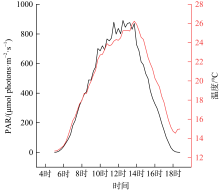
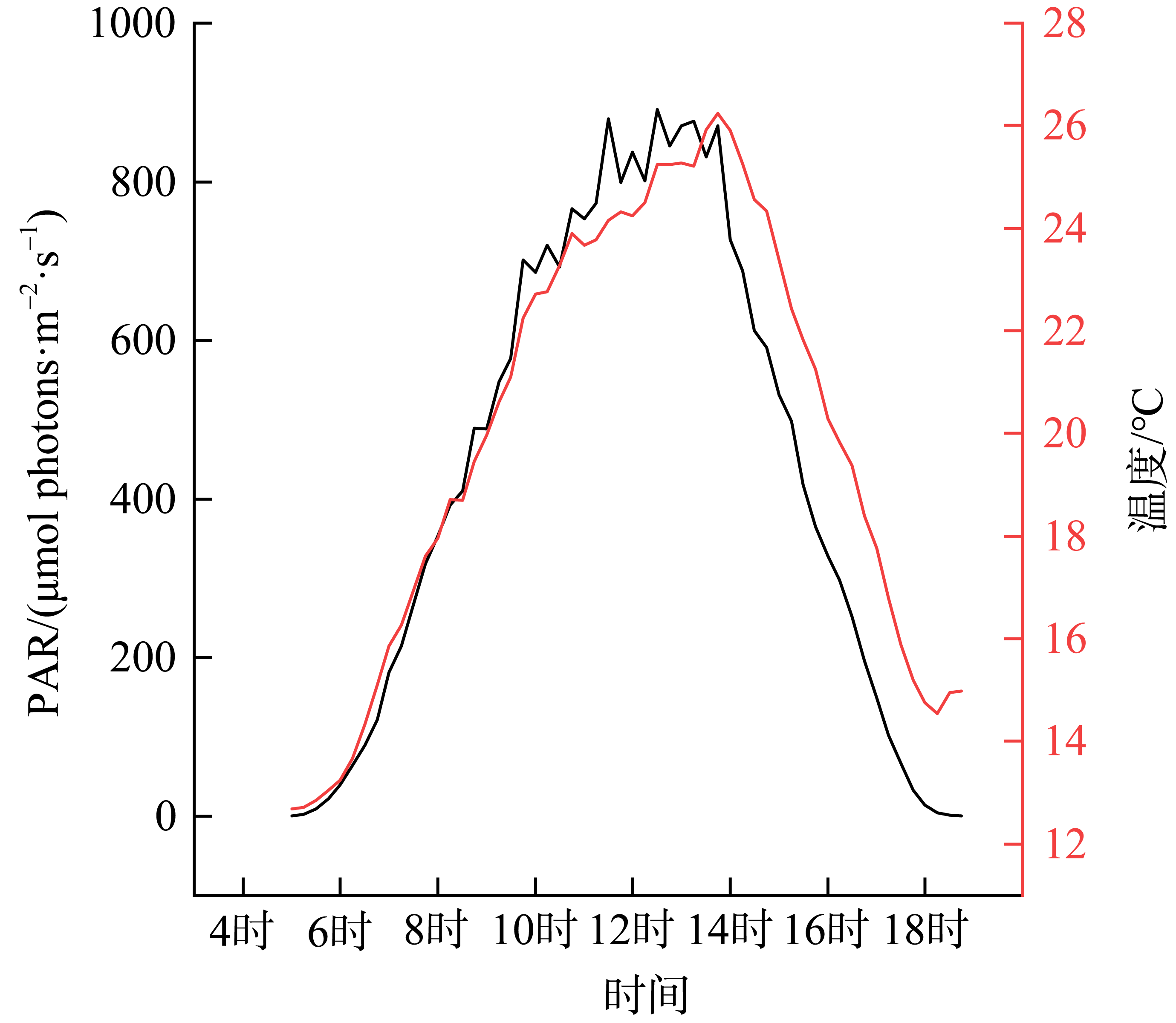
热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 72-84.doi: 10.11978/2024157CSTR: 32234.14.2024157
绿华岛4种潮间带大型海藻光合活性对升温及光质的响应
区嘉铭1( ), 汪舒涵1, 赵旭1,2,3,4, 陈健渠1, 孙佳宁1, 邹俏1, 王凯艺1, 章守宇1,2,3,4, 王凯1,2,3,4(
), 汪舒涵1, 赵旭1,2,3,4, 陈健渠1, 孙佳宁1, 邹俏1, 王凯艺1, 章守宇1,2,3,4, 王凯1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1.上海海洋大学海洋科学与生态环境学院, 上海 201306
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(珠海), 广东 珠海 519082
3.上海海洋大学海洋牧场工程技术研究中心, 上海 201306
4.农业农村部海洋牧场建设专家咨询委员会东海区海洋牧场综合工作站, 上海 201306
-
收稿日期:2024-08-15修回日期:2024-09-18出版日期:2025-05-10发布日期:2025-06-04 -
通讯作者:王凯 -
作者简介:区嘉铭(2000—), 男, 广东省珠海市人, 硕士研究生, 从事大型海藻生理生态研究。email: m220501210@st.shou.edu.cn
-
基金资助:南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(珠海)资助项目(SML2023SP237); 国家自然科学基金(41876191); 现代农业产业技术体系专项资金(CARS-50)
Response of photosynthetic activity to temperature rise and light quality of four intertidal macroalgae from Lühua Island, Zhejiang, China
