Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 36-44.doi: 10.11978/2020129CSTR: 32234.14.2020129
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Population genetic structure and historical dynamics of Trachurus japonicus in the China seas based on mitochondrial control region
REN Huimin1( ), ZHANG Heng2, XU Shasha1, LI Shengfa2, LI Jiansheng2, LI Zhihong3,4, HE Lijun1,2,4(
), ZHANG Heng2, XU Shasha1, LI Shengfa2, LI Jiansheng2, LI Zhihong3,4, HE Lijun1,2,4( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Estuarine and Coastal Research, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
2. East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Science, Shanghai 200090, China
3. School of Geographic Sciences, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
4. Institute of Eco-Chongming, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
-
Received:2020-11-02Revised:2021-02-22Online:2021-09-10Published:2021-02-25 -
Contact:HE Lijun E-mail:51183904026@stu.ecnu.edu.cn;ljhe@sklec.ecnu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2018YFD0900902);National Key Research and Development Program of China(2018YFD0900904);Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDB42030203);Shanghai Science and Technology Committee “Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan”“One Belt and One Road” International Cooperation Project of Shanghai(18230743200)
CLC Number:
- P735.541
Cite this article
REN Huimin, ZHANG Heng, XU Shasha, LI Shengfa, LI Jiansheng, LI Zhihong, HE Lijun. Population genetic structure and historical dynamics of Trachurus japonicus in the China seas based on mitochondrial control region[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 36-44.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Sampling information and genetic diversity parameters of Trachurus japonicus based on mitochondrial control region"
| 海区 | 位置信息 | 序列来源 | Genbank登陆号 | 样本数 | 单倍型数 | 单倍型多样性 (Hd±SD) | 核苷酸多样性 (π±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东海 | 东海-大陆架 | 本研究 | / | 30 | 30 | 1.000±0.009 | 0.01170±0.00066 |
| 福建近海 | HM212543~HM212595 | 60 | 53 | 1.000±0.004 | 0.01288±0.00061 | ||
| 合计 | / | / | 90 | 80 | 0.999±0.002 | 0.01248±0.00045 | |
