127-1129.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaa8380
pmid: 26045434
|
| [9] |
BAGGS E M, SMALES C L, BATEMAN E J, 2010. Changing pH shifts the microbial source as well as the magnitude of N2O emission from soil[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 46(8): 793-805.
|
| [10] |
BANGE H W, RAPSOMANIKIS S, ANDREAE M O, 1996. Nitrous oxide emissions from the Arabian Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 23(22): 3175-3178.
|
| [11] |
BANGE H W, RAPSOMANIKIS S, ANDREAE M O, 2001. Nitrous oxide cycling in the Arabian sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 106(C1): 1053-1065.
|
| [12] |
BARNES J, OWENS N J P, 1999. Denitrification and nitrous oxide concentrations in the Humber Estuary, UK, and adjacent coastal zones[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 37(3-7): 247-260.
|
| [13] |
BARNES J, UPSTILL-GODDARD R C, 2011. N2O seasonal distributions and air-sea exchange in UK estuaries: Implications for the tropospheric N2O source from European coastal waters[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 116(G1): G01006.
|
| [14] |
BERG P, KLEMEDTSSON L, ROSSWALL T, 1982. Inhibitory effect of low partial pressures of acetylene on nitrification[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 14(3): 301-303.
|
| [15] |
BIANCHI D, WEBER T S, KIKO R, et al, 2018. Global niche of marine anaerobic metabolisms expanded by particle microenvironments[J]. Nature Geoscience, 11(4): 263-268.
|
| [16] |
BORE E K, TURUNEN P, SIETIÖ O M, et al, 2024. Plant phenology modulates and undersown cover crops mitigate N2O emissions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 198: 109548.
|
| [17] |
BOWEN H, MAUL J E, CAVIGELLI M A, et al, 2020. Denitrifier abundance and community composition linked to denitrification activity in an agricultural and wetland soil[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 151: 103521.
|
| [18] |
BUTTERBACH-BAHL K, BAGGS E M, DANNENMANN M, et al, 2013. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: how well do we understand the processes and their controls[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 368(1621): 20130122.
|
| [19] |
CARANTO J D, LANCASTER K M, 2017. Nitric oxide is an obligate bacterial nitrification intermediate produced by hydroxylamine oxidoreductase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(31): 8217-8222.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704504114
pmid: 28716929
|
| [20] |
CARRASCO C, KARSTENSEN J, FARIAS L, 2017. On the nitrous oxide accumulation in intermediate waters of the eastern south Pacific Ocean[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 4: 24.
|
| [21] |
CHEN HUAI, WANG MENG, WU NING, et al, 2011. Nitrous oxide fluxes from the littoral zone of a lake on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 182(1-4): 545-553.
doi: 10.1007/s10661-011-1896-y
pmid: 21327481
|
| [22] |
CHENG XIANG, DONG YUE, FAN FUQIANG, et al, 2023. Shifts in the high-resolution spatial distribution of dissolved N2O and the underlying microbial communities and processes in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Water Research, 243: 120351.
|
| [23] |
CODISPOTI L A, 2010. Interesting times for marine N2O[J]. Science, 327(5971): 1339-1340.
|
| [24] |
COHEN Y, GORDON L I, 1979. Nitrous oxide production in the ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 84(C1): 347-353.
|
| [25] |
CRUTZEN P J, 1970. The influence of nitrogen oxides on the atmospheric ozone content[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 96(408): 320-325.
|
| [26] |
DAI M, WANG L, GUO X, et al, 2008. Nitrification and inorganic nitrogen distribution in a large perturbed river/estuarine system: the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Biogeosciences, 5(5): 1227-1244.
|
| [27] |
DOMEIGNOZ-HORTA L A, PUTZ M, SPOR A, et al, 2016. Non-denitrifying nitrous oxide-reducing bacteria - An effective N2O sink in soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 103: 376-379.
|
| [28] |
DOMEIGNOZ-HORTA L A, SPOR A, BRU D, et al, 2015. The diversity of the N2O reducers matters for the N2O: N2 denitrification end-product ratio across an annual and a perennial cropping system[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6: 971.
|
| [29] |
DONEY S C, 2010. The growing human footprint on coastal and open-ocean biogeochemistry[J]. Science, 328(5985): 1512-1516.
doi: 10.1126/science.1185198
pmid: 20558706
|
| [30] |
DONG L F, NEDWELL D B, STOTT A, 2006. Sources of nitrogen used for denitrification and nitrous oxide formation in sediments of the hypernutrified Colne, the nutrified Humber, and the oligotrophic Conwy estuaries, United Kingdom[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(1part2): 545-557.
