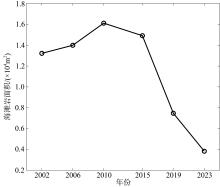
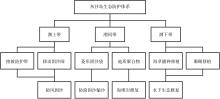
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 154-165.doi: 10.11978/2024230CSTR: 32234.14.2024230
• Marine geomorphology • Previous Articles Next Articles
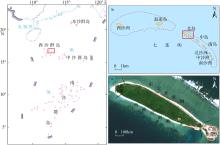
Study on the characteristics of shoreline changes and ecological protection strategies of coral sandy islands: A case study of North Island in the Xisha Islands, South China Sea
LIN Ting1,2( ), QU Jianjun2(
), QU Jianjun2( ), WU Zhifeng1,2, LI Yupei3
), WU Zhifeng1,2, LI Yupei3
- 1. School of Geography and Remote Sensing, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou 510006, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory(Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. Sansha Marine Protected Area Administration, Sansha 573199, China
-
Received:2024-12-10Revised:2025-02-17Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-10-14 -
Contact:QU Jianjun -
Supported by:PI Project of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML20220014)
CLC Number:
- P737.13
Cite this article
LIN Ting, QU Jianjun, WU Zhifeng, LI Yupei. Study on the characteristics of shoreline changes and ecological protection strategies of coral sandy islands: A case study of North Island in the Xisha Islands, South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 154-165.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
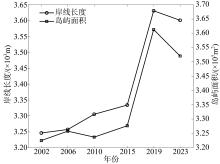
Tab. 1
High-resolution remote sensing images of North Island"
| 成像时间 | 遥感卫星 | 分辨率/m | 潮位/cm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全色 | 多光谱 | |||
| 2002-07-31 | QuickBird | 0.5 | 2.0 | 126 |
| 2006-06-23 | QuickBird | 0.5 | 2.0 | 130 |
| 2010-02-07 | WorldView-2 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 105 |
