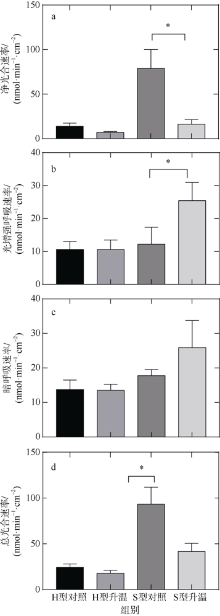
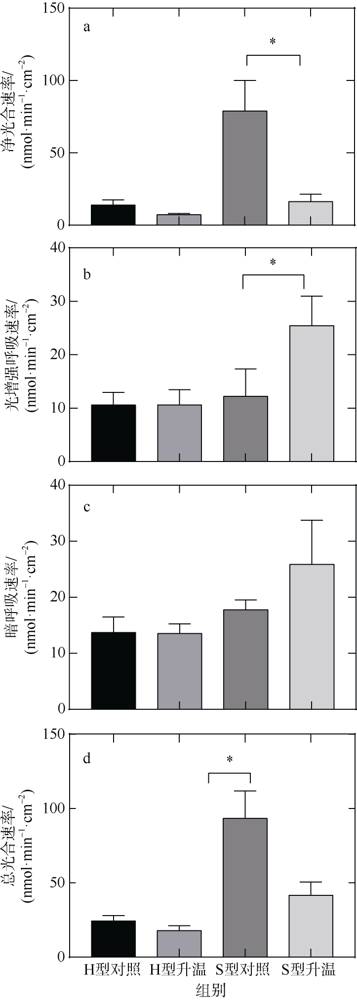
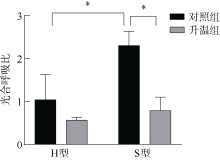
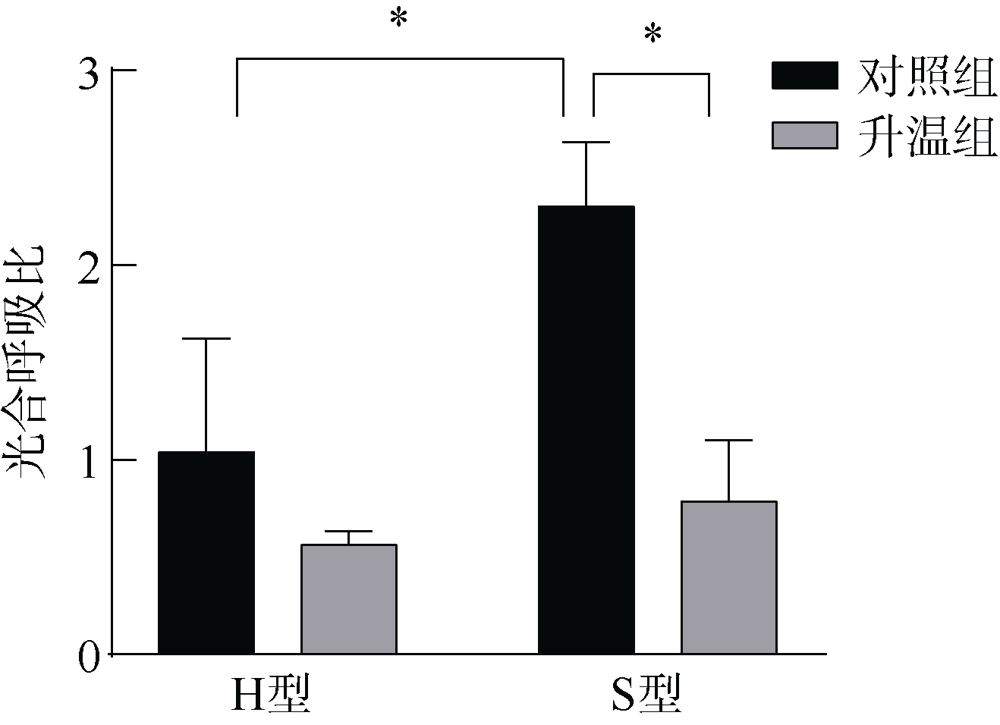
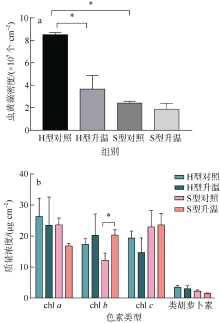