|
| [31] |
FRAME C H, CASCIOTTI K L, 2010. Biogeochemical controls and isotopic signatures of nitrous oxide production by a marine ammonia-oxidizing bacterium[J]. Biogeosciences, 7(9): 2695-2709.
|
| [32] |
FREING A, WALLACE D W R, BANGE H W, 2012. Global oceanic production of nitrous oxide[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 367(1593): 1245-1255.
|
| [33] |
FU GUIPING, ZHAO LIN, HUANGSHEN LINKUN, et al, 2019. Isolation and identification of a salt-tolerant aerobic denitrifying bacterial strain and its application to saline wastewater treatment in constructed wetlands[J]. Bioresource Technology, 290: 121725.
|
| [34] |
GRAF D R H, JONES C M, HALLIN S, 2014. Intergenomic comparisons highlight modularity of the denitrification pathway and underpin the importance of community structure for N2O emissions[J]. PLoS One, 9(12): e114118.
|
| [35] |
GRANGER P, DHAINAUT F, PIETRZIK S, et al, 2006. An overview: Comparative kinetic behaviour of Pt, Rh and Pd in the NO + CO and NO + H2 reactions[J]. Topics in Catalysis, 39(1): 65-76.
|
| [36] |
GRUBER N, GALLOWAY J N, 2008. An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle[J]. Nature, 451(7176): 293-296.
|
| [37] |
HALLIN S, PHILIPPOT L, LÖFFLER F E, et al, 2018. Genomics and ecology of novel N2O-reducing microorganisms[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 26(1): 43-55.
|
| [38] |
HAN BINGBING, YAO YANZHONG, LIU BIN, et al, 2024. Relative importance between nitrification and denitrification to N2O from a global perspective[J]. Global Change Biology, 30(1): e17082.
|
| [39] |
HARTMANN A A, BARNARD R L, MARHAN S, et al, 2013. Effects of drought and N-fertilization on N cycling in two grassland soils[J]. Oecologia, 171(3): 705-717.
doi: 10.1007/s00442-012-2578-3
pmid: 23297047
|
| [40] |
HINK L, NICOL G W, PROSSER J I, 2017. Archaea produce lower yields of N2O than bacteria during aerobic ammonia oxidation in soil[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 19(12): 4829-4837.
|
| [41] |
HOWARTH R, PAERL H W, 2008. Coastal marine eutrophication: Control of both nitrogen and phosphorus is necessary[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(49): E103.
|
| [42] |
HSU T C, KAO S J, 2013. Technical Note: Simultaneous measurement of sedimentary N2 and N2O production and a modified 15N isotope pairing technique[J]. Biogeosciences, 10(12): 7847-7862.
|
| [43] |
HU HANGWEI, CHEN DELI, HE JIZHENG, 2015. Microbial regulation of terrestrial nitrous oxide formation: understanding the biological pathways for prediction of emission rates[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 39(5): 729-749.
|
| [44] |
HU YAOHAO, WU JIAPENG, YE JIAQI, et al, 2023. The imbalance between N2O production and reduction by multi-microbial communities determines sedimentary N2O emission potential in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 190: 106119.
|
| [45] |
HYNES R K, KNOWLES R, 1978. Inhibition by acetylene of ammonia oxidation in Nitrosomonas europaea[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 4(6): 319-321.
|
| [46] |
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2013. Climate Change 2013:The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[R]. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press.
|
| [47] |
JI BIN, YANG KAI, ZHU LEI, et al, 2015a. Aerobic denitrification: a review of important advances of the last 30 years[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 20(4): 643-651.
|
| [48] |
JI QIXING, BABBIN A R, JAYAKUMAR A, et al, 2015b. Nitrous oxide production by nitrification and denitrification in the Eastern Tropical South Pacific oxygen minimum zone[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(24): 10755-10764.
|
| [49] |
JONES C M, GRAF D R H, BRU D, et al, 2013. The unaccounted yet abundant nitrous oxide-reducing microbial community: a potential nitrous oxide sink[J]. The ISME Journal, 7(2): 417-426.
|
| [50] |
JONES C M, HALLIN S, 2010. Ecological and evolutionary factors underlying global and local assembly of denitrifier communities[J]. The ISME Journal, 4(5): 633-641.
|
| [51] |
JONES C M, SPOR A, BRENNAN F P, et al, 2014. Recently identified microbial guild mediates soil N2O sink capacity[J]. Nature Climate Change, 4(9): 801-805.
