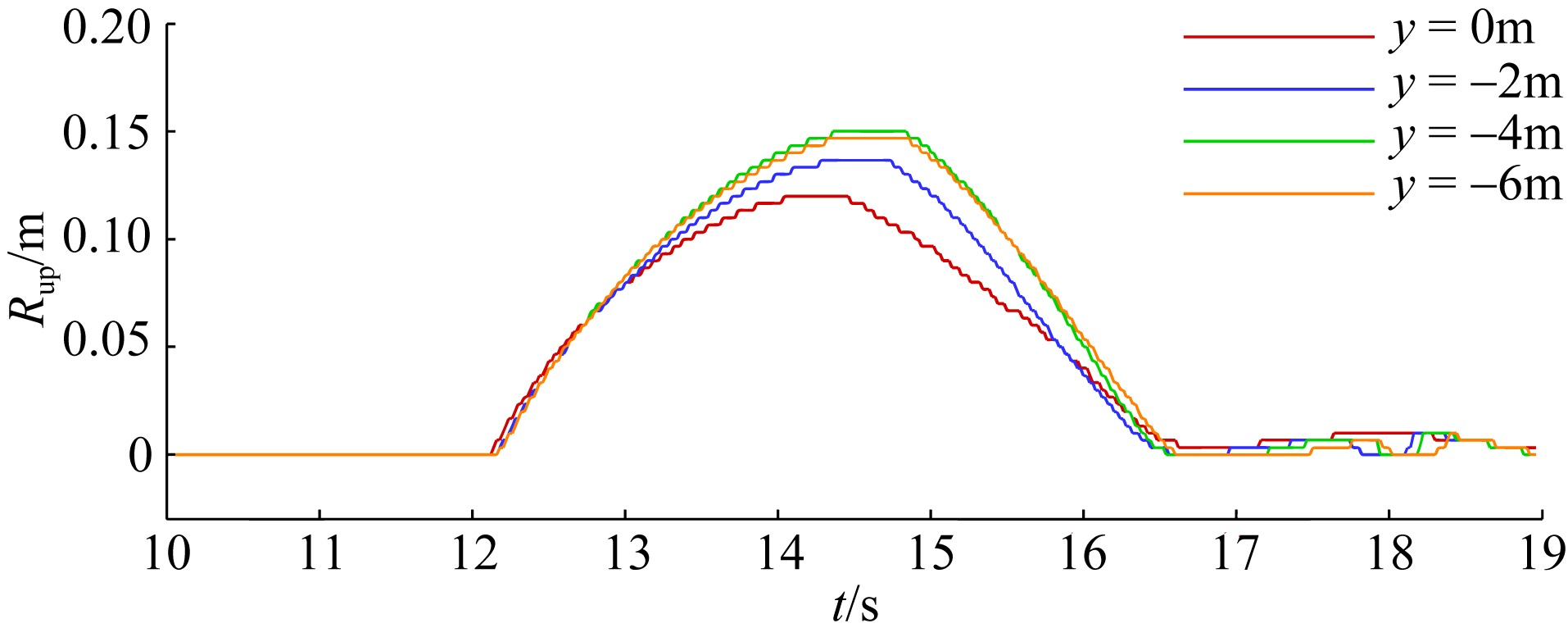
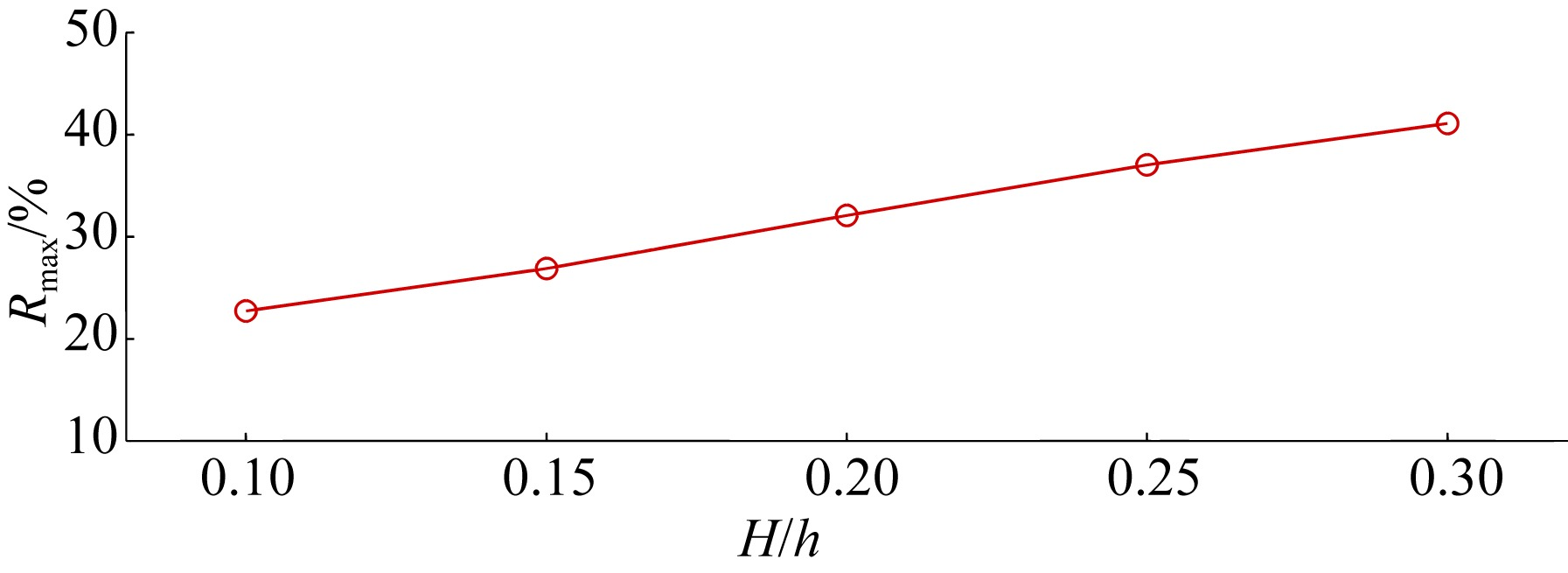
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 42-51.doi: 10.11978/2023005CSTR: 32234.14.2023005
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
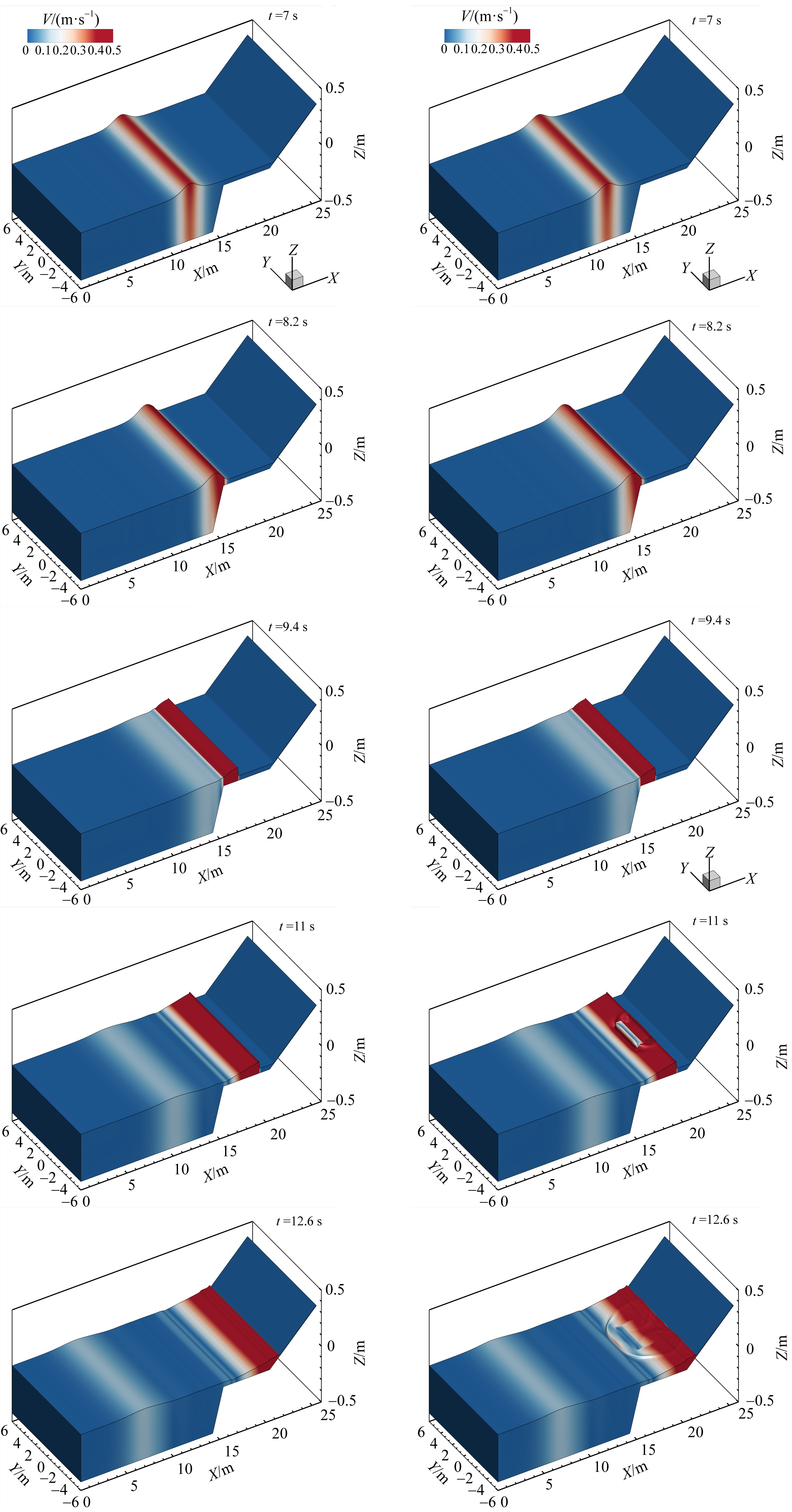
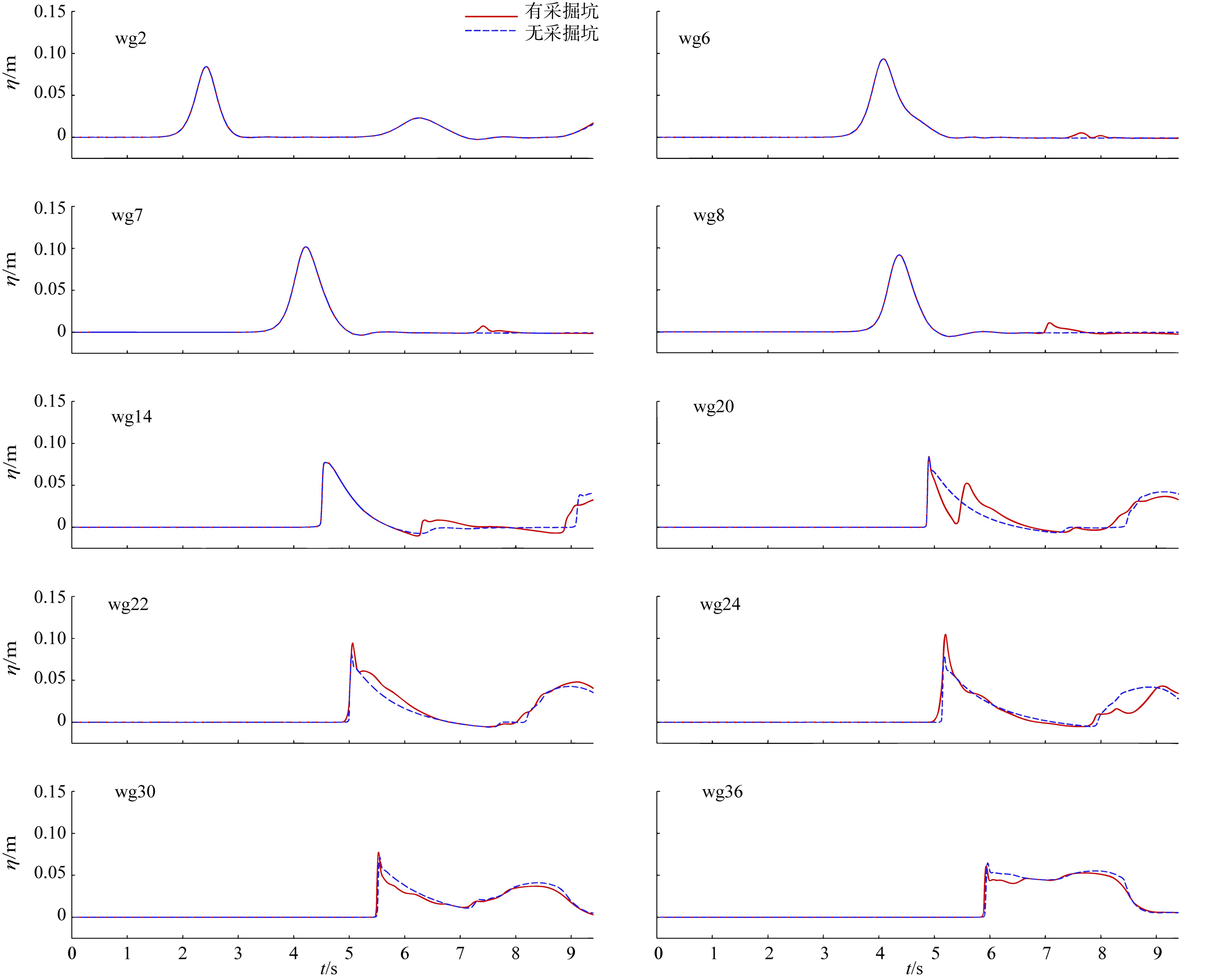
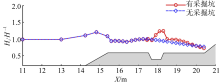
Three-dimensional numerical simulation of the influence of excavation pit on the hydrodynamic characteristics of solitary wave on fringing reef
LI Junjie1( ), QU Ke1,2,3(
), QU Ke1,2,3( ), WANG Xu1
), WANG Xu1
- 1. School of Hydraulic Engineering, Changsha University of Science & Technology, Changsha 410114, China
2. Key Laboratory of Dongting Lake Aquatic Eco-Environmental Control and Restoration of Hunan Province, Changsha 410114, China
3. Key Laboratory of Water-Sediment Sciences and Water Disaster Prevention of Hunan Province, Changsha 410114, China
-