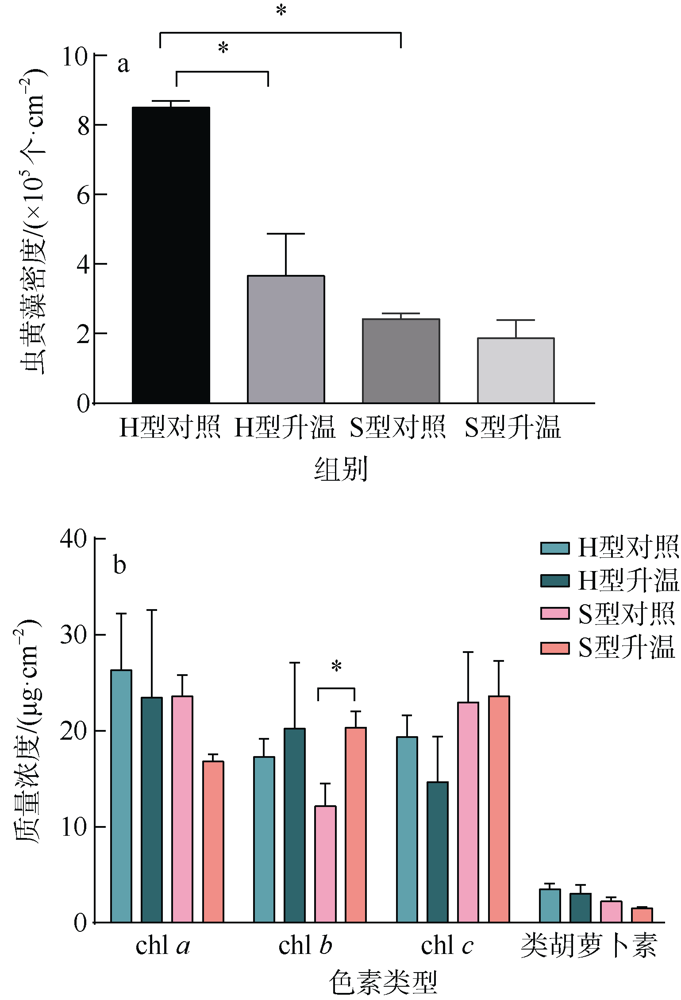
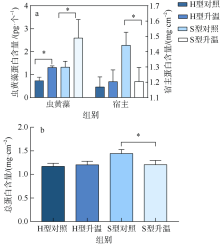
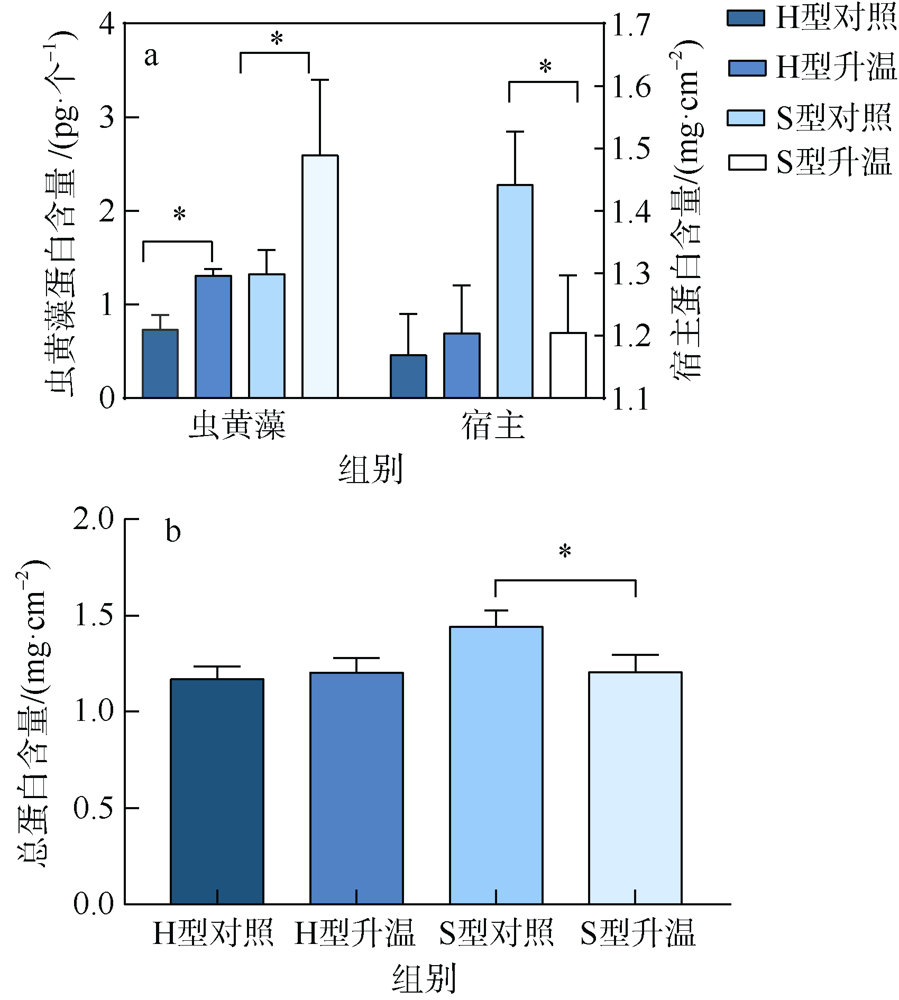
| [1] |
匡志远, 宋振亚, 董昌明, 2020. 基于机器学习订正模型的未来百年全球海表温度预估研究[J]. 气候变化研究快报, 9(4): 270-284.
