Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2018, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 12-19.doi: 10.11978/2017017CSTR: 32234.14.2017017
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
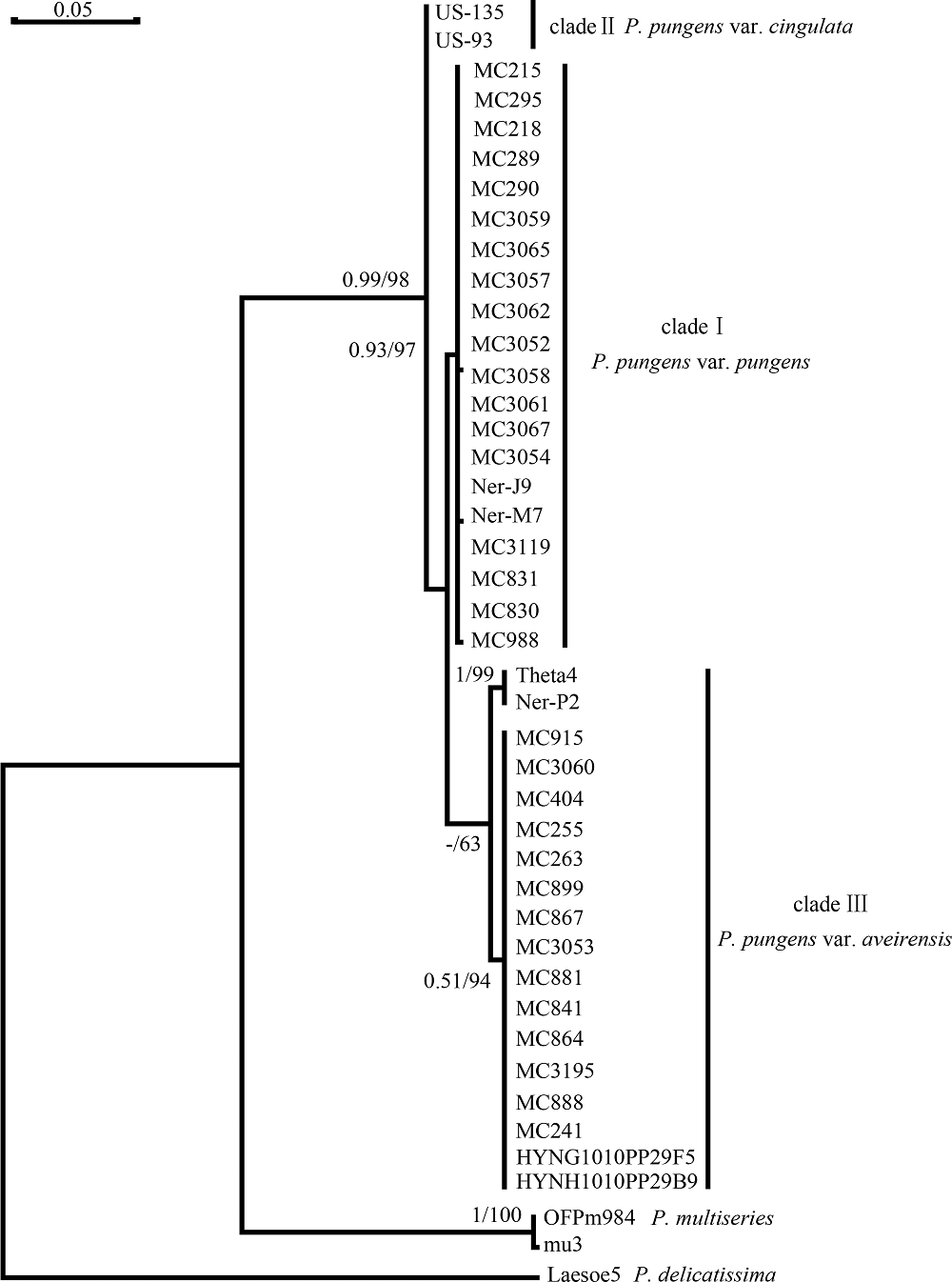
Studies on intraspecies diversity of Pseudo-nitzschia pungens from Chinese coastal waters*
Huanchang DONG1,2( ), Chunxiu HUANG1,2, Guoshuang XU1,2, Yang LI1,2(
), Chunxiu HUANG1,2, Guoshuang XU1,2, Yang LI1,2( )
)
- 1. Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Subtropical Biodiversity and Biomonitoring, College of Life Science, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
2. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Healthy and Safe Aquaculture, College of Life Science, South China Normal University,Guangzhou 510631, China
-
Received:2017-02-15Revised:2017-05-26Online:2018-01-20Published:2018-02-02 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570205, 31370235);Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou, China (201607010370)
CLC Number:
- P735.531
Cite this article
Huanchang DONG, Chunxiu HUANG, Guoshuang XU, Yang LI. Studies on intraspecies diversity of Pseudo-nitzschia pungens from Chinese coastal waters*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(1): 12-19.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
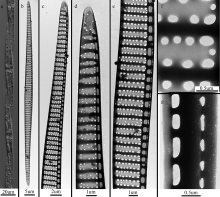
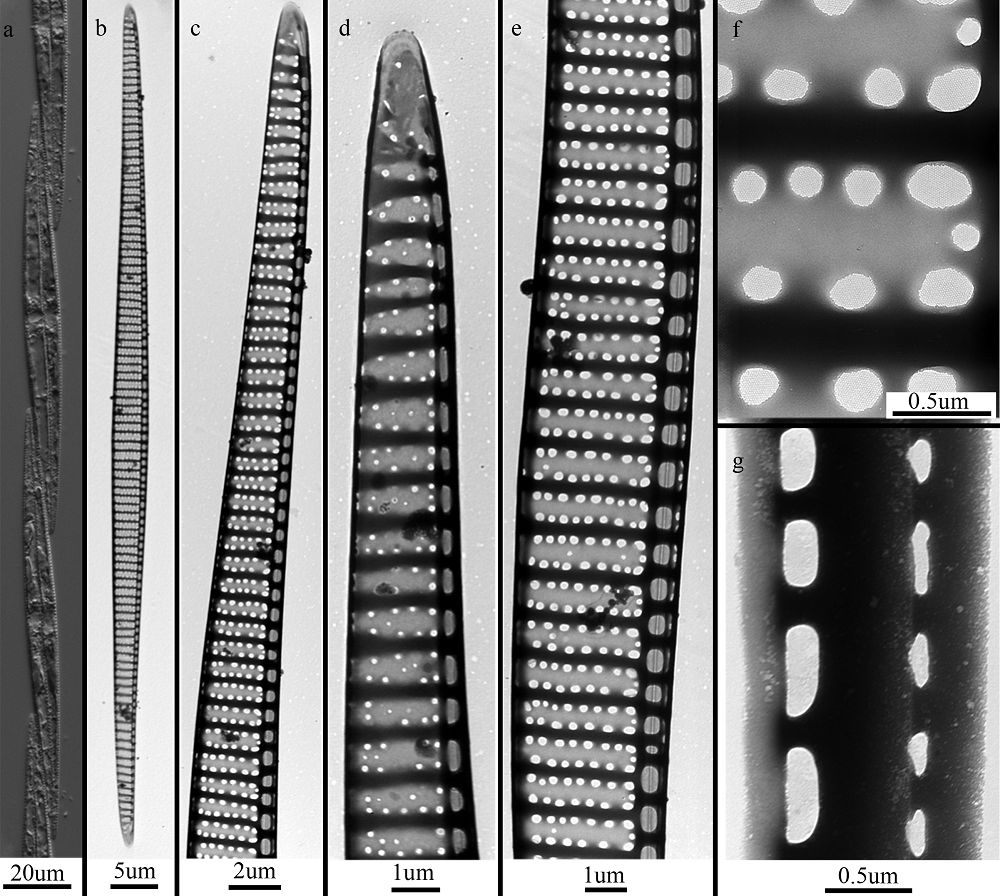
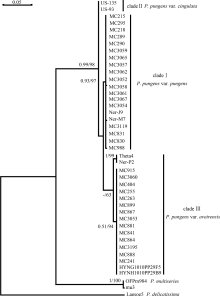
Tab. 1
List of P. pungens monoclonal strains established in this study"
| 株系 | 分离地点 | 采样时间 | 种名 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MC215 | 珠海 | 2013年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC218 | 葫芦岛 | 2013年8月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC241 | 惠州 | 2013年10月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC255 | 厦门 | 2013年11月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC263 | 青岛 | 2013年11月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC289 | 青岛 | 2014年2月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC290 | 青岛 | 2014年2月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC295 | 惠州 | 2014年4月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC404 | 惠州 | 2014年7月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC830 | 温州 | 2015年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC831 | 温州 | 2015年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC841 | 香港 | 2015年7月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC864 | 宁波 | 2015年8月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC867 | 宁波 | 2015年8月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC881 | 湛江 | 2015年8月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC888 | 湛江 | 2015年8月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC899 | 青岛 | 2015年9月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC915 | 深圳 | 2015年9月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC988 | 台湾海峡 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3052 