Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 1-18.doi: 10.11978/2019136CSTR: 32234.14.2019136
• Marine Biology • Next Articles
Genetic Structure and Diversity Analysis of Three Natural Populations of Tectus pyramis Based on Specific Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing*
HUANG Jing1,2( ), OU Zhekui1,2, LIU Wenguang1, HE Maoxian1(
), OU Zhekui1,2, LIU Wenguang1, HE Maoxian1( )
)
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Institution of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2019-12-22Revised:2020-02-28Online:2020-09-10Published:2020-02-28 -
Contact:Maoxian HE E-mail:1152524871@qq.com;hmx2@scsio.ac.cn -
About author:HUANG Jing (1993—). E-mail:1152524871@qq.com -
Supported by:Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA13020206);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental, Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018PY03);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental, Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018ZD02);Science and Technology Service Network Initiative of Chinese Academy of Sciences(KFJ-STS-ZDTP-055);Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China(2017B030314052)
CLC Number:
- P735.54
Cite this article
HUANG Jing, OU Zhekui, LIU Wenguang, HE Maoxian. Genetic Structure and Diversity Analysis of Three Natural Populations of Tectus pyramis Based on Specific Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 1-18.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
"
| Sample ID | Total Reads Number | GC Percentage / % | Q30 Percentage / % |
|---|---|---|---|
| SZ1 | 2646767 | 38.73 | 94.04 |
| SZ2 | 2868617 | 38.82 | 93.27 |
| SZ3 | 3060839 | 38.49 | 93.71 |
| SZ4 | 2928250 | 38.94 | 94.69 |
| SZ5 | 3236397 | 37.86 | 94.48 |
| SZ6 | 3043836 | 38.27 | 94.40 |
| SZ7 | 2817405 | 38.63 | 94.61 |
| SZ8 | 2655334 | 38.56 | 94.77 |
| SZ9 | 2725248 | 38.29 | 94.58 |
| SZ10 | 3277567 | 37.43 | 94.59 |
| SZ11 | 3492934 | 38.09 | 94.81 |
| SZ12 | 3137716 | 38.41 | 94.67 |
| SZ13 | 2039042 | 39.02 | 94.27 |
| SZ14 | 1444547 | 39.31 | 94.19 |
| SZ15 | 1654279 | 39.17 | 93.96 |
| SY1 | 1618225 | 39.35 | 94.28 |
| SY2 | 1683896 | 39.19 | 93.37 |
| SY3 | 1495848 | 39.33 | 93.70 |
| SY4 | 1645635 | 39.30 | 93.83 |
| SY5 | 1832431 | 38.72 | 94.03 |
| SY6 | 2114769 | 38.64 | 94.02 |
| SY7 | 2547407 | 37.89 | 93.08 |
| SY8 | 2000207 | 38.68 | 94.10 |
| SY9 | 2194326 | 38.79 | 94.68 |
| SY10 | 1967775 | 39.10 | 94.86 |
| SY11 | 1841572 | 39.09 | 94.93 |
| SY12 | 2123797 | 38.81 | 94.87 |
| SY13 | 2151154 | 39.17 | 94.85 |
| SY14 | 1954747 | 38.74 | 94.66 |
| SY15 | 2514960 | 37.97 | 93.42 |
| XS1 | 2060640 | 38.78 | 94.46 |
| XS2 | 3164280 | 38.32 | 93.82 |
| XS3 | 3272003 | 38.32 | 94.18 |
| XS4 | 3171569 | 37.92 | 93.92 |
| XS5 | 3202603 | 38.38 | 94.07 |
| XS6 | 2744002 | 38.28 | 93.71 |
| XS7 | 2303163 | 38.29 | 93.63 |
| XS8 | 3218785 | 37.93 | 93.95 |
| XS9 | 2972343 | 38.81 | 94.23 |
| XS10 | 2844445 | 37.76 | 92.61 |
| XS11 | 3272801 | 38.08 | 93.30 |
| XS12 | 3035468 | 38.46 | 93.76 |
| XS13 | 2943254 | 38.05 | 93.17 |
| XS14 | 2583726 | 38.19 | 93.10 |
| XS15 | 3196614 | 37.88 | 93.54 |
| Control | 1046368 | 43.03 | 92.64 |
"
| Sample ID | SLAF number | Total depth | Average depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| SZ1 | 101537 | 1843808 | 18.16 |