| 南海-北部湾 | 南海-防城港 | Genbank | FJ914949~FJ914987 /GQ382142~GQ382149 | 47 | 43 | 0.996±0.005 | 0.01302±0.00078 |
| 中国近海 | 东海-南海 | / | / | 137 | 118 | 0.998±0.001 | 0.01259±0.00041 |

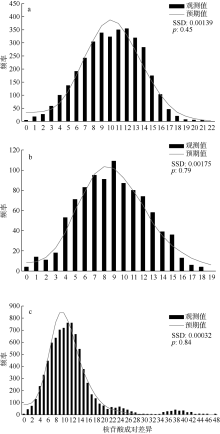
Fig. 1
Haplotype network of Trachurus japonicus based on mitochondrial control region. Geographic distribution information of each haplotype was distinguished using different colors: red ones from the Beibu Gulf in the South China Sea, blue ones from the East China Sea shelf, and yellow ones from coastal Fujian Province in the East China Sea"
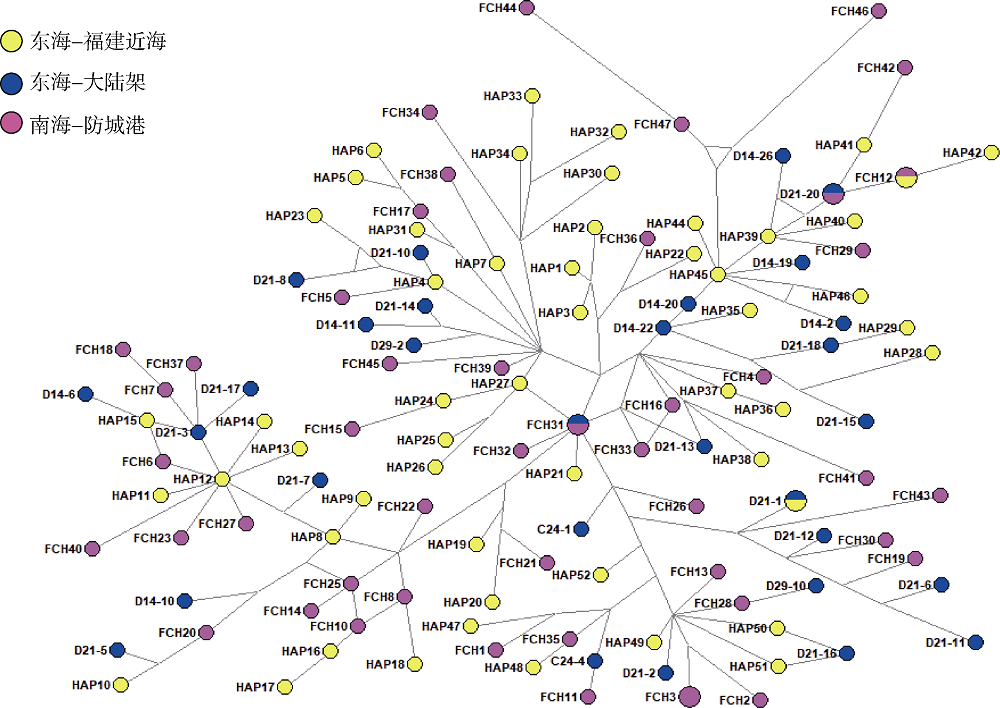
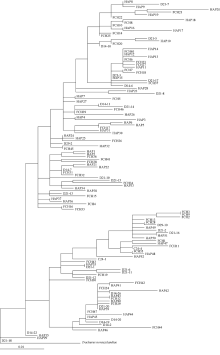
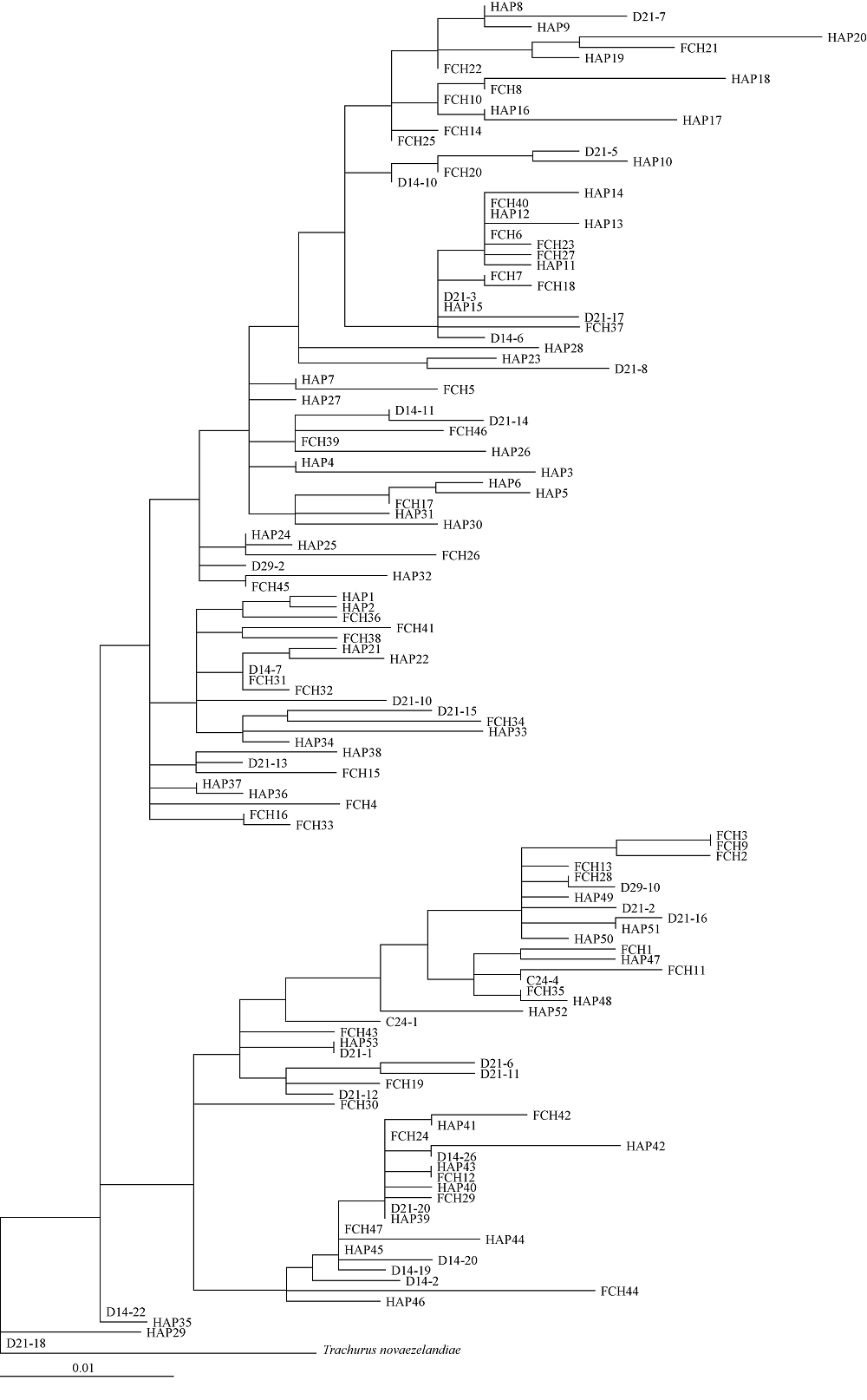
Fig. 2
Maximum likelihood tree of Trachurus japonicus based on mitochondrial control region. Geographic information of each haplotype is indicated: C/D from the East China Sea shelf, HAP from coastal Fujian Provincce in the East China Sea, and FCH from coastal Fangchenggang City in the Beibu Gulf of the South China Sea"
| [1] | 滨田律子, 马永钧, 1989. 东海竹(竹夹)鱼渔获量的变动[J]. 国外水产, (1):40-42 (in Chinese). |
| [2] | 曹宁, 高健, 2006. 东海竹荚鱼的开发利用和区域共同管理探讨[J]. 渔业经济研究, (5):25-29. |
| CAO NING, GAO JIAN, 2006. Study on utilization and regional cooperation management of Trachurus japonicus in the East China Sea[J]. Fisheries Economy Research, (5):25-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 刘舜斌, 1992. 东海竹荚鱼资源数量变动及现状[J]. 海洋渔业, (1):41-43 (in Chinese). |
| [4] | 马克平, 1993. 试论生物多样性的概念[J]. 生物多样性, 1(1):20-22. |
| MA KEPING, 1993. On the concept of biodiversity[J]. Chinese Biodiversity, 1(1):20-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 牛素芳, 苏永全, 王军, 等, 2011. 福建近海竹荚鱼线粒体DNA控制区和细胞色素b遗传多态性[J]. 中国水产科学, 18(1):66-74. |
| NIU SUFANG, SU YONGQUAN, WANG JUN, et al, 2011. Genetic polymorphism of mitochondrial control region and cyt b in Trachurus japonicus from Fujian coastal waters[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 18(1):66-74 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 萨姆布鲁克 J, 2009. 分子克隆实验指南 3版[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| SAMBROOK J, 2009. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (Third Edition)[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 邵帼瑛, 张敏, 2006. 东南太平洋智利竹荚鱼渔场分布及其与海表温关系的研究[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 15(4):468-472. |
