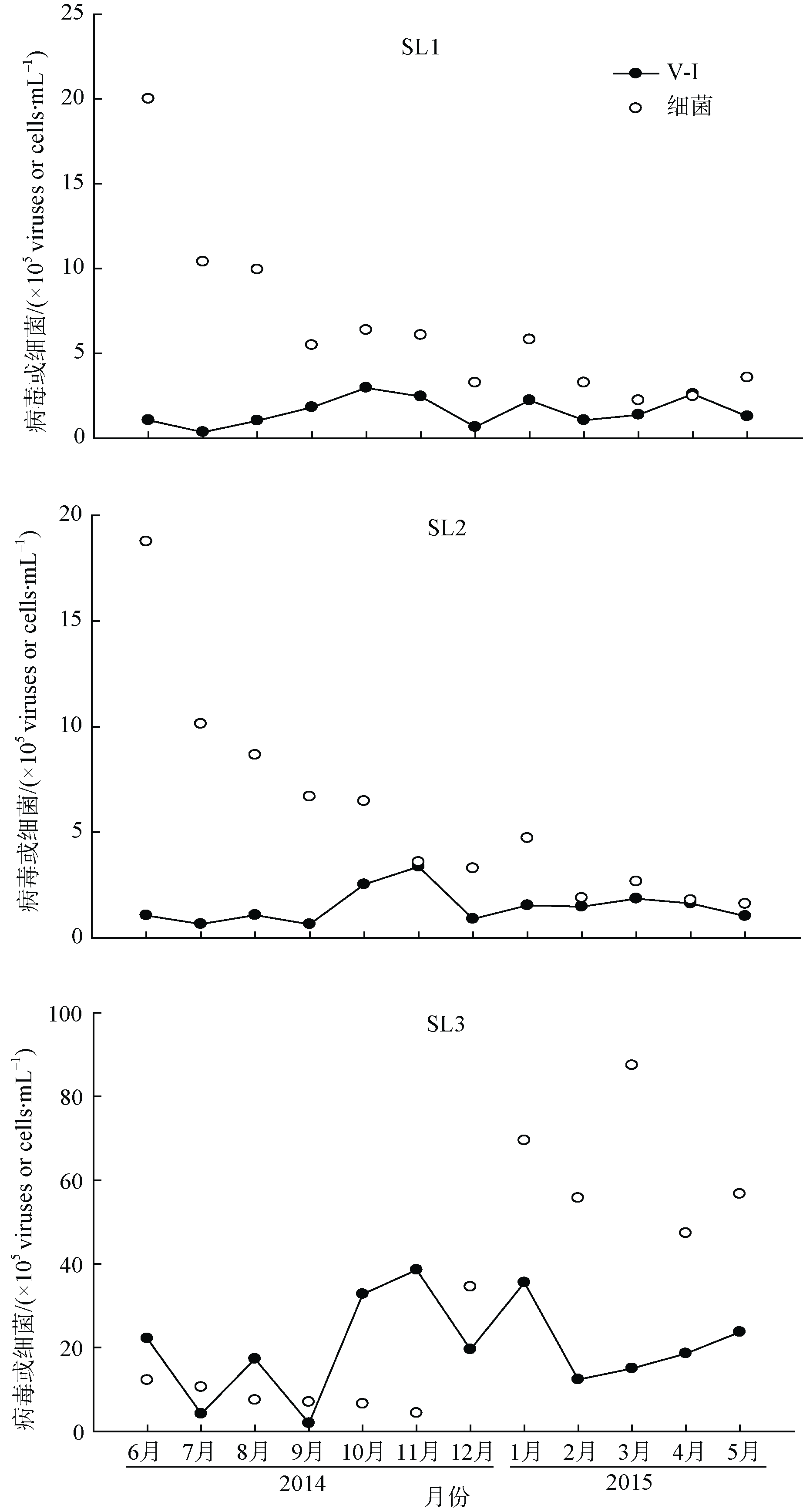
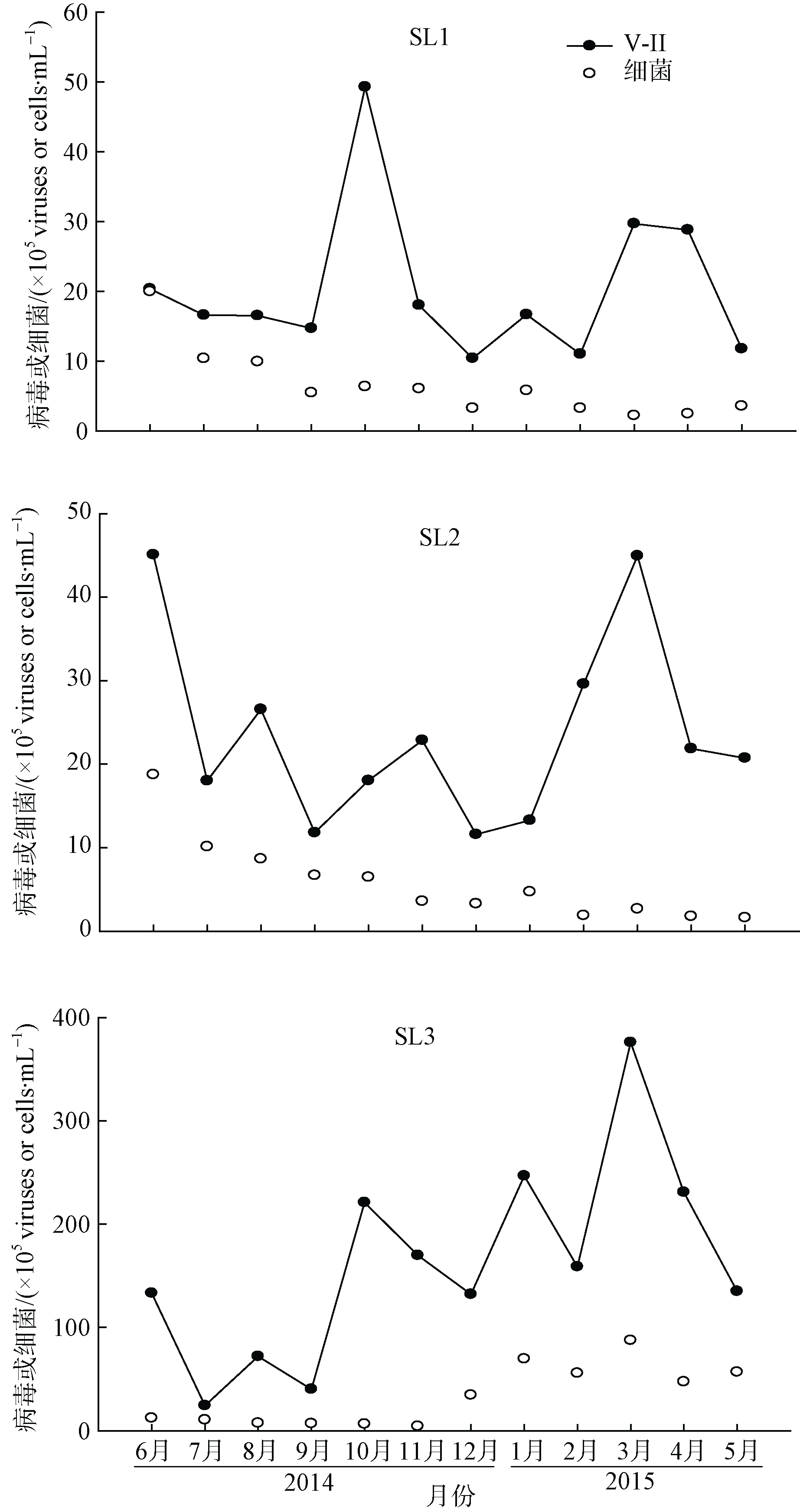
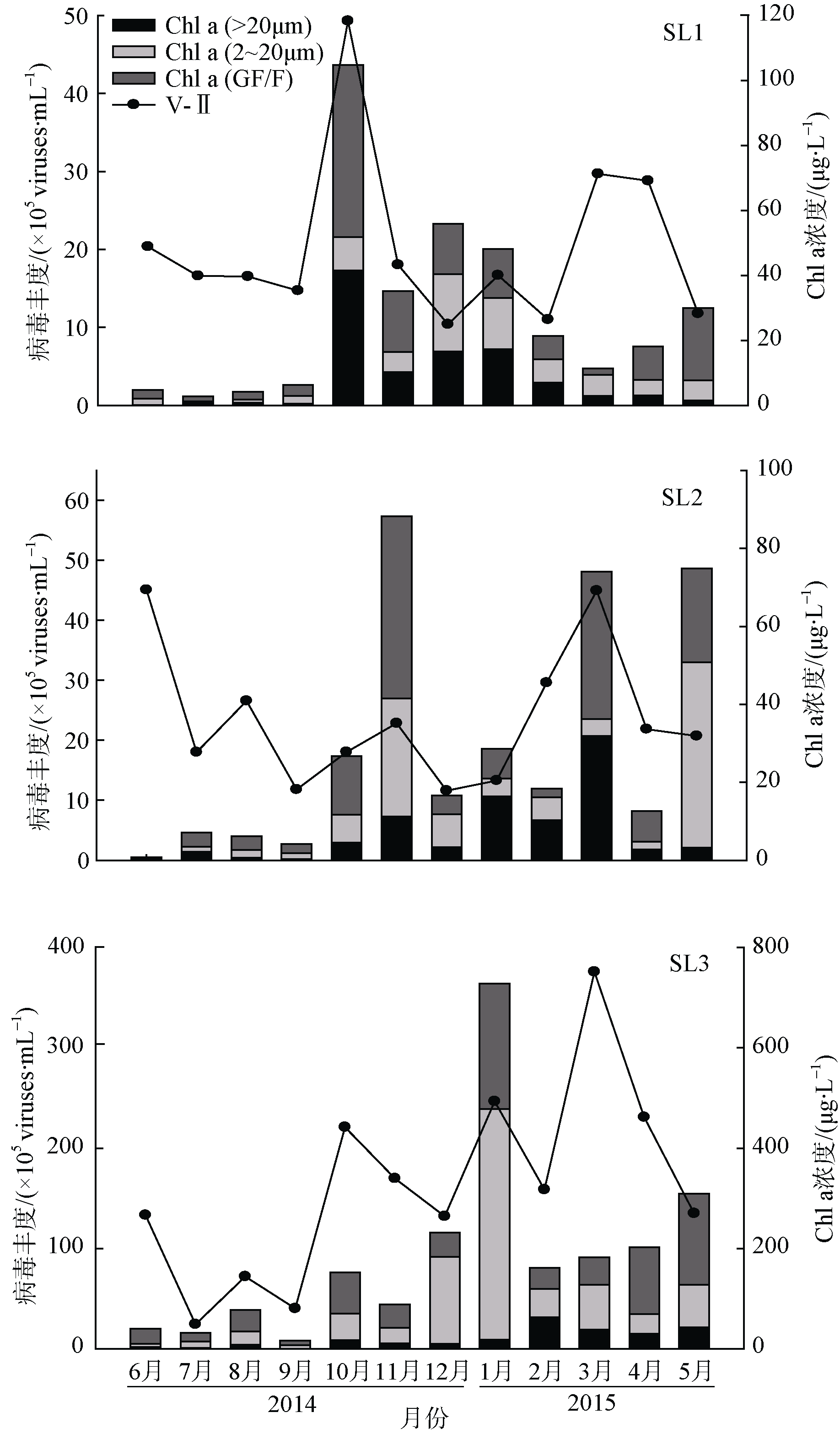
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2018, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 36-46.doi: 10.11978/2017064CSTR: 32234.14.2017064
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatiotemporal variations of virioplankton and bacterioplankton abundance in Sanya waters and their related environmental factors
Hongmei JING1( ), Yu WEI1,2, Liping ZHENG1, Qiutong XU1,2, Yue ZHANG1,2, Wenda ZHU1,2
), Yu WEI1,2, Liping ZHENG1, Qiutong XU1,2, Yue ZHANG1,2, Wenda ZHU1,2
- 1. Chinese Academy of Sciences Key Lab for Experimental Study under Deep-sea Extreme Conditions, Institute of Deep-sea Science and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sanya 572000, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2017-05-26Revised:2017-09-27Online:2018-04-10Published:2018-04-11 -
Supported by:Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIDSSE-201303);The National Natural Science Foundation of China (41406180)
Cite this article
Hongmei JING, Yu WEI, Liping ZHENG, Qiutong XU, Yue ZHANG, Wenda ZHU. Spatiotemporal variations of virioplankton and bacterioplankton abundance in Sanya waters and their related environmental factors[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(2): 36-46.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 2
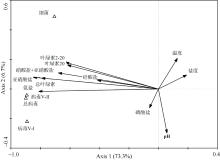
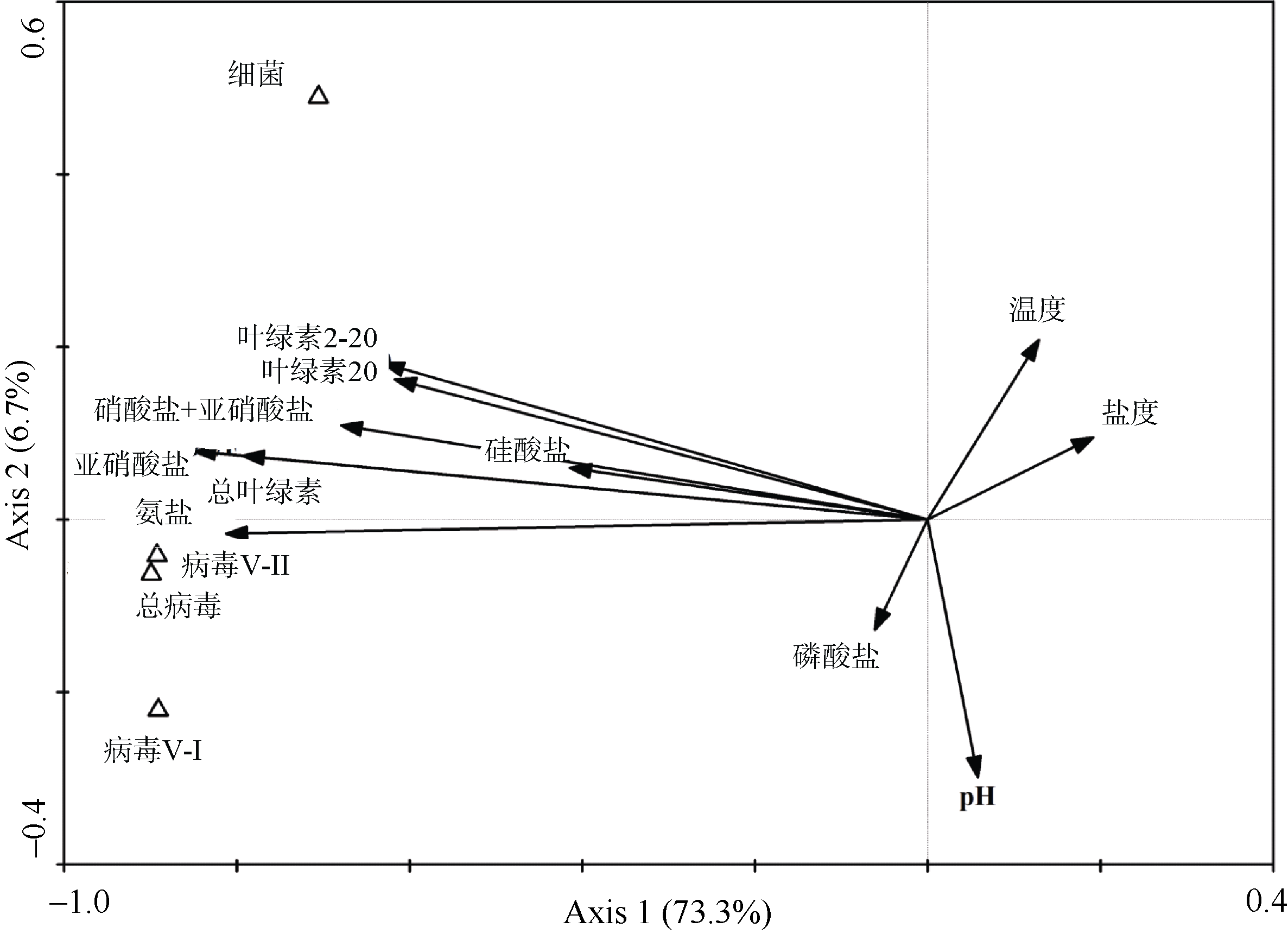
Pearson correlation coefficients between abundance of virioplankton, bacterioplankton and environmental parameters at station SL1"
| 相关影响因子 | Vir | Bac | VBR | Sal | Tem | pH | Chl a (>20μm) | Chl a (2~20μm) | Chl a (GF/F) | NO- 2 | NO- 2 +NO- 3 | PO3- 4 | SiO2- 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bac | -0.034 | ||||||||||||
| VBR | 0.632* | -0.549 | |||||||||||
| Sal | -0.310 | -0.337 | -0.068 | ||||||||||
| Tem | 0.039 | 0.668* | -0.396 | -0.826** | |||||||||
| pH | 0.395 | 0.287 | -0.267 | -0.221 | 0.371 | ||||||||
| Chl a (>20μm) | 0.637* | -0.192 | 0.163 | 0.267 | -0.335 | 0.507 | |||||||
| Chl a (2~20μm) | -0.052 | -0.424 | 0.060 | 0.724** | -0.769** | -0.134 | 0.571 | ||||||
