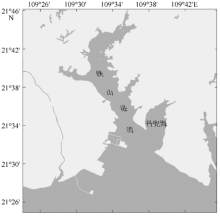
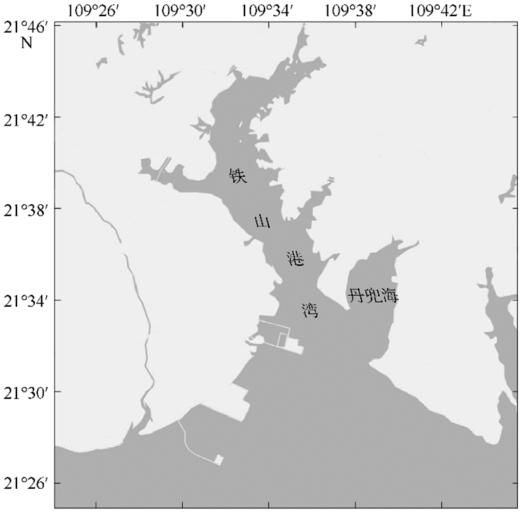
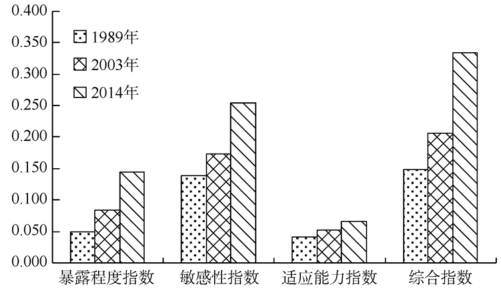
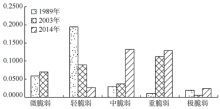
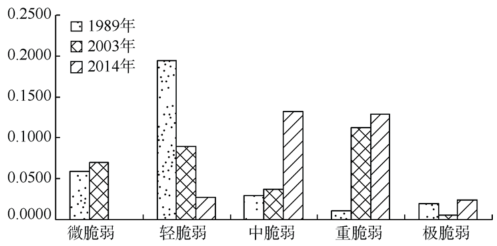
| [1] |
程建新, 肖佳媚, 陈明茹, 等, 2012. 兴化湾海湾生态系统退化评价[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 51(5): 944-950.
|
|
CHENG JIANXIN, XIAO JIAMEI, CHEN MINGRU, et al, 2012. Ecosystem degradation assessment of Xinghua Bay[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 51(5): 944-950 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
胡霞, 莫创荣, 周云新, 等, 2013. 广西北部湾红树林生态承载力评价[J]. 生态科学, 32(4): 480-486.
|
|
HU XIA, MO CHUANGRONG, ZHOU YUNXIN, et al, 2013. Ecological capacity assessment of mangrove in Guangxi Beibu Gulf[J]. Ecological Science, 32(4): 480-486 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
冷悦山, 孙书贤, 王宗灵, 等, 2008. 海岛生态环境的脆弱性分析与调控对策[J]. 海岸工程, 27(2): 58-64.
|
|
LENG YUESHAN, SUN SHUXIAN, WANG ZONGLING, et al, 2008. Vulnerability analysis of island ecological environment and regulating measures[J]. Coastal Engineering, 27(2): 58-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
李平星, 陈诚, 2014a. 基于VSD模型的经济发达地区生态脆弱性评价——以太湖流域为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(2): 237-243.
|
|
LI PINGXING, CHEN CHENG, 2014a. Ecological vulnerability assessment of economic developed region based on VSD model: The case of Taihu basin[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 23(2): 237-243 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
李平星, 樊杰, 2014b. 基于VSD模型的区域生态系统脆弱性评价——以广西西江经济带为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 29(5): 779-788.
|
|
LI PINGXING, FAN JIE, 2014b. Regional ecological vulnerability assessment based on VSD model: A case study of Xijiang River Economic Belt in Guangxi[j]. Journal of Natural Resources, 29(5): 779-788 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
李莎莎, 孟宪伟, 葛振鸣, 等, 2014. 海平面上升影响下广西钦州湾红树林脆弱性评价[J]. 生态学报, 34(10): 2702-2711.
|
|
LI SHASHA, MENG XIANWEI, GE ZHENMING, et al, 2014. Vulnerability assessment on the mangrove ecosystems in Qinzhou bay under sea level rise[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(10): 2702-2711 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
李信贤, 温远光, 何妙光, 1991. 广西红树林类型及生态[J]. 广西农学院学报, 10(4): 70-81.
|
|
LI XINXIAN, WEN GUANGYUAN, HE MIAOGUANG, 1991. The types and ecology of mangrove in Guangxi autonomous region[J]. Journal of Guangxi Agricultural College, 10(4): 70-81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
李玉琳, 高志刚, 韩延玲, 2006. 模糊综合评价中权值确定和合成算子选择[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 42(23): 38-42, 197.
