Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 61-70.doi: 10.11978/2021141CSTR: 32234.14.2021141
• Marine geomorphology • Previous Articles Next Articles
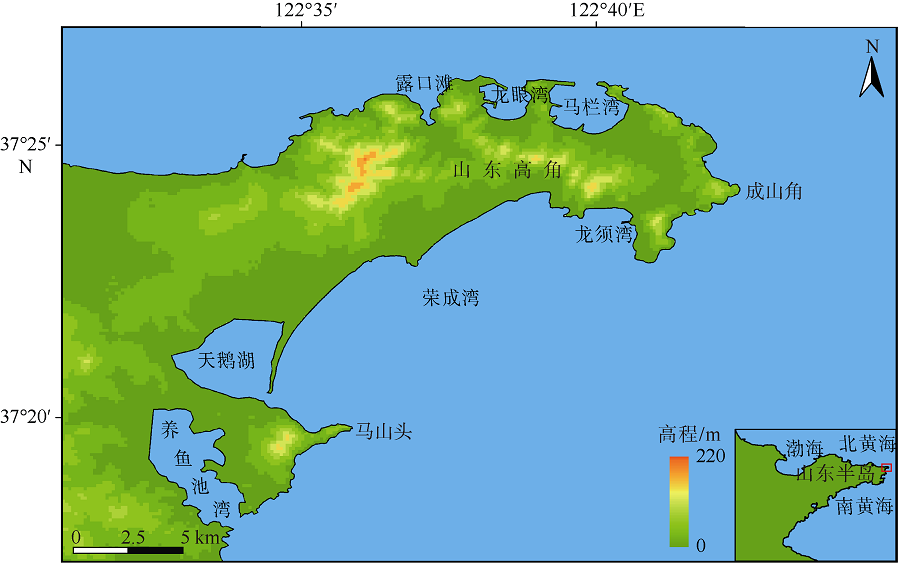
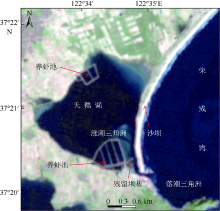
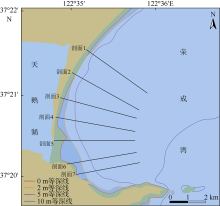
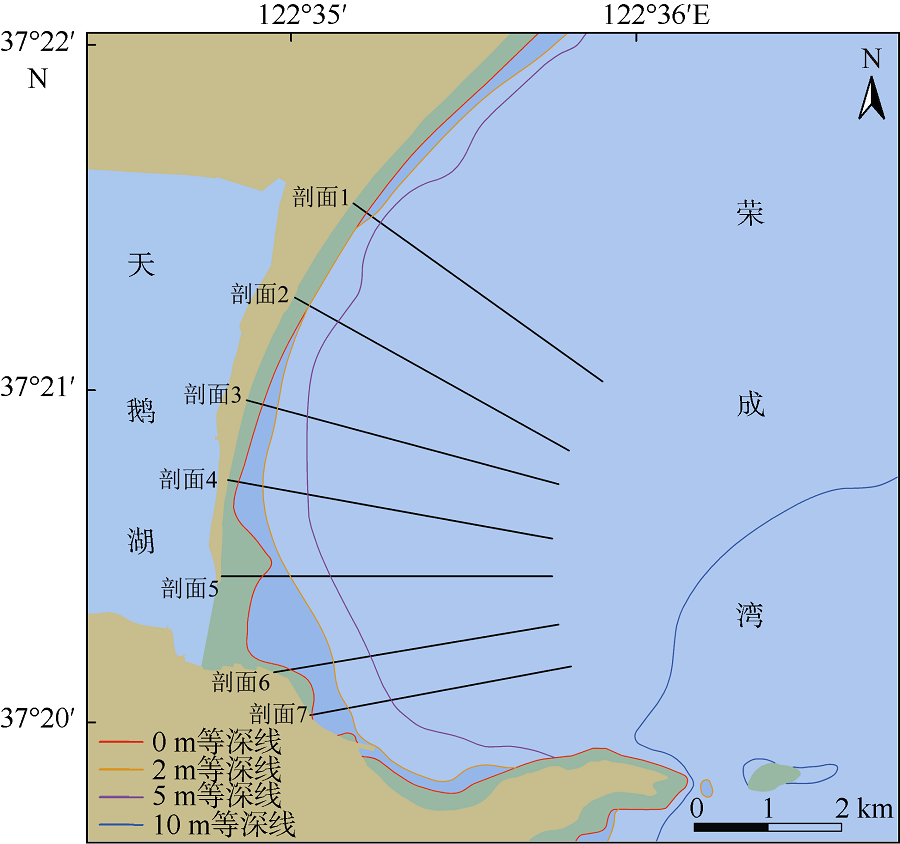
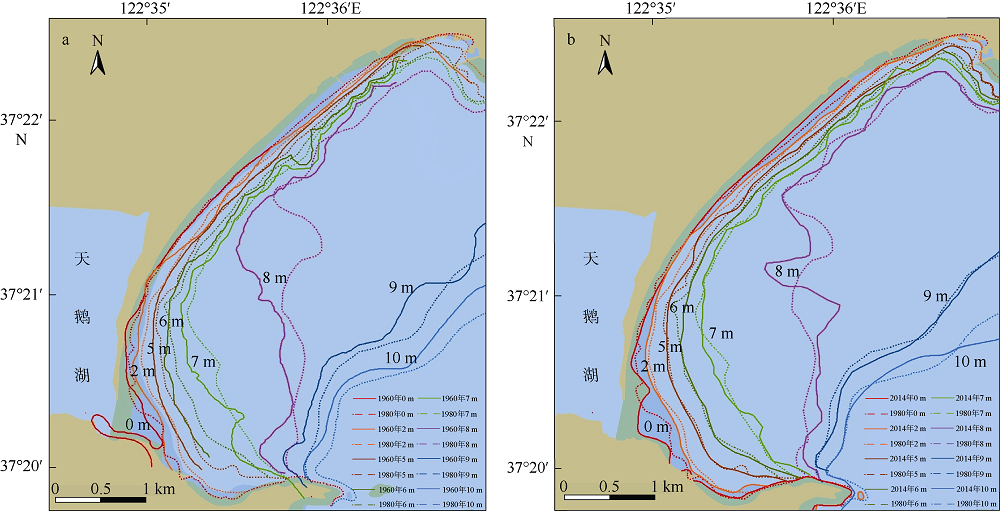
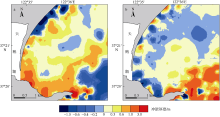
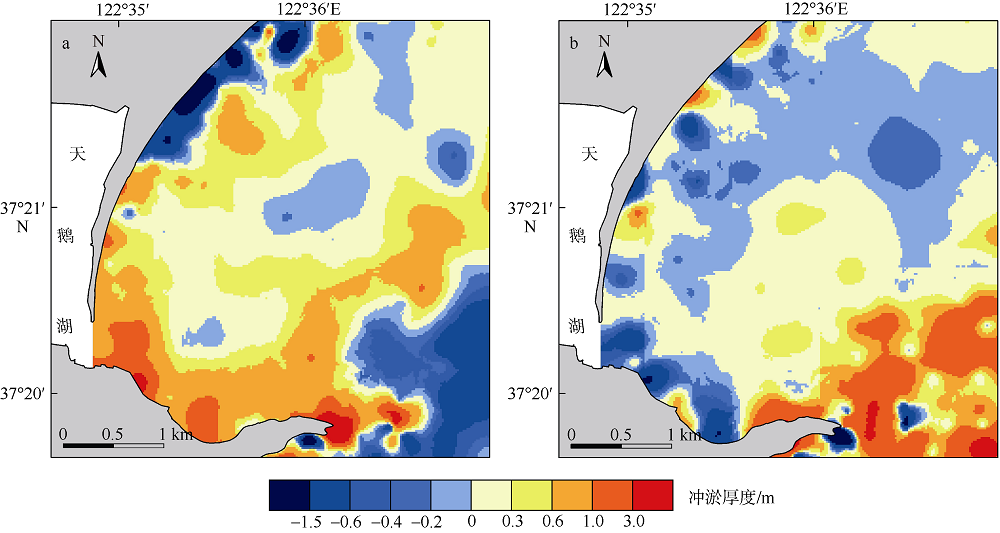
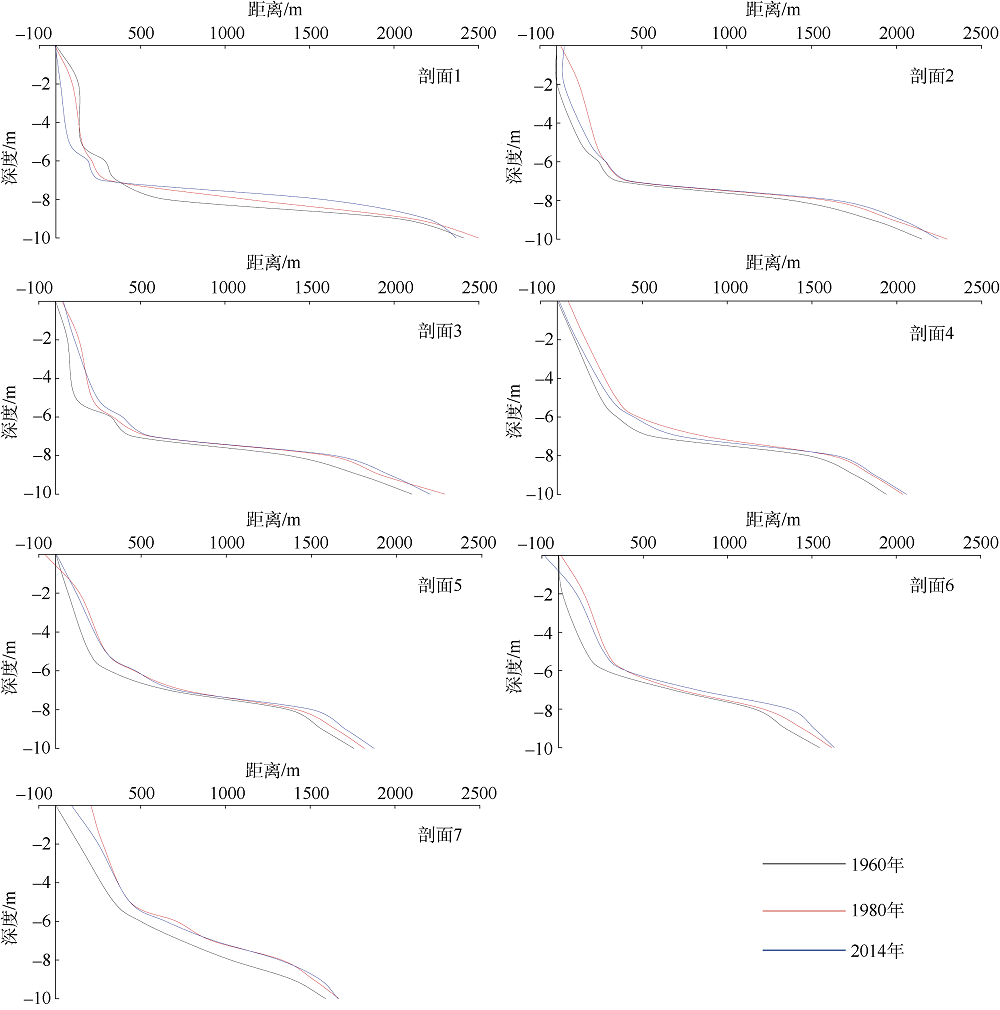
Erosion-deposition analysis of underwater slope on lagoon and sand barriers in the Swan Lake, Rongcheng, Shandong province
YU Jiankui( ), REN Zonghai, ZHAN Chao, ZHANG Yuchen, GENG Wenqian, WANG Qing(
), REN Zonghai, ZHAN Chao, ZHANG Yuchen, GENG Wenqian, WANG Qing( )
)
- Coastal Institute, Ludong University, Yantai 264025, China
-
Received:2021-10-23Revised:2021-11-14Online:2022-07-10Published:2021-11-21 -
Contact:WANG Qing E-mail:836013348@qq.com;schingwang@126.com -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of China-Shandong United Fund(U1706220);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41901006);Shandong Provincial Fund(ZR2019BD005);Shandong University Youth Innovation Technology Team(2020KJH002)
CLC Number:
- P737.13
Cite this article
YU Jiankui, REN Zonghai, ZHAN Chao, ZHANG Yuchen, GENG Wenqian, WANG Qing. Erosion-deposition analysis of underwater slope on lagoon and sand barriers in the Swan Lake, Rongcheng, Shandong province[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 61-70.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
陈西庆, 陈吉余, 1998. 长江三角洲海岸剖面闭合深度的研究——Bruun法则及其应用的基本问题[J]. 地理学报, 53(4): 323-331.
doi: 10.11821/xb199804004 |
|
CHEN XIQIN, CHEN JIYU, 1998. A study of closure depth on the profiles of the Changjiang deltaic coast on the fundamental problems associated with Bruun rule and its application[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 53(4): 323-331. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11821/xb199804004 |