|
|
KUANG ZHIYUAN, SONG ZHENYA, DONG CHANGMING, 2020. Study on the future projection of global sea surface temperature over 21st century using a biases correction model based on machine learning[J]. Climate Change Research Letters, 9(4): 270-284. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.12677/CCRL.2020.94031
|
| [2] |
梁宇娴, 俞晓磊, 郭亚娟, 等, 2020. 3种传统方法对不同珊瑚表面积测量的适用性及其校准方法——以3D扫描技术为基准[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(1): 85-93.
doi: 10.11978/2019039
|
|
LIANG YUXIAN, YU XIAOLEI, GUO YAJUAN, et al, 2020. Applicability and calibration methods of three traditional surface area measurement methods for different coral species — based on 3D scanning technology[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(1): 85-93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11978/2019039
|
| [3] |
吴英, 2018. 丛生盔形珊瑚(Galaxea fascicularis)两种形态型的结构特征与生长特性的比较分析[D]. 海口: 海南大学.
|
|
WU YING, 2018. Comparison and analysis of the structural characteristics and growth characteristics of two morphological types of Galaxea fascicularis[D]. Haikou: Hainan University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
俞晓磊, 江雷, 罗勇, 等, 2019. 异养营养对丛生盔形珊瑚代谢及共生藻光合生理的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 43(12): 81-88.
|
|
YU XIAOLEI, JIANG LEI, LUO YONG, et al, 2019. Effects of heterotrophy on the metabolism and symbiont photosynthetic physiology of Galaxea fascicularis[J]. Marine Sciences, 43(12): 81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
ANTHONY K R N, HOEGH-GULDBERG O, 2003. Variation in coral photosynthesis, respiration and growth characteristics in contrasting light microhabitats: an analogue to plants in forest gaps and understoreys?[J]. Functional Ecology, 17(2): 246-259.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2435.2003.00731.x
|
| [6] |
BAUMANN J, GROTTOLI A G, HUGHES A D, et al, 2014. Photoautotrophic and heterotrophic carbon in bleached and non-bleached coral lipid acquisition and storage[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 461: 469-478.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2014.09.017
|
| [7] |
BENNETT S, DUARTE C M, MARBÀ N, et al, 2019. Integrating within-species variation in thermal physiology into climate change ecology[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: biological Sciences, 374(1778): 20180550.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0550
|
| [8] |
BISCÉRÉ T, LORRAIN A, RODOLFO-METALPA R, et al, 2017. Nickel and ocean warming affect scleractinian coral growth[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 120(1-2): 250-258.
doi: S0025-326X(17)30411-3
pmid: 28526200
|
| [9] |
BOVE C B, UMBANHOWAR J, CASTILLO K D, 2020. Meta-analysis reveals reduced coral calcification under projected ocean warming but not under acidification across the Caribbean Sea[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7: 127.