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3053 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC3054 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3057 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3058 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3059 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3060 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| MC3061 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3062 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3065 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3067 | 珠海 | 2016年5月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3119 | 黄海 N:122°50′, E:32°00′ | 2016年7月 | P. pungens var. pungens |
| MC3195 | 台湾海峡 | 2016年8月 | P. pungens var. averiensis |
| [1] | 程兆第, 高亚辉, 刘师成, 1993. 福建沿岸微型硅藻[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 10-11 (in Chinese). |
| [2] | 黄春秀, 徐国双, 李扬, 2016. 大亚湾水域并基拟菱形藻的种类鉴定和产毒特征分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 41(5): 1118-1125. |
| HUAN CHUNXIU, XU GUOSHUANG, LI YANG, 2016. The identification of Pseudo-nitzschia decipiens from Daya bay and analysis of its domoic acid production[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 41(5): 1118-1125 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 李爱峰, 2005. 液-质联用技术分析海洋生物毒素的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所). |
| LI AIFENG, 2005. Studies on the analytical methods of marine biotoxins with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 吕颂辉, 齐雨藻, 1992. 南海大鹏湾的主要赤潮生物[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学), 13(3): 130-133. |
| LÜ SONGHUI, QI YUZAO, 1992. Main red tide causative species of Da Peng Bay, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Jinan University (Natural Science), 13(3): 130-133 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 徐国双, 李扬, 2015. 我国沿海拟菱形藻属的2新记录种及其产毒特征分析[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 23(6): 614-624. |
| XU GUOSHUANG, LI YANG, 2015. Two new records of diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia from Chinese waters and analysis of their domoic acid production[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 23(6): 614-624 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 杨军霞, 2007. 中国东南沿海四种拟菱形藻生长特性与毒素检测研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. |
| YANG JUNXIA, 2007. Growth characteristics and toxin determination of four species of Pseudo-nitzschia from Southeast China Sea[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | AMATO A, KOOISTRA W H C F, GHIRON J H L, et al, 2007. Reproductive isolation among sympatric cryptic species in marine diatoms[J]. Protist, 158(2): 193-207. |
| [8] | BATES S S, BIRD C J, DE FREITAS A S W, et al, 1989. Pennate diatom Nitzschia pungens as the primary source of domoic acid, a toxin in shellfish from eastern Prince Edward Island, Canada[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 46(7): 1203-1215. |