| Chl a (GF/F) | 0.636* | -0.224 | 0.173 | 0.069 | -0.124 | 0.669* | 0.891** | 0.387 | |||||
| NO- 2 | -0.031 | 0.838** | -0.333 | -0.185 | 0.397 | 0.087 | -0.184 | -0.194 | -0.188 | ||||
| NO- 2+NO- 3 | 0.154 | 0.799** | -0.288 | -0.281 | 0.432 | 0.188 | 0.022 | -0.157 | 0.011 | 0.957** | |||
| PO3- 4 | 0.163 | -0.410 | 0.431 | 0.155 | -0.509 | -0.036 | 0.265 | 0.545 | 0.204 | -0.214 | -0.206 | ||
| SiO2- 3 | 0.049 | 0.686* | -0.230 | -0.070 | 0.191 | 0.040 | -0.001 | -0.013 | -0.057 | 0.942** | 0.949** | -0.062 | |
| NH+ 4 | 0.005 | 0.777** | -0.238 | -0.203 | 0.432 | 0.073 | -0.235 | -0.258 | -0.147 | 0.955** | 0.893** | -0.311 | 0.857** |
Tab. 3
Pearson correlation coefficients between abundance of virioplankton, bacterioplankton and environmental parameters at station SL2"
| 相关影响因子 | Vir | Bac | VBR | Sal | Tem | pH | Chl a (>20μm) | Chl a (2~20μm) | Chl a (GF/F) | NO- 2 | NO- 2+NO- 3 | PO3- 4 | SiO2- 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bac | 0.332 | ||||||||||||
| VBR | 0.446 | -0.636* | |||||||||||
| Sal | -0.019 | -0.378 | 0.327 | ||||||||||
| Tem | 0.046 | 0.610* | -0.446 | -0.791** | |||||||||
| pH | -0.042 | 0.138 | -0.210 | 0.064 | 0.369 | ||||||||
| Chl a(>20μm) | 0.424 | -0.408 | 0.553 | 0.393 | -0.589* | -0.183 | |||||||
| Chl a(2~20μm) | -0.114 | -0.412 | 0.315 | 0.027 | 0.068 | 0.514 | 0.002 | ||||||
| Chl a(GF/F) | 0.278 | -0.422 | 0.438 | -0.015 | -0.146 | 0.318 | 0.605* | 0.601* | |||||
| NO- 2 | -0.491 | 0.046 | -0.499 | -0.486 | 0.348 | 0.255 | -0.433 | -0.103 | -0.112 | ||||
| NO- 2+NO- 3 | -0.247 | 0.241 | -0.525 | -0.541 | 0.450 | 0.023 | -0.488 | -0.241 | -0.311 | 0.613* | |||
| PO3- 4 | -0.285 | 0.148 | -0.311 | 0.406 | -0.193 | -0.083 | 0.157 | -0.364 | -0.347 | -0.18 | -0.318 | ||
| SiO2- 3 | -0.290 | 0.036 | -0.328 | 0.065 | -0.240 | -0.156 | -0.305 | -0.121 | -0.254 | 0.353 | 0.334 | -0.164 | |
| NH+ 4 | 0.638* | 0.492 | 0.123 | -0.074 | 0.253 | 0.281 | -0.116 | -0.052 | 0.057 | -0.079 | -0.303 | -0.188 | -0.200 |
Tab. 4
Pearson correlation coefficients between abundance of virioplankton, bacterioplankton and environmental parameters at station SL3"
