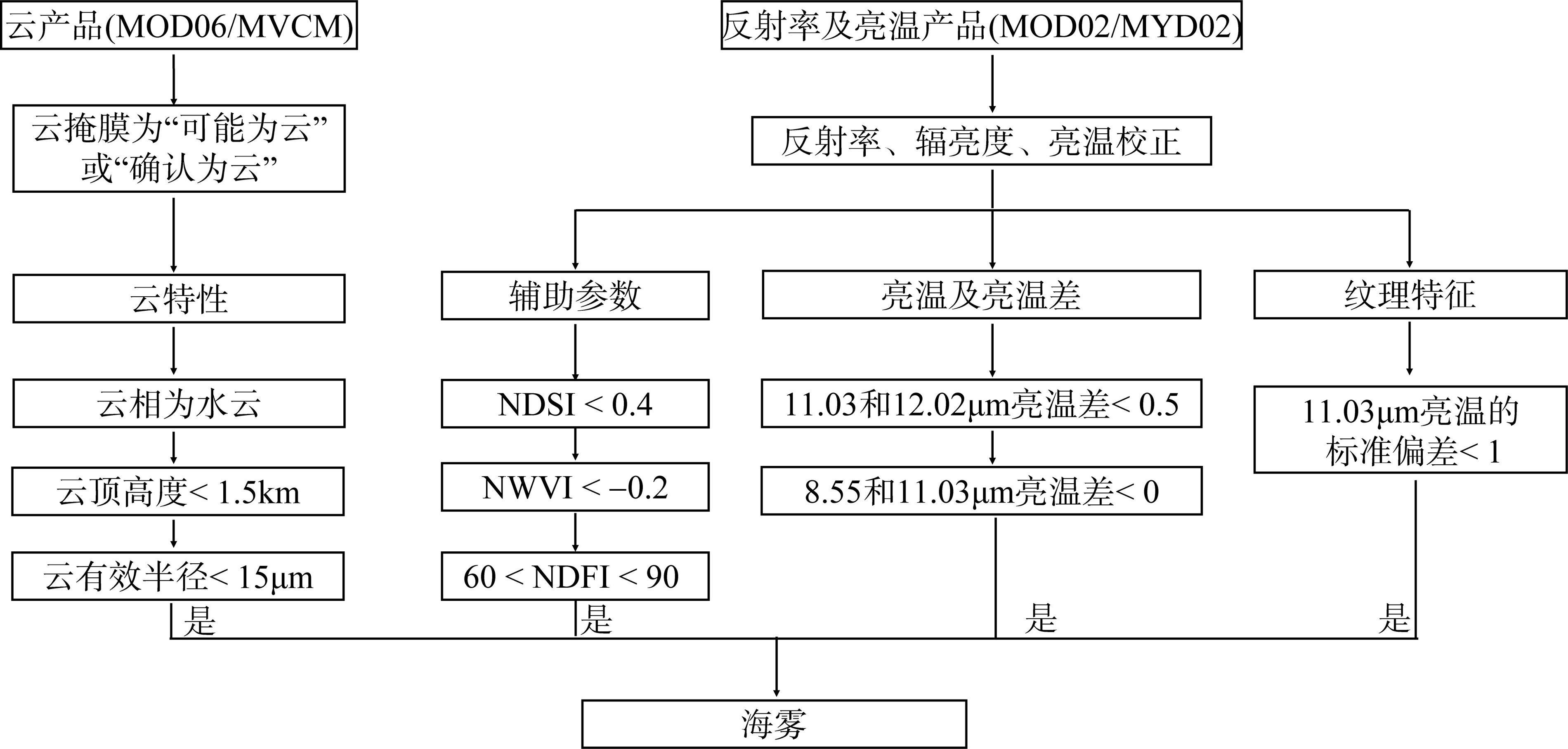
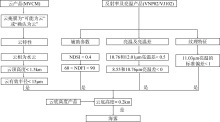
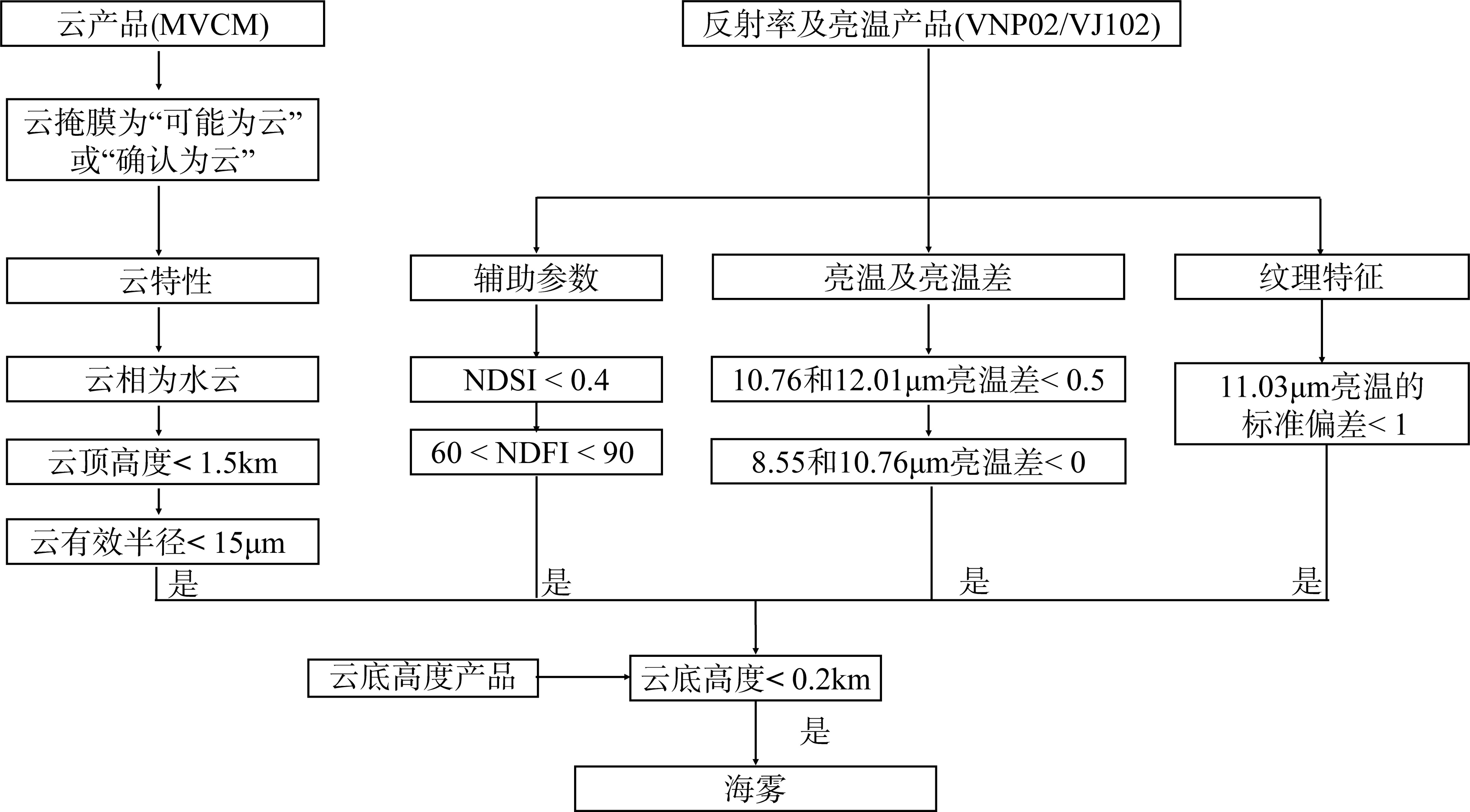
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 15-28.doi: 10.11978/2023015CSTR: 32234.14.2023015
• Marine Meteorology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on the multi-source satellite daytime sea fog detection technology based on cloud characteristics*
WANG Yu1( ), HU Chenyue1, QIU Zhongfeng1(
), HU Chenyue1, QIU Zhongfeng1( ), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao2, LIAO Kuo3
), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao2, LIAO Kuo3
- 1. Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2. Suqian Environmental Monitoring Center, Suqian 223800, China
3. Fujian Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Fuzhou 350008, China
-
Received:2023-02-08Revised:2023-03-11Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-03-23 -