|
| [2] | 陈逸雪, 姚亦鹏, 成文连, 等, 2020. 荣成天鹅湖碳、氮、磷空间分布特征及其来源解析研究[J]. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 51(5): 548-553. |
| CHEN YIXUE, YAO YIPENG, CHENG WENLIAN, et al, 2020. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the Rongcheng Swan Lake[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 51(5): 548-553. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 丛新, 匡翠萍, 武云龙, 等, 2021. 侵蚀浪条件下沉水植被对沙坝-潟湖海岸的冲淤影响研究[J/OL]. 热带海洋学报: 1-7. http://journal15.magtechjournal.com/Jwk3_rdhyxb/CN/10.11978/2021079. |
| CONG XIN, KUANG CUIPING, WU YUNLONG, et al, 2021. Study on erosion and deposition in a sandbar-lagoon system influenced by submerged vegetation under erosion wave conditions[J/OL]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 1-7. http://journal15.magtechjournal.com/Jwk3_rdhyxb/CN/10.11978/2021079. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 戴志军, 张小玲, 闫虹, 等, 2009. 台风作用下淤泥质海岸动力地貌响应[J]. 海洋工程, 27(2): 63-69, 95. |
| DAI ZHIJUN, ZHANG XIAOLING, YAN HONG, et al, 2009. Morphodynamic behavior of the mud coast in response to typhoon action[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 27(2): 63-69, 95. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 冯凌旋, 季永兴, 章馨谣, 等, 2020. 杭州湾北岸金山咀—龙泉港岸段近岸滩槽冲淤演变分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 38(3): 92-98. |
| FENG LINGXUAN, JI YONGXING, ZHANG XINYAO, et al, 2020. Analysis of erosion and deposition evolution of inshore shoals and channels along the Jinshanzui to Longquangang segment in the northern Hangzhou Bay[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 38(3): 92-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 高抒, 1998. 论海岸带受损环境恢复与改善之对策: 以山东半岛月湖为例[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 20(4): 123-126. |