| 相关影响因子 | Vir | Bac | VBR | Sal | Tem | pH | Chl a (>20μm) | Chl a (2~20μm) | Chl a (GF/F) | NO- 2 | NO- 2+NO- 3 | PO3- 4 | SiO2- 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bac | 0.677* | ||||||||||||
| VBR | 0.164 | -0.539 | |||||||||||
| Sal | 0.474 | 0.593* | -0.127 | ||||||||||
| Tem | -0.563 | -0.686* | 0.205 | -0.680* | |||||||||
| pH | 0.059 | -0.409 | 0.720** | -0.140 | 0.433 | ||||||||
| Chl a(>20μm) | 0.469 | 0.724** | -0.257 | 0.638* | -0.597* | -0.138 | |||||||
| Chl a(2~20μm) | 0.406 | 0.539 | -0.230 | 0.367 | -0.549 | -0.219 | 0.089 | ||||||
| Chl a(GF/F) | 0.456 | 0.564 | -0.167 | 0.394 | -0.316 | 0.047 | 0.312 | 0.759** | |||||
| NO- 2 | 0.531 | 0.452 | 0.159 | 0.351 | -0.719** | -0.143 | 0.220 | 0.633* | 0.250 | ||||
| NO- 2+NO- 3 | 0.109 | 0.078 | 0.153 | -0.132 | -0.517 | -0.196 | 0.001 | 0.266 | -0.171 | 0.776** | |||
| PO3- 4 | 0.403 | -0.018 | 0.528 | -0.002 | -0.327 | 0.233 | 0.091 | 0.298 | 0.130 | 0.488 | 0.449 | ||
| SiO2- 3 | -0.033 | -0.104 | 0.183 | -0.257 | -0.359 | -0.137 | -0.193 | 0.088 | -0.351 | 0.600* | 0.930** | 0.397 | |
| NH+ 4 | 0.277 | 0.167 | 0.203 | -0.016 | -0.521 | -0.074 | -0.033 | 0.604* | 0.181 | 0.851** | 0.837** | 0.712** | 0.738** |
Tab. 5
Pearson correlation coefficients between abundance of virioplankton, bacterioplankton and environmental parameters fo the overall level at the surveyed stations"
| 相关影响因子 | Vir | Bac | VBR | Sal | Tem | pH | Chl a (>20μm) | Chl a (2~20μm) | Chl a (GF/F) | NO- 2 | NO- 2+NO- 3 | PO3- 4 | SiO2- 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bac | 0.800** | ||||||||||||
| VBR | 0.331* | -0.230 | |||||||||||
| Tem | -0.211 | -0.218 | -0.054 | -0.621** | |||||||||
| pH | -0.117 | -0.273 | 0.236 | -0.014 | 0.389* | ||||||||
| Chl a(>20μm) | 0.546** | 0.614** | 0.033 | 0.280 | -0.461** | -0.042 | |||||||
| Chl a(2~20μm) | 0.582** | 0.639** | -0.029 | 0.071 | -0.303 | -0.178 | 0.251 | ||||||
| Chl a(GF/F) | 0.689** | 0.683** | 0.087 | -0.002 | -0.180 | -0.006 | 0.503** | 0.804** | |||||
| NO- 2 | 0.792** | 0.697** | 0.275 | -0.147 | -0.235 | -0.187 | 0.379* | 0.700** | 0.556** | ||||
| NO- 2+NO- 3 | 0.587** | 0.497** | 0.225 | -0.405* | -0.086 | -0.173 | 0.254 | 0.462** | 0.315 | 0.887** | |||
| PO3- 4 | 0.134 | -0.010 | 0.244 | 0.137 | -0.250 | 0.049 | 0.088 | 0.133 | 0.030 | 0.143 | 0.086 | ||