|
| [52] |
KAN CHEN, WANG FEIFEI, XIANG TAO, et al, 2024. Wastewater treatment plant effluents increase the global warming potential in a subtropical urbanized river[J]. Water Research, 266: 122349.
|
| [53] |
KHALIL K, MARY B, RENAULT P, 2004. Nitrous oxide production by nitrification and denitrification in soil aggregates as affected by O2 concentration[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36(4): 687-699.
|
| [54] |
KITS K D, JUNG M Y, VIERHEILIG J, et al, 2019. Low yield and abiotic origin of N2O formed by the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata[J]. Nature Communications, 10(1): 1836.
|
| [55] |
KOOL D M, MÜLLER C, WRAGE N, et al, 2009. Oxygen exchange between nitrogen oxides and H2O can occur during nitrifier pathways[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41(8): 1632-1641.
|
| [56] |
KOOL D M, WRAGE N, ZECHMEISTER-BOLTENSTERN S, et al, 2010. Nitrifier denitrification can be a source of N2O from soil: a revised approach to the dual-isotope labelling method[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 61(5): 759-772.
|
| [57] |
KOZLOWSKI J A, PRICE J, STEIN L Y, 2014. Revision of N2O-producing pathways in the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea ATCC 19718[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80(16): 4930-4935.
|
| [58] |
KOZLOWSKI J A, STIEGLMEIER M, SCHLEPER C, et al, 2016. Pathways and key intermediates required for obligate aerobic ammonia-dependent chemolithotrophy in bacteria and Thaumarchaeota[J]. The ISME Journal, 10(8): 1836-1845.
|
| [59] |
KUYPERS M M M, MARCHANT H K, KARTAL B, 2018. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(5): 263-276.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2018.9
pmid: 29398704
|
| [60] |
LEE J A, FRANCIS C A, 2017. Spatiotemporal characterization of San Francisco Bay denitrifying communities: a comparison of nirK and nirS diversity and abundance[J]. Microbial Ecology, 73(2): 271-284.
|
| [61] |
LI KAI, FANG FANG, WANG HAN, et al, 2017. Pathways of N removal and N2O emission from a one-stage autotrophic N removal process under anaerobic conditions[J]. Scientific Reports, 7: 42072.
|
| [62] |
LIN JIAN, LI LIN, PAN XIAOLI, et al, 2016. Catalytic decomposition of propellant N2O over Ir/Al2O3 catalyst[J]. AIChE Journal, 62(11): 3973-3981.
|
| [63] |
LIU YAN, TANG RUOLAN, LIU GUOLIANG, et al, 2024. Dicyandiamide addition delay nitrous oxide emission and shift its production pathway from denitrification to incomplete nitrification in maturation phase of composting[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 495: 153225.
|
| [64] |
LÖSCHER C R, KOCK A, KÖNNEKE M, et al, 2012. Production of oceanic nitrous oxide by ammonia-oxidizing archaea[J]. Biogeosciences, 9(7): 2419-2429.
|
| [65] |
MONTZKA S A, DLUGOKENCKY E J, BUTLER J H, 2011. Non-CO2 greenhouse gases and climate change[J]. Nature, 476(7358): 43-50.
|
| [66] |
MORENO-VIVIÁN C, CABELLO P, MARTÍNEZ-LUQUE M, et al, 1999. Prokaryotic nitrate reduction: molecular properties and functional distinction among bacterial nitrate reductases[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 181(21): 6573-6584.
|
| [67] |
MOSIER A C, FRANCIS C A, 2010. Denitrifier abundance and activity across the San Francisco Bay estuary[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2(5): 667-676.
doi: 10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00156.x
pmid: 23766254
|
| [68] |
MUÑOZ-HINCAPIÉ M, MORELL J M, CORREDOR J E, 2002. Increase of nitrous oxide flux to the atmosphere upon nitrogen addition to red mangroves sediments[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44(10): 992-996.
|
| [69] |
MURRAY R H, ERLER D V, EYRE B D, 2015. Nitrous oxide fluxes in estuarine environments: response to global change[J]. Global Change Biology, 21(9): 3219-3245.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.12923
pmid: 25752934
|
| [70] |
NAQVI S W A, BANGE H W, FARÍAS L, et al, 2010. Marine hypoxia/anoxia as a source of CH4 and N2O[J]. Biogeosciences, 7(7): 2159-2190.
|
| [71] |
NEVISON C D, LUEKER T J, WEISS R F, 2004. Quantifying the nitrous oxide source from coastal upwelling[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 18(1): GB1018.
|
| [72] |
NEVISON C D, WEISS R F, 1995. Global oceanic emissions of nitrous oxide[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 100(C8): 15809-15820.