| 2015-12-14 | GF-2 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 108 |
| 2019-08-11 | Worldview-2 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 138 |
| 2022-10-08 | Worldview-2 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 102 |
| 2023-03-09 | Worldview-2 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 80 |
| 2023-10-30 | ZY3-03 | 2.1 | 5.8 | 62 |
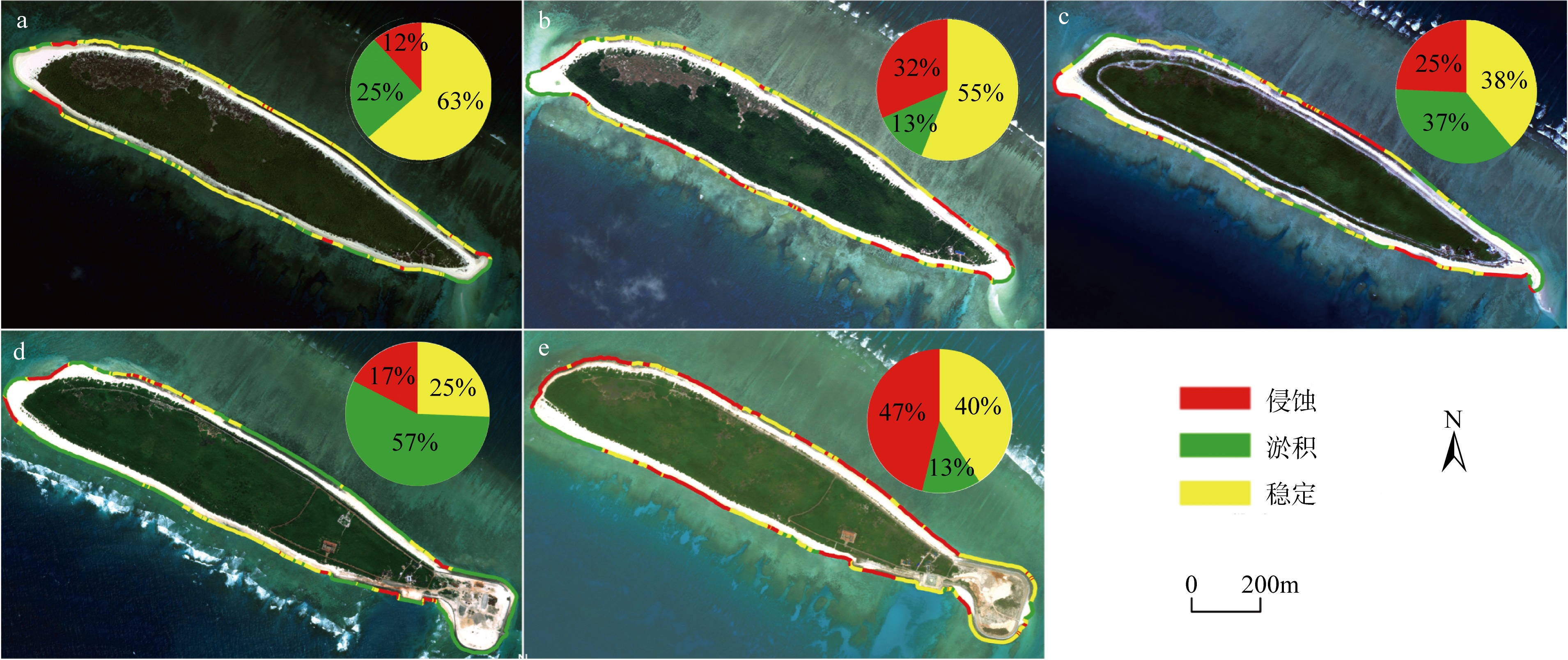
Tab. 2
Shoreline erosion conditions of North Island at different stages"
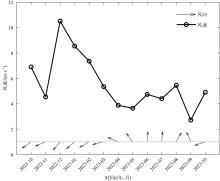
| 年份 | 最大侵蚀距离/m | 平均侵蚀距离/m | 最大侵蚀速率/(m·a-1) | 最大侵蚀速率/(m·a-1) | 侵蚀面积/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002—2006 | 34.26 | 12.54 | 8.79 | 3.22 | 4115 |
| 2006—2010 | 54.62 | 13.18 | 15.08 | 3.63 | 8193 |
| 2010—2015 | 35.63 | 10.11 | 6.09 | 1.73 | 6114 |
| 2015—2019 | 46.57 | 14.84 | 12.73 | 4.06 | 6397 |
| 2019—2023 | 56.84 | 10.11 | 15.62 | 2.82 | 11846 |
Tab. 3
Shoreline deposition conditions of North Island at different stages"
| 年份 | 最大淤积距离/m | 平均淤积距离/m | 最大淤积速率/(m·a-1) | 最大淤积速率/(m·a-1) | 淤积面积/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002—2006 | 33.00 | 8.13 | 8.47 | 2.08 | 7400 |
| 2006—2010 | 48.79 | 14.11 | 13.47 | 3.89 | 6070 |
| 2010—2015 | 43.14 | 8.99 | 7.38 | 1.53 | 10082 |
| 2015—2019 | 110.67 | 18.59 | 30.26 | 5.08 | 40049 |
| 2019—2023 | 16.80 | 6.55 | 4.70 | 1.83 | 3002 |
| [1] |
李晓敏, 2021. 南海西沙群岛珊瑚岛礁高分遥感监测与动态研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
李元超, 陈石泉, 郑新庆, 等, 2018. 永兴岛及七连屿造礁石珊瑚近10年变化分析[J]. 海洋学报, 40(8): 97-109.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
刘胜, 2024. 珊瑚礁生态系统研究的发展、挑战与希望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(3): 1-2.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
龙丽娟, 杨芳芳, 韦章良, 2019. 珊瑚礁生态系统修复研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(6): 1-8.