| SiO2- 3 | 0.359* | 0.271 | 0.198 | -0.353* | -0.142 | -0.161 | 0.072 | 0.275 | 0.067 | 0.720** | 0.908** | 0.078 | |
| NH+ 4 | 0.714** | 0.571** | 0.312 | -0.335* | -0.146 | -0.162 | 0.271 | 0.677** | 0.536** | 0.938** | 0.905** | 0.204 | 0.771** |
| [1] | 白洁, 李岿然, 李正炎, 等, 2003. 渤海春季浮游细菌分布与生态环境因子的关系[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 33(6): 841-846. |
| BAI JIE, LI KUIRAN, LI ZHENGYAN, et al, 2003. Relationship between the environmental factors and distribution of bacterioplankton in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 33(6): 841-846 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 国家海洋局海口海洋环境监测中心站, 2005. 三亚湾海滩“泥化”和海岸侵蚀原因及治理对策研究报告[R]. 海口: 国家海洋局海口海洋环境监测中心站. |
| [3] | 刘晶晶, 杜萍, 曾江宁, 等, 2011a. 夏季长江口浮游细菌和浮游病毒的分布特征及环境制约因素[J]. 海洋学研究, 29(3): 118-124. |
| LIU JINGJING, DU PING, ZENG JIANGNING, et al, 2011b. Distribution of bacterioplankton and virioplankton and their relationship with the environmental factors in summer in Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent East China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 29(3): 118-124 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 刘晶晶, 曾江宁, 杜萍, 等, 2011b. 长江口及邻近海域夏、冬季浮游病毒丰度分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(3): 793-799. |
| LIU JINGJING, ZENG JIANGNING, DU PING, et al, 2011a. Abundance distribution of virioplankton in Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent East China Sea in summer and winter[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(3): 793-799 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 卢龙飞, 汪岷, 梁彦韬, 等, 2013. 东海、黄海浮游病毒及异养细菌的分布研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 44(5): 1339-1346. |
| LU LONGFEI, WANG MIN, LIANG YANTAO, et al, 2013. Distribution of virioplankton, heterotrophic bacteria in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 44(5): 1339-1346 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 史君贤, 陈忠元, 宁修仁, 等, 1992. 长江口及其附近海域细菌和三磷酸腺苷的分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 23(3): 288-296. |
