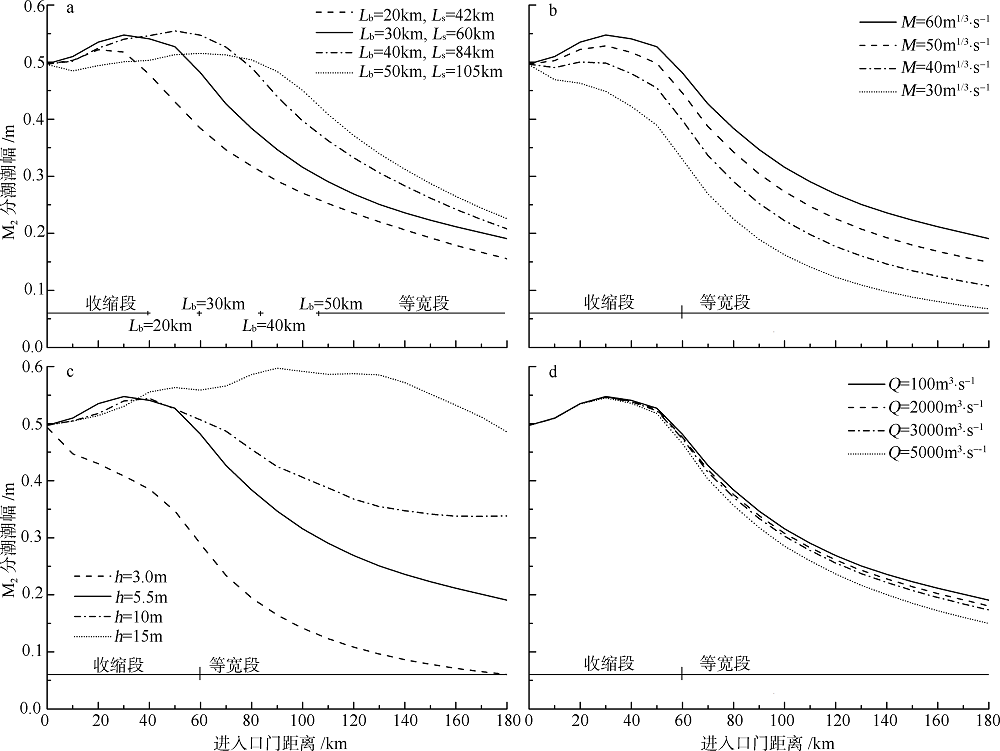
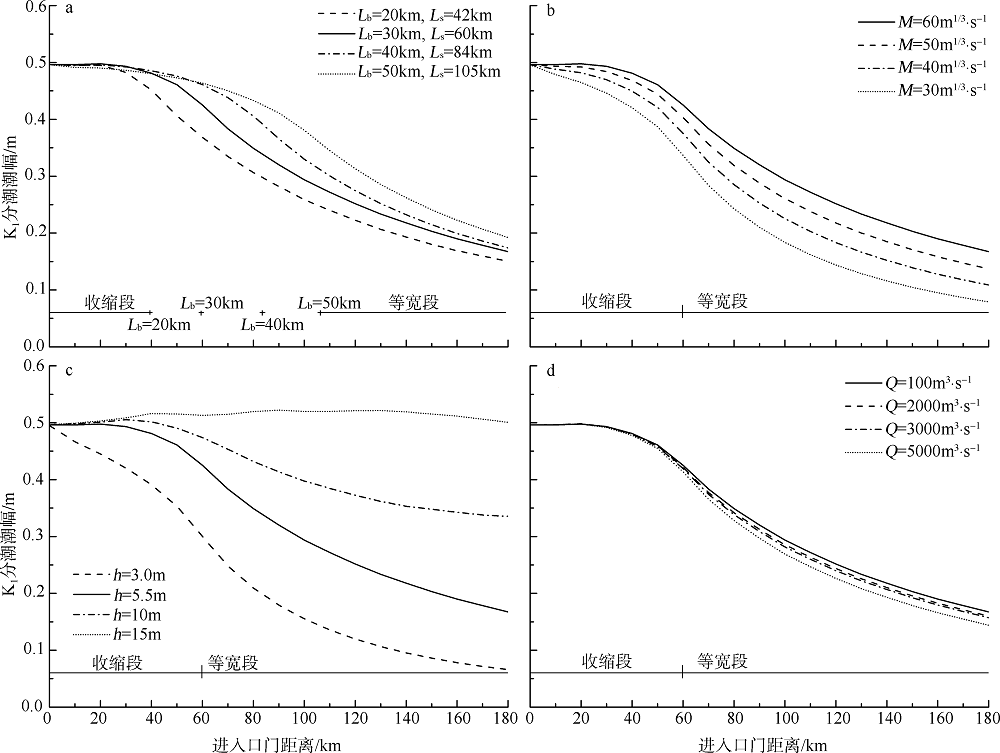
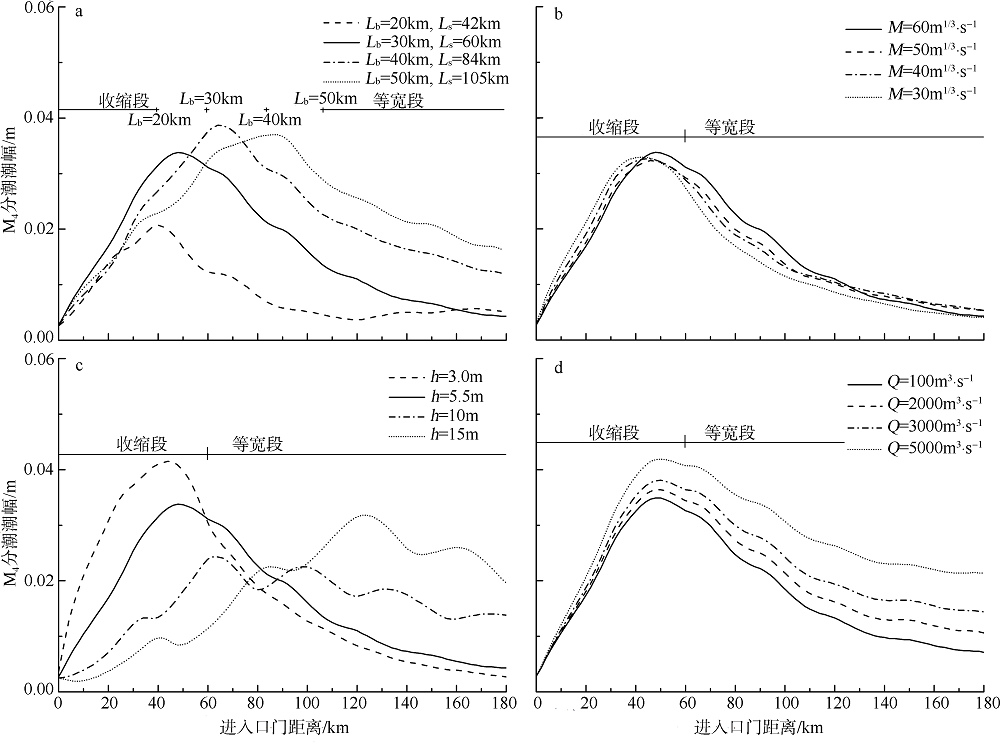