OU Jiaming1( ), WANG Shuhan1, ZHAO Xu1,2,3,4, CHEN Jianqu1, SUN Jianing1, ZOU Qiao1, WANG Kaiyi1, ZHANG Shouyu1,2,3,4, WANG Kai1,2,3,4(
), WANG Shuhan1, ZHAO Xu1,2,3,4, CHEN Jianqu1, SUN Jianing1, ZOU Qiao1, WANG Kaiyi1, ZHANG Shouyu1,2,3,4, WANG Kai1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. College of Oceanography and Ecological Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai), Zhuhai 519082, China
3. Engineering Technology Research Center of Marine Ranching, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
4. Marine Ranching Comprehensive Workstation of the East China Sea, Expert Advisory Committee of Marine Ranching Construction, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Shanghai 201306, China
-
Received:2024-08-15Revised:2024-09-18Online:2025-05-10Published:2025-06-04 -
Contact:WANG Kai -
Supported by:Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai)(SML2023SP237); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41876191); China Agriculture Research System(CARS-50)
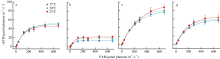
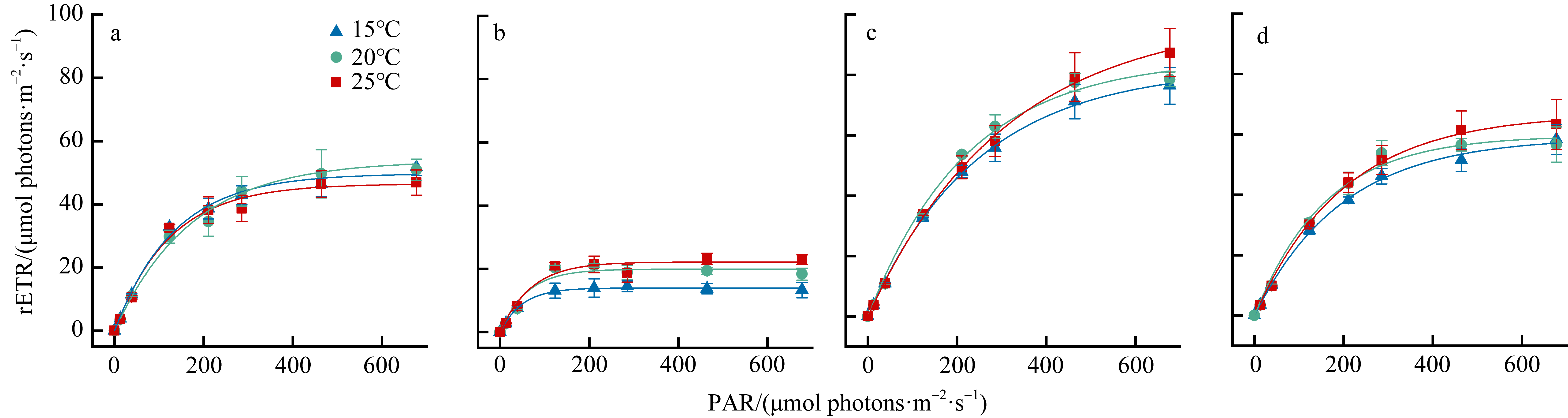
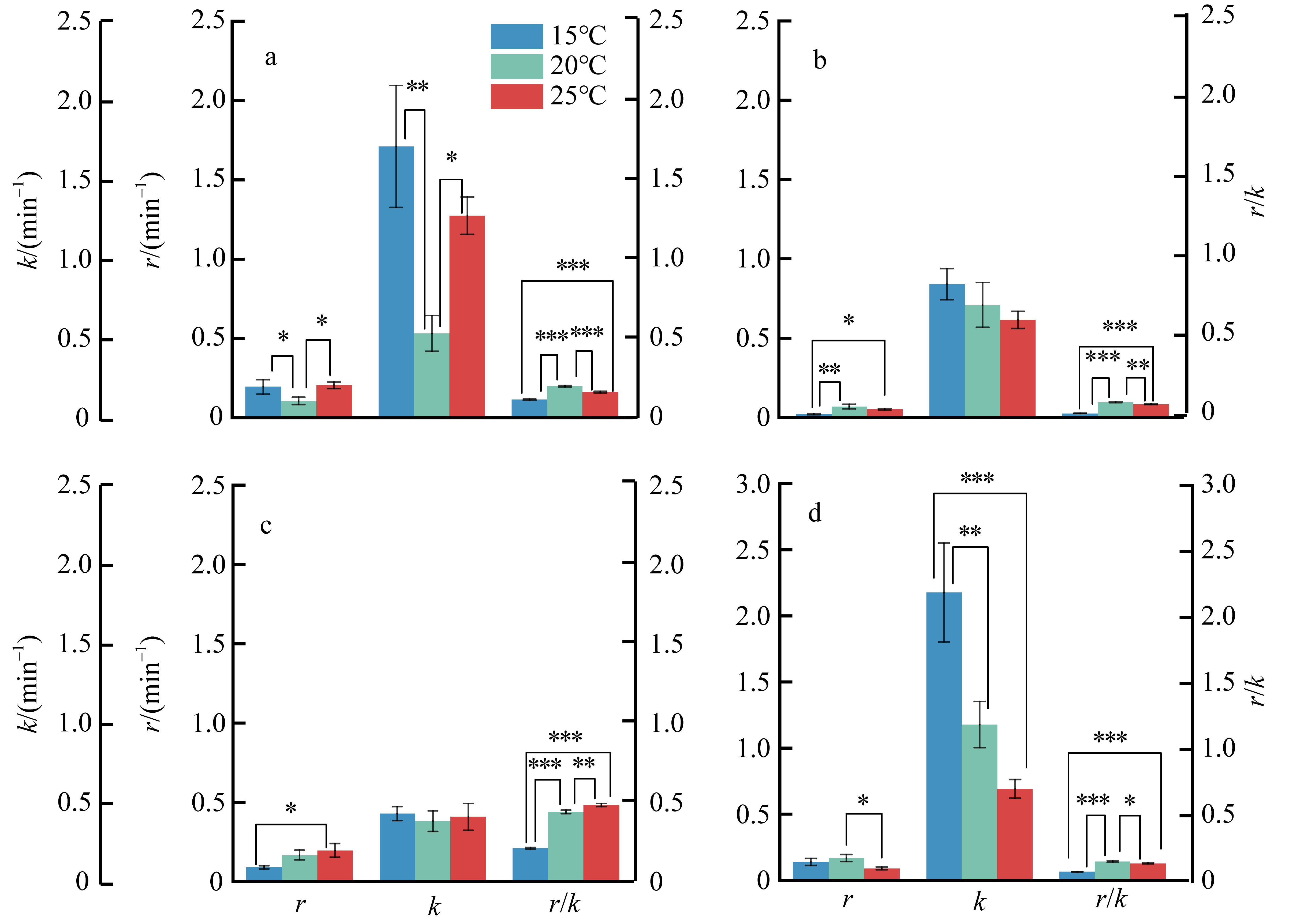
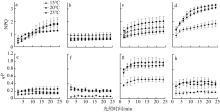
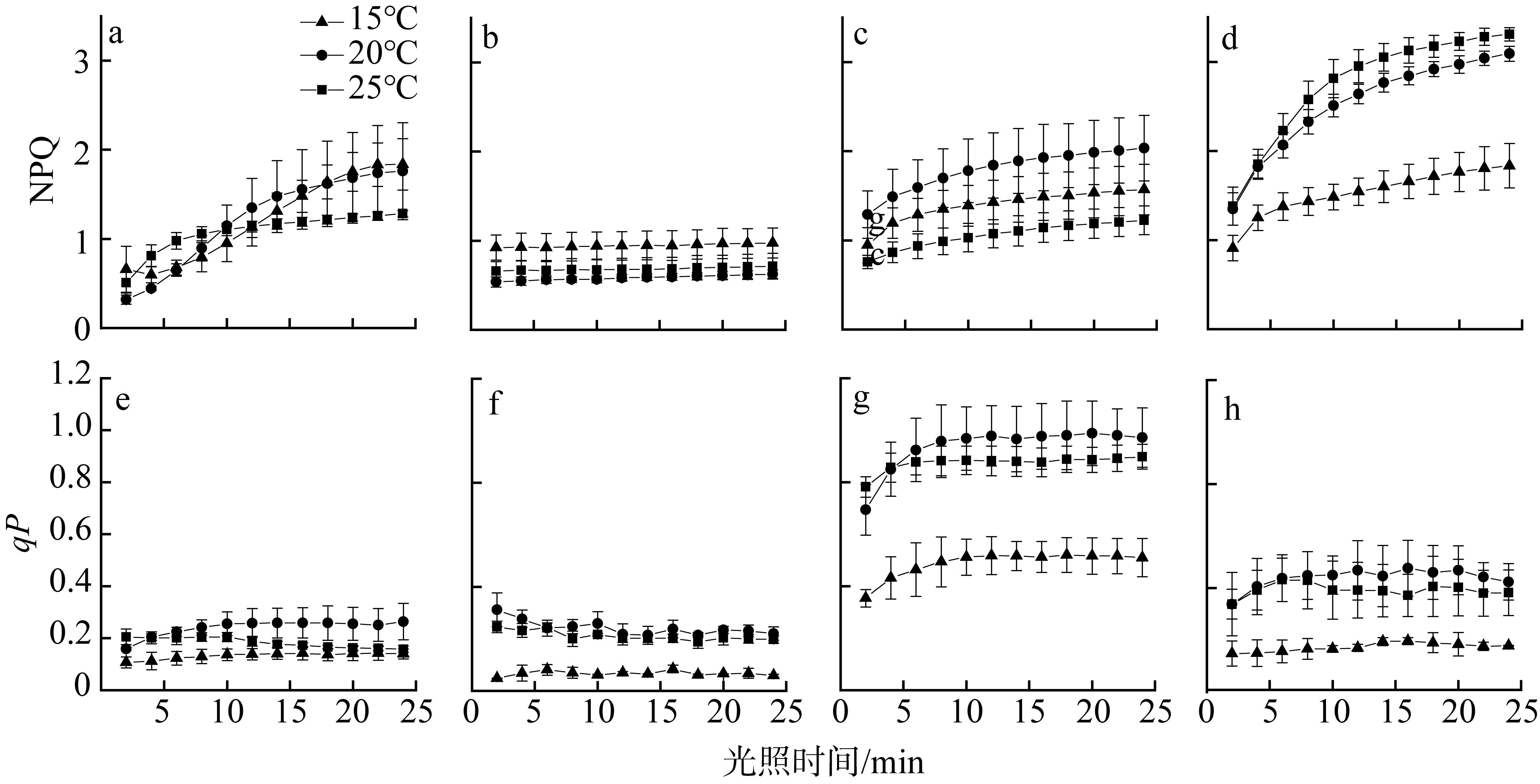
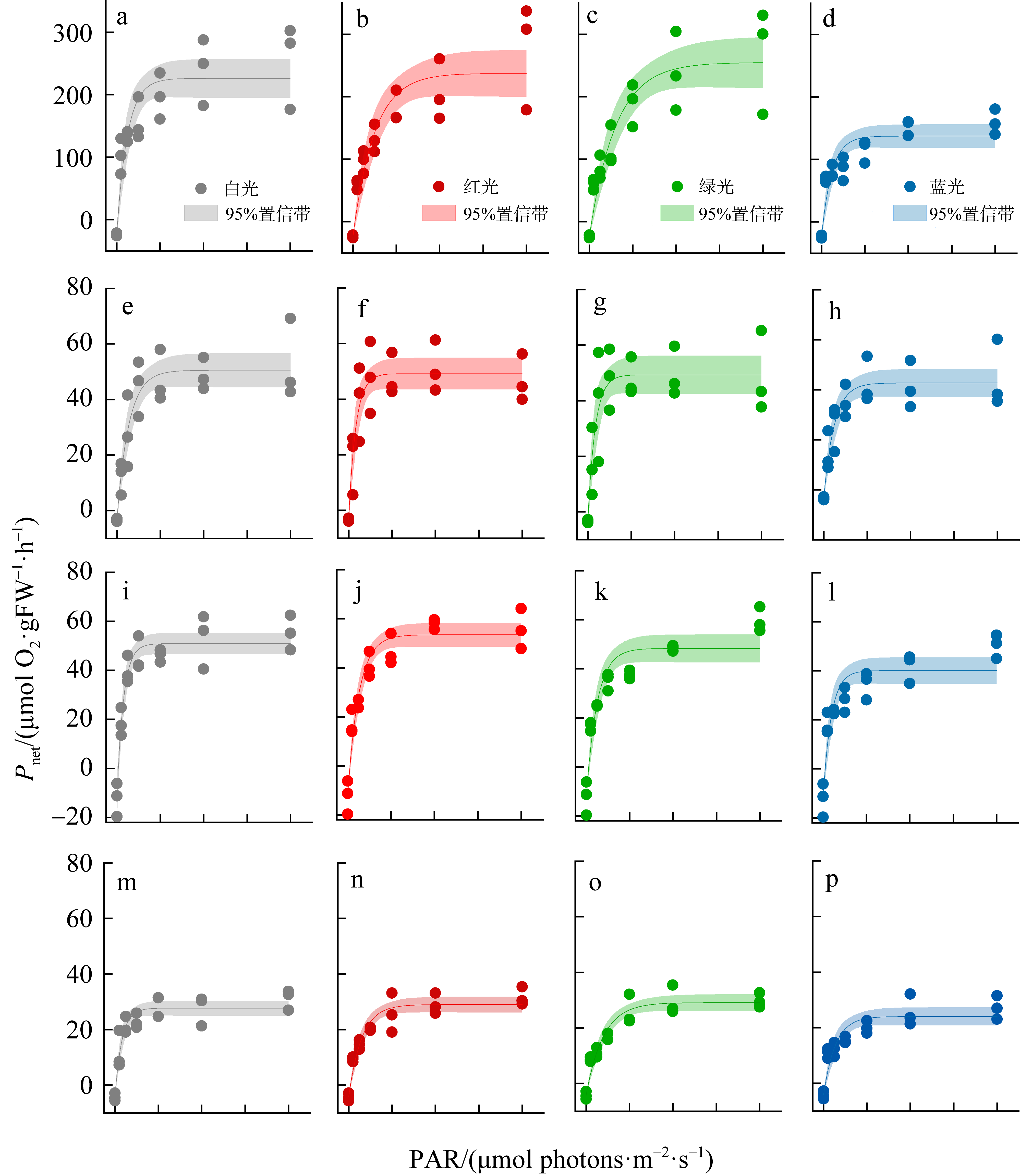
摘要: 为揭示岛礁潮间带大型海藻对升温的光合响应, 以及它们在不同光质下的光合效率, 并为岛礁海藻场建设与藻种培育提供理论依据, 利用叶绿素荧光和光合放氧技术, 研究了绿华岛潮间带4种大型海藻(孔石莼、舌状蜈蚣藻、鼠尾藻和羊栖菜)对升温(温度分别为15℃、20℃、25℃)和不同光质(白、红、绿、蓝光)的光合响应。结果显示: 升温降低这些海藻光系统Ⅱ (photosystem Ⅱ, PSⅡ)的最大量子产量(Fv/Fm), 但显著提升它们在强光下(900μmol photons·m-2·s-1)的有效量子产量[Y(Ⅱ)]、光合修复与损伤速率的比值(r/k)及光化学淬灭(photochemical quenching, qP); 升温显著增大羊栖菜的非光化学淬灭(NPQ), 但显著降低舌状蜈蚣藻的NPQ。与其他海藻相比, 鼠尾藻具有最高的最大相对电子传递速率(rETRmax)、半饱和光强(Ek)、qP和r/k。这些海藻在白、红、绿光下的最大放氧速率(Pmax)无显著差异, 但在蓝光下显著降低, 其中孔石莼的降幅最大。研究表明, 不同海藻对升温和光质的光合响应存在较大差异, 短暂升温有助于4种潮间带大型海藻抵御退潮后的强光, 并提高其在强光下的光合活性, 其中鼠尾藻比其他3种海藻展现出更高的光合活性、耐光性和更好的温度适应性。此外, 在红光和绿光下较强的光合效率反映了这些海藻对潮间带浅水环境的良好适应性。
中图分类号:
- Q945.11
引用本文
区嘉铭, 汪舒涵, 赵旭, 陈健渠, 孙佳宁, 邹俏, 王凯艺, 章守宇, 王凯. 绿华岛4种潮间带大型海藻光合活性对升温及光质的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 72-84.