Contact:WANG Yu, QIU Zhongfeng E-mail:yuwang@nuist.edul.cn;zhongfeng.qiu@nuist.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976165);Advanced Program for FY Satellite Applications (2022)(FY-APP-2022.0610)
CLC Number:
- P714.2
Cite this article
WANG Yu, HU Chenyue, QIU Zhongfeng, ZHAO Dongzhi, WU Daomao, LIAO Kuo. Research on the multi-source satellite daytime sea fog detection technology based on cloud characteristics*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 15-28.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 2
Information of sea fog events used in the spectral radiance and cloud properties analysis"
| 序号 | 日期(年-月-日) | 区域 | 观测时间(UTC) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODIS(Terra) | MODIS(Aqua) | VIIRS(S-NPP) | VIIRS(NOAA-20) | |||
| 1 | 2015-01-10 | 黄海 | 02:20 | 05:35 | 04:48, 04:54 | — |
| 2 | 2015-03-30 | 黄海 | 03:15 | — | 05:06, 03:30 | — |
| 3 | 2015-04-29 | 黄海、渤海 | — | 05:10 | 04:06, 04:29 | — |
| 4 | 2015-04-30 | 黄海 | 02:35 | — | 05:24 | — |
| 2015-05-01 | 黄海、东海 | 01:40, 03:15 | 04:55 | 05:06 | — | |
| 5 | 2015-06-09 | 黄海 | 03:20 | 05:00 | 04:36 | — |
