Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 54-63.doi: 10.11978/2022083CSTR: 32234.14.2022083
Previous Articles Next Articles
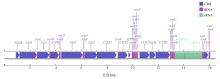
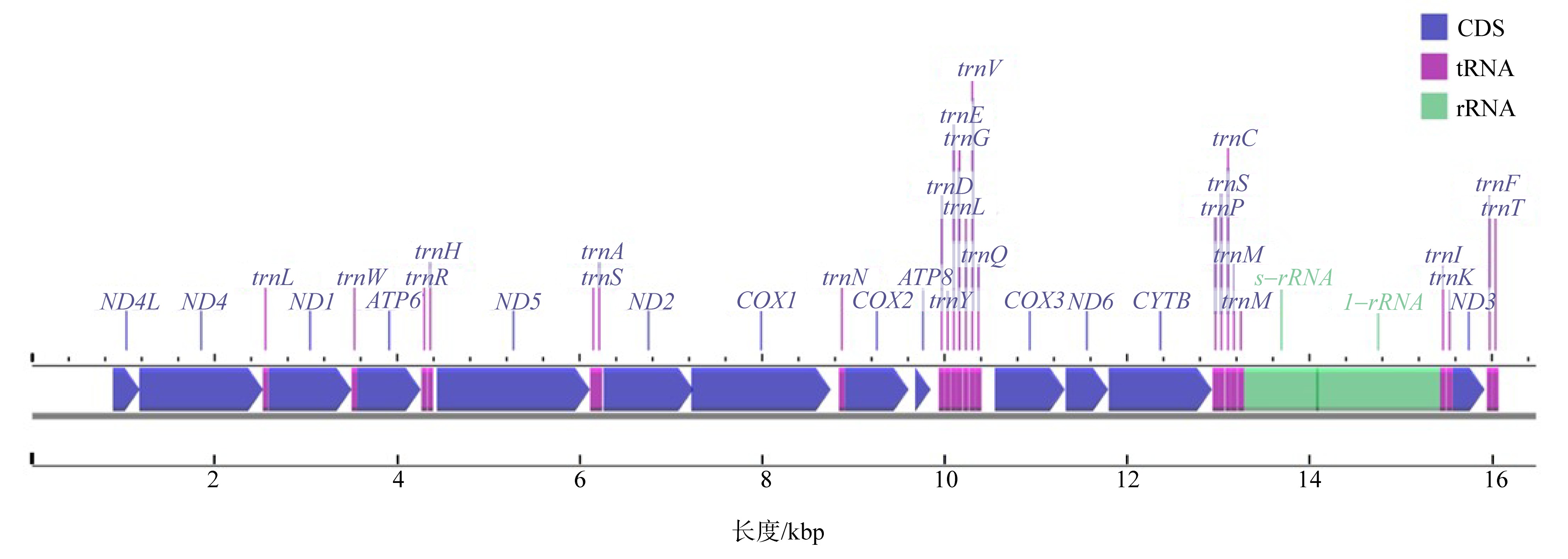
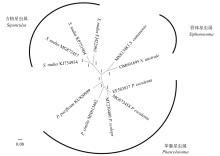
Mitogenome characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of Siphonosoma australe in Hainan
HUANG Peixian1,2( ), YAO Xuemei1,2(
), YAO Xuemei1,2( ), YU Qiaochi1,2, ZHANG Jiayu1,2
), YU Qiaochi1,2, ZHANG Jiayu1,2
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Marine Resource Utilization in South China Sea, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
2. College of Ocean, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
-
Received:2022-04-19Revised:2022-07-22Online:2023-03-10Published:2022-07-27 -
Contact:YAO Xuemei. email:yaoxuemei72@163.com -
Supported by:Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China(319MS013)
Cite this article
HUANG Peixian, YAO Xuemei, YU Qiaochi, ZHANG Jiayu. Mitogenome characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of Siphonosoma australe in Hainan[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 54-63.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
List of the outer groups"
| 属 | 物种 | 采样地 | GenBank 登录号 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方格星虫属Sipunculus | 光裸方格星虫(Sipunculus nudus) | Concarneau, France | FJ422961 |
| Beibu Bay, China | MG873457 | ||
| Gulei, China | KJ754934 | ||
| Yantai, China | KP751904 | ||
| 革囊星虫属Phascolosoma | 可口革囊星虫(Phascolosoma esculenta) | Beibu Bay, China | MG873458 |
| Wenzhou, China | EF583817 | ||
| 太平洋革囊星虫(Phascolosoma pacificum) | Chuuk, Micronesia | KU820989 | |
| 厥目革囊星虫(Phascolosoma scolops) | Beibu Bay, China | MT239480 | |
| 类革囊星虫(Phascolosoma similis) | Beibu Bay, China | MN813482 | |
| 管体星虫属Siphonosoma | 库岛管体星虫(Siphonosoma cumanense) | Beibu Bay, China | MN813483 |
Tab. 3
RSCU of mtDNA protein-coding sequence in Siphonosoma australe"
| 氨基酸 | 密码子 | 次数 | RSCU | 氨基酸 | 密码子 | 次数 | RSCU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phe | UUU | 236 | 1.45 | Tyr | UAU | 91 | 1.35 |