| GAO SHU, 1998. On the restoration and improvement of deteriorated coastal environments, with spectial reference to Yuehu Logoon, Shandong peninsula, China[J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 20(4): 123-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 高抒, 贾建军, 于谦, 2021. 绿色海堤的沉积地貌与生态系统动力学原理: 研究综述[J/OL]. 热带海洋学报: 1-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RDHY20211011000.htm. |
| GAO SHU, JIA JIANJUN, YU QIAN, 2021. Green sea dykes: an overview of their principles of sediment, geomorphology and ecosystem dynamics[J/OL]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 1-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RDHY20211011000.htm. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 贾建军, 2001. 小型潮汐汊道系统的沉积动力过程与演化[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所. |
| JIA JIANJUN, 2001. Sediment dynamic processes and evolution of small tidal inlet systems[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 贾建军, 高抒, 薛允传, 2003. 山东荣成月湖潮汐汊道的时间-流速不对称特征[J]. 海洋学报, 25(3): 68-76. |
| JIA JIANJUN, GAO SHU, XUE YUNCHUAN, 2003. Patterns of time-velocity asymmetry at the Yuehu Inlet, Shandong peninsula, China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 25(3): 68-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 贾建军, 高抒, 薛允传, 等, 2004. 山东荣成月湖潮汐汊道系统的沉积物平衡问题——兼论人类活动的影响[J]. 地理科学, 24(1): 83-88. |
| JIA JIANJUN, GAO SHU, XUE YUNCHUAN, et al, 2004. Sediment budget of Yuehu lagoon and implications for human activities, Shandong peninsula, China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 24(1): 83-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 牟晓燕, 杨永亮, 李春雁, 等, 1999. 山东半岛荣成湾月湖环境特征研究[J]. 青岛大学学报, (4): 56-59. |
| MU XIAOYAN, YANG YONGLIANG, LI CHUNYAN, et al, 1999. Environmental characteristics of seawater in the Yuehu inlet, Rongcheng bay, China[J]. Journal of Qingdao University, (4): 56-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 王永红, 庄振业, 李学伦, 2000. 山东荣成湾沿岸输沙率及沙嘴的演化动态[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 20(4): 31-35. |