doi: 10.11978/2019066 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2019066 |
|
| [5] |
陆文赋, 屈建军, 赵爱国, 等, 2024. 猫头刺盾状移动式固沙障防沙效应风洞模拟试验研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 44(3): 84-92.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
屈建军, 李绍武, 蒋冲, 等, 2023. 珊瑚沙质岸线防浪固沙障水槽模拟试验研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 43(6): 18-24.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
王丽荣, 余克服, 赵焕庭, 等, 2014. 南海珊瑚礁经济价值评估[J]. 热带地理, 34(1): 44-49.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
吴钟解, 王道儒, 涂志刚, 等, 2011. 西沙生态监控区造礁石珊瑚退化原因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 33(4): 140-146.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
肖海婷, 黄荣永, 刘羿, 等, 2024. 台风影响下西沙灰沙岛的时空变化特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 44(02): 157-177.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
阎根齐, 吴昊, 2024. 中国人对西沙群岛历史认知与风力、潮流、海浪作用下的变迁研究[J]. 热带地理, 44(2): 258-268.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003822 |
|
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003822 |
|
| [11] |
叶锦昭, 1996. 西沙群岛环境水文特征[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 35(S1): 19-25.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
张婷, 林柳, 蹇丽, 等, 2020. 西沙群岛七连屿绿海龟(Chelonia mydas)产卵场海滩垃圾调查[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(7): 2408-2415.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
赵焕庭, 王丽荣, 袁家义, 2016. 南海诸岛珊瑚礁可持续发展[J]. 热带地理, 36(1): 55-65.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002800 |
|
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002800 |
|
| [14] |
赵美霞, 姜大朋, 张乔民, 2017. 珊瑚岛的动态演变及其稳定性研究综述[J]. 热带地理, 37(5): 694-700.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002988 |
|
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002988 |
|
| [15] |
赵娜, 2018. 西沙七连屿珊瑚礁区海滩岩研究[D]. 广州:中国科学院南海海洋研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
赵中伟, 赵璇, 陈天然, 等, 2024. 西沙群岛珊瑚礁2015—2023海岸地貌演化与其区域海洋环境特征的关联性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 44(4): 25-44.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
周胜男, 施祺, 周桂盈, 等, 2019. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁砾洲地貌特征[J]. 海洋科学, 43(6): 48-59.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
周毅, 徐少春, 张晓梅, 等, 2020. 海洋牧场海草床生境构建技术[J]. 科技促进发展, 16(2): 200-205.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [1] | CHEN Yuchen, FU Dongyang, TAO Bangyi, LI Jizhe, ZHU Yixian, LIU Bei, LIN Ye, CHAI Xia. Study on remote sensing monitoring and time series change of shallow sea topography of typical islands and reefs in the South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 140-153. |
| [2] | XIAO Haiting, HUANG Rongyong, LIU Yi, YU Kefu. Spatiotemporal changes of lime-sand islands in the Xisha Islands under the impacts of typhoons [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 157-177. |
| [3] | CONG Xin, KUANG Cuiping, WU Yunlong, XIA Zilong. Study of the erosion and deposition in a sandbar-lagoon system influenced by submerged vegetation under erosion wave conditions [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 31-37. |
| [4] | GUO Junli, SHI Lianqiang, CHEN Shenliang, ZHANG Min, CHANG Yang, ZHANG Daheng. Dynamic variations of different sedimentary geomorphology of sandy and gravel embayed beaches on the Zhujiajian Island during typhoon season [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 82-96. |
| [5] | FENG Bingbin, WANG Riming, LI Shushi, HUANG Hu, HU Baoqing. Changes of the artificial beach profile in the Qinzhou Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 51-60. |
| [6] | YU Jiankui, REN Zonghai, ZHAN Chao, ZHANG Yuchen, GENG Wenqian, WANG Qing. Erosion-deposition analysis of underwater slope on lagoon and sand barriers in the Swan Lake, Rongcheng, Shandong province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 61-70. |
| [7] | XI Yangyang, WANG Riming, FENG Bingbin, CHEN Bo. Morphodynamic processes of the Yintan Beach in response to typhoon [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 97-104. |
| [8] | ZHANG Daheng, SHI Lianqiang, GONG Zhaohui, GUO Junli. Evolution characteristics of beach erosion and accretion at the Riyue Bay under the combined impacts of winter waves and artificial island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 71-81. |
| [9] | Shibing ZHU,Danni HU,Huiling ZHANG,Chunhua ZENG,Zhehua LI,Zhiqiang LI. Analysis of short-term temporal and spatial changes and sedimentary dynamics at the middle section of Haikou Bay Beach * [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 77-85. |
|
||