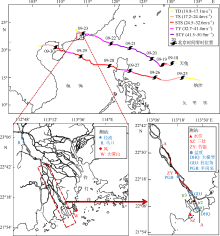
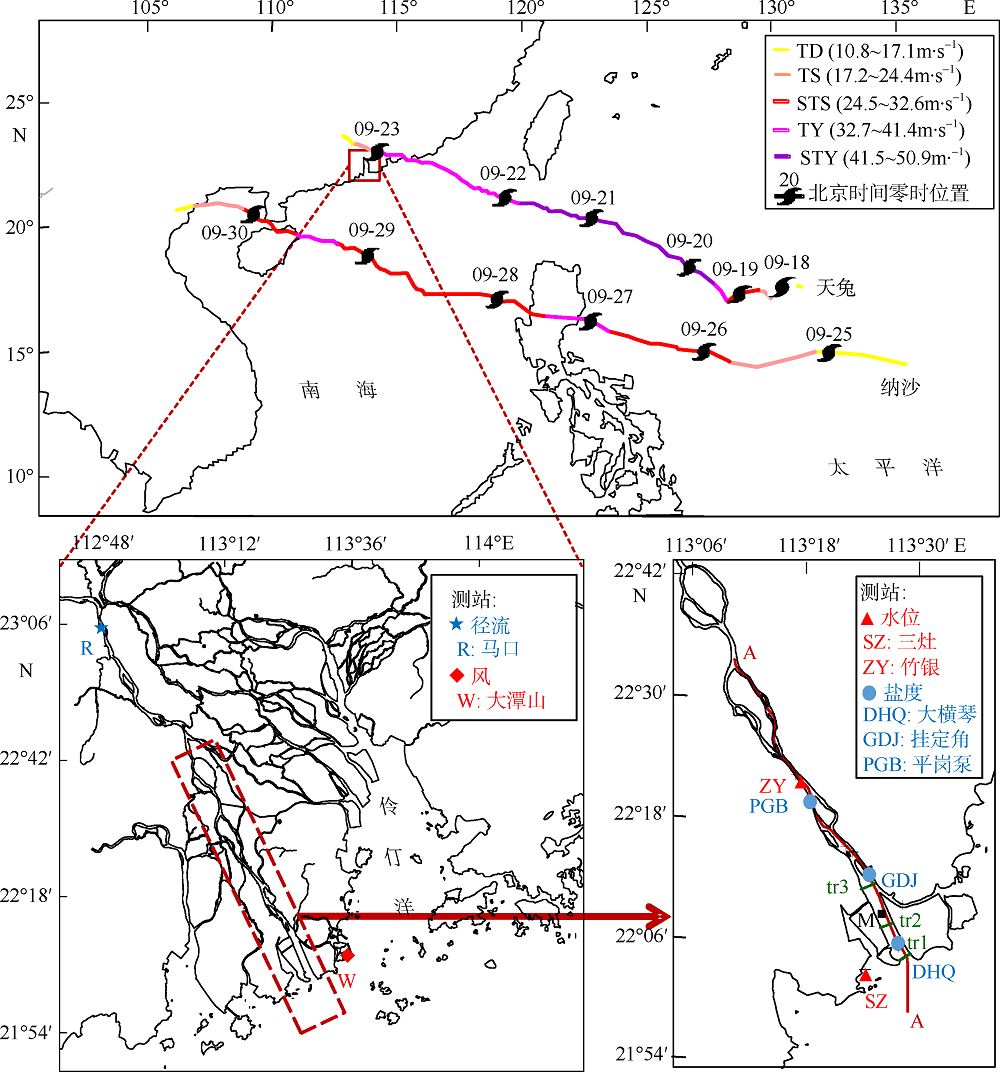
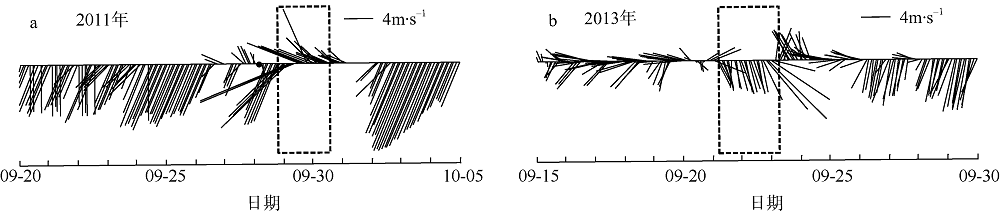
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 53-67.doi: 10.11978/2018081CSTR: 32234.14.2018081
• Marine Hydrography • Previous Articles Next Articles
The particular influence caused by typhoon path on salt intrusion in the Modaomen Waterway, China
Mingjie PAN1,2,Jun KONG1( ),Fang YANG3,Zhaoyang LUO1,Weisheng ZHANG1,Li JING1,4,Qing WANG1,Zhanchen LI5
),Fang YANG3,Zhaoyang LUO1,Weisheng ZHANG1,Li JING1,4,Qing WANG1,Zhanchen LI5
- 1. Key Laboratory of Coastal Disaster and Defence (Hohai University), Ministry of Education, Nanjing 210098, China
2. Nanjing Hawksoft Technology Company Limited, Nanjing 211100, China
3. Scientific Research Institute, Pearl River Water Resources Commission, Guangzhou 510611, China