OU Jiaming, WANG Shuhan, ZHAO Xu, CHEN Jianqu, SUN Jianing, ZOU Qiao, WANG Kaiyi, ZHANG Shouyu, WANG Kai. Response of photosynthetic activity to temperature rise and light quality of four intertidal macroalgae from Lühua Island, Zhejiang, China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(3): 72-84.
表1
不同温度下孔石莼、舌状蜈蚣藻、鼠尾藻和羊栖菜的Fv/Fm与稳态光曲线拟合参数"
| 参数 | 温度/℃ | 孔石莼 | 舌状蜈蚣藻 | 鼠尾藻 | 羊栖菜 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fv/Fm | 25 | 0.73±0.01b | 0.55±0.04b | 0.71±0.01c | 0.67±0.03b |
| 20 | 0.75±0.01a | 0.55±0.02b | 0.72±0.01b | 0.66±0.01b | |
| 15 | 0.76±0.01a | 0.60±0.02a | 0.74±0.01a | 0.72±0.02a | |
| rETRmax/(μmol electron·m-2·s-1) | 25 | 46.48±1.93b | 22.21 ± 1.14a | 99.04±2.69a | 66.82±1.53a |
| 20 | 53.82±5.20a | 19.93 ± 1.07b | 85.4±3.25b | 59.64±2.29b | |
| 15 | 49.74±1.57ab | 13.98 ± 0.25c | 82.4±1.24c | 59.02±1.33b | |
| α | 25 | 0.38±0.02a | 0.32 ± 0.02b | 0.34±0.00b | 0.33±0.01b |
| 20 | 0.31±0.00b | 0.34 ± 0.03a | 0.38±0.01a | 0.38±0.01a | |
| 15 | 0.38±0.01a | 0.28 ± 0.01c | 0.32±0.00c | 0.30±0.00c | |