|
| [73] |
PHILIPPOT L, ANDERT J, JONES C M, et al, 2011. Importance of denitrifiers lacking the genes encoding the nitrous oxide reductase for N2O emissions from soil[J]. Global Change Biology, 17(3): 1497-1504.
|
| [74] |
PUNSHON S, MOORE R M, 2004. Nitrous oxide production and consumption in a eutrophic coastal embayment[J]. Marine Chemistry, 91(1-4): 37-51.
|
| [75] |
QIN SHUPING, PANG YAXING, HU HUIXIAN, et al, 2024. Foliar N2O emissions constitute a significant source to atmosphere[J]. Global Change Biology, 30(2): e17181.
|
| [76] |
QUICK A M, JEFFERY REEDER W, FARRELL T B, et al, 2016. Controls on nitrous oxide emissions from the hyporheic zones of streams[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(21): 11491-11500.
|
| [77] |
QUICK A M, REEDER W J, FARRELL T B, et al, 2019. Nitrous oxide from streams and rivers: A review of primary biogeochemical pathways and environmental variables[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 191: 224-262.
|
| [78] |
RAVISHANKARA A R, DANIEL J S, PORTMANN R W, 2009. Nitrous oxide (N2O): The dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century[J]. Science, 326(5949): 123-125.
doi: 10.1126/science.1176985
pmid: 19713491
|
| [79] |
ROBERTSON L A, KUENEN J G, 1984. Aerobic denitrification—old wine in new bottles[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 50(5/6): 525-544.
|
| [80] |
ROSAMOND M S, THUSS S J, SCHIFF S L, 2012. Dependence of riverine nitrous oxide emissions on dissolved oxygen levels[J]. Nature Geoscience, 5(10): 715-718.
|
| [81] |
SAARENHEIMO J, RISSANEN A J, ARVOLA L, et al, 2015. Genetic and environmental controls on nitrous oxide accumulation in lakes[J]. PLoS One, 10(3): e0121201.
|
| [82] |
SANFORD R A, WAGNER D D, WU QINGZHONG, et al, 2012. Unexpected nondenitrifier nitrous oxide reductase gene diversity and abundance in soils[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(48): 19709-19714.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211238109
pmid: 23150571
|
| [83] |
SANTORO A E, BUCHWALD C, MCILVIN M R, et al, 2011. Isotopic signature of N2O produced by marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea[J]. Science, 333(6047): 1282-1285.
|
| [84] |
SEITZINGER S P, KROEZE C, 1998. Global distribution of nitrous oxide production and N inputs in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 12(1): 93-113.
|
| [85] |
SHAW L J, NICOL G W, SMITH Z, et al, 2006. Nitrosospira spp. can produce nitrous oxide via a nitrifier denitrification pathway[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 8(2): 214-222.
|
| [86] |
SHI XIUZHEN, HU HANGWEI, ZHU-BARKER X, et al, 2017. Nitrifier-induced denitrification is an important source of soil nitrous oxide and can be inhibited by a nitrification inhibitor 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 19(12): 4851-4865.
|
| [87] |
SHOUN H, TANIMOTO T, 1991. Denitrification by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum and involvement of cytochrome P-450 in the respiratory nitrite reduction[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 266(17): 11078-11082.
|
| [88] |
SOLOMON S, QIN D, MANNING M R, et al, 2007. Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. contribution of working Group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. summary for policymakers[R]. Geneva: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
|
| [89] |
STEIN L, 2011. Surveying N2O-producing pathways in bacteria[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 486: 131-152.
doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381294-0.00006-7
pmid: 21185434
|
| [90] |
SUN LIN, SHEWA W A, BOSSY K, et al, 2024. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification framework for decentralized systems: Long-term study utilizing rope-type biofilm media under field conditions[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 956: 177337.
|
| [91] |
TAKAYA N, CATALAN-SAKAIRI M A B, SAKAGUCHI Y, et al, 2003. Aerobic denitrifying bacteria that produce low levels of nitrous oxide[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(6): 3152-3157.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.6.3152-3157.2003
pmid: 12788710
|
| [92] |
TAN EHUI, ZOU WENBIN, ZHENG ZHENZHEN, et al, 2020. Warming stimulates sediment denitrification at the expense of anaerobic ammonium oxidation[J]. Nature Climate Change, 10(4): 349-355.
|
| [93] |
TEIXEIRA E I, FISCHER G, VAN VELTHUIZEN H, et al, 2013. Global hot-spots of heat stress on agricultural crops due to climate change[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 170: 206-215.