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00127
|
| [10] |
COLOMBO-PALLOTTA M F, RODRÍGUEZ-ROMÁN A, IGLESIAS-PRIETO R, 2010. Calcification in bleached and unbleached Montastraea faveolata: evaluating the role of oxygen and glycerol[J]. Coral Reefs, 29(4): 899-907.
doi: 10.1007/s00338-010-0638-x
|
| [11] |
DA SILVAFONSECA J, DE BARROSMARANGON I L F, MARQUES J A, et al, 2017. Effects of increasing temperature alone and combined with copper exposure on biochemical and physiological parameters in the zooxanthellate scleractinian coral Mussismilia harttii[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 190: 121-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.07.002
|
| [12] |
DARLING E S, ALVAREZ‐FILIP L, OLIVER T A, et al, 2012. Evaluating life-history strategies of reef corals from species traits[J]. Ecology Letters, 15(12): 1378-1386.
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01861.x
pmid: 22938190
|
| [13] |
DIAS M, FERREIRA A, GOUVEIA R, et al, 2018. Synergistic effects of warming and lower salinity on the asexual reproduction of reef-forming corals[J]. Ecological Indicators, 98: 334-348.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.11.011
|
| [14] |
DÍAZ-ALMEYDA E M, PRADA C, OHDERA A H, et al, 2017. Intraspecific and interspecific variation in thermotolerance and photoacclimation in Symbiodinium dinoflagellates[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284(1868): 20171767.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2017.1767
|
| [15] |
DUNN S R, BYTHELL J C, LE TISSIER M D A, et al, 2002. Programmed cell death and cell necrosis activity during hyperthermic stress-induced bleaching of the symbiotic sea anemone Aiptasia sp.[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 272(1): 29-53.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00036-9
|
| [16] |
ENRÍQUEZ S, MÉNDEZ E R, HOEGH-GULDBERG O, et al, 2017. Key functional role of the optical properties of coral skeletons in coral ecology and evolution[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284(1853): 20161667.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2016.1667
|
| [17] |
GIBBIN E M, KRUEGER T, PUTNAM H M, et al, 2018. Short-term thermal acclimation modifies the metabolic condition of the coral holobiont[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5: 10.
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00010
|
| [18] |
GROVER R, MAGUER J F, ALLEMAND D, et al, 2008. Uptake of dissolved free amino acids by the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 211(6): 860-865.
doi: 10.1242/jeb.012807
|
| [19] |
HAGEDORN M, CARTER V L, LAGER C, et al, 2016. Potential bleaching effects on coral reproduction[J]. Reproduction, Fertility and Development, 28(8): 1061-1071.
doi: 10.1071/RD15526
|
| [20] |
HUGHES A D, GROTTOLI A G, 2013. Heterotrophic compensation: a possible mechanism for resilience of coral reefs to global warming or a sign of prolonged stress?[J]. PLoS One, 8(11): e81172.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081172
|
| [21] |
HUGHES T P, ANDERSON K D, CONNOLLY S R, et al, 2018. Spatial and temporal patterns of mass bleaching of corals in the Anthropocene[J]. Science, 359(6371): 80-83.
doi: 10.1126/science.aan8048
pmid: 29302011
|
| [22] |
INNIS T, ALLEN-WALLER L, BROWN K T, et al, 2021. Marine heatwaves depress metabolic activity and impair cellular acid-base homeostasis in reef-building corals regardless of bleaching susceptibility[J]. Global Change Biology, 27(12): 2728-2743.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.15622
|
| [23] |
KING N G, MCKEOWN N J, SMALE D A, et al, 2018. The importance of phenotypic plasticity and local adaptation in driving intraspecific variability in thermal niches of marine macrophytes[J]. Ecography, 41(9): 1469-1484.
doi: 10.1111/ecog.03186
|
| [24] |
LIN ZHENYUE, CHEN MINGLIANG, DONG XU, et al, 2017. Transcriptome profiling of Galaxea fascicularis and its endosymbiont Symbiodinium reveals chronic eutrophication tolerance pathways and metabolic mutualism between partners[J]. Scientific Reports, 7: 42100.
doi: 10.1038/srep42100
|
| [25] |
LOHR K E, PATTERSON J T, 2017. Intraspecific variation in phenotype among nursery-reared staghorn coral Acropora cervicornis (Lamarck, 1816)[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 486: 87-92.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2016.10.005
|
| [26] |
MARTA D, 2020. Vulnerability of reef-building corals towards global change[D]. Lisboa: Universidade de Lisboa, Faculdade de Ciências.
|
| [27] |
MIDDLEBROOK R, ANTHONY K R N, HOEGH-GULDBERG O, et al, 2012. Thermal priming affects symbiont photosynthesis but does not alter bleaching susceptibility in Acropora millepora[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 432-433: 64-72.