Received:2023-03-23Revised:2023-04-28Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-03-13 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFC3103601); National Natural Science Foundation of China(51839002); Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China(2021JJ20043)
Cite this article
LI Junjie, QU Ke, WANG Xu. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of the influence of excavation pit on the hydrodynamic characteristics of solitary wave on fringing reef[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 42-51.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
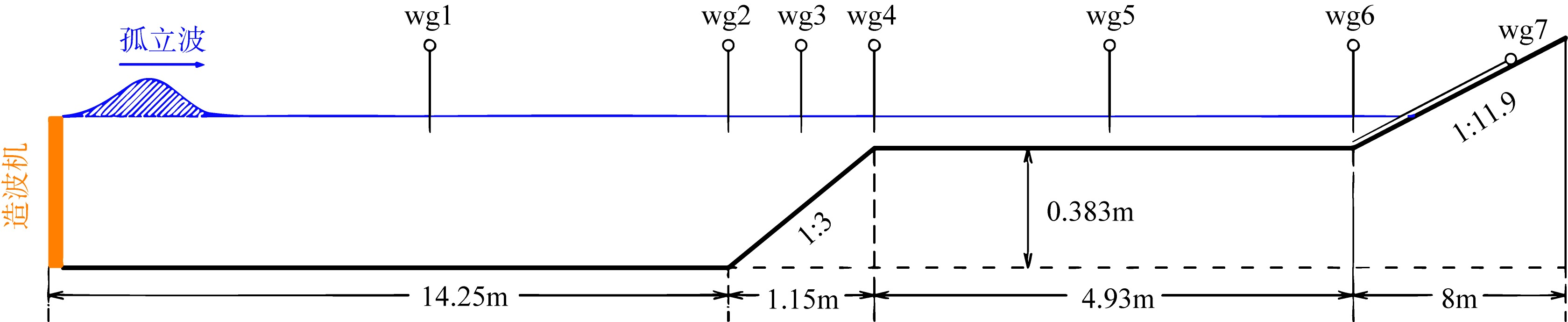
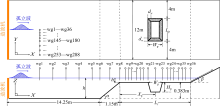
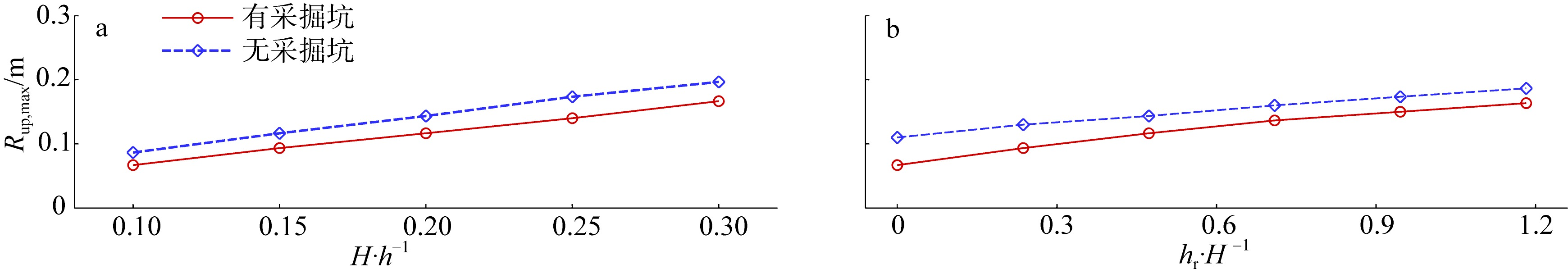
Tab. 1
Parameter setup of numerical simulation"
| 工况 | 入射波高/m | 礁坪水深/m | 采掘坑宽度/m | 采掘坑位置/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.0423 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| A2 | 0.06345 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| A3 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| A4 | 0.10575 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| A5 | 0.1269 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| B1 | 0.0423 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| B2 | 0.06345 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| B3 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| B4 | 0.10575 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| B5 | 0.1269 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| C1 | 0.0846 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| C2 | 0.0846 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 |
| C3 | 0.0846 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 |
| C4 | 0.0846 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 |
| C5 | 0.0846 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| D1 | 0.0846 | 0 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| D2 | 0.0846 | 0.02 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| D3 | 0.0846 | 0.06 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| D4 | 0.0846 | 0.08 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| D5 | 0.0846 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
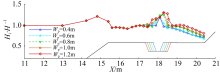
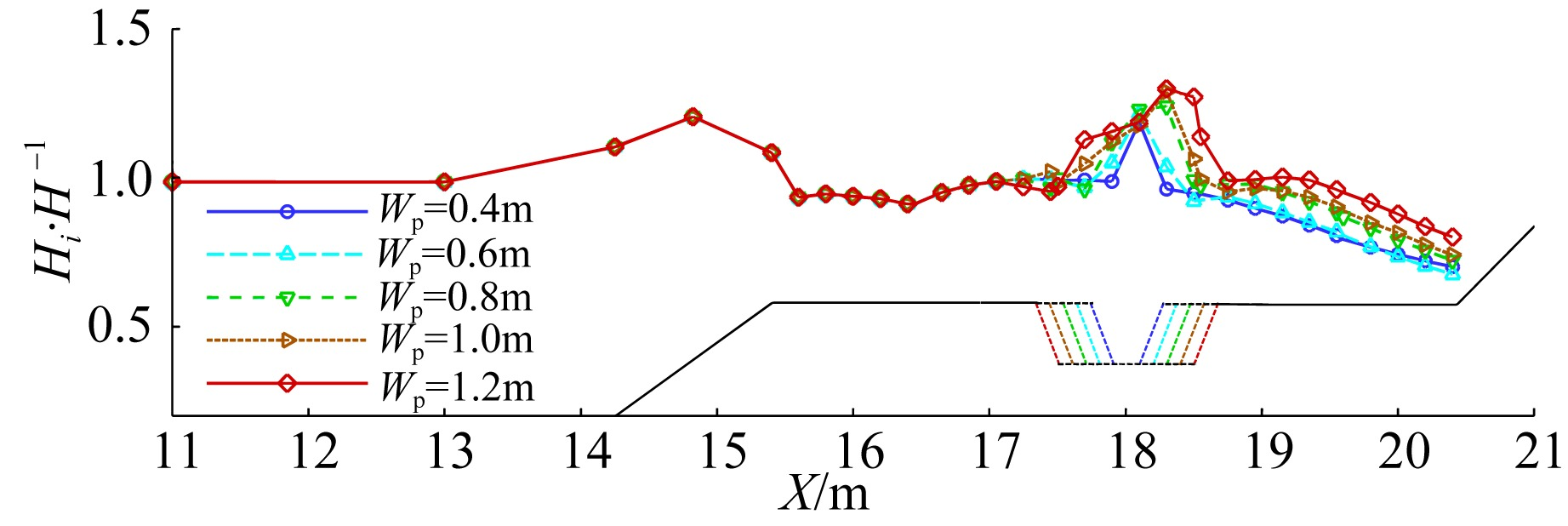
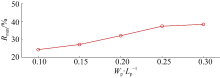
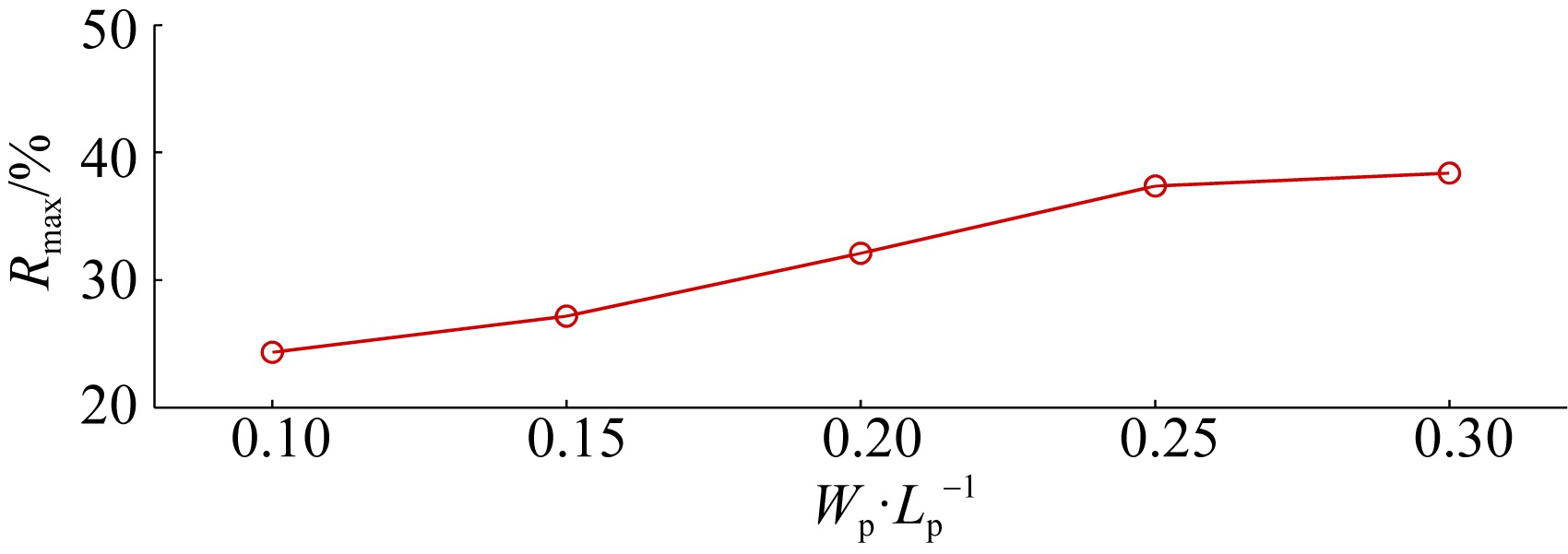
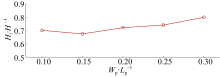
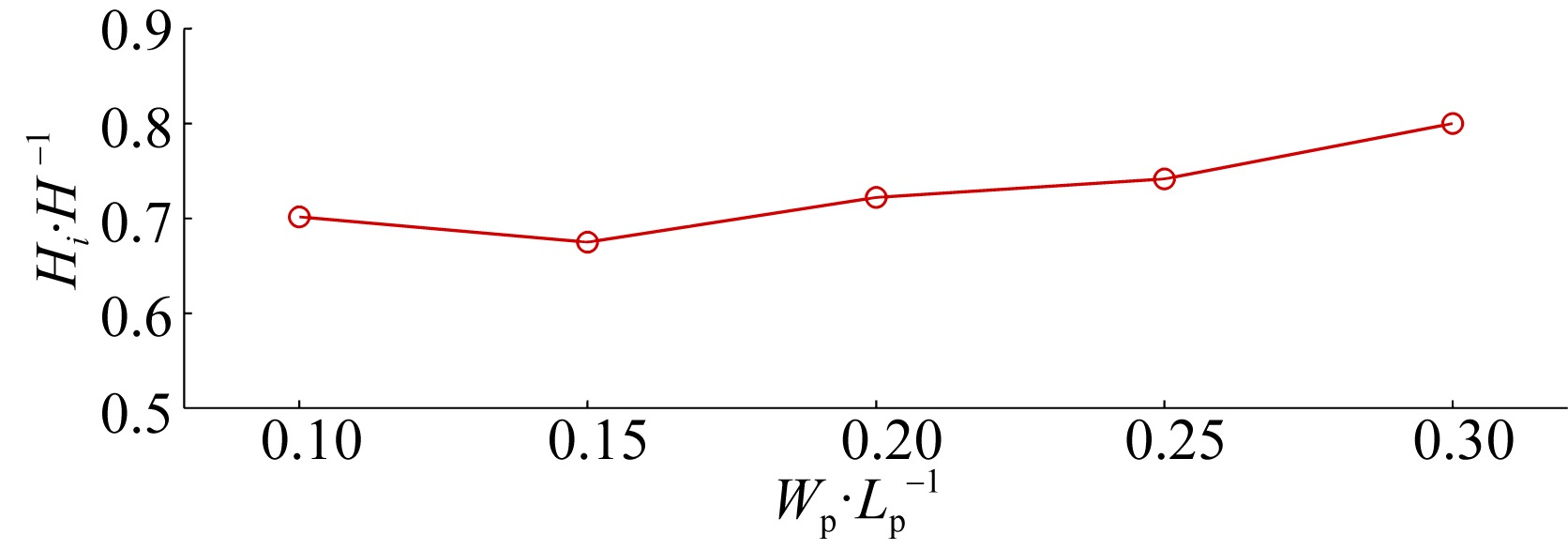
| E1 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0.4 | 2.5 |
| E2 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0.6 | 2.5 |
| E3 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 1.0 | 2.5 |
| E4 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 1.2 | 2.5 |
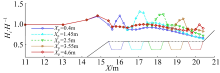
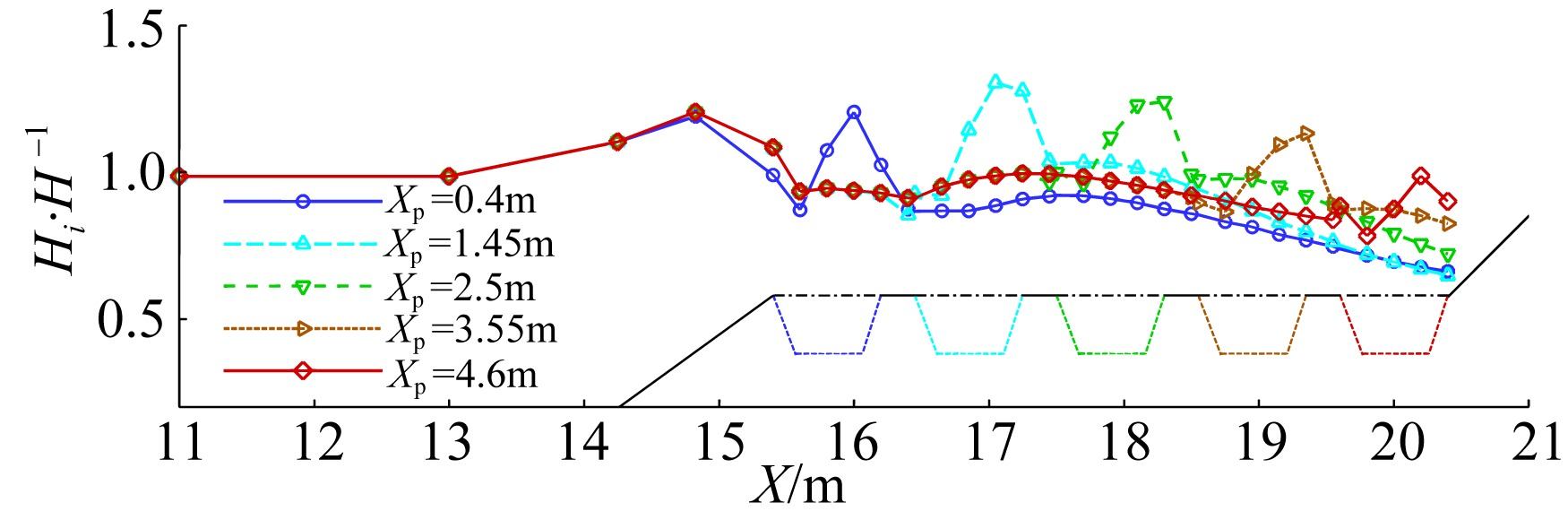
| F1 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| F2 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 1.45 |
| F3 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 3.55 |
