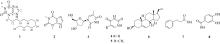
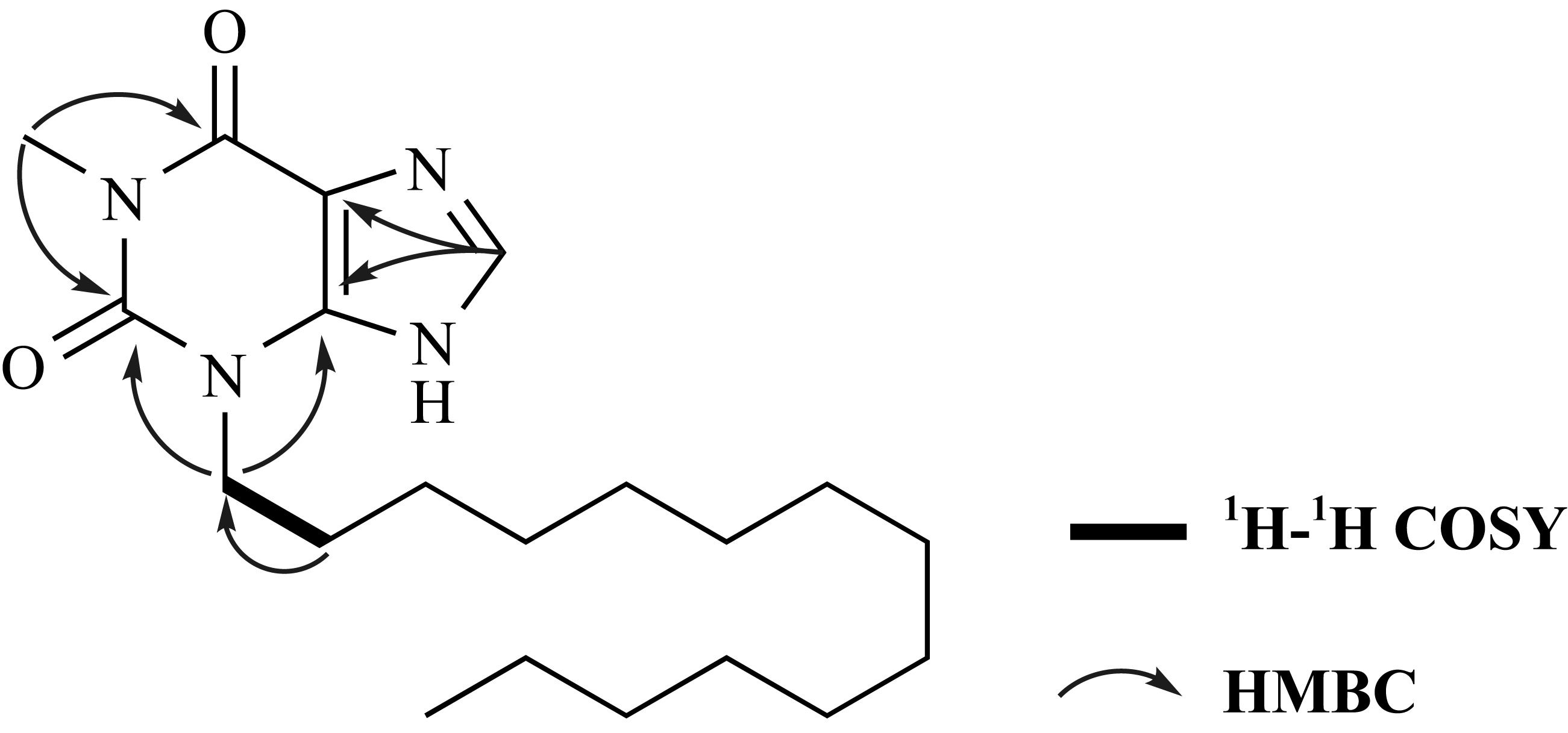
| [1] |
高锦明, 沈杰, 杨雪, 等, 2001. 黄白红菇的化学成分[J]. 云南植物研究, 23(3): 385-393.
|
|
GAO JINMING, SHEN JIE, YANG XUE, et al, 2001. The constituents of Russula ochroleuca basidiomycetes[J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 23(3): 385-393 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
高亚欣, 王昊, 戴好富, 等, 2023. 西沙短指软珊瑚Sinularia flexibilis中具有肿瘤细胞毒活性的甾体化合物[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 56-63.