| [9] | BATES S S, DE FREITAS A S W, MILLEY J E, et al, 1991. Controls on domoic acid production by the diatom Nitzschia pungens f. multiseries in culture: nutrients and irradïance[J]. Canada Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 48(7): 1136-1144. |
| [10] | BATES S S, GARRISON D L, HORNER R A, 1998. Bloom dynamics and physiology of domoic-acid-producing Pseudo- nitzschia species[M]//ANDERSON D M, CEMBELLA A D, HALLEGRAEFF G M. Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag: 267-292. |
| [11] | CASTELEYN G, CHEPURNOV V A, LELIAERT F, et al, 2008. Pseudo-nitzschia pungens (Bacillariophyceae): a cosmopolitan diatom species?[J]. Harmful Algae, 7(2): 241-257. |
| [12] | CASTELEYN G, ADAMS N G, VANORMELINGEN P, et al, 2009. Natural hybrids in the marine diatom Pseudo-nitzschia pungens (Bacillariophyceae): genetic and morphological evidence[J]. Protist, 160(2): 343-354. |
| [13] | CHURRO C I, CARREIRA C C, RODRIGUES F J, et al, 2009. Diversity and abundance of potentially toxic Pseudo-nitzschia Peragallo in Aveiro coastal lagoon, Portugal and description of a new variety, P. pungens var. aveirensis var. nov.[J]. Diatom Research, 24(1): 35-62. |
| [14] | FEHLING J, DAVIDSON K, BATES S S, 2005. Growth dynamics of non-toxic Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima and toxic P. seriata (Bacillariophyceae) under simulated spring and summer photoperiods[J]. Harmful Algae, 4(4): 763-769. |
| [15] | GUILLARD R R L, HARGRAVES P E, 1993. Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte[J]. Phycologia, 32(3): 234-236. |
| [16] | HALL T A, 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT[J]. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41(2): 95-98. |
| [17] | HASLE G R, 1995. Pseudo-nitzschia pungens and P. multiseries (Bacillariophyceae): nomenclatural history, morphology, and distribution[J]. Journal of Phycology, 31(3): 428-435. |
| [18] | HASLE G R, LANGE C B, SYVERTSEN E E, 1996. A review of Pseudo-nitzschia, with special reference to the Skagerrak, North Atlantic, and adjacent waters[J]. Helgoländer Meeresuntersu -chungen, 50(2): 131-175. |
| [19] | HASLE G R, SYVERTSEN E E, 1997. The genus Pseudo -nitzschia[M]//TOMAS C R. Identifying Marine Phytoplankton. San Diego: Academic Press: 307-324. |
| [20] | HASLE G R, 2002. Are most of the domoic acid-producing species of the diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia cosmopolites?[J]. Harmful Algael, 1(2): 137-146. |
| [21] | KIM J H, PARK B S, KIM J H, et al, 2015. Intraspecific diversity and distribution of the cosmopolitan species Pseudo-nitzschia pungens (Bacillariophyceae): morphology, genetics, and ecophysiology of the three clades[J]. Journal of Phycology, 51(1): 159-172. |
| [22] | LELONG A, HÉGARET H, SOUDANT P, et al, 2012. Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) species, domoic acid and amnesic shellfish poisoning: revisiting previous paradigms[J]. Phycologia, 51(2): 168-216. |