| SZ2 | 101886 | 2006414 | 19.69 |
| SZ3 | 103244 | 2188358 | 21.20 |
| SZ4 | 107505 | 2029284 | 18.88 |
| SZ5 | 108067 | 2338011 | 21.63 |
| SZ6 | 107524 | 2135565 | 19.86 |
| SZ7 | 106819 | 1963328 | 18.38 |
| SZ8 | 109780 | 1860332 | 16.95 |
| SZ9 | 108621 | 1894662 | 17.44 |
| SZ10 | 106877 | 2366741 | 22.14 |
| SZ11 | 113736 | 2502851 | 22.01 |
| SZ12 | 109751 | 2190045 | 19.95 |
| SZ13 | 103761 | 1101996 | 10.62 |
| SZ14 | 98465 | 781192 | 7.93 |
| SZ15 | 100450 | 937431 | 9.33 |
| SY1 | 97381 | 954691 | 9.80 |
| SY2 | 98004 | 1017468 | 10.38 |
| SY3 | 95481 | 909506 | 9.53 |
| SY4 | 96922 | 996596 | 10.28 |
| SY5 | 99774 | 1213282 | 12.16 |
| SY6 | 101941 | 1350287 | 13.25 |
| SY7 | 103004 | 1781398 | 17.29 |
| SY8 | 101915 | 1228982 | 12.06 |
| SY9 | 102675 | 1319548 | 12.85 |
| SY10 | 101263 | 1145948 | 11.32 |
| SY11 | 101126 | 1068060 | 10.56 |
| SY12 | 103524 | 1246384 | 12.04 |
| SY13 | 103145 | 1282700 | 12.44 |
| SY14 | 103038 | 1148245 | 11.14 |
| SY15 | 106571 | 1495169 | 14.03 |
| XS1 | 103543 | 1212705 | 11.71 |
| XS2 | 113977 | 2033850 | 17.84 |
| XS3 | 113800 | 2082711 | 18.30 |
| XS4 | 113523 | 2059873 | 18.14 |
| XS5 | 114052 | 2075178 | 18.20 |
| XS6 | 112858 | 1763198 | 15.62 |
| XS7 | 109594 | 1472432 | 13.44 |
| XS8 | 113536 | 2157654 | 19.00 |
| XS9 | 112609 | 1938036 | 17.21 |
| XS10 | 111522 | 1808792 | 16.22 |
| XS11 | 113827 | 1923615 | 16.90 |
| XS12 | 112561 | 1792407 | 15.92 |
| XS13 | 112568 | 1747609 | 15.52 |
| XS14 | 110288 | 1502944 | 13.63 |
| XS15 | 113093 | 1927904 | 17.05 |
| Total | 218422 | 73797190 | 337.87 |
"
| Sample ID | Total SNP number | SNP number | Hetloci ratio / % | Integrity ratio / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZ1 | 2010144 | 1101454 | 10.65 | 54.79 |
| SZ2 | 2010144 | 1108987 | 10.99 | 55.16 |
| SZ3 | 2010144 | 1124233 | 11.03 | 55.92 |
| SZ4 | 2010144 | 1225287 | 11.18 | 60.95 |
| SZ5 | 2010144 | 1199917 | 11.03 | 59.69 |
| SZ6 | 2010144 | 1231716 | 11.21 | 61.27 |
| SZ7 | 2010144 | 1205136 | 10.93 | 59.95 |
| SZ8 | 2010144 | 1185877 | 11.65 | 58.99 |
| SZ9 | 2010144 | 1206178 | 11.23 | 60.00 |
| SZ10 | 2010144 | 1192230 | 10.94 | 59.31 |
| SZ11 | 2010144 | 1283751 | 12.85 | 63.86 |
| SZ12 | 2010144 | 1249074 | 11.64 | 62.13 |
| SZ13 | 2010144 | 1222192 | 10.91 | 60.80 |
| SZ14 | 2010144 | 1061836 | 9.44 | 52.82 |
| SZ15 | 2010144 | 1102628 | 9.75 | 54.85 |
| SY1 | 2010144 | 1038006 | 9.95 | 51.63 |
| SY2 | 2010144 | 1039742 | 9.99 | 51.72 |
| SY3 | 2010144 | 991652 | 9.56 | 49.33 |
| SY4 | 2010144 | 1027875 | 9.87 | 51.13 |
| SY5 | 2010144 | 1040267 | 10.05 | 51.75 |
| SY6 | 2010144 | 1122866 | 10.85 | 55.85 |
| SY7 | 2010144 | 1097668 | 11.22 | 54.60 |
| SY8 | 2010144 | 1126900 | 10.79 | 56.06 |
| SY9 | 2010144 | 1164083 | 11.26 | 57.91 |
| SY10 | 2010144 | 1138116 | 10.73 | 56.61 |
| SY11 | 2010144 | 1130375 | 10.70 | 56.23 |
| SY12 | 2010144 | 1182425 | 11.26 | 58.82 |
| SY13 | 2010144 | 1154786 | 11.52 | 57.44 |
| SY14 | 2010144 | 1155444 | 11.03 | 57.48 |
| SY15 | 2010144 | 1223114 | 12.02 | 60.84 |
| XS1 | 2010144 | 1149640 | 11.35 | 57.19 |
| XS2 | 2010144 | 1300295 | 13.19 | 64.68 |
| XS3 | 2010144 | 1307590 | 13.18 | 65.04 |
| XS4 | 2010144 | 1295832 | 13.14 | 64.46 |