|
| [28] |
MITTERER R M, 1978. Amino acid composition and metal binding capability of the skeletal protein of corals[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 28(1): 173-180.
|
| [29] |
MOBERG F, FOLKE C, 1999. Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems[J]. Ecological Economics, 29(2): 215-233.
doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00009-9
|
| [30] |
MUSCATINE L, MCCLOSKEY L R, MARIAN R E, 1981. Estimating the daily contribution of carbon from zooxanthellae to coral animal respiration[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 26(4): 601-611.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1981.26.4.0601
|
| [31] |
NAKAJIMA Y, SHINZATO C, SATOH N, et al, 2015. Novel polymorphic microsatellite markers reveal genetic differentiation between two sympatric types of Galaxea fascicularis[J]. PLoS One, 10(7): e0130176.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130176
|
| [32] |
NAKAJIMA Y, ZAYASU Y, SHINZATO C, et al, 2016. Genetic differentiation and connectivity of morphological types of the broadcast-spawning coral Galaxea fascicularis in the Nansei Islands, Japan[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 6(5): 1457-1469.
doi: 10.1002/ece3.1981
|
| [33] |
RAZAK T B, ROFF G, LOUGH J M, et al, 2020. Growth responses of branching versus massive corals to ocean warming on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 705: 135908.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135908
|
| [34] |
RODOLFO-METALPA R, MARTIN S, FERRIER-PAGÈS C, et al, 2010. Response of the temperate coral Cladocora caespitosa to mid- and long-term exposure to pCO2 and temperature levels projected for the year 2100 AD[J]. Biogeosciences, 7(1): 289-300.
doi: 10.5194/bg-7-289-2010
|
| [35] |
SAMIEI J V, SALEH A, MEHDINIA A, et al, 2015. Photosynthetic response of Persian Gulf acroporid corals to summer versus winter temperature deviations[J]. PeerJ, 3: e1062.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.1062
|
| [36] |
SCHOEPF V, GROTTOLI A G, LEVAS S J, et al, 2015. Annual coral bleaching and the long-term recovery capacity of coral[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 282(1819): 20151887.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.1887
|
| [37] |
TOTH L T, STATHAKOPOULOS A, KUFFNER I B, et al, 2019. The unprecedented loss of Florida’s reef-building corals and the emergence of a novel coral-reef assemblage[J]. Ecology, 100(9): e02781.
|
| [38] |
VIMALA T, POONGHUZHALI T V, 2015. Estimation of pigments from seaweeds by using acetone and DMSO[J]. International Journal of Science and Research, 4(10): 1850-1854.
|
| [39] |
WANGPRASEURT D, HOLM J B, LARKUM A W D, et al, 2017. In vivo microscale measurements of light and photosynthesis during coral bleaching: evidence for the optical feedback loop?[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 59.
|
| [40] |
WEPFER P H, NAKAJIMA Y, HUI F K C, et al, 2020. Metacommunity ecology of Symbiodiniaceae hosted by the coral Galaxea fascicularis[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 633: 71-87.
doi: 10.3354/meps13177
|
| [41] |
WOOLDRIDGE S A, 2014. Assessing coral health and resilience in a warming ocean: why looks can be deceptive[J]. BioEssays, 36(11): 1041-1049.
doi: 10.1002/bies.201400074
pmid: 25303686
|
| [42] |
XU SHENDONG, YU KEFU, TAO SHICHEN, et al, 2018. Evidence for the thermal bleaching of Porites corals from 4.0 ka B.P. in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 123(1): 79-94.
doi: 10.1002/2017JG004091
|
 ), 俞晓磊1,2,3,4, 梁宇娴1,2,3, 张喆1,2,3,4, 黄晖1,2,3, 周伟华1,2,3(
), 俞晓磊1,2,3,4, 梁宇娴1,2,3, 张喆1,2,3,4, 黄晖1,2,3, 周伟华1,2,3( ), 袁翔城1,2,3(
), 袁翔城1,2,3( )
)
 ), YU Xiaolei1,2,3,4, LIANG Yuxian1,2,3, ZHANG Zhe1,2,3,4, HUANG Hui1,2,3, ZHOU Weihua1,2,3(
), YU Xiaolei1,2,3,4, LIANG Yuxian1,2,3, ZHANG Zhe1,2,3,4, HUANG Hui1,2,3, ZHOU Weihua1,2,3( ), YUAN Xiangcheng1,2,3(
), YUAN Xiangcheng1,2,3( )
)