| Ek/(μmol photons·m-2·s-1) | 25 | 122.7±8.91b | 69.12±7.36a | 305.85±11.33a | 199.7±6.92a |
| 20 | 172.24±17.47a | 59.05±6.76a | 222.79±12.52c | 158.8±9.86b | |
| 15 | 132.73±7.13b | 49.17±1.90b | 245.46±5.31b | 196.67±6.76a |
表2
孔石莼、舌状蜈蚣藻、鼠尾藻和羊栖菜的光质P-I曲线拟合参数"
| 参数 | 光质 | U. pertusa | G. livida | S. thunbergii | S. fusiforme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmax/(μmol O2·g-1FW·h-1) | 白 | 250.28±14.77a | 53.89±2.93a | 63.09±4.26a | 32.05±1.28a |
| 红 | 261.64±17.98a | 52.59±2.71ab | 65.87±2.31a | 33.34±1.34a | |
| 绿 | 279.00±19.68a | 52.70±3.28ab | 60.71±2.70a | 33.44±1.42a | |
| 蓝 | 161.55±8.92b | 46.16±2.64b | 52.49±2.56b | 28.35±1.56b | |
| α(P)/[(μmol O2·g-1FW·h-1)/(μmol photons m-2·s-1)] | 白 | 5.09±1.02a | 0.99±0.18a | 2.09±0.39a | 1.00±0.16a |
| 红 | 2.64±0.48b | 1.59±0.33a | 1.28±0.15b | 0.56±0.07b | |
| 绿 | 2.31±0.40b | 1.55±0.38a | 1.22±0.18b | 0.42±.051b | |
| 蓝 | 3.45±0.66ab | 0.96±0.19a | 1.41±0.26ab | 0.52±0.09b | |
| Rd/(μmol O2·g-1FW·h-1) | — | -24.19±2.00 | -3.38±0.46 | -12.20±3.85 | -4.31±1.16 |