| F4 | 0.0846 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 4.6 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.12.005 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/0378-3839(96)00009-9 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014165 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.3390/jmse7040109 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00426431 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.11.005 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2017.01.003 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106486 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1098/rsta.2006.1824 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2015.11.009 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108208 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2020.103700 |
| [19] |
|
| [1] | WANG Xu, QU Ke, WANG Zijun, YANG Yuanping, WANG Chao, ZHANG Liangbin. Numerical simulation study on the effect of wind on the hydrodynamic characteristics of undular tidal bores seawall [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 116-130. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xinwen, LIN Guanying, LI Ruixiang, YANG Wei, LIU Tongmu, ZHOU Baocheng, YIN Liqiang, DING Yibo. Design and application of internal solitary wave monitoring system based on the Tiantong communication [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 180-189. |
| [3] | GAO Rongze, QU Ke, REN Xingyue, WANG Xu. Application of convolutional neural network methods in the evolution of hydrodynamic characteristics of tsunamis like-wave over fringing reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 68-75. |
| [4] | ZHANG Liangbin, QU Ke, HUANG Jingxuan, WANG Xu, GUO Lei. Numerical simulation study of the influences of onshore wind on overtopping characteristics of coastal seawall under focused wave [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 63-73. |
| [5] | XIE Botao, HUANG Bigui, YANG Wei, LI Ruixiang, ZHANG Yan, LIU Tongmu, LI Xiangyi. Characteristic statistics and analysis of internal waves in the continental slope area west of the Dongsha Plateau on the northern South China Sea in the autumn of 2021* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 29-41. |