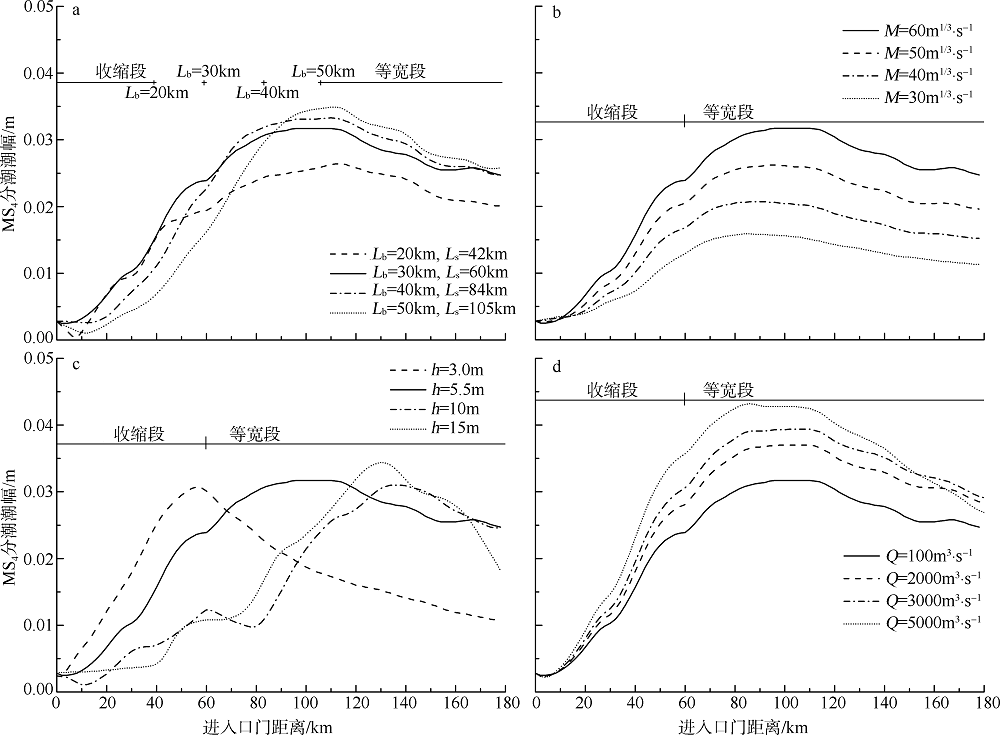
| [1] |
丁芮, 陈学恩, 曲念东 , 2015. 珠江口及邻近海域潮波数值模拟——Ⅰ模型的建立和分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 45(11):1-9.