| SHI JUNXIAN, CHEN ZHONGYUAN, NING XIUREN, et al, 1992. The distribution patterns of bacteria and ATP in the Changjiang River estuary and its adjacent east China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 23(3): 288-296 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 思源, 2015. 三亚海洋“热带雨林”保护现状[J]. 海洋世界, (10): 20-23. |
| [8] | 王海丽, 杨季芳, 屠霄霞, 等, 2011. 象山港海洋病毒时空分布特征及其环境影响因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 31(5): 834-844. |
| WANG HAILI, YANG JIFANG, TU XIAOXIA, et al, 2011. Spatiotemporal distribution of marine viruses with related to environmental factors in the Xiangshan Bay[J]. China Environmental Science, 31(5): 834-844 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 王建, 王骥, 1984. 浮游植物叶绿素与脱镁叶绿素的测定方法[J]. 植物科学学报, 2(2): 321-328. |
| WANG JIAN, WANG JI.1984The method for the determination of chlorophyll and phaeopigments in phytoplankton[J]. Wuhan Botanical Research, 2(2): 321-328 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 王健, 2013. 渤海浮游病毒的时空分布及其与异养细菌的相关性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| WANG JIAN, 2013. The spatial and temporal distribution of virioplankton and correlation with heterotrophic bacteria in the Bohai Sea[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 赵美霞, 余克服, 张乔民, 等, 2010. 近50年来三亚鹿回头岸礁活珊瑚覆盖率的动态变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 41(3): 440-447. |
| ZHAO MEIXIA, YU KEFU, ZHANG QIAOMIN, et al, 2010. Long-term change in coral cover in Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 41(3): 440-447 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 赵三军, 肖天, 岳海东, 2003. 秋季东、黄海异养细菌(Heterotrophic Bacteria)的分布特点[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 34(3): 295-305. |
| ZHAO SANJUN, XIAO TIAN, YUE HAIDONG, 2003. The distribution of heterotrophic bacteria and some related factors in the east China and Yellow Sea during fall[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 34(3): 295-305 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 赵希涛, 陈欣树, 郑范, 等, 1996. 海南三亚鹿回头半岛珊瑚礁和连岛坝的发育[J]. 第四纪研究, 16(1): 48-58. |
| ZHAO XITAO, CHEN XINSHU, ZHENG FAN, et al, 1996. Development of the coral reefs and tombolo of Luhuitou peninsula, Sanya City, Hainan Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 16(1): 48-58 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 周伟华, 王汉奎, 董俊德, 等, 2006. 三亚湾秋、冬季浮游植物和细菌的生物量分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 26(8): 2633-2639. |
