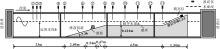
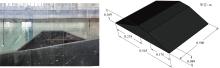
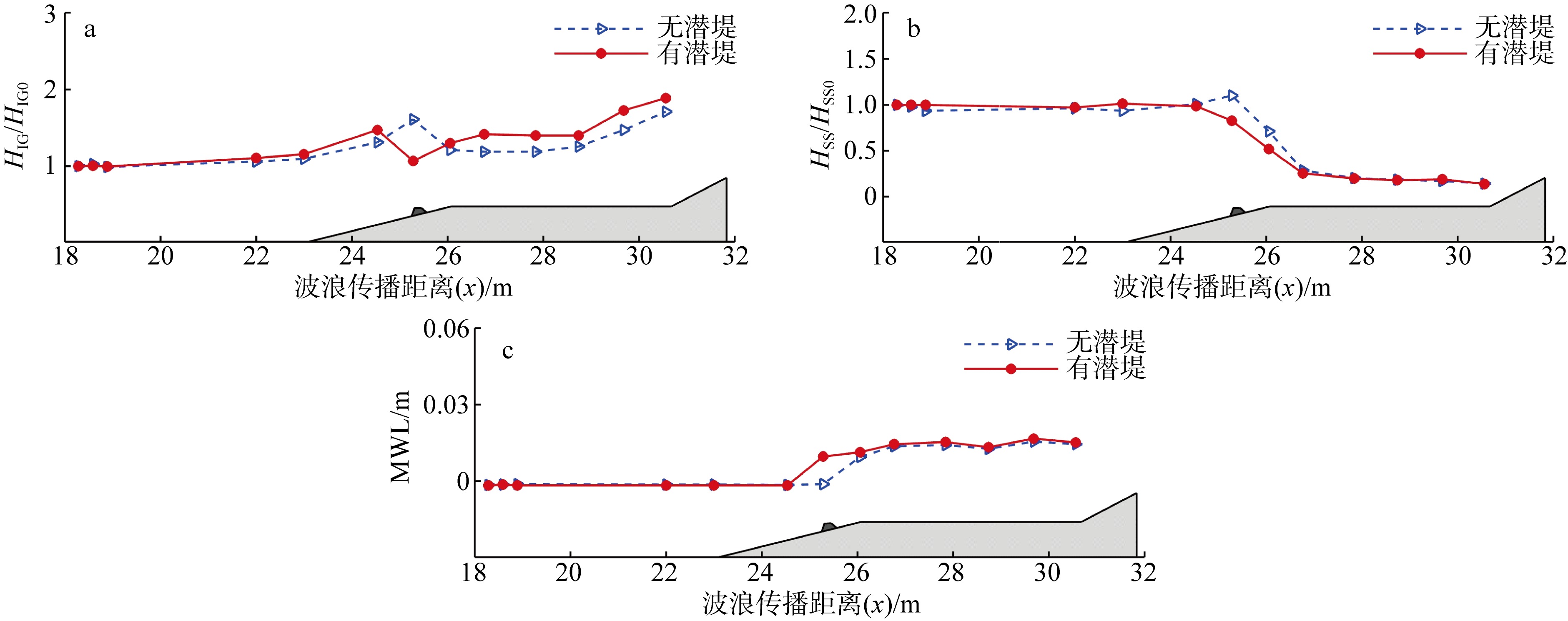
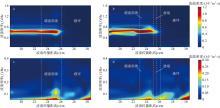
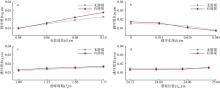
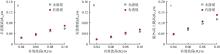
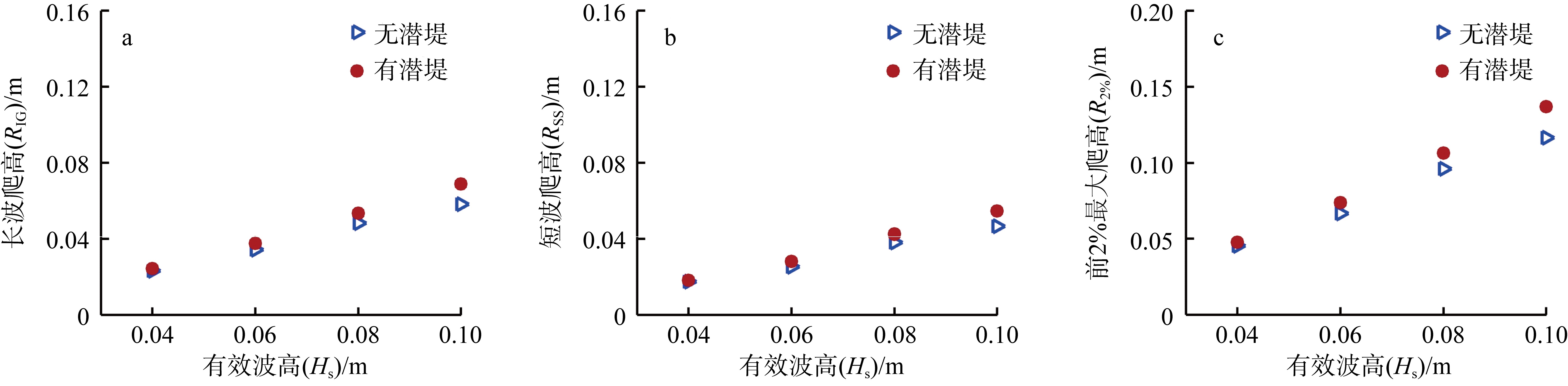
| [1] |
范海荣, 许峰, 王俊, 等, 2015. 潜堤对波浪传播变形的物理模型试验研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 37(1): 121-128.