| XS5 | 2010144 | 1310729 | 13.41 | 65.20 |
| XS6 | 2010144 | 1269962 | 12.86 | 63.17 |
| XS7 | 2010144 | 1197594 | 11.65 | 59.57 |
| XS8 | 2010144 | 1268115 | 12.84 | 63.08 |
| XS9 | 2010144 | 1267870 | 12.57 | 63.07 |
| XS10 | 2010144 | 1235461 | 12.47 | 61.46 |
| XS11 | 2010144 | 1313024 | 13.94 | 65.31 |
| XS12 | 2010144 | 1287328 | 13.38 | 64.04 |
| XS13 | 2010144 | 1280442 | 13.48 | 63.69 |
| XS14 | 2010144 | 1253266 | 12.95 | 62.34 |
| XS15 | 2010144 | 1293659 | 13.75 | 64.35 |
"
| Marker | Pos | p-value (SY : XS) | p-value (SY : SZ) | p-value (XS : SZ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marker3275 | 8 | 5.97×10-4 | 3.32×10-5 | 2.09×10-12 |
| Marker5368 | 96 | 6.42×10-5 | 5.24×10-16 | 5.83×10-6 |
| Marker16106 | 153 | 2.51×10-4 | 8.04×10-5 | 8.21×10-13 |
| Marker29414 | 71 | 8.05×10-5 | 8.05×10-5 | 1.52×10-14 |
| Marker31028 | 126 | 1.30×10-4 | 8.24×10-4 | 7.82×10-12 |
| Marker32764 | 118 | 5.54×10-13 | 1.10×10-5 | 9.93×10-4 |
| Marker35459 | 119 | 1.72×10-10 | 3.60×10-4 | 5.97×10-4 |
| Marker39352 | 151 | 3.28×10-5 | 6.11×10-4 | 2.02×10-13 |
| Marker40948 | 162 | 5.83×10-12 | 9.06×10-4 | 3.33×10-4 |
| Marker43655 | 114 | 5.19×10-5 | 9.18×10-6 | 5.24×10-16 |
| Marker43655 | 195 | 2.46×10-4 | 1.89×10-6 | 5.24×10-16 |
| Marker48466 | 76 | 9.12×10-4 | 4.49×10-4 | 4.79×10-11 |
| Marker54309 | 156 | 7.97×10-4 | 6.72×10-4 | 6.70×10-11 |
| Marker56258 | 144 | 9.77×10-4 | 2.29×10-6 | 1.54×10-14 |
| Marker56258 | 153 | 9.77×10-4 | 2.29×10-6 | 1.54×10-14 |
| Marker56258 | 177 | 9.77×10-4 | 2.29×10-6 | 1.54×10-14 |
| Marker56258 | 187 | 9.77×10-4 | 2.29×10-6 | 1.54×10-14 |
| Marker56258 | 196 | 9.77×10-4 | 2.29×10-6 | 1.54×10-14 |
| Marker57704 | 38 | 1.83×10-12 | 8.31×10-5 | 4.12×10-4 |
| Marker57704 | 56 | 1.83×10-12 | 8.31×10-5 | 4.12×10-4 |
| Marker58004 | 63 | 7.97×10-4 | 1.10×10-5 | 9.23×10-14 |
| Marker58004 | 192 | 7.97×10-4 | 1.10×10-5 | 9.23×10-14 |
| Marker58561 | 4 | 1.78×10-14 | 2.59×10-6 | 4.78×10-4 |
| Marker58831 | 165 | 7.08×10-4 | 9.92×10-5 | 1.01×10-11 |
| Marker58831 | 179 | 7.08×10-4 | 9.92×10-5 | 1.01×10-11 |
| Marker59195 | 168 | 8.50×10-14 | 3.92×10-5 | 5.09×10-4 |
| Marker61327 | 50 | 4.25×10-4 | 5.13×10-4 | 1.01×10-12 |
| Marker62076 | 121 | 9.36×10-5 | 3.65×10-5 | 2.88×10-14 |
| Marker62305 | 23 | 4.53×10-5 | 7.45×10-5 | 8.23×10-15 |
| Marker64435 | 95 | 5.78×10-5 | 3.54×10-13 | 7.07×10-4 |
| Marker64938 | 164 | 1.26×10-6 | 1.29×10-4 | 5.24×10-16 |
| Marker64938 | 192 | 1.26×10-6 | 1.29×10-4 | 5.24×10-16 |
| Marker65298 | 19 | 1.26×10-6 | 4.05×10-4 | 4.66×10-15 |
| Marker72476 | 169 | 7.75×10-5 | 9.41×10-4 | 4.08×10-11 |
| Marker74137 | 39 | 9.84×10-4 | 4.89×10-6 | 1.78×10-14 |
| Marker74137 | 160 | 4.09×10-5 | 1.66×10-5 | 7.13×10-16 |
| Marker74137 | 197 | 4.09×10-5 | 1.66×10-5 | 7.13×10-16 |
| Marker77452 | 27 | 3.34×10-4 | 1.62×10-4 | 9.40×10-12 |
| Marker77571 | 174 | 7.37×10-4 | 4.81×10-7 | 2.00×10-15 |
| Marker78614 | 80 | 9.63×10-4 | 9.43×10-5 | 5.49×10-12 |
| Marker79010 | 46 | 5.56×10-6 | 5.96×10-4 | 1.13×10-14 |
| Marker79010 | 96 | 5.56×10-6 | 5.96×10-4 | 1.13×10-14 |
| Marker80829 | 28 | 4.18×10-5 | 6.72×10-4 | 9.86×10-13 |
| Marker85121 | 127 | 2.97×10-4 | 1.04×10-4 | 2.02×10-13 |
| Marker86368 | 91 | 3.80×10-4 | 1.03×10-9 | 9.11×10-4 |
| Marker89723 | 73 | 2.82×10-5 | 4.83×10-4 | 3.55×10-13 |