| UUC | 90 | 0.55 | UAC | 44 | 0.65 | ||
| Leu | UUA | 226 | 2.17 | His | CAU | 56 | 1.30 |
| UUG | 20 | 0.19 | CAC | 30 | 0.70 | ||
| CUU | 173 | 1.66 | Gln | CAA | 62 | 1.70 | |
| CUC | 68 | 0.65 | CAG | 11 | 0.30 | ||
| CUA | 127 | 1.22 | Asn | AAU | 71 | 1.31 | |
| CUG | 10 | 0.10 | AAC | 37 | 0.69 | ||
| Ile | AUU | 226 | 1.52 | Lys | AAA | 79 | 1.82 |
| AUC | 71 | 0.48 | AAG | 8 | 0.18 | ||
| Met | AUA | 161 | 1.71 | Asp | GAU | 34 | 1.05 |
| AUG | 27 | 0.29 | GAC | 31 | 0.95 | ||
| Val | GUU | 78 | 1.70 | Glu | GAA | 63 | 1.70 |
| GUC | 25 | 0.55 | GAG | 11 | 0.30 | ||
| GUA | 73 | 1.60 | Cys | UGU | 24 | 1.33 | |
| GUG | 7 | 0.15 | UGC | 12 | 0.67 | ||
| Ser | UCU | 117 | 2.77 | Trp | UGA | 87 | 1.81 |
| UCC | 41 | 0.97 | UGG | 9 | 0.19 | ||
| UCA | 84 | 1.99 | Arg | CGU | 22 | 1.22 | |
| UCG | 7 | 0.17 | CGC | 11 | 0.61 | ||
| AGU | 19 | 0.45 | CGA | 33 | 1.83 | ||
| AGC | 13 | 0.31 | CGG | 6 | 0.33 | ||
| AGA | 51 | 1.21 | Pro | CCU | 71 | 1.41 | |
| AGG | 6 | 0.14 | CCC | 29 | 0.57 | ||
| Thr | ACU | 93 | 1.52 | CCA | 95 | 1.88 | |
| ACC | 38 | 0.62 | CCG | 7 | 0.14 | ||
| ACA | 102 | 1.67 | Gly | GGU | 44 | 0.91 | |
| ACG | 12 | 0.20 | GGC | 28 | 0.58 | ||
| Ala | GCU | 96 | 1.39 | GGA | 98 | 2.02 | |
| GCC | 53 | 0.77 | GGG | 24 | 0.49 | ||
| GCA | 115 | 1.67 | |||||
| GCG | 12 | 0.17 |
Tab. 4
Amino acid quantity of protein-coding genes in sipunculan mitochondrial genomes of 7 species (3 genera)"
| 星虫名称 | ATP6 | ATP8 | CYTB | COX1 | COX2 | COX3 | ND1 | ND2 | ND3 | ND4 | ND4L | ND5 | ND6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 可口革囊星虫 | 231 | 54 | 378 | 519 | 231 | 267 | 304 | 323 318 | 121 | 450 451 | 94 | 571 562 | 157 |
| 太平洋革囊星虫 | 231 | 49 | 378 | 518 | 227 | 263 | 308 | 319 | 118 | 450 | 94 | 572 | 157 |
| 类革囊星虫 | 231 | 53 | 378 | 519 | 230 | 267 | 303 | 327 | 121 | 450 | 94 | 571 | 157 |
| 厥目革囊星虫 | 231 | 54 | 378 | 519 | 229 | 291 | 304 | 320 | 121 | 451 | 94 | 572 | 157 |
| 光裸方格星虫 | 229 234 | 52 53 | 379 | 516 519 | 231 230 | 259 | 314 312 | 328 327 329 | 119 117 | 452 454 | 93 | 565 571 | 157 |