| 6 | 2016-03-03 | 黄海 | 02:10 | 05:25 | 04:06, 05:48 | — |
| 2016-03-04 | 黄海、渤海 | 02:50 | 04:30 | 03:48, 05:30 | — | |
| 7 | 2018-03-24 | 黄海 | 03:05 | 04:40, 04:45 | 04:24 | 03:36, 05:12, 05:18 |
| 2018-03-25 | 黄海 | 02:10 | 05:25 | 04:06, 05:48 | 04:54, 05:00 | |
| 2018-03-26 | 黄海 | 02:50 | 04:30 | 03:48, 05:30 | — | |
| 8 | 2018-05-10 | 黄海 | 02:20 | 04:00, 05:35 | 04:42 | 03:54, 05:36 |
| 9 | 2020-02-12 | 渤海 | 02:50 | 04:30 | 03:48, 05:30 | — |
| 10 | 2020-05-16 | 黄海 | — | 04:40 | 04:24 | 05:18 |
| 11 | 2020-05-23 | 黄海 | 03:10 | 04:45 | 03:54 | 04:42 |
| 总计影像数 | 14景 | 15景 | 23景 | 9景 | ||
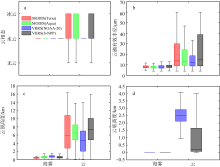
Fig. 1
Box plot of cloud phase(a); cloud effective radius(b); cloud top height(c); cloud base height(d) of sea fog and cloud in Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. The five horizontal lines in box plot from top to bottom represent the maximum value, upper quartile, median, lower quartile, and minimum value, respectively, while the vertical lines indicate the range of data variation"