| WANG YONGHONG, ZHUANG ZHENYE, LI XUELUN, 2000. The calculation of alongshore silt discharge rates and evolution development of sandspit in the Rongcheng bay, Shandong peninsula[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 20(4): 31-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 魏合龙, 庄振业, 1997. 山东荣成湾月湖地区的潟湖-潮汐汊道体系[J]. 湖泊科学, (2): 135-140. |
| WEI HELONG, ZHUANG ZHENYE, 1997. Study on the evolution of Yuehu lake-tidal inlet system, Rongcheng bay, Shandong province[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, (2): 135-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 魏烈群, 2021. 荣成天鹅湖解磷菌的分离筛选及其对沉积物磷释放的影响[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学. |
| WEI LIEQUN, 2021. Isolation and screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and the effect on phosphorus release from the sediments in Rongcheng Swan Lake[D]. Yantai: Yantai University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 薛允传, 2000. 山东半岛月湖潮汐汊道沉积物输运与堆积[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所. |
| XUE YUNCHUAN, 2000. Transport and accumulation of sediment in tidal channel of Yuehu Lake in Shandong peninsula[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciencesy. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 薛允传, 高抒, 贾建军, 2002. 山东荣成湾月湖口门落潮干道的推移质输运[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 33(4): 356-363. |
| XUE YUNCHUAN, GAO SHU, JIA JIANJUN, 2002. Bedload transport within the ebb channel of a tidal inlet system, Swan Lake, Shandong peninsula, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 33(4): 356-363. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 杨留柱, 杨莉玲, 潘洪州, 等, 2019. 人类活动影响下的钦州湾近期滩槽冲淤演变特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(6): 41-50. |
| YANG LIUZHU, YANG LILING, PAN HONGZHOU, et al, 2019. Characteristics of recent evolution in Qinzhou Bay influenced by human activities[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(6): 41-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 殷效彩, 杨永亮, 乌大年, 等, 1999. 山东荣成湾月湖沉积底泥重金属研究[J]. 青岛大学学报, (4): 75-79. |