| Ek/(μmol photons m-2·s-1) | 白 | 49.21±11.23b | 54.59±11.11a | 30.22±5.05b | 32.06±5.73b |
| 红 | 98.95±21.49a | 33.13±7.56a | 51.65±6.90a | 59.79±8.78a | |
| 绿 | 120.90±25.50a | 33.96±9.26a | 49.88±8.53a | 79.03±11.26a | |
| 蓝 | 46.84±10.15b | 48.29±10.76a | 37.19±7.71ab | 54.46±11.26ab | |
| Ec/(μmol photons m-2·s-1) | 白 | 5.00±1.00b | 3.53±0.62a | 6.49±1.66b | 4.63±0.74b |
| 红 | 9.60±1.71a | 2.20±0.45a | 10.75±1.24a | 8.28±1.05a | |
| 绿 | 10.96±1.85a | 2.25±0.55a | 11.37±1.69a | 10.91±1.30a | |
| 蓝 | 7.60±1.44ab | 3.67±0.72a | 10.00±1.83ab | 8.99±1.61a |
| [1] |
程晓鹏, 2019. 大型海藻光合活性对不同温度和光照的响应[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学:21.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
程晓鹏, 章守宇, 林军, 等, 2020. 海带孢子体光合活性对不同温度和光照的响应[J]. 水产学报, 44(2): 234-244.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
杜响, 骆其君, 陈海敏, 2023. 不同绿藻对模拟酸雨胁迫的生理生化响应特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 115-123.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
付倩倩, 李航霄, 吴海龙, 等, 2018. 光强对缘管浒苔(Ulva linza)光合生理特性和短期温度效应的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 49(5): 967-974.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
龚静雨, 2020. 大型海藻生长和光合功能对不同LED光质的响应研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学:43.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
郭赣林, 董双林, 董云伟, 2006. 温度及其波动对孔石莼生长及光合作用的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 36(6): 941-945.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
何培民, 段元亮, 刘巧, 等, 2021. 我国近海大型海藻生态修复策略与典型案例[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 40(4): 557-563.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
黄永健, 崔建军, 陈心怡, 等, 2023. 异枝江蓠对温度和光照强度的光合生理响应[J]. 南方水产科学, 19(4): 139-147.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李宝齐, 徐智广, 李凌雪, 等, 2024. 海黍子对强光的光合响应及适应能力研究[J]. 海洋渔业, 46(3): 361-370.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李刚, 万明月, 史晓寒, 等, 2022. 中沙大环礁四种大型海藻的光生理特征比较及其对升温的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(3): 101-110.