|
|
DING RUI, CHEN XUEEN, QU NIANDONG , 2015. Three-dimensional high-resolution numerical study of the tide and circulation in the pearl river estuary and its adjacent waters part Ⅰ: model building and analysis[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 45(11):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
鲁盛 , 2016. 长江口潮波传播的非线性特征及影响机制研究[D]. 南京: 河海大学.
|
|
LU SHENG , 2016. Study on nonlinear characteristics and influence mechanisms of tidal propagation in the Yangtze estuary[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
欧素英, 杨清书, 杨昊 , 等, 2017. 河口三角洲径流和潮汐相互作用模型及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(5):1-8.
|
|
OU SUYING, YANG QINGSHU, YANG HAO , et al, 2017. The development and application of river-tide harmonic model[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(5):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
杨明远, 严以新, 孔俊 , 等, 2008. 珠江口水流泥沙运动模拟研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 18-19.
|
| [5] |
DRONKERS J , 1986. Tidal asymmetry and estuarine morphology[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 20(2-3):117-131.
doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201620150620
pmid: 27598844
|
| [6] |
DRONKERS J J , 1964. Tidal computations in rivers and coastal waters[M]. Amsterdam: North-Holland Pub. Co.: 518.
|
| [7] |
GODIN G , 1985. Modification of river tides by the discharge[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 111(2):257-274.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1985)111:2(257)
|
| [8] |
GONG WENPING, SCHUTTELAARS H, ZHANG HENG , 2016. Tidal asymmetry in a funnel-shaped estuary with mixed semidiurnal tides[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 66(5):637-658.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-016-0943-1
|
| [9] |
GUO LEICHENG, VAN DER WEGEN M, JAY D A , et al, 2015. River-tide dynamics: exploration of nonstationary and nonlinear tidal behavior in the Yangtze River estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 120(5):3499-3521.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC010491
|
| [10] |
HUNT J N , 1964. Tidal oscillations in estuaries[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 8(4):440-455.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.220
pmid: 30708292
|
| [11] |
JAY D A, FLINCHEM E P , 1997. Interaction of fluctuating river flow with a barotropic tide: a demonstration of wavelet tidal analysis methods[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 102(C3):5705-5720.
|
| [12] |
LU SHENG, TONG CHAOFENG, LEE D Y , et al, 2015. Propagation of tidal waves up in Yangtze Estuary during the dry season[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 120(9):6445-6473.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v120.9
|
| [13] |
MAZUMDER N C, BOSE S , 1995. Formation and propagation of tidal bore[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 121(3):167-175.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1995)121:3(167)
|
| [14] |
NIDZIEKO N J , 2010. Tidal asymmetry in estuaries with mixed semidiurnal/diurnal tides[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 115(C8):C08006.
|
| [15] |
PAWLOWICZ R, BEARDSLEY B, LENTZ S , 2002. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in MATLAB using T_TIDE[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 28(8):929-937.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226611
pmid: 31910214
|
| [16] |
PRANDLE D , 2009. Estuaries[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
|
| [17] |
SONG DEHAI, WANG XIAOHUA, KISS A E , et al, 2011. The contribution to tidal asymmetry by different combinations of tidal constituents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C12):C12007.
|
| [18] |
VAN RIJN L C , 2011. Principles of fluid flow and surface waves in rivers, estuaries, seas, and oceans[M]. Netherlands: Aqua Publications: 8112-8113.
|
| [19] |
ZHANG WEI, CAO YU, ZHU YULIANG , et al, 2018. Unravelling the causes of tidal asymmetry in deltas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 564:588-604.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.07.023
|
 ), ZHANG Wei2, GAO Xiangyu3
), ZHANG Wei2, GAO Xiangyu3