4. Nanjing Institute of Environmental Sciences, Ministry of Environmental Protection, Nanjing 210042, China
5. Beihai Navy Engineer Design Institute, Qingdao 266012, China
-
Received:2018-08-06Revised:2018-11-24Online:2019-05-20Published:2019-06-17 -
Contact:Jun KONG E-mail:kongjun999@126.com -
Supported by:Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Pearl River Estuary Dynamics and Associated Process Regulation, Ministry of Water Resources([2018]KJ07);Open Fund for Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Coastal Disaster and Protection Education(201706)
CLC Number:
- P731.2
Cite this article
Mingjie PAN,Jun KONG,Fang YANG,Zhaoyang LUO,Weisheng ZHANG,Li JING,Qing WANG,Zhanchen LI. The particular influence caused by typhoon path on salt intrusion in the Modaomen Waterway, China[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 53-67.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Summary of numerical experiments performed"
| 试验 | 路径 | 径流量/(m3·s-1) | 风况 |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-1 | 纳沙 | 1000 | 全局风 |
| U-1 | 天兔 | 1000 | 全局风 |
| N-2 | 纳沙 | 2000 | 全局风 |
| U-2 | 天兔 | 2000 | 全局风 |
| N-3 | 纳沙 | 3000 | 全局风 |
| U-3 | 天兔 | 3000 | 全局风 |
| N-4 | 纳沙 | 4000 | 全局风 |
| U-4 | 天兔 | 4000 | 全局风 |
| N-6 | 纳沙 | 6000 | 全局风 |
| U-6 | 天兔 | 6000 | 全局风 |
| N-8 | 纳沙 | 8000 | 全局风 |
| U-8 | 天兔 | 8000 | 全局风 |
| N-nlw | 纳沙 | 2000 | 无局地风 |
| U-nlw | 天兔 | 2000 | 无局地风 |
| N-nw | 纳沙 | 实测流量过程 | 去除台风作用(即9月28日至10月1日期间无风) |
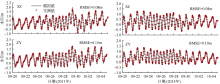
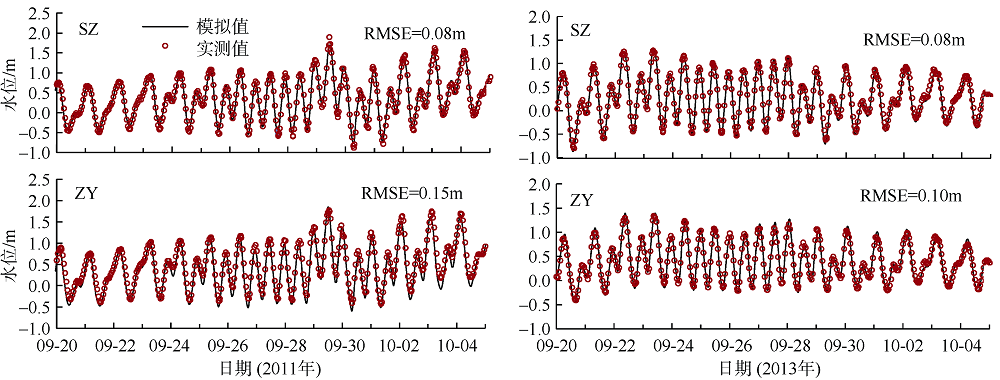
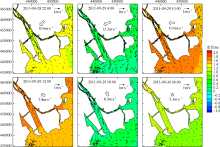