|
|
FAN HAIRONG, XU FENG, WANG JUN, et al, 2015. Experimental study of wave transmission over a submerged breakwater[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 37(1): 121-128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
任冰, 唐洁, 王国玉, 等, 2018. 规则波在岛礁地形上传播变化特性的试验[J]. 科学通报, 63(Z1): 590-600.
|
|
REN BING, TANG JIE, WANG GUOYU, et al, 2018. Experimental investigation of monochromatic wave transformation characteristics over the coral reefs[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(Z1): 590-600 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
王超, 屈科, 王旭, 等, 2024. 类海啸波在非平整岛礁上传播与演变的试验研究[J]. 热带地理, 44(10): 1838-1846.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240428
|
|
WANG CHAO, QU KE, WANG XU, et al, 2024. Experimental study on complex hydrodynamics of tsunami-like waves over fringing reefs with uneven flat topography[J]. Tropical Geography, 44(10): 1838-1846 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240428
|
| [4] |
王旭, 屈科, 门佳, 2024. 人工采砂坑对规则波岸礁水动力特性的影响研究[J]. 海洋通报, 43(1): 69-85.
|
|
WANG XU, QU KE, MEN JIA, 2024. Study on the effects of artificial excavation pits on the hydrodynamic characteristics of regular wave over fringing reef[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 43(1): 69-85 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
姚宇, 何天城, 唐政江, 等, 2019. 珊瑚礁礁坪宽度对波浪传播变形及增水影响的实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(2): 13-19.
doi: 10.11978/2018079
|
|
YAO YU, HE TIANCHENG, TANG ZHENGJIANG, et al, 2019. Laboratory study on the effect of varying reef-flat width on wave transformation and wave-induced setup[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(2): 13-19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2018079
|
| [6] |
姚宇, 钟翔, 2023. 岛礁水沙动力学研究综述[J]. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版), 20(4): 1-10.
|
|
YAO YU, ZHONG XIANG, 2023. A review of water-sediment dynamics around the reef islands[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science & Technology (Natural Science), 20(4): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
赵恩金, 徐照妍, 潘新颖, 等, 2019. 人工沙滩与潜堤结合岸滩防护工程数值研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 49(6): 119-125.
|
|
ZHAO ENJIN, XU ZHAOYAN, PAN XINYING, et al, 2019. Numerical study on the coastal protection engineering of combination of artificial beach and submerged breakwater[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 49(6): 119-125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
BUCKLEY M L, LOWE R J, HANSEN J E, et al, 2016. Wave setup over a fringing reef with large bottom roughness[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(8): 2317-2333.
|
| [9] |
DATTATRI J, RAMAN H, SHANKAR N J, 1978. Performance characteristics of submerged breakwaters[C]// Coastal Engineering 1978. Hamburg: American Society of Civil Engineers: 2153-2171.
|
| [10] |
FANG KEZHAO, XIAO LI, LIU ZHONGBO, et al, 2022. Experiment and RANS modeling of solitary wave impact on a vertical wall mounted on a reef flat[J]. Ocean Engineering, 244: 110384.
|
| [11] |
GOURLAY M R, 1996. Wave set-up on coral reefs. 1. Set-up and wave-generated flow on an idealised two dimensional horizontal reef[J]. Coastal Engineering, 27(3-4): 161-193.
|
| [12] |
LIU WEIJIE, SHAO KEQI, NING YUE, et al, 2020. Numerical study of the impact of climate change on irregular wave Run-up over reef-fringed coasts[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 34(2): 162-171.
|
| [13] |
LOWE R J, SHAVIT U, FALTER J L, et al, 2008. Modeling flow in coral communities with and without waves: a synthesis of porous media and canopy flow approaches[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 53(6): 2668-2680.
|
| [14] |
MONISMITH S G, ROGERS J S, KOWEEK D, et al, 2015. Frictional wave dissipation on a remarkably rough reef[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(10): 4063-4071.
|
| [15] |
NING YUE, LIU WEIJIE, ZHAO XIZENG, et al, 2019. Study of irregular wave Run-up over fringing reefs based on a shock-capturing Boussinesq model[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 84: 216-224.
|
| [16] |
QU K, WANG X, YAO Y, et al, 2024. Numerical investigation of infragravity wave hydrodynamics at fringing reef with a permeable layer[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 275: 105212.
|
| [17] |
STOCKDON H F, HOLMAN R A, HOWD P A, et al, 2006. Empirical parameterization of setup, swash, and runup[J]. Coastal Engineering, 53(7): 573-588.
|
| [18] |
STORLAZZI C D, LOGAN J B, FIELD M E, 2003. Quantitative morphology of a fringing reef tract from high-resolution laser bathymetry: Southern Molokai, Hawaii[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 115(11): 1344-1355.
|
| [19] |
YAO Y, LO E Y M, HUANG Z H, et al, 2009. An experimental study of wave-induced set-up over a horizontal reef with an idealized ridge[C]// ASME 2009 28th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering. Honolulu: ASME: 383-389.
|
 ), 屈科1,2,3(
), 屈科1,2,3( ), 王超1, 喻仞石1, 张泽1
), 王超1, 喻仞石1, 张泽1
 ), QU Ke1,2,3(
), QU Ke1,2,3( ), WANG Chao1, YU Renshi1, ZHANG Ze1
), WANG Chao1, YU Renshi1, ZHANG Ze1