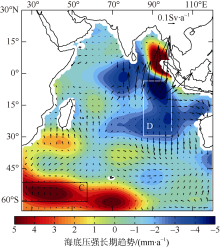
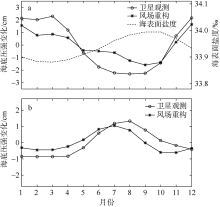
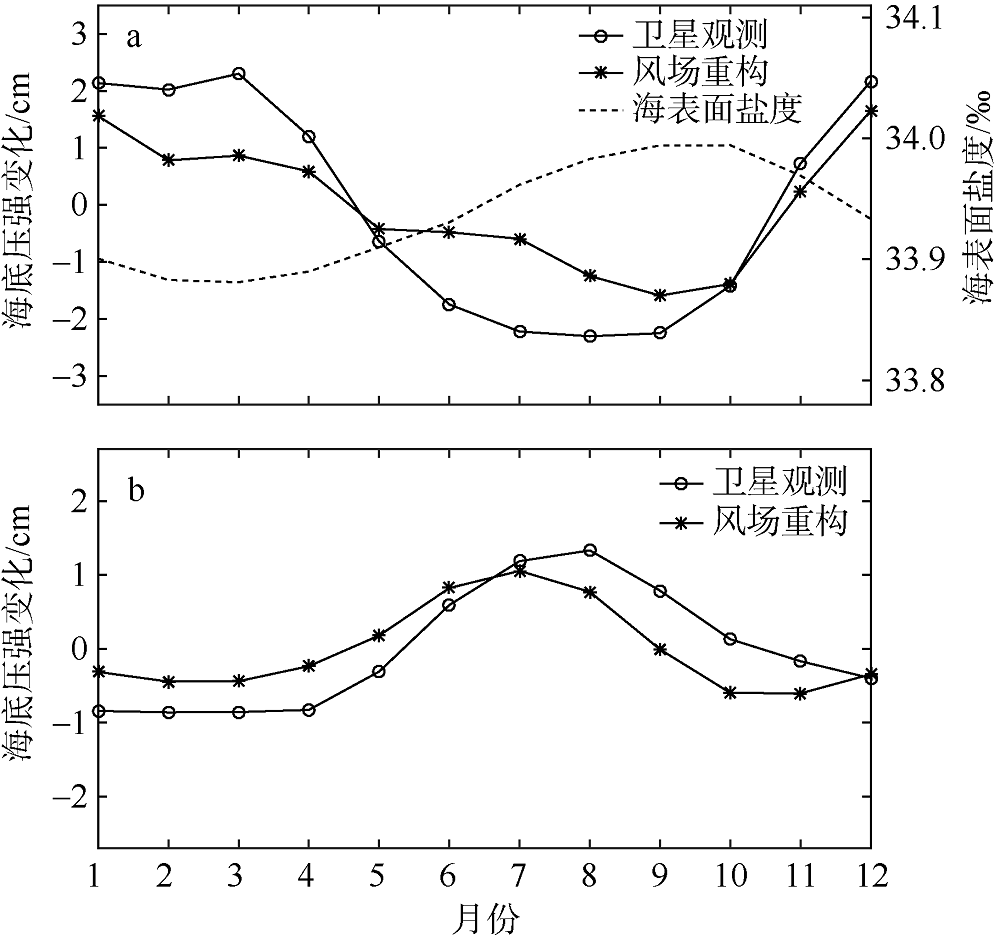
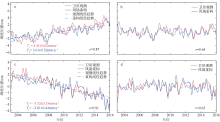
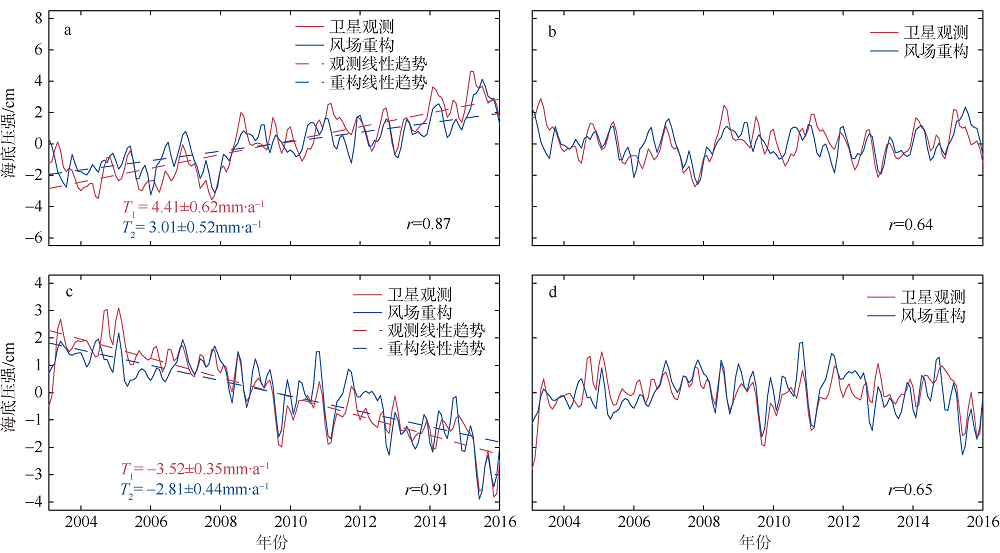
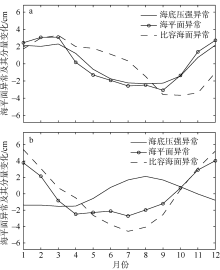
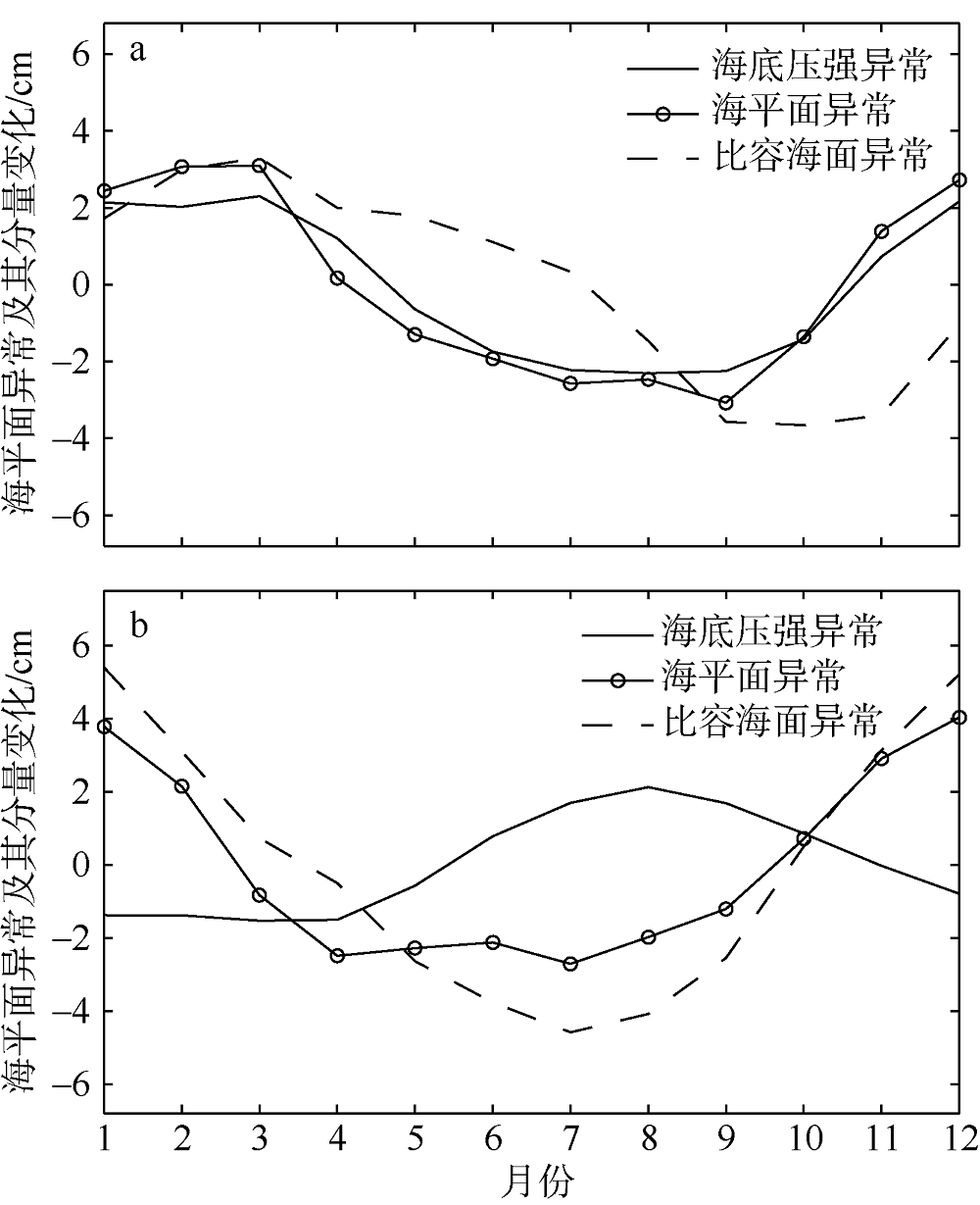
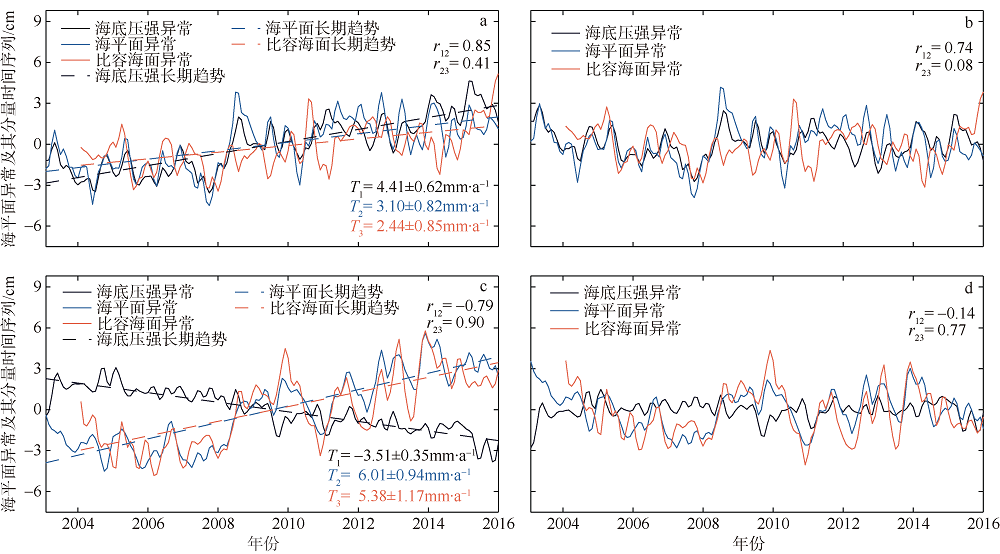
| [1] |
BOENING C, LEE T, ZLOTNICKI V , 2011. A record‐high ocean bottom pressure in the South Pacific observed by GRACE[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(4):L04602.
|
| [2] |
CABANES C, HUCK T, DE VERDIÈRE A C , 2006. Contributions of wind forcing and surface heating to interannual sea level variations in the Atlantic Ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 36(9):1739-1750.
|
| [3] |
CAZENAVE A, LLOVEL W , 2010. Contemporary sea level rise[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2:145-173.
|
| [4] |
CHAMBERS D P, WILLIS J K , 2009. Low‐frequency exchange of mass between ocean basins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 114(C11):C11008.
|
| [5] |
CHAMBERS D P, SCHRÖTER J , 2011. Measuring ocean mass variability from satellite gravimetry[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 52(5):333-343.
|
| [6] |
CHAMBERS D P, CAZENAVE A, CHAMPOLLION N , et al, 2017. Evaluation of the global mean sea level budget between 1993 and 2014[M] //CAZENAVE A, CHAMPOLLION N, PAUL F. Integrative Study of the Mean Sea Level and Its Components. Cham: Springer:315-333.