| Marker89828 | 32 | 7.08×10-4 | 8.14×10-4 | 2.12×10-9 |
| Marker91169 | 142 | 9.10×10-4 | 1.61×10-4 | 9.61×10-12 |
| Marker91169 | 143 | 9.10×10-4 | 3.97×10-4 | 2.55×10-11 |
| Marker91169 | 193 | 9.10×10-4 | 1.61×10-4 | 9.61×10-12 |
| Marker93033 | 35 | 5.09×10-4 | 3.39×10-4 | 5.69×10-12 |
| Marker94025 | 137 | 8.55×10-4 | 4.15×10-4 | 3.54×10-13 |
| Marker96746 | 95 | 3.15×10-4 | 6.99×10-4 | 5.37×10-11 |
| Marker97131 | 48 | 9.89×10-5 | 9.28×10-6 | 4.03×10-15 |
| Marker97131 | 64 | 9.89×10-5 | 1.66×10-5 | 8.23×10-15 |
| Marker97651 | 49 | 3.07×10-4 | 2.13×10-4 | 1.38×10-11 |
| Marker99962 | 152 | 6.07×10-5 | 4.60×10-4 | 2.87×10-12 |
| Marker101446 | 75 | 2.31×10-4 | 4.98×10-4 | 6.74×10-11 |
| Marker102130 | 123 | 2.82×10-5 | 6.46×10-4 | 2.32×10-13 |
| Marker103561 | 24 | 5.74×10-4 | 7.97×10-4 | 3.29×10-11 |
| Marker106244 | 7 | 3.73×10-4 | 1.53×10-4 | 1.18×10-13 |
| Marker114322 | 156 | 2.85×10-5 | 8.53×10-4 | 2.44×10-12 |
| Marker114487 | 160 | 9.77×10-4 | 2.06×10-4 | 6.96×10-11 |
| Marker115710 | 9 | 3.72×10-4 | 7.06×10-5 | 4.07×10-13 |
| Marker115710 | 37 | 3.72×10-4 | 4.05×10-4 | 9.61×10-12 |
| Marker116654 | 73 | 1.91×10-4 | 8.85×10-5 | 2.22×10-13 |
| Marker120806 | 120 | 3.64×10-4 | 7.18×10-10 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker128452 | 23 | 4.11×10-13 | 2.60×10-4 | 8.79×10-6 |
| Marker130399 | 64 | 2.87×10-12 | 9.76×10-4 | 2.59×10-5 |
| Marker131746 | 129 | 4.78×10-4 | 6.66×10-4 | 9.09×10-11 |
| Marker134085 | 78 | 1.05×10-11 | 4.50×10-4 | 2.22×10-4 |
| Marker135504 | 57 | 2.29×10-7 | 7.97×10-4 | 5.24×10-16 |
| Marker136107 | 156 | 8.50×10-14 | 6.40×10-4 | 6.95×10-6 |
| Marker142198 | 82 | 4.78×10-4 | 3.68×10-4 | 1.48×10-11 |
| Marker146079 | 23 | 7.48×10-4 | 8.24×10-5 | 1.44×10-12 |
| Marker146079 | 58 | 7.48×10-4 | 8.24×10-5 | 1.44×10-12 |
| Marker149477 | 131 | 8.47×10-4 | 5.31×10-4 | 1.62×10-10 |
| Marker153118 | 160 | 7.93×10-4 | 8.65×10-4 | 6.32×10-10 |
| Marker157365 | 21 | 9.10×10-4 | 1.45×10-4 | 1.62×10-12 |
| Marker164040 | 135 | 7.36×10-4 | 5.21×10-4 | 2.70×10-10 |
| Marker165818 | 206 | 2.35×10-15 | 7.26×10-5 | 1.67×10-4 |
| Marker169492 | 68 | 3.34×10-4 | 1.39×10-4 | 1.25×10-12 |
| Marker170499 | 42 | 2.35×10-4 | 3.12×10-4 | 9.23×10-14 |
| Marker170499 | 61 | 2.35×10-4 | 3.12×10-4 | 9.23×10-14 |
| Marker170499 | 70 | 2.35×10-4 | 3.12×10-4 | 9.23×10-14 |
| Marker170499 | 85 | 2.35×10-4 | 3.12×10-4 | 9.23×10-14 |
| Marker173073 | 161 | 5.88×10-4 | 3.19×10-8 | 3.44×10-17 |
| Marker174886 | 165 | 8.39×10-15 | 3.44×10-6 | 4.12×10-4 |
| Marker174886 | 174 | 8.39×10-15 | 3.44×10-6 | 4.12×10-4 |
| Marker176168 | 67 | 5.49×10-12 | 2.51×10-4 | 3.74×10-4 |
| Marker177413 | 57 | 6.14×10-4 | 1.15×10-4 | 3.74×10-12 |
| Marker181332 | 62 | 1.75×10-4 | 6.40×10-4 | 2.02×10-11 |
| Marker181637 | 22 | 1.98×10-4 | 2.38×10-5 | 2.83×10-12 |
| Marker181637 | 23 | 1.98×10-4 | 2.38×10-5 | 2.83×10-12 |
| Marker181637 | 33 | 4.98×10-4 | 1.24×10-5 | 2.83×10-12 |
| Marker181637 | 36 | 1.98×10-4 | 2.38×10-5 | 2.83×10-12 |
| Marker182931 | 24 | 4.13×10-5 | 2.31×10-4 | 5.69×10-14 |
| Marker182931 | 36 | 4.13×10-5 | 2.31×10-4 | 5.69×10-14 |
| Marker182931 | 38 | 4.99×10-4 | 2.31×10-4 | 1.44×10-12 |
| Marker182931 | 114 | 4.99×10-4 | 4.90×10-4 | 7.37×10-12 |
| Marker182931 | 171 | 4.99×10-4 | 2.31×10-4 | 1.44×10-12 |