|
|
GAO YAXIN, WANG HAO, DAI HAOFU, et al, 2023. Cytotoxic steroids from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis collected off the Xisha[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42(5): 56-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
何茂群, 高峰, 鞠建刚, 2014. 毛菊苣根乙酸乙酯提取部位的化学成分[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 16(7): 70-71.
|
|
HE MAOQUN, GAO FENG, JU JIANGANG, 2014. Chemical constituents in ethyl acetate extracts from roots of Cichorium Glandulosum[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 16(7): 70-71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
季宇彬, 郑婷, 尹姣定, 2018. 中国南海海绵Cinachyrella sp. 的化学成分研究[J]. 中国海洋药物, 37(2): 7-12.
|
|
JI YUBIN, ZHENG TING, YIN JIAODING, 2018. Chemical constituents from chinese marine sponge Cinachyrella sp.[J]. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 37(2): 7-12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
李瑞玉, 2008. 中国海洋生物名录[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:360.
|
|
LI RUIYU, 2008. Checklist of marine biota of china seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press:360 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
邵军丽, 李林秋, 戴娟秀, 等, 2016. CCK-8试剂用于测定活细胞数量的细节研究[J]. 生物技术世界, 13(5): 31-32 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
谭雁鸿, 李基兴, 林秀萍, 等, 2019. 中国南海软珊瑚真菌Eupenicillium sp. DX-SER3 (KC871024) 的次级代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(2): 43-47.
doi: 10.11978/2018072
|
|
TAN YANHONG, LI JIXING, LIN XIUPING, et al, 2019. Study on the secondary metabolites from the south china sea soft coral-derived fungus Eupenicillium sp. DX-SER3 (KC871024)[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(2): 43-47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
王晓岚, 郁开北, 彭树林, 2008. 铁苋菜地上部分的化学成分研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 33(12): 1415-1417.
|
|
WANG XIAOLAN, YU KAIBEI, PENG SHULIN, 2008. Chemical constituents of aerial part of Acalypha australis[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 33(12): 1415-1417 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
张文, MARGHERITA G, 郭跃伟, 等, 2006. 中国南海石珊瑚Tubastraea sp. 化学成分研究[J]. 中国天然药物, 4(2): 94-97.
|
|
ZHANG WEN, MARGHERITA G, GUO YUEWEI, et al, 2006. Chemical studies on the South China sea stony coral Tubastraea sp.[J]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 4(2): 94-97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
BEDARD P L, HYMAN D M, DAVIDS M S, et al, 2020. Small molecules, big impact: 20 years of targeted therapy in oncology[J]. The Lancet, 395(10229): 1078-1088.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30164-1
|
| [11] |
DAWE R D, WRIGHT J L C, 1987. An improved route to pregna-5, 20-dien-3β-ol (muricin aglycone): carbon and proton nuclear magnetic resonance assignments for the aglycone and a number of related pregnene derivatives[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 65(3): 666-669.
doi: 10.1139/v87-114
|
| [12] |
HAQUE N, PARVEEN S, TANG TINGTING, et al, 2022. Marine natural products in clinical use[J]. Marine Drugs, 20(8): 528.
doi: 10.3390/md20080528
|
| [13] |
IOANNOU E, ABDEL-RAZIK A F, ALEXI X, et al, 2008. Pregnanes with antiproliferative activity from the gorgonian Eunicella cavolini[J]. Tetrahedron, 64(51): 11797-11801.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2008.09.078
|
| [14] |
MONTUORI E, HYDE C A C, CREA F, et al, 2023. Marine natural products with activities against prostate cancer: recent discoveries[J]. Interntional Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2): 1435.
|
| [15] |
NIGORA R, KHAYRULLA B, NURMIRZA B, et al, 2021. Secondary metabolites produced by endophytic Pantoea ananatis derived from roots of Baccharoides anthelmintica and their effect on melanin synthesis in murine B16 cells[J]. Natural Product Research, 35(5): 796-801.
doi: 10.1080/14786419.2019.1597354
|
 ), HE Jeyi3, BAI Meng1,2, YI Xiangxi1,2, LIU Xinming1,2, LUO Lianxiang3,4, GAO Chenghai1,2(
), HE Jeyi3, BAI Meng1,2, YI Xiangxi1,2, LIU Xinming1,2, LUO Lianxiang3,4, GAO Chenghai1,2( )
)