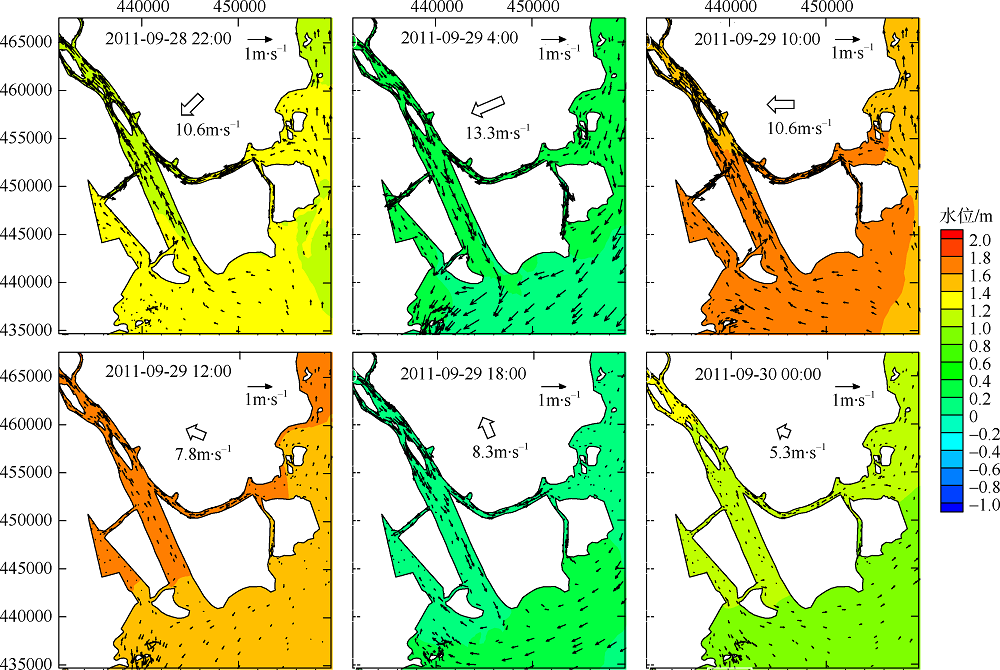
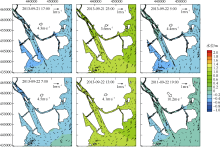
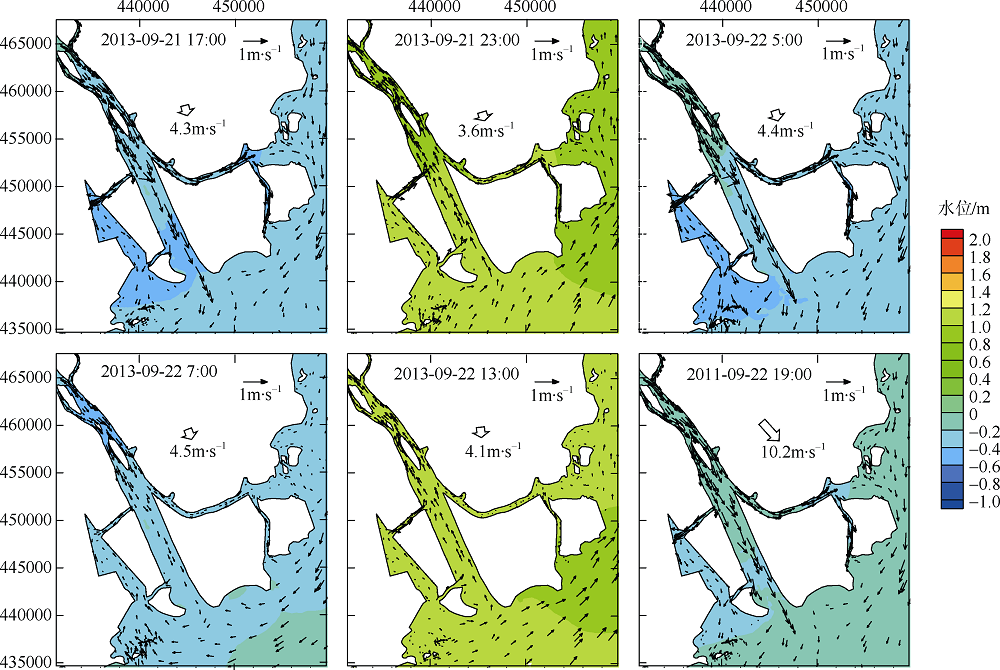
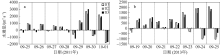
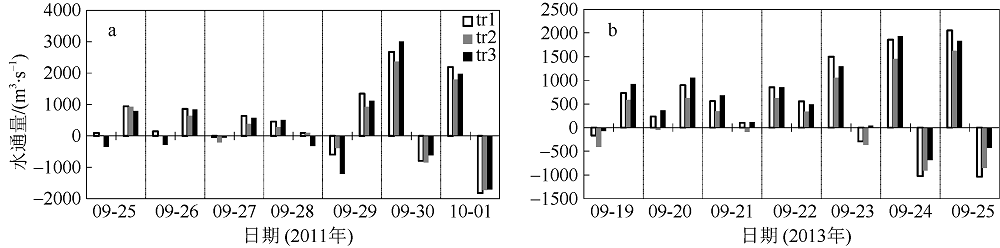
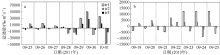
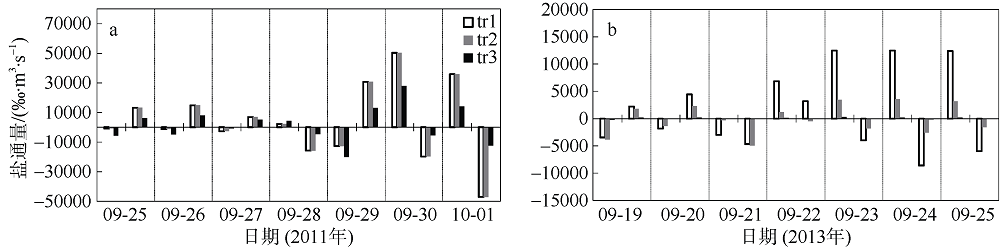
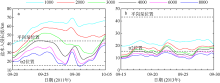
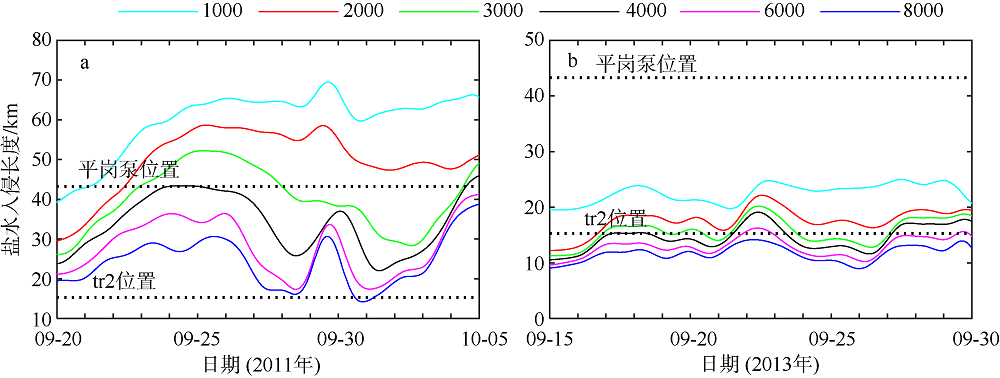
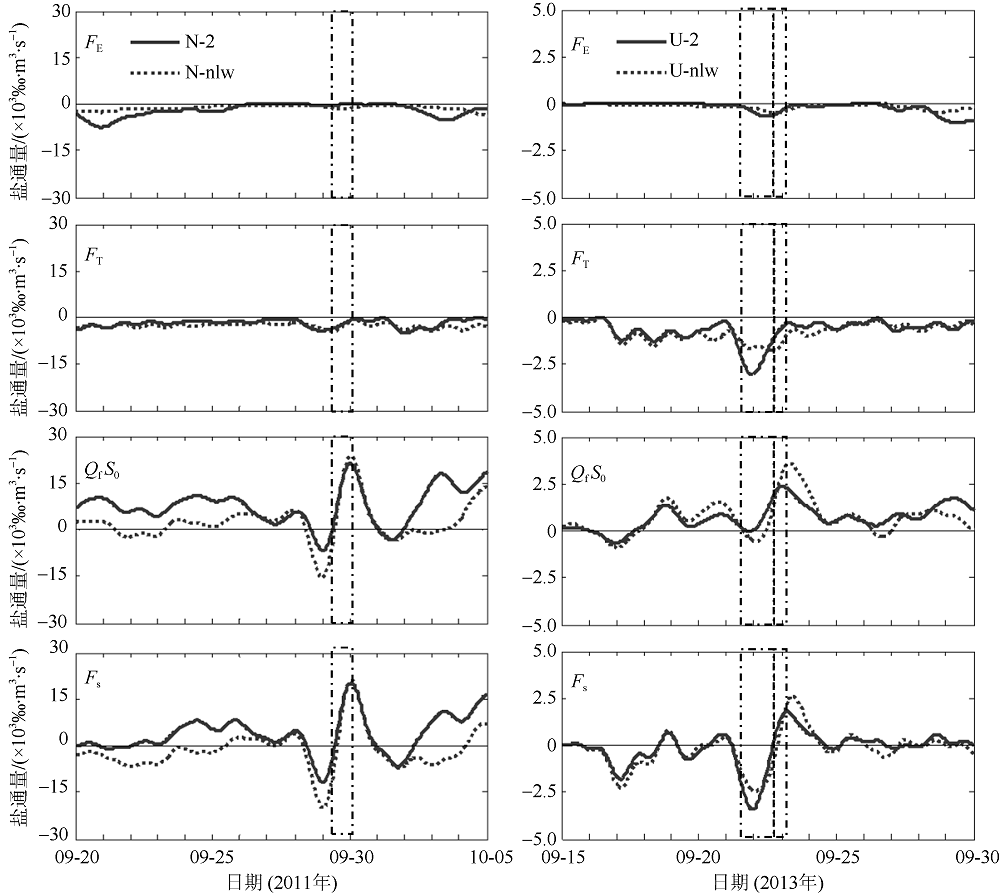
Fig. 11
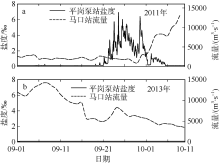
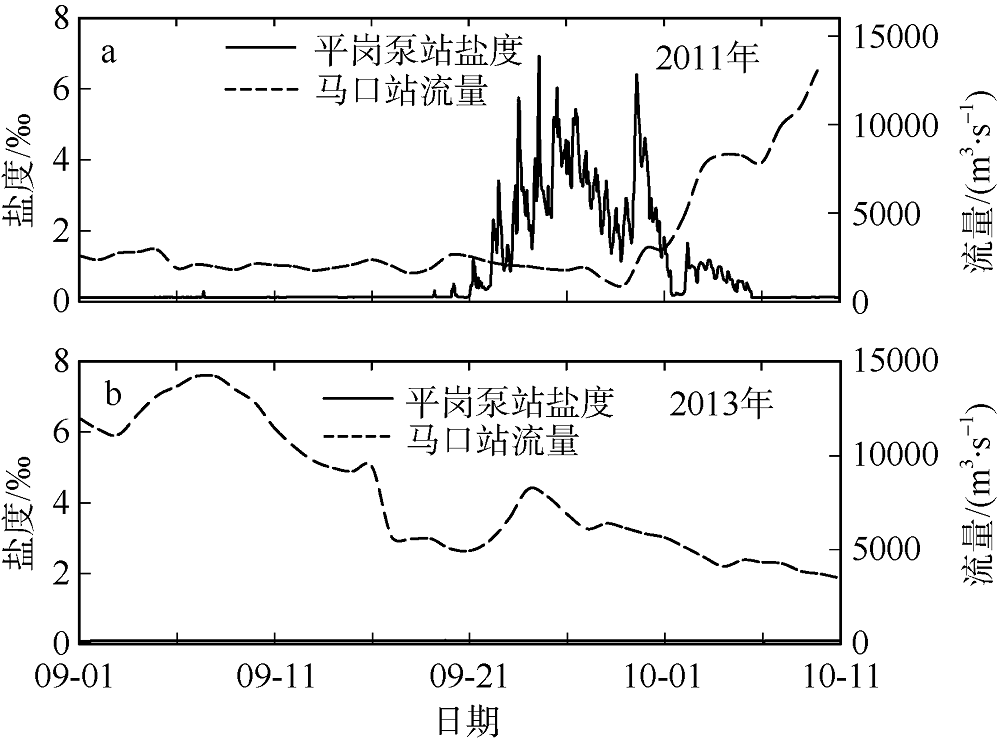
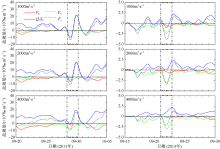
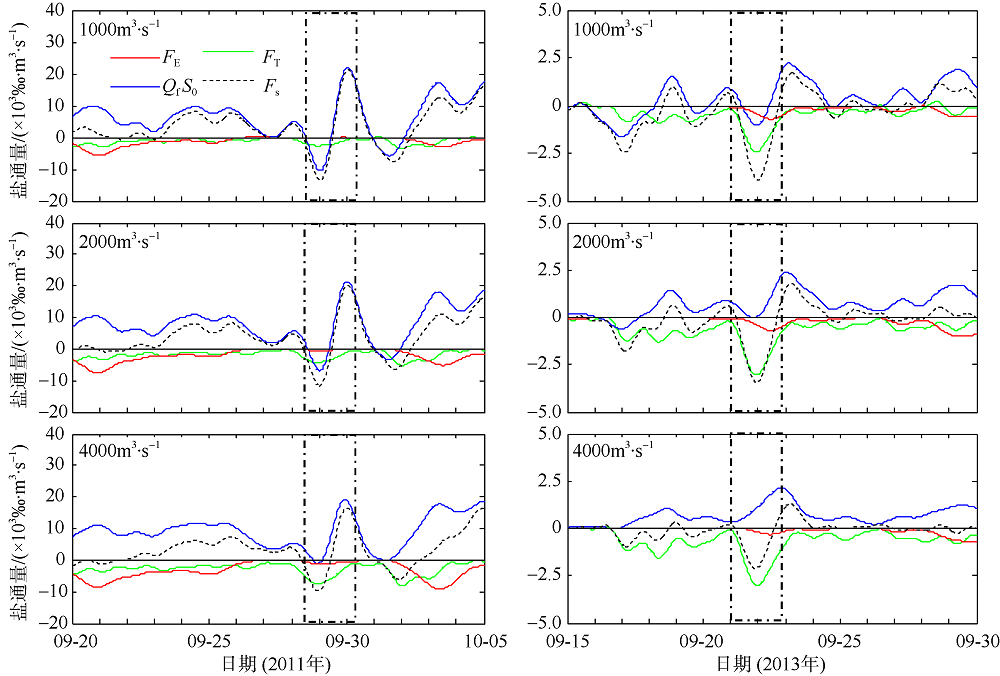
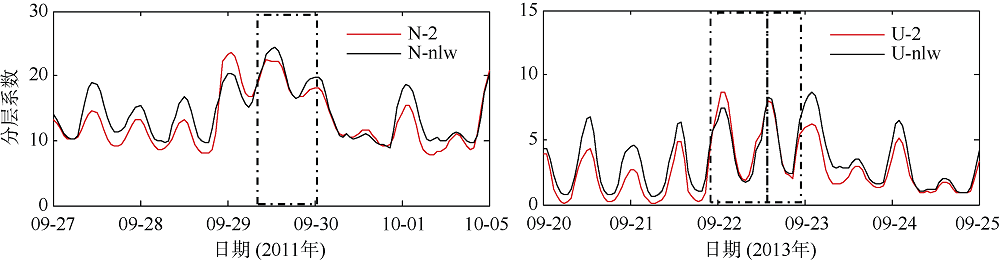
Temporal changes of 33-h low-pass-filtered salt flux transects with 2000 m3·s-1 river discharge during Nesat (2011) and Usagi (2013). Positive value means seaward, negative value means landward, and the dashed