| Marker184767 | 188 | 1.95×10-12 | 3.64×10-4 | 2.07×10-5 |
| Marker185952 | 36 | 3.34×10-4 | 2.43×10-4 | 1.89×10-11 |
| Marker186713 | 35 | 1.46×10-6 | 3.41×10-5 | 3.44×10-17 |
| Marker190981 | 52 | 4.12×10-4 | 8.23×10-5 | 7.84×10-13 |
| Marker192459 | 199 | 7.33×10-4 | 3.39×10-4 | 1.88×10-11 |
| Marker195736 | 85 | 1.72×10-4 | 7.11×10-4 | 1.59×10-11 |
| Marker195973 | 95 | 7.07×10-4 | 5.24×10-16 | 4.75×10-7 |
| Marker197784 | 195 | 8.47×10-4 | 5.80×10-4 | 3.01×10-11 |
| Marker202019 | 15 | 5.21×10-4 | 1.19×10-4 | 8.82×10-12 |
| Marker202019 | 84 | 5.21×10-4 | 1.19×10-4 | 8.82×10-12 |
| Marker203633 | 31 | 2.19×10-11 | 7.35×10-4 | 5.69×10-4 |
| Marker204262 | 11 | 4.11×10-5 | 7.37×10-4 | 1.89×10-11 |
| Marker204262 | 76 | 6.80×10-4 | 7.37×10-4 | 5.49×10-10 |
| Marker204262 | 145 | 4.11×10-5 | 7.37×10-4 | 1.89×10-11 |
| Marker204262 | 159 | 4.11×10-5 | 7.37×10-4 | 1.89×10-11 |
| Marker204262 | 162 | 4.11×10-5 | 7.37×10-4 | 1.89×10-11 |
| Marker204262 | 169 | 4.11×10-5 | 7.37×10-4 | 1.89×10-11 |
| Marker204894 | 204 | 4.99×10-4 | 4.90×10-4 | 7.37×10-12 |
| Marker215169 | 49 | 2.59×10-5 | 9.10×10-4 | 8.12×10-13 |
| Marker217857 | 37 | 7.82×10-4 | 5.13×10-4 | 6.01×10-12 |
| Marker217857 | 81 | 7.82×10-4 | 5.13×10-4 | 6.01×10-12 |
| Marker219928 | 157 | 1.15×10-13 | 6.49×10-4 | 5.18×10-6 |
| Marker220971 | 29 | 8.47×10-4 | 2.38×10-4 | 7.37×10-12 |
| Marker227957 | 59 | 3.55×10-4 | 2.89×10-6 | 1.13×10-14 |
| Marker240685 | 145 | 3.25×10-4 | 1.52×10-4 | 2.22×10-13 |
| Marker253092 | 204 | 9.93×10-4 | 1.10×10-5 | 5.54×10-13 |
| Marker253901 | 155 | 5.53×10-4 | 3.77×10-4 | 4.50×10-11 |
| Marker268253 | 137 | 1.07×10-5 | 3.17×10-12 | 5.97×10-4 |
| Marker273125 | 41 | 8.30×10-4 | 6.05×10-4 | 3.69×10-10 |
| Marker273125 | 51 | 8.30×10-4 | 6.05×10-4 | 3.69×10-10 |
| Marker273125 | 59 | 8.30×10-4 | 6.05×10-4 | 3.69×10-10 |
| Marker273125 | 67 | 8.30×10-4 | 6.05×10-4 | 3.69×10-10 |
| Marker273125 | 147 | 8.30×10-4 | 6.05×10-4 | 3.69×10-10 |
| Marker273125 | 187 | 8.30×10-4 | 6.05×10-4 | 3.69×10-10 |
| Marker280356 | 52 | 8.65×10-4 | 8.85×10-5 | 1.19×10-11 |
| Marker281848 | 160 | 2.56×10-4 | 6.58×10-4 | 1.38×10-11 |
| Marker289553 | 74 | 9.36×10-5 | 2.07×10-5 | 3.65×10-14 |
| Marker289553 | 128 | 9.36×10-5 | 2.07×10-5 | 3.65×10-14 |
| Marker296021 | 144 | 4.18×10-5 | 2.99×10-4 | 2.35×10-15 |
| Marker298184 | 70 | 3.93×10-6 | 2.61×10-5 | 3.44×10-17 |
| Marker308966 | 59 | 8.21×10-13 | 2.49×10-4 | 1.24×10-4 |
| Marker330769 | 199 | 1.58×10-4 | 3.40×10-4 | 2.02×10-11 |
| Marker350607 | 45 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 49 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 71 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 73 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 74 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 82 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 141 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 163 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker350607 | 181 | 2.63×10-10 | 1.48×10-4 | 4.58×10-4 |
| Marker362138 | 51 | 1.48×10-4 | 1.38×10-4 | 8.82×10-12 |
| Marker389768 | 132 | 3.05×10-4 | 7.36×10-4 | 6.74×10-11 |
| Marker475043 | 205 | 1.26×10-5 | 2.37×10-4 | 8.23×10-15 |
"
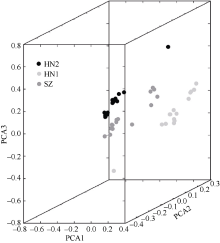
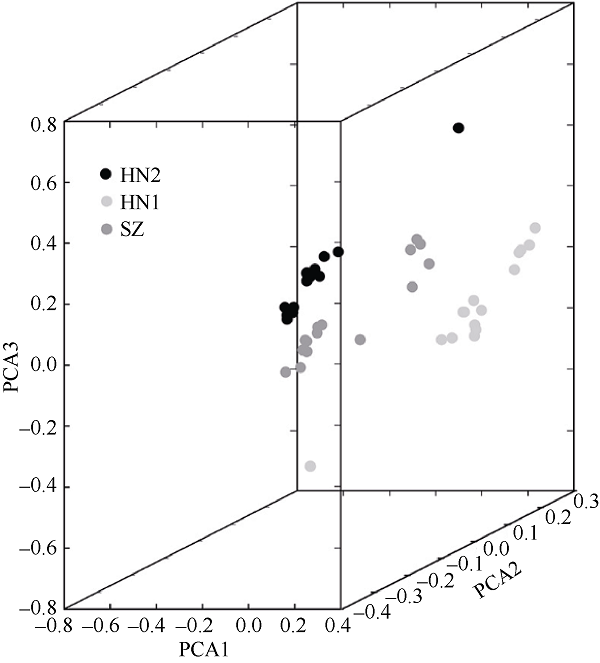