| [23] | LIM H C, LEAW C P, SU S N P, et al, 2012. Morphology and molecular characterization of Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) from Malaysian Borneo, including the new species Pseudo- nitzschia circumpora sp. nov[J]. Journal of Phycology, 48(5): 1232-1247. |
| [24] | LIM H C, TENG S T, LEAW C P, et al, 2013. Three novel species in the Pseudo-nitzschia pseudodelicatissima complex: P. batesiana sp. nov., P. lundholmiae sp. nov., and P. fukuyoi sp. nov. (Bacillariophyceae) from the Strait of Malacca, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Phycology, 49(5): 902-916. |
| [25] | LÜ SONGHUI, LI YANG, LUNDHOLM N, et al, 2012. Diversity, taxonomy and biogeographical distribution of the genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) in Guangdong coastal waters, South China Sea[J]. Nova Hedwigia, 95(1/2): 123-152. |
| [26] | LUNDHOLM N, SKOV J, POCKLINGTON R, et al, 1994. Domoic acid, the toxic amino acid responsible for amnesic shellfish poisoning, now in Pseudonitzschia seriata (Bacillariophyceae) in Europe[J]. Phycologia, 33(6): 475-478. |
| [27] | LUNDHOLM N, DAUGBJERG N, MOESTRUP Ø, 2002. Phylogeny of the Bacillariaceae with emphasis on the genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) based on partial LSU rDNA[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 37: 115-134. |
| [28] | LUNDHOLM N, 2017. Bacillariophyceae, in IOC-UNESCO taxonomic reference list of harmful micro algae[EB/OL]. . |
| [29] | MILLER M A, PFEIFFER W, SCHWARTZ T, 2010. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees[C]//Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE). New Orleans, LA, USA: IEEE: 1-8. |
| [30] | MOSCHANDREOU K K, BAXEVANIS A D, KATIKOU P, et al, 2012. Inter- and intra-specific diversity of Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) in the northeastern Mediterranean[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 47(3): 321-339. |
| [31] | NYLANDER J A A, 2004. MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary biology centre, Uppsala university [EB/OL]. . |
| [32] | QI Y Z, WAND J, ZHENG L, 1994. The taxonomy and bloom ecology of Pseudo-nitzschia on the coasts of China[C]//Proceedings IOC-WESTPAC Third International Scientific Symposium. Bali, Indonesia: Indonesia Institute of Sciences: 88-95. |
| [33] | RHODES L, WHITE D, SYHRE M, et al, 1996. Pseudo-nitzschia species isolated from New Zealand coastal waters: domoic acid production in vitro and links with shellfish toxicity[M]//YASUMOTO T, OSHIMA Y, FUKUYO Y. Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms, Paris: IOC UNESCO: 155-158. |
| [34] | RONQUIST F, TESLENKO M, VAN DER MARK P, et al, 2012. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space[J]. Systematic Biology, 61(3): 539-542. |
| [35] | SKOV J, LUNDHOLM N, MOESTRUP Ø, et al, 1999. Potentially toxic phytoplankton: 4. The diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Diatomophyceae/Bacillariophyceae)[C]//ICES Identification Leaflets for Plankton No. 185. Copenhagen: ICES: 23. |