| SHAO GUOYING, ZHANG MIN, 2006. A study on correlation of fishing ground distribution of jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyi) versus SST in the southeast Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Shanghai Fisheries University, 15(4):468-472 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 《世界大洋性渔业概况》编写组, 2011. 世界大洋性渔业概况[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. |
| COMPILATION OF WORD OCEANIC FISHERY STATUS, 2011. World Oceanic Fishery Status[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 唐涛, 周明成, 2005. 动物辞典下[M]. 呼和浩特: 远方出版社: 245-246(in Chinese). |
| [10] | 张丽艳, 牛素芳, 张曼, 等, 2014. 基于AFLP分子标记探讨福建近海竹荚鱼群体遗传多样性[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 53(1):120-125. |
| ZHANG LIYAN, NIU SUFANG, ZHANG MAN, et al, 2014. New evidence to the genetic diversity of Trachurus japonicus in the coastal waters of Fujian Province based on AFLP makers[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 53(1):120-125 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 张秋华, 程家骅, 徐汉祥, 等, 2007. 东海区渔业资源及其可持续利用[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社: 256-263(in Chinese). |
| [12] |
AVISE J C, ARNOLD J, BALL R M, et al, 1987. Intraspecific phylogeography: The mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 18(1):489-522.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.18.110187.002421 |
| [13] |
BANDELT H J, FORSTER P, RÖHL A, 1999. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16(1):37-48.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026036 |
| [14] | BERGER E M, 1983. Population genetics of marine gastropods and bivalves[M]//RUSSELL-HUNTER W D. The mollusca. Volume 6: Ecology. London: Academic Press: 563-596. |
| [15] | BROWN W M, 1985. The mitochondrial genome of animals[M] //Molecular evolutionary genetics. New York: Plenum Press: 95-130. |
| [16] |
CÁRDENAS L, HERNÁNDEZ C E, POULIN E, et al, 2005. Origin, diversification, and historical biogeography of the genus Trachurus (Perciformes: Carangidae)[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 35(2):496-507.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2005.01.011 |
| [17] |
FU Y X, 1997. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection[J]. Genetics, 147(2):915-925.
doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.2.915 |
| [18] |
GUINDON S, DUFAYARD J F, LEFORT V, et al, 2010. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0[J]. Systematic Biology, 59(3):307-321.
doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syq010 |
| [19] |
HE LIJUN, ZHANG AIBING, WEESE D, et al, 2010. Late Pleistocene population expansion of Scylla paramamosain along the coast of China: A population dynamic response to the Last Interglacial sea level highstand[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 385(1-2):20-28.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2010.01.019 |
| [20] |
HE LIJUN, MUKAI T, CHU K H, et al, 2015. Biogeographical role of the Kuroshio Current in the amphibious mudskipper Periophthalmus modestus indicated by mitochondrial DNA data[J]. Scientific Reports, 5:15645.
doi: 10.1038/srep15645 |
| [21] |
KATAYAMA S, YAMADA H, ONODERA K, et al, 2019. Age and growth from Oita and Miyagi Prefectures of Japanese jack mackerel Trachurus japonicus[J]. Fisheries Science, 85(3):475-481.
doi: 10.1007/s12562-019-01302-6 |
| [22] |
KITAMURA A, TAKANO O, TAKATA H, et al, 2001. Late Pliocene-early Pleistocene paleoceanographic evolution of the Sea of Japan[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 172(1-2):81-98.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00272-3 |
| [23] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K, 2016. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33(7):1870-1874.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 |
| [24] |
LAMBECK K, ESAT T M, POTTER E K, 2002. Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years[J]. Nature, 419(6903):199-206.
doi: 10.1038/nature01089 |
| [25] |
LEIS J, SWEATMAN H, READER S, 1996. What the pelagic stages of coral reef fishes are doing out in blue water: Daytime field observations of larval behavioural capabilities[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 47(2):401-411.
doi: 10.1071/MF9960401 |
| [26] | LEVINTON J S, KOEHN R K, 1976. Population genetics of mussels[M]//BAYNE B L (Ed). Marine mussels: their ecology and physiology. International biological programme, 10. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 357-384. |
| [27] |
LIBRADO P, ROZAS J, 2009. DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data[J]. Bioinformatics, 25(11):1451-1452.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187 |
| [28] | MCMANUS J W, 1985. Marine speciation, tectonics and sea-level changes in southeast Asia[C]// Proceedings of the 5th international coral reef congress. Tahiti:133-138. |
| [29] |
POSADA D, CRANDALL K A, 1998. MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution[J]. Bioinformatics, 14(9):817-818.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817 |
| [30] |
RAMÍREZ J D, DUQUE M C, GUHL F, 2011. Phylogenetic reconstruction based on Cytochrome b (Cyt b) gene sequences reveals distinct genotypes within Colombian Trypanosoma cruzi Ⅰ populations[J]. Acta Tropica, 119(1):61-65.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2011.04.009 |
| [31] | ROGERS A R, HARPENDING H C, 1992. Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 9(3):552-569. |
| [32] |
SASSA C, TAKAHASHI M, NISHIUCHI K, et al, 2014. Distribution, growth and mortality of larval jack mackerel Trachurus japonicus in the southern East China Sea in relation to oceanographic conditions[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 36(2):542-556.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbt134 |
| [33] | SCHNEIDER S, ROESSLI D, EXCOFIER L, 2000. ARLEQUIN ver 2.000: A software for population genetic data analysis[Z]. Switzerland: Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, Dept. of Anthropology and Ecology, University of Geneva: 47-50. |
| [34] |
SELKOE K A, D’ALOIA C C, CRANDALL E D, et al, 2016. A decade of seascape genetics: contributions to basic and applied marine connectivity[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 554:1-19.
doi: 10.3354/meps11792 |
| [35] |
SONG NA, JIA NING, YANAGIMOTO T, et al, 2013. Genetic differentiation of Trachurus japonicus from the Northwestern Pacific based on the mitochondrial DNA control region[J]. Mitochondrial DNA, 24(6):705-712.