|
| [94] |
TIAN HANQIN, XU RONGTING, CANADELL J G, et al, 2020. A comprehensive quantification of global nitrous oxide sources and sinks[J]. Nature, 586(7828): 248-256.
|
| [95] |
VITOUSEK P M, ABER J D, HOWARTH R W, et al, 1997. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences[J]. Ecological Applications, 7(3): 737-750.
|
| [96] |
WAN XIANHUI S, SHENG HUAXIA, LIU LI, et al, 2023. Particle-associated denitrification is the primary source of N2O in oxic coastal waters[J]. Nature Communications, 14(1): 8280.
|
| [97] |
WANG SHUO, LI SHENGJIE, JI MINGFEI, et al, 2024. Long-neglected contribution of nitrification to N2O emissions in the Yellow River[J]. Environmental Pollution, 351: 124099.
|
| [98] |
WANKEL S D, ZIEBIS W, BUCHWALD C, et al, 2017. Evidence for fungal and chemodenitrification based N2O flux from nitrogen impacted coastal sediments[J]. Nature Communications, 8: 15595.
|
| [99] |
WARD B B, DEVOL A H, RICH J J, et al, 2009. Denitrification as the dominant nitrogen loss process in the Arabian Sea[J]. Nature, 461(7260): 78-81.
|
| [100] |
WONG WEI WEN, LEHMANN M F, KUHN T, et al, 2021. Nitrogen and oxygen isotopomeric constraints on the sources of nitrous oxide and the role of submarine groundwater discharge in a temperate eutrophic salt-wedge estuary[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 66(4): 1068-1082.
|
| [101] |
WRAGE N, VAN GROENIGEN J W, OENEMA O, et al, 2005. A novel dual-isotope labelling method for distinguishing between soil sources of N2O[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 19(22): 3298-3306.
pmid: 16220527
|
| [102] |
WRAGE N, VELTHOF G L, VAN BEUSICHEM M L, et al, 2001. Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33(12-13): 1723-1732.
|
| [103] |
XIE RONGRONG, LIN LAICHANG, SHI CHENGCHUN, et al, 2024. Elucidating the links between N2O dynamics and changes in microbial communities following saltwater intrusions[J]. Environmental Research, 245: 118021.
|
| [104] |
YEERKEN S, DENG MIN, LI LU, et al, 2024. Evaluating the role of high N2O affinity complete denitrifiers and non-denitrifying N2O reducing bacteria in reducing N2O emissions in river[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 479: 135602.
|
| [105] |
YOON S, NISSEN S, PARK D, et al, 2016. Nitrous oxide reduction kinetics distinguish bacteria harboring clade I NosZ from those harboring clade II NosZ[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 82(13): 3793-3800.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00409-16
pmid: 27084012
|
| [106] |
YOSHIDA M, ISHII S, OTSUKA S, et al, 2010. nirK-harboring denitrifiers are more responsive to denitrification-inducing conditions in rice paddy soil than nirS-harboring bacteria[J]. Microbes and Environments, 25(1): 45-48.
|
| [107] |
ZHAO SIYAN, WANG QING, ZHOU JIEMIN, et al, 2018. Linking abundance and community of microbial N2O-producers and N2O-reducers with enzymatic N2O production potential in a riparian zone[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 642: 1090-1099.
|
| [108] |
ZHOU XINYI, FUJIWARA T, HIDAKA T, et al, 2023. Evaluation of nitrous oxide emission during ammonia retention from simulated industrial wastewater by microaerobic activated sludge process[J]. Water Research, 247: 120780.
|
| [109] |
ZHU GUIBING, WANG SHANYUN, WANG WEIDONG, et al, 2013a. Hotspots of anaerobic ammonium oxidation at land-freshwater interfaces[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(2): 103-107.
|
| [110] |
ZHU XIA, BURGER M, DOANE T A, et al, 2013b. Ammonia oxidation pathways and nitrifier denitrification are significant sources of N2O and NO under low oxygen availability[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(16): 6328-6333.
|
| [111] |
ZUMFT W G, 1997. Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 61(4): 533-616.
doi: 10.1128/mmbr.61.4.533-616.1997
pmid: 9409151
|
| [112] |
ZUMFT W G, KRONECK P M H, 2006. Respiratory transformation of nitrous oxide (N2O) to dinitrogen by Bacteria and Archaea[J]. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 52: 107-227.
|
 ), ZHANG Baoshan1(
), ZHANG Baoshan1( ), WU Jiapeng1, LONG Aimin2,3
), WU Jiapeng1, LONG Aimin2,3