| [36] | TAMMILEHTO A, NIELSEN T G, KROCK B, et al, 2015. Induction of domoic acid production in the toxic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia seriata by calanoid copepods[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 159: 52-61. |
| [37] | TENG S T, LIM P T, LIM H C, et al, 2015. A non-toxigenic but morphologically and phylogenetically distinct new species of Pseudo-nitzschia, P. sabit sp. nov. (Bacillariophyceae)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 51(4): 706-725. |
| [38] | TENG S T, TAN S N, LIM H C, et al, 2016. High diversity of Pseudo-nitzschia along the northern coast of Sarawak (Malaysian Borneo), with descriptions of P. bipertita sp. nov. and P. limii sp. nov. (Bacillariophyceae)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 52(6): 973-989. |
| [39] | TRAINER V L, WEKELL J C, HORNER R A, et al, 1998. Domoic acid production by Pseudo-nitzschia pungens[C]// REGUERA B, BLANCO J, FERNÁNDEZ M L, et al. Harmful Algae. Paris: Xunta de Galicia and the IOC of UNESCO: 337-340. |
| [40] | TRAINER V L, BATES S S, LUNDHOLM N, et al, 2012. Pseudo-nitzschia physiological ecology, phylogeny, toxicity, monitoring and impacts on ecosystem health[J]. Harmful Algae, 14: 271-300. |
| [41] | VILLAC M C, FRYXELL G A, 1998. Pseudo-nitzschia pungens var. cingulata var. nov. (Bacillariophyceae) based on field and culture observations[J]. Phycologia, 37(4): 269-274. |
| [42] | WU HAIYAN, GUO MENGMENG, TAN ZHIJUN, et al, 2014. Liquid chromatography quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry for multiclass screening and identification of lipophilic marine biotoxins in bivalve mollusks[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 1358: 172-180. |
| [43] | YANG ZHENBO, HODGKISS I J, 2002. Potentially harmful Pseudo-nitzschia species in Hong Kong coastal waters[M]//HO K C, LIN H Y, YU Z X. Prevention and Management of Harmful Algal Blooms in the South China Sea. Hong Kong: Ao HABSCS: 123-128. |
| [44] | ZOU J Z, ZHOU M J, ZHANG C, 1993. Ecological features of toxic Nitzschia pungens Grunow in Chinese coastal waters[M]//SMAYDA T J, SHIMIZU Y. Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea. Amsterdam: Elsevier: 651-657. |
| [1] | HUO Jiaxin, LI Yingxin, SONG Yan, ZHU Qing, ZHOU Weihua, YUAN Xiangcheng, HUANG Hui, LIU Sheng. Complete mitochondrial genome of Cladopsammia gracilis and Rhizopsammia wettsteini (Scleractinia, Dendrophylliidae) and its phylogenetic implications* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 22-30. |
| [2] | LI Nenghui, HUANG Qing, LI Hang, ZENG Jun, WU Kefeng, TAN Huaqiang. Taxonomic study of four species of Gracilaria (Gracilariaceae, Rhodophyta) in Zhanjiang based on morphological and molecular data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 34-47. |
| [3] | LI Yunpeng, WANG Zhicheng, ZHANG Long, ZHANG Wei, DU Mengda, SUN Yi, ZHANG Zhifeng. Development of gonads with annual cycle in Anlactinia sinensis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 120-126. |