| ZHOU WEIHUA, WANG HANKUI, DONG JUNDE, et al, 2006. Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass and their relationship with the environmental factors in autumn and winter in the Sanya Bay, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(8): 2633-2639 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 周伟华, 王汉奎, 董俊德, 等, 2007. 海南岛三亚湾浮游植物和细菌生物量时空分布特征及环境制约因素研究[J]. 海洋学报, 29(6): 110-119. |
| ZHOU WEIHUA, WANG HANKUI, DONG JUNDE, et al, 2007. Spatial-temporal variations of phytoplankton and bacterioplankton biomass and their environmental limiting factors in the Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 29(6): 110-119 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 张奇亚, 2002. 浮游病毒[J]. 水生生物学报, 26(6): 691-696. |
| ZHANG QIYA, 2002. Virioplankton[J]. Acta Hydrobiology Sinica, 26(6): 691-696 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [17] | BUNSE C, PINHASSI J, 2017. Marine bacterioplankton seasonal succession dynamics[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 25(6): 494-505. |
| [18] | COCHRAN P K, PAUL J H, 1998. Seasonal abundance of lysogenic bacteria in a subtropical estuary[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64(6): 2308-2312. |
| [19] | DAI MINHAN, WANG LIFANG, GUO XIANGHUI, et al, 2008. Nitrification and inorganic nitrogen distribution in a large perturbed river/estuarine system: the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Biogeosciences, 5(5): 1227-1244. |
| [20] | FUHRMAN J A, 1999. Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects[J]. Nature, 399(6736): 541-548. |
| [21] | FUHRMAN J A, HEWSON I, SCHWALBACH M S, et al, 2006. Annually reoccurring bacterial communities are predictable from ocean conditions[J]. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(35): 13104-13109. |
| [22] | GILBERT J A, FIELD D, SWIFT P, et al, 2009. The Seasonal structure of microbial communities in the Western English Channel[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 11(12): 3132-3139. |
| [23] | KENT A D, YANNARELL A C, RUSAK J A, et al, 2007. Synchrony in aquatic microbial community dynamics[J]. The ISME Journal, 1(1): 38-47. |