| YIN XIAOCAI, YANG YONGLIANG, WU DANIAN, et al, 1999. Geochemical study of sediments from Yuehu inlet[J]. Journal of Qingdao University, (4): 75-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 应铭, 李九发, 陈沈良, 等, 2007. 黄河三角洲飞雁滩动力特征与地形剖面塑造[J]. 海洋通报, 26(4): 13-22. |
| YING MING, LI JIUFA, CHEN SHENLIANG, et al, 2007. Dynamics characteristics and topographic profiles shaping process of Feiyantan at the Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 26(4): 13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 张文斌, 董昭皆, 徐书童, 等, 2019. 微生物和藻类分解对荣成天鹅湖沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 38(4): 561-567. |
| ZHANG WENBIN, DONG ZHAOJIE, XU SHUTONG, et al, 2019. Effects of microorganism and algal decomposition on nitrogen and phosphorus release from the sediments in Rongcheng Swan Lake[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 38(4): 561-567. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 中国海湾志编纂委员会, 1991. 中国海湾志-第三分册, 山东半岛北部和东部海湾[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. (in Chinese) |
| [22] | 中国海湾志编纂委员会, 1997. 中国海湾志[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | GAO S, ZHUANG Z Y, WEI H L, et al, 1998. Physical processes affecting the health of coastal embayments:an example from the Yuehu inlet, Shandong Peninsula, China[M]// Health of the Yellow Sea. Seoul: The Earth Love Publication Association: 314-329. |
| [24] |
GAO SHU, JIA JIANJUN, 2004. Sediment and carbon accumulation in a small tidal basin: Yuehu, Shandong Peninsula, China[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 4(1): 63-69.
doi: 10.1007/s10113-003-0064-5 |
| [25] |
JIA JIANJUN, GAO SHU, XUE YUNCHUAN, 2003. Sediment dynamic processes of the Yuehu inlet system, Shandong peninsula, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 57(5-6): 783-801.
doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00406-7 |
| [26] | NICHOLS M M, BOON J D, 1994. Sediment transport processes in coastal lagoons[M]// Elsevier Oceanography Series. Elsevier, 60: 157-219. |
| [27] | PETHICK J, 1984. An introduction to coastal geomorphology[M]. London: Edward Arnold. |
| [28] | SPEER P E, AUBREY D G, 1985. A study of non-linear tidal propagation in shallow inlet/estuarine systems Part II: Theory[J]. Estuarine, Coastsal and Shelf Science, 21(2): 207-224. |
| [1] | CONG Xin, KUANG Cuiping, WU Yunlong, XIA Zilong. Study of the erosion and deposition in a sandbar-lagoon system influenced by submerged vegetation under erosion wave conditions [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 31-37. |
| [2] | GUO Junli, SHI Lianqiang, CHEN Shenliang, ZHANG Min, CHANG Yang, ZHANG Daheng. Dynamic variations of different sedimentary geomorphology of sandy and gravel embayed beaches on the Zhujiajian Island during typhoon season [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 82-96. |
| [3] | FENG Bingbin, WANG Riming, LI Shushi, HUANG Hu, HU Baoqing. Changes of the artificial beach profile in the Qinzhou Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 51-60. |
| [4] | XI Yangyang, WANG Riming, FENG Bingbin, CHEN Bo. Morphodynamic processes of the Yintan Beach in response to typhoon [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 97-104. |
| [5] | ZHANG Daheng, SHI Lianqiang, GONG Zhaohui, GUO Junli. Evolution characteristics of beach erosion and accretion at the Riyue Bay under the combined impacts of winter waves and artificial island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 71-81. |
| [6] | Shibing ZHU,Danni HU,Huiling ZHANG,Chunhua ZENG,Zhehua LI,Zhiqiang LI. Analysis of short-term temporal and spatial changes and sedimentary dynamics at the middle section of Haikou Bay Beach * [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 77-85. |
|
||