| 库岛管体星虫 | 231 | 54 | 379 | 513 | 231 | 275 | 303 | 318 | 114 | 448 | 94 | 569 | 155 |
| 澳洲管体星虫 | 231 | 56 | 377 | 510 | 232 | 293 | 303 | 327 | 116 | 452 | 94 | 559 | 155 |
Tab. 5
Genetic variation analysis of major encoding genes in sipunculan mitochondrial genomes of 7 species (3 genera)"
| 基因名称 | 总位点数 | 保守位点数 | 变异位点数 | 变异位点比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATP6 | 669 | 226 | 443 | 66.22 |
| ATP8 | 144 | 24 | 120 | 83.33 |
| CYTB | 1131 | 550 | 581 | 51.37 |
| COX1 | 1531 | 824 | 707 | 46.18 |
| COX2 | 680 | 328 | 352 | 51.76 |
| COX3 | 780 | 342 | 438 | 56.15 |
| ND1 | 906 | 368 | 538 | 59.38 |
| ND2 | 944 | 215 | 729 | 77.22 |
| ND3 | 344 | 126 | 218 | 63.37 |
| ND4 | 1329 | 402 | 927 | 69.75 |
| ND4L | 282 | 77 | 205 | 72.70 |
| ND5 | 1657 | 523 | 1134 | 68.44 |
| ND6 | 466 | 118 | 348 | 74.68 |
| 12S rRNA | 753 | 295 | 458 | 60.82 |
| 16S rRNA | 980 | 423 | 557 | 56.84 |
| [1] |
陈子安, 杜晓东, 王庆恒, 等, 2007. 3种星虫线粒体16S rRNA、COI和Cytb基因片段的序列比较[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 27(4): 3-10.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
傅静, 孙啸, 2003. 基于全基因组的系统发生分析[J]. 生物技术, (6): 53-56.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
黄族豪, 刘迺发, 2010. 动物线粒体基因组变异研究进展[J]. 生命科学研究, 14(2): 166-171.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
蒋文枰, 李家乐, 郑润玲, 等, 2010. 褶纹冠蚌线粒体基因组全序列分析[J]. 遗传, 32(2): 153-162.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
兰国宝, 杨素芳, 谢体三, 等, 2007. 星虫动物门系统发生研究进展[J]. 广西科学, 14(2): 186-192.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
李凤鲁, 周红, 王玮, 1992. 中国沿海管体星虫属(星虫动物门)的研究[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 22(1): 97-102.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
孟乾, 张志勇, 张志伟, 等, 2020. 斑石鲷和条石鲷线粒体基因组密码子使用分析[J]. 水产科学, 39(5): 702-709.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
彭银辉, 周于娜, 刘旭佳, 等, 2017. 基于线粒体控制区序列的光裸方格星虫群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 水产学报, 41(10): 1542-1551.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
乔立君, 姚雪梅, 余巧驰, 2022. 海南澳洲管体星虫卵细胞发育及生殖周期研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(5): 161-169.