|
| [7] |
CHEN J L, WILSON C R, TAPLEY B D , 2013. Contribution of ice sheet and mountain glacier melt to recent sea level rise[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(7):549-552.
|
| [8] |
CHENG XUHUA, LI LIJUAN, DU YAN , et al, 2013. Mass-induced sea level change in the northwestern North Pacific and its contribution to total sea level change[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(15):3975-3980.
|
| [9] |
CHENG XUHUA, XIE SHANGPING, DU YAN , et al, 2016. Interannual-to-decadal variability and trends of sea level in the South China Sea[J]. Climate Dynamics, 46(9-10):3113-3126.
|
| [10] |
GILL A E, NILLER P P , 1973. The theory of the seasonal variability in the ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 20(2):141-177.
|
| [11] |
JOHNSON G C, CHAMBERS D P , 2013. Ocean bottom pressure seasonal cycles and decadal trends from GRACE Release-05: ocean circulation implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(9):4228-4240.
|
| [12] |
KANZOW T, FLECHTNER F, CHAVE A , et al, 2005. Seasonal variation of ocean bottom pressure derived from Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE): local validation and global patterns[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 110(C9):C09001.
|
| [13] |
LI JIANKE, CLARKE A J , 2007. Interannual sea level variations in the South Pacific FROM 5° to 28° S[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 37(12):2882-2894.
|
| [14] |
MERRIFIELD M A, THOMPSON P R, LANDER M , 2012. Multidecadal sea level anomalies and trends in the western tropical Pacific[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(13):L13602.
|
| [15] |
PIECUCH C G , 2013. Dynamics of satellite-derived interannual ocean bottom pressure variability in the western tropical North Pacific[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(10):5117-5128.
|
| [16] |
PIECUCH C G, PONTE R M , 2014. Annual cycle in southern tropical Indian Ocean bottom pressure[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 44(6):1605-1613.
|
| [17] |
QUINN K J, PONTE R M , 2012. High frequency barotropic ocean variability observed by GRACE and satellite altimetry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(7):L07603.
|
| [18] |
THOMSON R E, TABATA S , 1989. Steric sea level trends in the northeast Pacific Ocean: possible evidence of global sea level rise[J]. Journal of Climate, 2(6):542-553.
|
| [19] |
VIVIER F, KELLY K A, HARISMENDY M , 2005. Causes of large-scale sea level variations in the Southern Ocean: analyses of sea level AND A barotropic model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 110(C9):C09014.
|