box marks the typhoon effect period; FE、FT、QFS0、FS refer to the steady shear salt flux, the tidal oscillatory salt flux, the advective salt flux and the net salt flux, respectively"
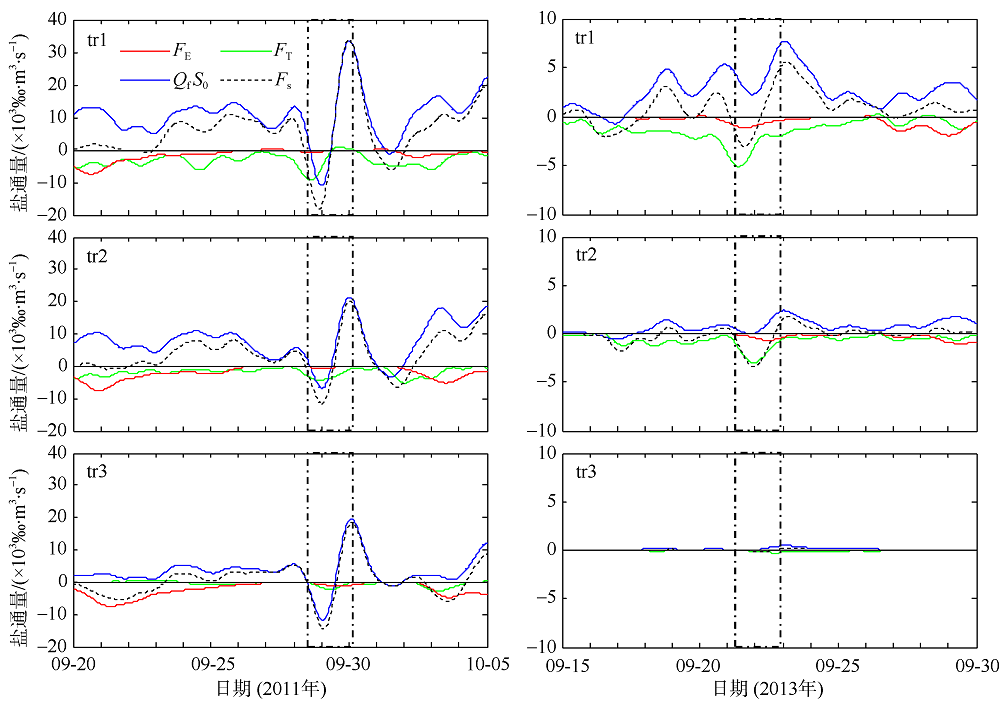
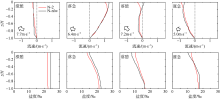
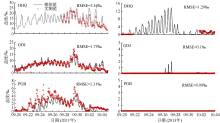
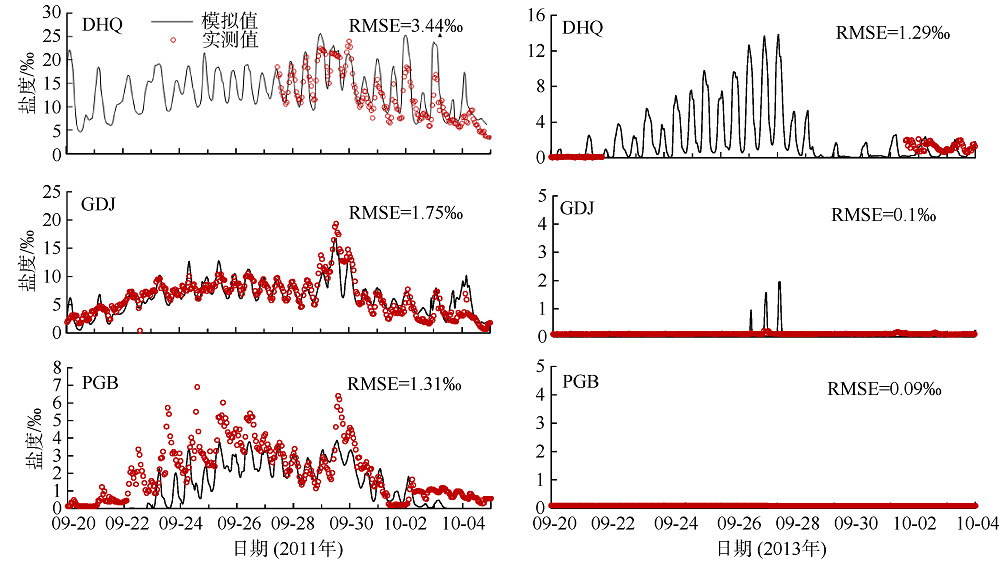
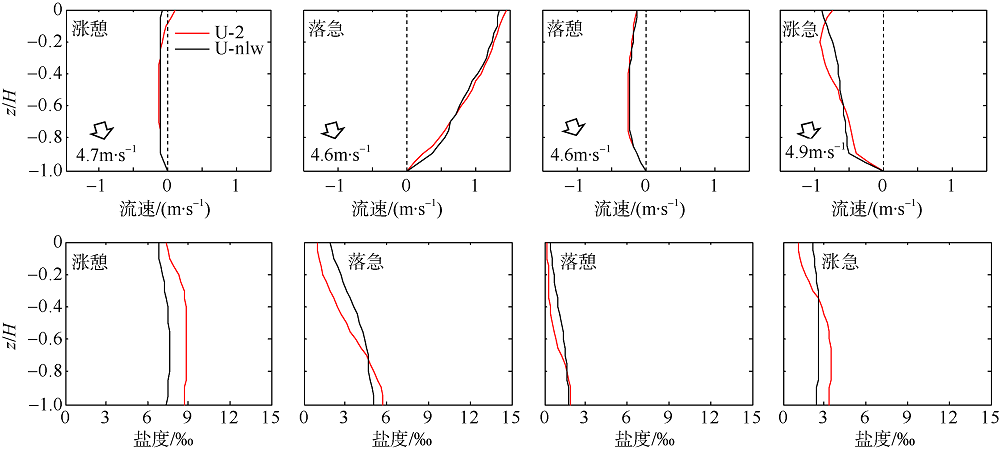
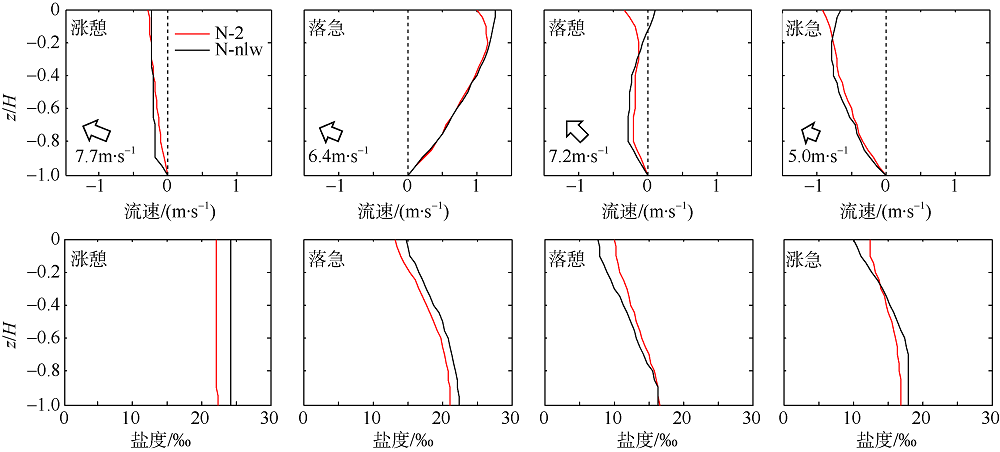
Fig. 16
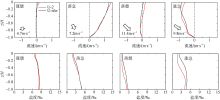
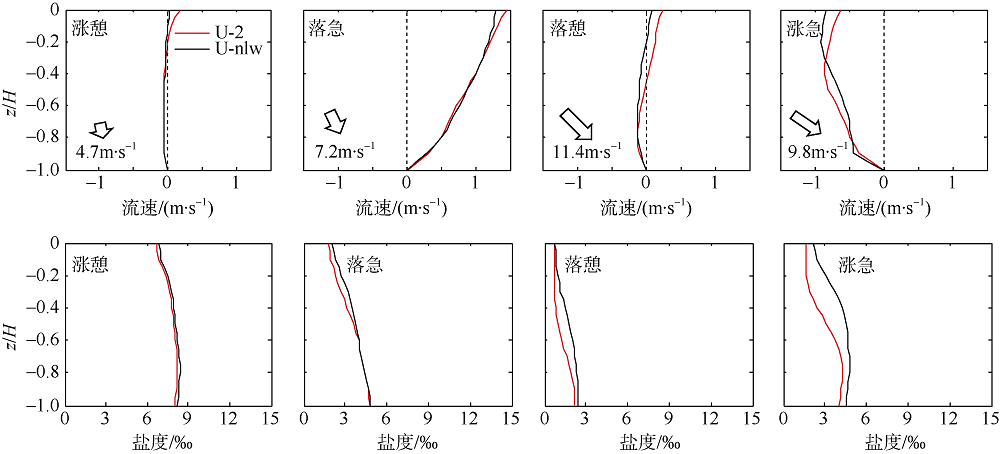
Comparison of vertical velocity and salinity distribution of up-estuary wind case (N-2) and no local wind case (N-nlw) during selected tidal cycle in the Nesat (2011) The dotted line in the figure is the velocity direction distinguishing line, positive value of velocity means seaward, and negative value means landward; z is the water depth value and H is the total water depth value"