doi: 10.11978/2021105 |
|
|
|
| [11] |
刘棋琴, 羊芃, 马明婕, 等, 2018. 温度对4种大型海藻氮磷吸收效率及光合生理特性的影响[J]. 水生生物学报, 42(5): 1050-1056.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
杨宇峰, 罗洪添, 王庆, 等, 2021. 大型海藻规模栽培是增加海洋碳汇和解决近海环境问题的有效途径[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 36(3): 259-269.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
张建琳, 包炎琳, 孙彬, 等, 2023. 下三横山岛潮间带大型海藻群落构成及季节变化[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 42(2): 225-234.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
章守宇, 崔潇, 汪振华, 等, 2021. 枸杞岛贻贝养殖筏架附着海藻的群落结构[J]. 水产学报, 45(5): 726-739.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
赵旭, 2022. 枸杞岛海藻场大型海藻光合生理及生态效应研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学:17.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
赵旭, 王霄, 李训猛, 等, 2024. 天然海藻场中大型海藻有机碳含量及碳汇能力估算研究——以浙江枸杞岛潮下带为例[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 46(03): 82-89.
|
|
doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2024.03.010 |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(03)00136-5 pmid: 12878019 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.01.009 pmid: 24556033 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.03.016 pmid: 24746927 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1007/s11120-010-9536-x pmid: 20224940 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery443 pmid: 30576461 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
pmid: 13363902 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78526-5 pmid: 33293562 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01935 pmid: 26864015 |
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [1] | 曾昭钧, 孙立伟, 谢恩义. 围氏马尾藻(Sargassum wightii)周年生长及有性生殖的早期发育研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 44-52. |
| [2] | 杨宇峰, 邹立功, 贺志理, 张永雨, 王庆. 大型海藻负排放理论技术研究与应用展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 27-36. |
| [3] | 王庆, 任辉, 柯志新. 广东南澳海水养殖区中小型浮游动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 92-103. |
| [4] | 周伟华, 李颖心, 郭亚娟, 霍嘉欣, 宋严, 朱晴, 袁翔城, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海水酸化和升温对两种造礁石珊瑚生长和钙化的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 49-57. |
| [5] | 江志坚, Chanaka Isuranga PREMARATHNE, 方扬, 林基桢, 吴云超, 刘松林, 黄小平. 铵态氮加富对贝克喜盐草光合作用、谷氨酰胺合成酶和氨基酸成分的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 116-125. |
| [6] | 杨芳芳, 肖志梁, 韦章良, 黄怡, 龙丽娟. 海水酸化与升温对孔石藻(Porolithon cf. onkodes)生长钙化的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 87-97. |
| [7] | 史晓寒, 邹定辉, 何泉, 李刚. 不同光强下长茎葡萄蕨藻(Caulerpa lentillifera)直立枝和匍匐枝的光生理特征及其对升温的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 150-160. |
| [8] | 张喆, 俞晓磊, 梁宇娴, 何茜, 黄晖, 袁翔城, 周伟华. 海水升温对非虫黄藻共生型珊瑚Cladopsammia sp.的生理影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 141-149. |
| [9] | 何茜, 俞晓磊, 梁宇娴, 张喆, 黄晖, 周伟华, 袁翔城. 升温对丛生盔形珊瑚两种形态型代谢和共生藻光合生理的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 133-140. |
| [10] | 刘小菊, 施祺, 陶士臣, 杨红强, 张喜洋, 周胜男. 近165年来中沙环礁中北暗沙滨珊瑚生长率及其对海温变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 64-73. |
| [11] | 宋嘉诚, 戚洪帅, 张弛, 蔡锋, 尹航. 潮汐影响下海滩前滨波浪传播耗能过程分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 146-153. |
| [12] | 李刚, 万明月, 史晓寒, 秦耿, 麦广铭, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 邹定辉. 中沙大环礁四种大型海藻的光生理特征比较及其对升温的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 101-110. |
| [13] | 戴晓娟, 胡韧, 罗洪添, 王庆, 胡晓娟, 白敏冬, 杨宇峰. 大型海藻龙须菜凋落物分解对水质的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1): 91-98. |
| [14] | 张才学, 周伟男, 孙省利, 宋之光. 硇洲岛大型海藻群落的季节演替*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(1): 74-84. |
| [15] | 王卉,李恒翔,李路,严岩. 大亚湾大型海藻丛的大角玻璃钩虾种群分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(4): 52-58. |
|
||