doi: 10.3109/19401736.2013.773982 |
| [36] |
TAJIMA F, 1989. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypojournal by DNA polymorphism[J]. Genetics, 123(3):585-595.
doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.3.585 |
| [37] |
TAMAKI K, HONZA E, 1991. Global tectonics and formation of marginal basins: Role of the western Pacific[J]. Episodes, 14(3):224-230.
doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1991/v14i3/005 |
| [38] |
THOMPSON J D, GIBSON T J, PLEWNIAK F, et al, 1997. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 25(24):4876-4882.
doi: 10.1093/nar/25.24.4876 |
| [39] |
WANG JIE, TSANG L M, DONG YUNWEI, 2015. Causations of phylogeographic barrier of some rocky shore species along the Chinese coastline[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 15(1):114.
doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0387-0 |
| [40] |
WANG PINXIAN, 1999. Response of Western Pacific marginal seas to glacial cycles: paleoceanographic and sedimentological features[J]. Marine Geology, 156(1-4):5-39.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00172-8 |
| [41] | WRIGHT S, 1978. Evolution and the genetics of populations. Volume 4: Variability within and among Natural Populations[M]. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. |
| [42] | YAMADA U, TOKIMURA M, HORIKAWA H, et al, 2007. Fishes and fisheries of the East China and Yellow Seas[M]. Tokyo: Tokai University Press: 666-668(in Japanese). |
| [43] |
YODA M, SHIRAISHI T, YUKAMI R, et al, 2014. Age and maturation of jack mackerel Trachurus japonicus in the East China Sea[J]. Fisheries Science, 80(1):61-68.
doi: 10.1007/s12562-013-0687-5 |
| [44] |
ZHOU FALIN, JIANG SHIGUI, JIANG YONG JIE, et al, 2009. Population genetic structure of the tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon) in the coastal waters of South China, based on mitochondrial DNA control region sequences[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 25(4):411-416.
doi: 10.1111/jai.2009.25.issue-4 |
| [1] | ZOU Congcong, WANG Lijuan, WU Zhihao, YOU Feng. Population genetic structure of Japanese anchovy (Engraulis japonicus) in the Yellow Sea based on mitochondrial control region sequences* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 25-35. |
| [2] | Min LI, Xiaolan KONG, Youwei XU, Zuozhi CHEN. Genetic polymorphism of the Brushtooth lizardfish Saurida undosquamis based on mitochondrial D-loop sequences [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 42-49. |
| [3] | Xiaolin HUANG, Wenjun LI, Heizhao LIN, Yukai YANG, Tao LI, Wei YU, Zhong HUANG. Genetic variations among Siganus oramin populations in coastal waters of southeast China based on mtDNA control region sequences [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 45-51. |
| [4] | Zhiying ZHAO, Liyun LIANG, Lirong BAI. Analysis of genetic diversity among three wild populations of Penaeus monodon using microsatellite marker [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 65-72. |
| [5] | WENG Zhaohong, XIE Yangjie, XIAO Zhiqun, WANG Yilei. Analysis of genetic diversity in several wild and hatchery populations of Crassostrea angulata from south Fujian and south Guangdong [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(3): 94-98. |
| [6] | SHI Xiao-feng1, 2, SU Yong-quan1, WANG Wen-cheng1, WANG Jun1. Population genetic structure of three stocks of Acanthopagrus schlegelii based on mtDNA control region sequences [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(1): 56-63. |
| [7] | LIU Li, ZHAO Jie, GUO Yu-song, LIU Chu-wu. Study on the AFLP primer selection and genetic diversities of 4 Snappers [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(4): 112-116. |
| [8] | LI Li-hao,YU Da-hui,HUANG Gui-ju,DU Bo,FU Yun,TONG Xin,GUO Yi-hui,YE Wei. Comparison of genetic diversity among stocks of Oreochromis niloticus, O. aureus and red tilapia based on microsatellite DNA [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(2): 102-109. |
| [9] | JI Lei,OU You-jun,LI Jia-er. Genetic polymorphism of three cultured populations of golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus as revealed by microsatellites [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(3): 62-68. |
| [10] | GUO Yu-song,WANG Zhong-duo,LIU Chu-wu,CHEN Zhi-ming,LIU Yun. Isolation and genetic diversity analysis of microsatellites from nine species of familiar snappers [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(3): 82-86. |
|
||