| [4] | HAN Tong, LI Jingjing, LIU Zhengyi, LIU Kai, Zhang Jinhao, QIN Song, ZHONG Zhihai. The seed morphology and internal characteristics of seagrass, surfgrass Phyllospadix iwatensis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 105-113. |
| [5] | GUO Junli, SHI Lianqiang, CHEN Shenliang, ZHANG Min, CHANG Yang, ZHANG Daheng. Dynamic variations of different sedimentary geomorphology of sandy and gravel embayed beaches on the Zhujiajian Island during typhoon season [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 82-96. |
| [6] | LIU Jinmei, HUANG Bingxin, DING Lanping, WANG Xuecong, YAN Jing, YAN Panzhu, ZHANG Yao. Morphological and phylogenetic studies of Yonagunia formosana in southeastern Hainan province, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 76-82. |
| [7] | LI Yonghang, JIA Lei, NI Yugen, HE Jian, MU Zelin, WEN Mingming, SHAN Chenchen. Geophysical characteristics and favorable occurrence signs of marine sand-gravel body in Taiwan banks* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 101-110. |
| [8] | WANG Ling, WANG Bin, LI Jian, YU Kaiqi, ZHAO Fang. Morphology characteristics and formation mechanisms of submarine pockmarks in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 72-84. |
| [9] | NIU Biaobiao, ZHAI Mengyi, LI Yang. Morphological and Phylogenetic Studies on Chaetoceros seychellarus [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 44-49. |
| [10] | LONG Chao, LUO Zhaohe, WEI Zhangliang, YANG Fangfang, LI Ru, LONG Lijuan. Morphology and phylogeny of zooxanthellae Effrenium voratum from Luhuitou reef in Sanya, Hainan province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 35-43. |
| [11] | DAI Zhijun, ZHOU Xiaoyan, WANG Jie, HU Baoqing. Review and prospect of mangrove tidal flat sedimentary dynamics [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 69-75. |
| [12] | LIU Jinmei, JIANG Jingjing, MA Xin, HUANG Bingxin, YANG Nan, LIU Meiyuan, DING Lanping. Morphological taxonomy of genus Hypnea (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) from eastern Guangdong, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 99-110. |
| [13] | MENG Tian, CHEN Zuo, ZHU Jun, ZOU Xiaoxiao, FU Qingyan, BAO Shixiang. Morphological and molecular study on marine green alga, Halimeda velasquezii, first recorded in Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 114-121. |
| [14] | Juan DONG, Guangbo REN, Yabin HU, Jinzhao PANG, Yi MA. Construction and classification of coral reef geomorphic unit system based on high-resolution remote sensing: using 8-band Worldview-2 Image as an example [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 116-129. |
| [15] | Lifen HUANG, Qun LI, Songhui LÜ, Liang ZHANG, Xuedong XIE. Morphology, phylogeny and toxicity of Coolia tropicalis (Dinophyceae) from the Xisha Islands, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(3): 86-97. |
|
||