| [6] | FU Chengchong, LI Fuyu, CHEN Dandan, HOU Jing, WANG Jun, LI Yuanchao, WANG Daoru, WANG Yan. The genetic structure and connectivity of Porites lutea metapopulation of the fringing reefs around the Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 64-77. |
| [7] | XIE Jieshuo, GONG Yankun, NIU Jianwei, HE Yinghui, CHEN Zhiwu, XU Jiexin, CAI Shuqu. Spatial-temporal variations of the dynamic parameters of internal solitary waves in the Sulu-Celebes Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 132-142. |
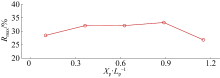
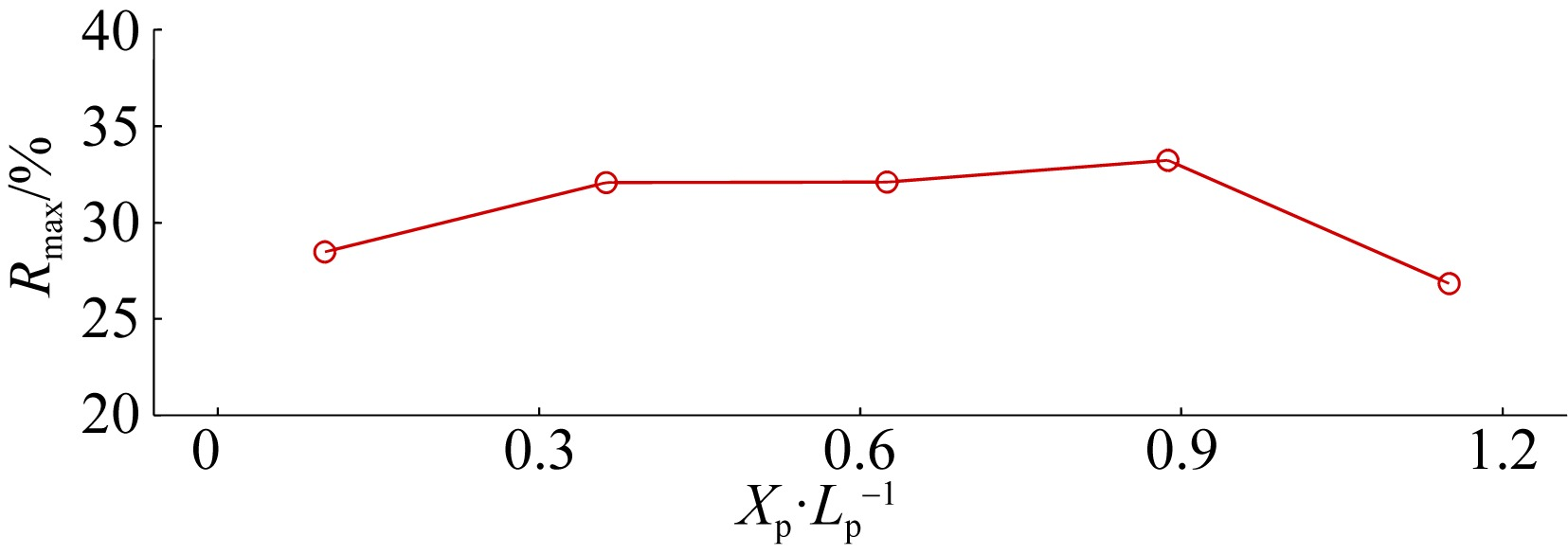
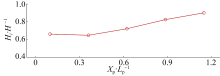
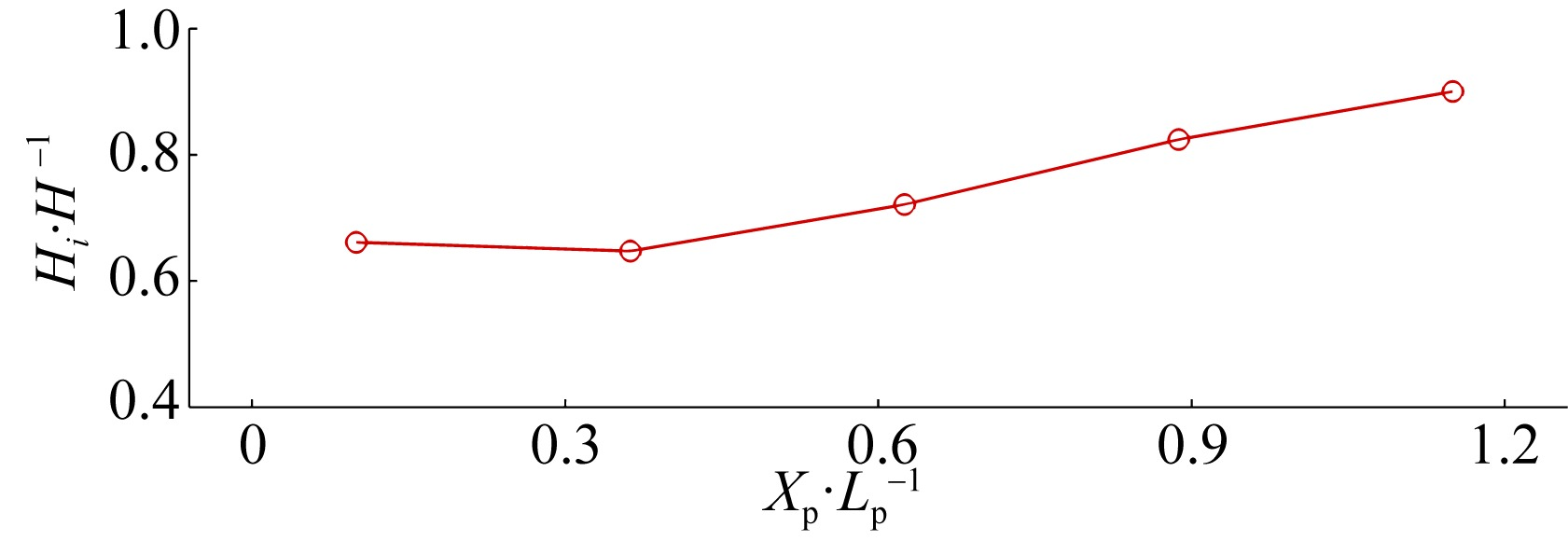
| [8] | KUANG Min, YAO Yu, CHEN Xianjin, ZHANG Qiming, JIANG Changbo. Laboratory study of wave processes over reef coasts under the impact of an excavation pit with varying pit locations [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 14-21. |
| [9] | FANG Zhou, YAN Sheng-fu, WANG Xu. Comparative study of three wave-generating methods for internal solitary waves in a two-layer fluid [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(4): 31-36. |
| [10] | LI Zi-mu, CAI Shu-qun, CHEN Ju, CHEN Rong-yu, WANG Dong-xiao, DU Yan. Preliminary analysis of observations by deep submersible mooring in west Luzon Strait during 2010 to 2011 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 10-16. |
| [11] | SHI Xin-gang, LIU Yao-hua, LAN Zhi-gang, SONG Ji-wen, HE Qi, LEI Fang-hui, WANG Jun-qin, HUANG Bi-gui, ZHU Xue-ming. The characteristics of internal solitary waves at Liuhua in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(6): 22-27. |
| [12] | LI Qi, HUANG Hua, ZHAN Jie-min, BAO Yun, GUO Lin, XU Xiao-nan. Solitary wave-induced seepage effects on the bottom of vertical cylinder resting on porous seabed [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 42-47. |
|
||