| Sample ID | PCA1 | PCA2 | PCA3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SZ1 | 0.28 | -0.09 | 0.24 |
| SZ2 | 0.29 | -0.08 | 0.22 |
| SZ3 | 0.27 | -0.10 | 0.21 |
| SZ4 | 0.10 | -0.29 | 0.02 |
| SZ5 | 0.05 | -0.28 | -0.07 |
| SZ6 | 0.11 | -0.30 | 0.03 |
| SZ7 | 0.13 | -0.27 | 0.06 |
| SZ8 | 0.15 | -0.27 | 0.07 |
| SZ9 | 0.12 | -0.28 | 0.04 |
| SZ10 | 0.09 | -0.29 | -0.02 |
| SZ11 | 0.06 | -0.33 | -0.06 |
| SZ12 | 0.10 | -0.30 | -0.01 |
| SZ13 | 0.11 | -0.14 | -0.06 |
| SZ14 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| SZ15 | 0.19 | -0.04 | 0.06 |
| SY1 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.04 |
| SY2 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.02 |
| SY3 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.08 |
| SY4 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
| SY5 | 0.26 | 0.22 | -0.03 |
| SY6 | 0.21 | 0.15 | -0.13 |
| SY7 | 0.19 | 0.16 | -0.16 |
| SY8 | 0.20 | 0.14 | -0.17 |
| SY9 | 0.22 | 0.10 | -0.10 |
| SY10 | 0.22 | 0.13 | -0.08 |
| SY11 | 0.21 | 0.14 | -0.13 |
| SY12 | 0.19 | 0.08 | -0.18 |
| SY13 | 0.21 | 0.11 | -0.11 |
| SY14 | 0.18 | 0.12 | -0.20 |
| SY15 | -0.17 | -0.10 | -0.50 |
| XS1 | -0.03 | 0.25 | 0.41 |
| XS2 | -0.36 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| XS3 | -0.36 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| XS4 | -0.36 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| XS5 | -0.36 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| XS6 | -0.35 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| XS7 | -0.33 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| XS8 | -0.34 | 0.05 | 0.08 |
| XS9 | -0.33 | 0.06 | 0.10 |
| XS10 | -0.36 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| XS11 | -0.42 | 0.01 | -0.05 |
| XS12 | -0.41 | 0.02 | -0.04 |
| XS13 | -0.42 | 0.02 | -0.05 |
| XS14 | -0.41 | 0.04 | -0.05 |
| XS15 | -0.43 | 0.02 | -0.07 |
| [1] |
ALEXANDER D H, NOVEMBRE J, LANGE K, 2009. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals[J]. Genome Research, 19(9):1655-1664.
pmid: 19648217 |
| [2] | BAI ZHIYI, HAN XUEKAI, LUO MING, et al, 2015. Constructing a microsatellite-based linkage map and identifying QTL for pearl quality traits in triangle pearl mussel (Hyriopsis cumingii)[J]. Aquaculture, 437:102-110. |
| [3] | BEERLI P, 2008. MIGRATE-N: estimation of population sizes and gene flow using the coalescent[Z]. http://htmlpopgen.sc.fsu.edu/Migrate/. |
| [4] |
BERTNESS M D, GAINES S D, 1993. Larval dispersal and local adaptation in acorn barnacles[J]. Evolution, 47(1):316-320.
doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1993.tb01221.x pmid: 28568103 |
| [5] | CHEN FUXIAO, PU LIYUN, ZENG GUANGQIONG, et al, 2015. Study on the induced breeding techniques of Trochus pyramis born[J]. Fishery Modernization, 42(6):11-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [6] | CHEN H T, YAN XIAOHAI, SHAW P T, et al, 1996. A numerical simulation of wind stress and topographic effects on the Kuroshio Current Path near Taiwan[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 26(9):1769-1802. |
| [7] |
CHEN SHIQIANG, HUANG ZEFENG, Dai YI, et al, 2013. The Development of 7E chromosome-specific molecular markers for Thinopyrum elongatum based on SLAF-seq technology[J]. PLoS One, 8(6):e65122.