|
|
LI YULIN, GAO ZHIGANG, HAN YANLING, 2006. The determination of weight value and the choice of composite operators in fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 42(23): 38-42, 197 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
卢昌义, 吝涛, 叶勇, 等, 2011. 红树林生态退化机制评估指标体系构建与漳江河口案例研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 30(1): 97-102.
|
|
LU CHANGYI, LIN TAO, YE YONG, et al, 2011. Indicator system for assessing mangrove ecological degradation and a case study of the Zhangjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 30(1): 97-102 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
莫权芳, 钟仕全, 2014. 基于Landsat数据的铁山港区红树林变迁及其驱动力分析研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 14(23): 8-14.
|
|
MO QUANFANG, ZHONG SHIQUAN, 2014. Analysis of mangrove changes and its driving forces based on landsat data in Tieshangang[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 14(23): 8-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
彭欣, 仇建标, 陈少波, 等, 2009. 乐清湾生态系统脆弱性研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 27(3): 111-118.
|
|
PENG XIN, QIU JIANBIAO, CHEN SHAOBO, et al, 2009. The study on the vulnerability of the ecosystem in Yueqingwan Bay[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 27(3): 111-118 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
王丽婧, 郭怀成, 刘永, 等, 2005. 邛海流域生态脆弱性及其评价研究[J]. 生态学杂志, 24(10): 1192-1196.
|
|
WANG LIJING, GUO HUAICHENG, LIU YONG, et al, 2005. Ecological fragility of Qionghai Lake basin and its assessment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24(10): 1192-1196 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
韦蔓新, 范航清, 何本茂, 等, 2013. 广西铁山港红树林区水体的营养水平与结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(4): 84-91.
|
|
WEI MANXIN, FAN HANGQING, HE BENMAO, et al, 2013. Nutritional level and component characteristic of water in mangrove area of Tieshan Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(4): 84-91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
魏晓旭, 赵军, 魏伟, 等, 2016. 中国县域单元生态脆弱性时空变化研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(2): 726-739.
|
|
WEI XIAOXU, ZHAO JUN, WEI WEI, et al, 2016. Spatial and temporal changes of ecological vulnerability per county unit in China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(2): 726-739 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
伍淑婕, 2007. 广西红树林生态系统服务功能分类体系研究[J]. 贺州学院学报, 23(2): 122-125.
|
|
WU SHUJIE, 2007. Classification systems for the mangrove forest ecosystem service functions in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Hezhou University, 23(2): 122-125 (in Chinese).
|
| [16] |
徐明德, 曹露, 何娟, 等, 2011. 基于GIS的生态环境脆弱性模糊综合评价[J]. 中国水土保持, (6): 19-21.
|
|
XU MINGDE, CAO LU, HE JUAN, et al, 2011. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation on frangibility of ecological environment based on GIS[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, (6): 19-21 (in Chinese).
|
| [17] |
张云峰, 2010. 江苏盐城海岸湿地生态系统脆弱性评价体系构建[J]. 淮阴师范学院学报(自然科学), 9(1): 39-44.
|
|
ZHANG YUNFENG, 2010. The research on assessment system of coastal wetland based on its ecological vulnerability in Yancheng Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Huaiyin Teachers College (Natural Science), 9(1): 39-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
郑耀辉, 王树功, 陈桂珠, 2010. 滨海红树林湿地生态系统健康的诊断方法和评价指标[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(1): 111-116.
|
|
ZHENG YAOHUI, WANG SHUGONG, CHEN GUIZHU, 2010. Diagnostic methods and assessment indictors for mangrove wetland ecosystem health[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(1): 111-116 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
中国海湾志编纂委员会, 1993. 中国海湾志: 第十二分册(广西海湾)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
|
|
Editorial Committee of the Chinese Gulf Journal, 1993. Twelfth Chinese Journal of the Gulf (Guangxi Bay)[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press (in Chinese).
|
| [20] |
钟慧琪, 鲍姗姗, 韩宇, 等, 2017. 福建罗源湾海湾生态系统脆弱性评价[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 36(1): 16-23.
|
|
ZHONG HUIQI, BAO SHANSHAN, HAN YU, et al, 2017. Assessment on the vulnerability of Luoyuan Bay ecosystem, Fujian[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 36(1): 16-23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [21] |
POLSKY C, NEFF R, YARNAL B, 2007. Building comparable global change vulnerability assessments: The vulnerability scoping diagram[J]. Global Environmental Change, 17(3-4): 472-485.
|
 ), 黄子眉2, 陈剑锋2, 王欣1, 韦江玲3
), 黄子眉2, 陈剑锋2, 王欣1, 韦江玲3
 ), Zimei HUANG2, Jianfeng CHEN2, Xin WANG1, Jiangling WEI3
), Zimei HUANG2, Jianfeng CHEN2, Xin WANG1, Jiangling WEI3