| [24] | MARIE D, BRUSSAARD C P D, THYRHAUG R, et al, 1999. Enumeration of marine viruses in culture and natural samples by flow cytometry[J]. Applied and environmental Microbiology, 65(1): 45-52. |
| [25] | PATTEN N L, MITCHELL J G, MIDDELBOE M, et al, 2008. Bacterial and viral dynamics during a mass coral spawning period on the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 50(3): 209-220. |
| [26] | POMEROY L R, WILLIAMS P J I, AZAM F, et al, 2007. The microbial loop[J]. Oceanography, 20(2): 28-33. |
| [27] | SOROKIN Y I, SOROKIN P Y, 2009. Analysis of plankton in the southern Great Barrier Reef: abundance and roles in throphodynamics[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 89(2): 235-241. |
| [28] | STEWARD G F, CULLEY A I, WOOD-CHARLSON E M, 2013. Marine viruses[M]//LEVIN S A. Encyclopedia of Biodiversity. 2nd ed. London, United Kingdom: Elsevier Inc.: 127-144. |
| [29] | SUTTLE C A, 2005. Viruses in the sea[J]. Nature, 437(7057): 356-361. |
| [30] | SUTTLE C A, 2007. Marine viruses—major players in the global ecosystem[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 5(10): 801-812. |
| [31] | THINGSTAD T F, 2000. Elements of a theory for the mechanisms controlling abundance, diversity, and biogeochemical role of lytic bacterial viruses in aquatic systems[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 45(6): 1320-1328. |
| [32] | WEINBAUER M G, 2004. Ecology of prokaryotic viruses[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 28(2): 127-181. |
| [33] | WOMMACK K E, COLWELl R R, 2000. Virioplankton: viruses in aquatic ecosystems[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 64(1): 69-114. |
| [34] | ZHANG CHENGLONG, HUANG HUI, YE CHENG, et al, 2013. Diurnal and seasonal variations of carbonate system parameters on Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 96: 65-74. |