pmid: 23762296 |
| [8] |
DAVEY J W, CEZARD T, FUENTES‐UTRILLA P, et al, 2013. Special features of RAD sequencing data: implications for genotyping[J]. Molecular Ecology, 22(11):3151-3164.
pmid: 23110438 |
| [9] |
DE HOON M J L, IMOTO S, NOLAN J, et al, 2004. Open source clustering software[J]. Bioinformatics, 20(9):1453-1454.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth078 pmid: 14871861 |
| [10] | DURAND P, WADA K T, BLANC F, 1993. Genetic variation in wild and hatchery stocks of the black pearl oyster, Pinctada margarififera, from Japan[J]. Aquaculture, 110(1):27-40. |
| [11] |
GAN JIANPING, LIU ZHIQIANG, HUI C R, 2016. A three-layer alternating spinning circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(8):2309-2315.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-16-0044.1 |
| [12] | GONG WEI, GU LEI, ZHANG DIANXIANG, 2010. Low genetic diversity and high genetic divergence caused by inbreeding and geographical isolation in the populations of endangered species Loropetalum subcordatum (Hamamelidaceae) endemic to China[J]. Conservation Genetics, 11(6):2281-2288. |
| [13] | GRANT W A S, BOWEN B W, 1998. Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation[J]. Journal of Heredity, 89(5):415-426. |
| [14] |
HAMBLIN M T, WARBURTON M L, BUCKLER E S, 2007. Empirical comparison of simple sequence repeats and single nucleotide polymorphisms in assessment of maize diversity and relatedness[J]. PLoS One, 2(12):e1367.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001367 pmid: 18159250 |
| [15] |
HAN YIPENG, ZHAO XUE, LIU DONGYUAN, et al, 2016. Domestication footprints anchor genomic regions of agronomic importance in soybeans[J]. New Phytologist, 209(2):871-884.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13626 pmid: 26479264 |
| [16] |
HE ZIWEN, ZHAI WEIWEI WEN HAIJUN, et al, 2011. Two evolutionary histories in the genome of rice: the roles of domestication genes[J]. PLoS Genetics, 7(6):e1002100.
pmid: 21695282 |
| [17] | HUANG HUIRUN, WEI WU, ZHANG JIXIU, et al, 2016. A genetic delineation of Patchouli (Pogostemon cablin) revealed by specific‐locus amplified fragment sequencing: JSE[J]. Journal of Systematics & Evolution, 54(5):491-501. |
| [18] | JARRET R L, AUSTIN D F, 1994. Genetic diversity and systematic relationships in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) and related species as revealed by RAPD analysis[J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 41(3):165-173. |
| [19] |
KENT W J, 2002. BLAT-the BLAST-like alignment tool[J]. Genome Research, 12(4):656-664.
doi: 10.1101/gr.229202 pmid: 11932250 |
| [20] |
KIMURA M, 1980. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 16(2):111-120.
doi: 10.1007/BF01731581 pmid: 7463489 |
| [21] | KONG LINGFENG, BAI JIE, LI QI, 2014. Comparative assessment of genomic SSR, EST-SSR and EST-SNP markers for evaluation of the genetic diversity of wild and cultured Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas Thunberg[J]. Aquaculture, 420-421:S85-S91. |
| [22] |
KOZICH J J, WESTCOTT S L, BAXTER N T, et al, 2013. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(17):5112-5120.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01043-13 pmid: 23793624 |
| [23] |
KWONG J C, MCCALLUM N, SINTCHENKO V, et al, 2015. Whole genome sequencing in clinical and public health microbiology[J]. Pathology, 47(3):199-210.
doi: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000235 pmid: 25730631 |
| [24] |
LAGHARI M Y, Lashari P, Zhang X, et al, 2013. Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTL) for body weight, length and condition factor traits in backcross (BC1) family of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.)[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 41:721-731.
pmid: 24368591 |
| [25] |
LAMBECK K, ESAT T M, POTTER E K, 2002. Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years[J]. Nature, 419(6903):199-206.
doi: 10.1038/nature01089 pmid: 12226674 |
| [26] | LI FANGYUAN, FENG YONGQIN, WU HONGLIU, et al, 2008. Histological studies on reproductive system of male in Trochus pyramis born[J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 26(2):153-156 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [27] |
LI H, DURBIN R, 2009. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform[J]. Bioinformatics, 25(14):1754-1760.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 pmid: 19451168 |
| [28] |
LI HENG, HANDSAKER B, WYSOKER A, et al, 2009a. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools[J]. Bioinformatics, 25(16):2078-2079.
pmid: 19505943 |
| [29] |
LI MINGZHOU, TIAN SHILIN, JIN LONG, et al, 2013. Genomic analyses identify distinct patterns of selection in domesticated pigs and Tibetan wild boars[J]. Nature Genetics, 45(12):1431-1438.
doi: 10.1038/ng.2811 |
| [30] |
LI RUIQIANG, YU CHANG, LI YINGRUI, et al, 2009b. SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment[J]. Bioinformatics, 25(15):1966-1967.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp336 pmid: 19497933 |
| [31] |
LI ZHEN, WEI SHENGJUAN, LI HEJUN, et al, 2017. Genome-wide genetic structure and differentially selected regions among Landrace, Erhualian, and Meishan pigs using specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing[J]. Scientific Reports, 7(1):10063.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09969-6 pmid: 28855565 |
| [32] |
MCKENNA A, HANNA M, BANKS E, et al, 2010. The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Genome Research, 20(9):1297-1303.
doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110 pmid: 20644199 |
| [33] | SHI YU, XU MENG, HUANG JING, et al, 2019. Transcriptome analysis of mantle tissues reveals potential biomineralization-related genes in Tectus pyramis Born[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part D: Genomics and Proteomics, 29:131-144. |
| [34] |
SIMAKOV O, MARLETAZ F, CHO S J, et al, 2013. Insights into bilaterian evolution from three spiralian genomes[J]. Nature, 493(7433):526-531.
doi: 10.1038/nature11696 pmid: 23254933 |
| [35] |
SUN XIAOWEN, LIU DONGYUAN, ZHANG XIAOFENG, et al, 2013. SLAF-seq: an efficient method of large-scale De novo SNP discovery and genotyping using high-throughput sequencing[J]. PloS ONE, 8(3):e58700.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058700 pmid: 23527008 |
| [36] |
TAMURA K, STECHER G, PETERSON D, et al, 2013. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30(12):2725-2729.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197 pmid: 24132122 |
| [37] | TABANGIN M E, WOO J G, MARTIN L J, 2009. The effect of minor allele frequency on the likelihood of obtaining false positives[J]. BMC Proceedings 3, (S7):S41. |
| [38] |
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative, 2000. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Nature, 408(6814):796-815.
doi: 10.1038/35048692 pmid: 11130711 |
| [39] |
WANG W H, WANG J Y, ZHANG T, et al, 2015. Genome-wide association study of growth traits in Jinghai Yellow chicken hens using SLAF-seq technology[J]. Animal Genetics, 50(2):175-176.
doi: 10.1111/age.12346 pmid: 26365057 |
| [40] |
WANG WENTING, XU BING, ZHANG DAYONG, et al, 2016a. Phylogeography of postglacial range expansion in Juglans mandshurica (Juglandaceae) reveals no evidence of bottleneck, loss of genetic diversity, or isolation by distance in the leading-edge populations[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 102:255-264.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.06.005 pmid: 27346642 |
| [41] |
WANG WENHAO, ZHANG TAO, WANG JINYU, et al, 2016b. Genome-wide association study of 8 carcass traits in Jinghai Yellow chickens using specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing technology[J]. Poultry Science, 95(3):500-506.
doi: 10.3382/ps/pev266 pmid: 26614681 |
| [42] |
WEIR B S, COCKERHAM C C, 1984. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure[J]. Evolution, 38(6):1358-1370.
pmid: 28563791 |
| [43] | WOODRUF D S, 2003. Neogene marine transgressions, palaeogeography and biogeographic transitions on the Thai-Malay Peninsula[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 30(4):551-567. |
| [44] |
WRIGHT S, 1931. Evolution in Mendelian populations[J]. Genetics, 16(2):97-159.
pmid: 17246615 |
| [45] | WU HONGLIU, LI FANGYUAN, FENG YONGQIN, et al, 2008. Studies on microstructure of female reproductive system in Trochus pyramis born[J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 26(3):249-252 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [46] | WU SHANZENG, GUAN YUNYAN, HUANG XIANDE, et al, 2013a. Development of 25 novel microsatellite loci and genetic variation analysis in breeding populations of the Pearl Oyster, Pinctada fucata[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 44(4):600-609. |
| [47] | WU Y L, YI G J, HUANG B Z, et al, 2013b. The Advancement of research on Banana germplasm resources in China[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 975(975):147-153. |
| [48] | XIONG GANG, ZHOU XAINWEN, WANG XIAOQING, et al, 2019. Mitochondrial genome and genetic diversity of Snail Babylonia lutosa[J]. Fisheries Science, 38(1):26-33. |
| [49] | ZHANG CHUNFANG, LIU YONG, LIANG FEILONG, et al, 2008. Studies on artifical promoting maturation and inducing spawning in Trochus pyramis born[J]. Marine Sciences, 32(5):6-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [50] |
ZHANG DAPENG, CERVANTES J, HUAMÁN Z, et al, 2000. Assessing genetic diversity of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) cultivars from tropical America using AFLP[J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 47(6):659-665.
doi: 10.1023/A:1026520507223 |
| [51] | ZHANG JUNLONG, SHI HUAFENG, XU FENGSHAN, et al, 2014. Are Acila divaricata and Acila mirabilis one species or two distinct species? Evidence from COI mitochondrial DNA[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 13(2):283-289. |
| [52] |
ZHANG YAN, ZHANG JINPENG, HUANG LONG, et al, 2015. A high-density genetic map for P genome of Agropyron Gaertn. Based on specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq)[J]. Planta, 242(6):1335-1347.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2372-7 pmid: 26232919 |
| [53] |
ZHANG YAXIN, WANG LINHAI, XIN HUAIGEN, et al, 2013. Construction of a high-density genetic map for sesame based on large scale marker development by specific length amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 13:141.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-141 pmid: 24060091 |
| [54] |
ZHANG ZHEN, SHANG HAIHONG, SHI YUNZHEN, et al, 2016. Construction of a high-density genetic map by specific locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq) and its application to Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) analysis for boll weight in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum.)[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 16:79.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0741-4 pmid: 27067834 |
| [55] |
ZHU WENYING, HUANG LONG, CHEN LONG, et al, 2016. A high-density genetic linkage map for cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): based on specific length amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing and QTL analysis of fruit traits in cucumber[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7:437.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00437 pmid: 27148281 |
|
||