doi: 10.11978/2021143 |
|
|
|
| [10] |
申欣, 2012. 星虫动物线粒体基因组全序列的基因排列和特征比较[J]. 水产科学, 31(9): 554-559.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
宋素霞, 2015. 中国沿海光裸方格星虫线粒体基因组分析及遗传多样性研究[D]. 福建: 集美大学.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
宋素霞, 丁少雄, 鄢庆枇, 等, 2017. 中国沿海光裸方格星虫6个地理群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 水产学报, 41(8): 1183-1191.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
孙萌, 2021. 基于多基因对寡膜纲纤毛虫重要类群分子系统学的研究[D]. 黑龙江: 哈尔滨师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
夏立萍, 徐鸣, 郭宝英, 等, 2021. 等边浅蛤线粒体全基因组测序和系统发育研究[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 40(2): 93-100.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
于黎, 张亚平, 2006. 系统发育基因组学——重建生命之树的一条迷人途径[J]. 遗传, 28(11): 1445-1450.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
钟声平, 蒋艳, 刘永宏, 等, 2020. 广西5种常见星虫动物的线粒体基因组特征和系统进化分析[J]. 广西科学, 27(5): 532-540.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
周红, 李凤鲁, 王玮, 2007. 中国动物志, 无脊椎动物. 第四十六卷, 星虫动物门螠虫动物门[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1093/genetics/159.2.623 pmid: 11606539 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.2307/2413324 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1007/s00227-010-1402-z |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1111/maec.12104 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1463-6409.2011.00507.x |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2014.10.019 pmid: 25450098 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187 pmid: 19346325 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
pmid: 12470944 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-27 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1093/sysbio/sys029 pmid: 22357727 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-136 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.06.021 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1111/ivb.2003.122.issue-3 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121 pmid: 21546353 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-581-7_12 pmid: 18629668 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1731378 |
| [1] | ZHAO Zhongwei, WU Lingyun, GAO Weijian, LI Wei. A study of the effect of shore platform morphology on coastal erosion of rocky cliffs in the Wucaiwan Bay, E’man, Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 106-115. |
| [2] | ZENG Weite, ZHANG Dongqiang, LIU Bing, YANG Yongpeng, ZHANG Hangfei, WU Duoyu, WANG Xiaolin. Distribution, main controlling factors and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface seawater of the Northern Bay of Hainan Island, south China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 156-167. |
| [3] | QIAO Lijun, YAO Xuemei, YU Qiaochi. Development of oocytes and reproductive cycle of Siphonosoma australe in Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 161-169. |
| [4] | LIU Jinmei, HUANG Bingxin, DING Lanping, WANG Xuecong, YAN Jing, YAN Panzhu, ZHANG Yao. Morphological and phylogenetic studies of Yonagunia formosana in southeastern Hainan province, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 76-82. |
| [5] | NIU Biaobiao, ZHAI Mengyi, LI Yang. Morphological and Phylogenetic Studies on Chaetoceros seychellarus [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 44-49. |
| [6] | LONG Chao, LUO Zhaohe, WEI Zhangliang, YANG Fangfang, LI Ru, LONG Lijuan. Morphology and phylogeny of zooxanthellae Effrenium voratum from Luhuitou reef in Sanya, Hainan province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 35-43. |
| [7] | WANG Yuanqi, YANG Yang, ZHOU Liang, WANG Yaping, GAO Shu. Interpreting the origin of coastal boulders on a coral reef flat at Xiaodonghai of Hainan Island based on storm wave energy analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 110-121. |
| [8] | MENG Tian, CHEN Zuo, ZHU Jun, ZOU Xiaoxiao, FU Qingyan, BAO Shixiang. Morphological and molecular study on marine green alga, Halimeda velasquezii, first recorded in Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 114-121. |
| [9] | Lichun JIANG, Qun LI, Songhui LÜ. Morphology and Phylogenetics study on the species of Amphidinium (Gymnodinials, Dinophyceae) from Weizhou Island, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(3): 106-115. |
| [10] | Lifen HUANG, Qun LI, Songhui LÜ, Liang ZHANG, Xuedong XIE. Morphology, phylogeny and toxicity of Coolia tropicalis (Dinophyceae) from the Xisha Islands, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(3): 86-97. |
| [11] | Yongmei LI, Rui LIU, Nan YANG, Lanping DING, Bingxin HUANG, Yixiao WANG, Yanwei CHEN. Morphological taxonomy of four species of genus Gracilaria (Gracilariaceae, Rhodophyta) from Hainan Province, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 29-37. |
| [12] | Xingru FENG, Jinyuan LI, Baoshu YIN, Dezhou YANG, Haiying CHEN, Guandong GAO. Characteristics of ocean waves in coastal area of Dongfang, Hainan Island based on observations [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 1-8. |
| [13] | Jiangxing DONG, Wei SHI, Xiaoyu KONG, Shixi CHEN. Characteristic analysis of the complete mitogenome of Plagiopsetta glossa and a possible mechanism for gene rearrangement [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(1): 1-11. |
| [14] | Bin CHEN, Wei HE, Haitao LI, Peng WU, Yuzhang Xiao, Xiangli LYU, Jing HE. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of Sagittidae (Chaetognatha) in the South China Sea based on mitochondrial CO#cod#x02160; gene [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(6): 100-108. |
| [15] | Junpeng ZHAO, Yihan LI, Wenping GONG. The seasonal and sporadic variation of the spreading of a small tropical river plume and its associated dynamics [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(4): 67-76. |
|
||