| [1] | 吕爱琴, 杜文印 , 2006. 磨刀门水道咸潮上溯成因分析[J]. 广东水利水电, ( 5):50-53. |
| LV AIQIN, DU WENYIN , 2006. Salty tide tracing back reason in Modaomen waterway[J]. Guangdong Water Resources and Hydropower, ( 5):50-53 (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 叶荣辉, 钱燕, 孔俊 , 等, 2013. 珠江三角洲大系统风暴潮数学模型建立与验证[J]. 人民长江, 44(21):76-80. |
| YE RONGHUI, QIAN YAN, KONG JUN , et al, 2013. Mathematical model establishment and verification for large scale storm surge in Pearl River Delta[J]. Yangtze River, 44(21):76-80. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] |
CHEN SHUISEN, FANG LIGANG, ZHANG LIXIN , et al, 2009. Remote sensing of turbidity in seawater intrusion reaches of Pearl River Estuary - a case study in Modaomen water way, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 82(1):119-127.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.01.003 |
| [4] |
CHO K H, WANG H V, SHEN JIAN , et al, 2012. A modeling study on the response of Chesapeake Bay to hurricane events of Floyd and Isabel[J]. Ocean Modelling, 49-50:22-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2012.02.005 |
| [5] | FLATO G, MAROTZKE J, ABIODUN B , et al, 2013. Evaluation of Climate Models[C]// Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 741-866. |
| [6] |
FUJII T, MAEDA J, ISHIDA N , et al, 2002. An analysis of a pressure pattern in severe Typhoon Bart hitting the Japanese Islands in 1999 and a comparison of the gradient wind with the observed surface wind[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 90(12-15):1555-1568.
doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00270-2 |
| [7] |
GONG WENPING, SHEN JIAN , 2011. The response of salt intrusion to changes in river discharge and tidal mixing during the dry season in the Modaomen Estuary, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 31(7-8):769-788.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.01.011 |
| [8] | GONG WENPING, MAA J P-Y, HONG BO , et al, 2014. Salt transport during a dry season in the Modaomen Estuary, Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 100:139-150. |
| [9] |
HANSEN D V, RATTRAY M JR , 1966. New dimensions in estuary classification[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 11(3):319-326.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1966.11.3.0319 |
| [10] |
HERBECK L S, UNGER D, KRUMME U , et al, 2011. Typhoon-induced precipitation impact on nutrient and suspended matter dynamics of a tropical estuary affected by human activities in Hainan, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 93(4):375-388.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.05.004 |
| [11] | KUO A, PARK K , 1992. Transport of hypoxic waters: an estuary-subestuary exchange[M] //PRANDLE D. Dynamics and exchanges in estuaries and the coastal zone. Washington: American Geophysical Union: 599-615. |
| [12] |
LERCZAK J A, GEYER W R, CHANT R J , 2006. Mechanisms driving the time-dependent salt flux in a partially stratified estuary[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 36(12):2296-2311.
doi: 10.1175/JPO2959.1 |
| [13] |
LI CHUNYAN, WEEKS E, REGO J L , 2009. In situ measurements of saltwater flux through tidal passes of Lake Pontchartrain estuary by Hurricanes Gustav and Ike in September 2008[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(19):L19609.
doi: 10.1029/2009GL039802 |
| [14] | LI MING, ZHONG LIEJUN, BOICOURT W C , et al, 2006. Hurricane-induced storm surges, currents and destratification in a semi-enclosed bay[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(2):L02604. |
| [15] |
PURKIANI K, BECHERER J, KLINGBEIL K , et al, 2016. Wind induced variability of estuarine circulation in a tidally energetic inlet with curvature[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(5):3261-3277.
doi: 10.1002/2015JC010945 |
| [16] |
SCULLY M E, FRIEDRICHS C, BRUBAKER J , 2005. Control of estuarine stratification and mixing by wind-induced straining of the estuarine density field[J]. Estuaries, 28(3):321-326.
doi: 10.1007/BF02693915 |
| [17] |
YANG T-N, LEE T-Q, MEYERS P A , et al, 2011. The effect of typhoon induced rainfall on settling fluxes of particles and organic carbon in Yuanyang Lake, subtropical Taiwan[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(6):1171-1179.
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.07.016 |
| [18] |
YUAN RUI, ZHU JIANRONG, WANG BIAO , 2015. Impact of sea-level rise on saltwater intrusion in the Pearl River estuary[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 31(2):477-487.
doi: 10.2112/jcoastres-d-13-00063.1 |
| [19] |
ZHANG Y J, YE FEI, STANEV E V , et al, 2016. Seamless cross-scale modeling with SCHISM[J]. Ocean Modelling, 102:64-81.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2016.05.002 |
| [1] | SUN Zeming, HAN Shuzong, WANG Mingjie, SU Hanxiang. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [2] | YAN Jing, WEI Xing. Geomorphological changes and dynamic responses of the Huangmaohai Estuary in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 9-20. |
| [3] | DENG Guotong, LIU Mincong, XING Jiuxing, SHENG Jinyu, ZHOU Kai, CHEN Shengli. Analysis on the influencing factors of storm surges near Shenzhen [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 91-100. |
| [4] | Chuang XU,Yongji XU,Jiatang HU,Shiyu LI,Jintao LIU. Study on the seasonal and interannual variability of river plume in the Pearl River Estuary based on a high-resolution ocean dynamic model [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 43-52. |
| [5] | LUO Shihao, JING Zhiyou, QI Yiquan, XIE Qiang. Numerical study on sub-mesoscale processes in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(5): 10-19. |
| [6] | LIU Zufa, GUAN Shuai, ZHANG Ganhao, DING Bo, LIN Yingyan, ZHA Xini. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of saltwater intrusion into the Humen estuary based on FVCOM [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(2): 10-18. |
| [7] | LUO Jing, LI Ming, SUN Zhi-lin, WANG Wei. Numerical simulation of tidal hydrodynamics and sediment transport in Liverpool Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(5): 40-50. |
| [8] | WANG Dao-ru,WANG Hua-jie,LI Yuan-chao,YANG Yi,LIANG Wen. Preliminary study of coral larvae supplementary source around Leizhou Peninsula [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(2): 26-32. |
| [9] | LIAO Jie,ZHOU Di,ZHAO ZHONGXIAN,. Numerical Models of the Tectono-Thermal Evolution of Rift Basins and Their Applications to the Northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(6): 41-51. |
| [10] |
YANG Xiao-qiu1,2,SHI Xiao-bin1,XU He-hua1,XU Xing3,LI Guan-bao4,GUO Xing-wei5,LUO Xian-hu3 . SELECTING SIMPLIFIED MODEL FOR DUAL-PROBE SEAFLOOR IN-SITU HEAT-FLOW METER [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(4): 28-34. |
|
||