| [1] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [2] | LIANG Yuxian, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, ZHANG Yuyang, LIAN Wenke, CHEN Lunju, HUANG Hui. Focusing on supplementing and restoring degraded coral reefs with key groups of reef-building coral - paradigms in the restoration of Xidao Island’s coral reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 166-176. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yuyang, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, LUO Yong, ZHOU Tiancheng, LIAN Jiansheng, HUANG Hui. Study on relocation effect of scleractinian coral in the Fenghuang Island, Sanya* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 177-186. |
| [4] | LI Cai, LIU Cong, ZHANG Xianqing, CHEN Fei, XIAO Zhihui, YANG Zeming, ZHENG Yuanning, ZHOU Wen, XU Zhantang. Development and Application of the Multiangle Volume Scattering and Attenuation Meter (VSAM)* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 1-11. |
| [5] | Xinming LEI, Hui HUANG, Jiansheng LIAN, Yuyang ZHANG, Jianhui YANG. [RETRACTED] Species composition of coralline algae and its spatial characteristics related to environmental factors in Sanya coral reefs, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 79-88. |
| [6] | Youjun WANG, Cuilian XU, Simin HU, Tao LI, Sheng LIU. Diel variation of community structure of planktonic ciliates in coastal ecosystem of Sanya Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 72-80. |
| [7] | CHEN Biao1, 2, CHEN Yong-qiang1, 3, HUANG Hui1, 3, XIE Qiang4, 5, JIANG Yu-feng1, 2, LEI Xin-ming1, JIANG Lei1, 2, ZHANG Shi-ze1, 2, ZHOU Guo-wei1, 3. Analysis of reflectance by Acropora hyacinthus in Luhuitou, Sanya of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(1): 71-76. |
| [8] | ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Jie-xiang, ZHANG Yu-bin, LU Dong-wei, DING Yu-jing, SUN Xing-li. Temporal and spatial distributions of bacterioplankton biomass and the influenced factors in Shenzhen Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 65-71. |
| [9] | ZHAO Mei-xia,YU Ke-fu,ZHANG Qiao-min,SHI Qi. Evaluating the sustainability of coral reefs in Sanya of Hainan Island using marine ecological footprint [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(2): 74-80. |
| [10] | JIANG Fa-jun,HU Zhang-li,HU Chao-qun. Correlation between spatial-temporal distribution of bacterioplankton and environmental factors in the Dapeng Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 96-100. |
|
||