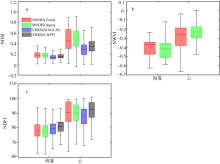
Fig. 2
Box plot of normalized difference snow index(a); normalized water vapor index(b); normalized difference fog index(c) of sea fog and cloud in Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. The five horizontal lines in box plot from top to bottom represent the maximum value, upper quartile, median, lower quartile, and minimum value, respectively, while the vertical lines indicate the range of data variation"
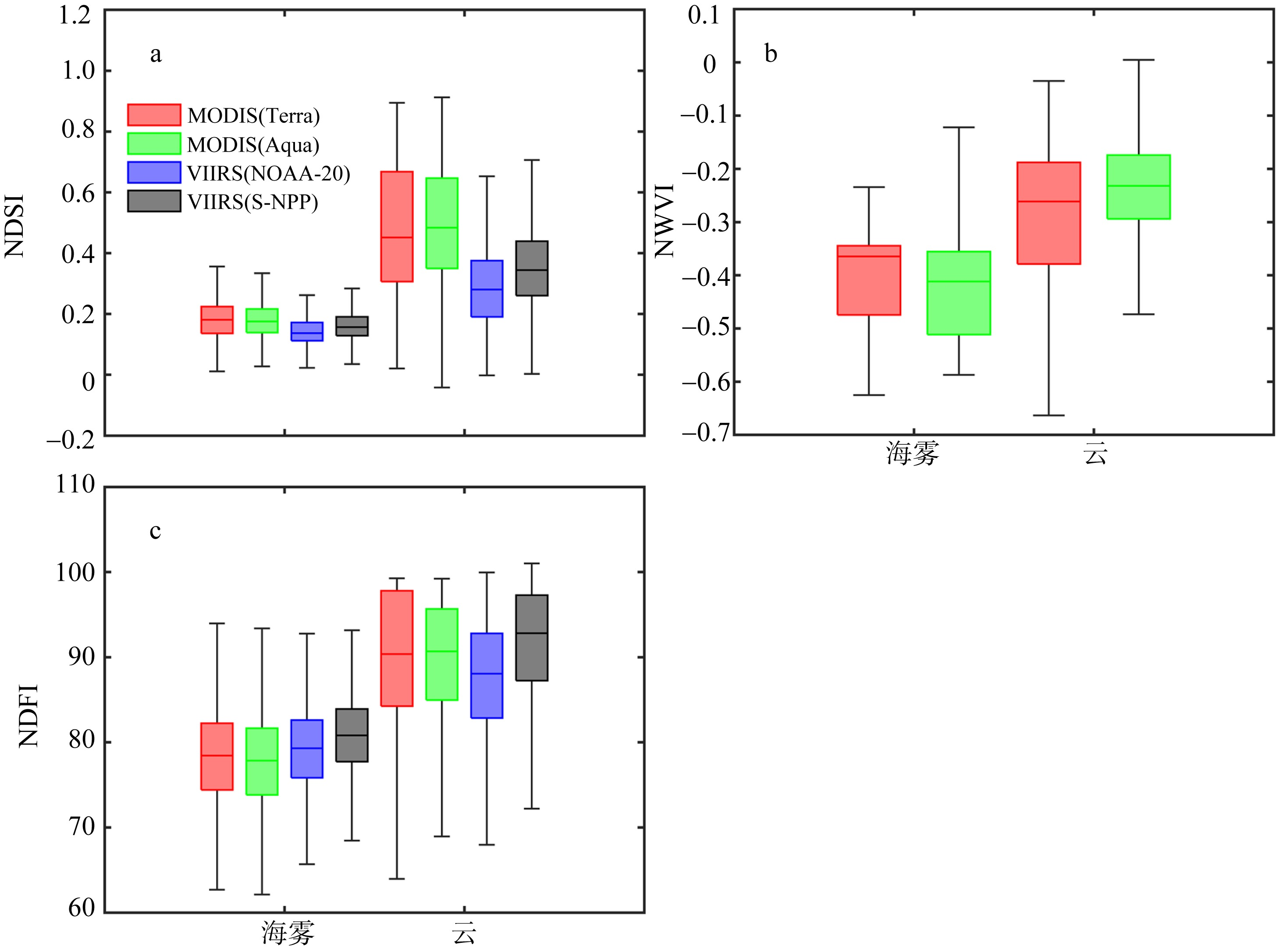
Fig. 3
Box plot of brightness temperature difference between the bands of 11.03 and 12.02 μm (a); brightness temperature difference between the bands of 8.55 and 11.03 μm (b) of sea fog and cloud in Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. The five horizontal lines in box plot from top to bottom represent the maximum value, upper quartile, median, lower quartile, and minimum value, respectively, while the vertical lines indicate the range of data variation"
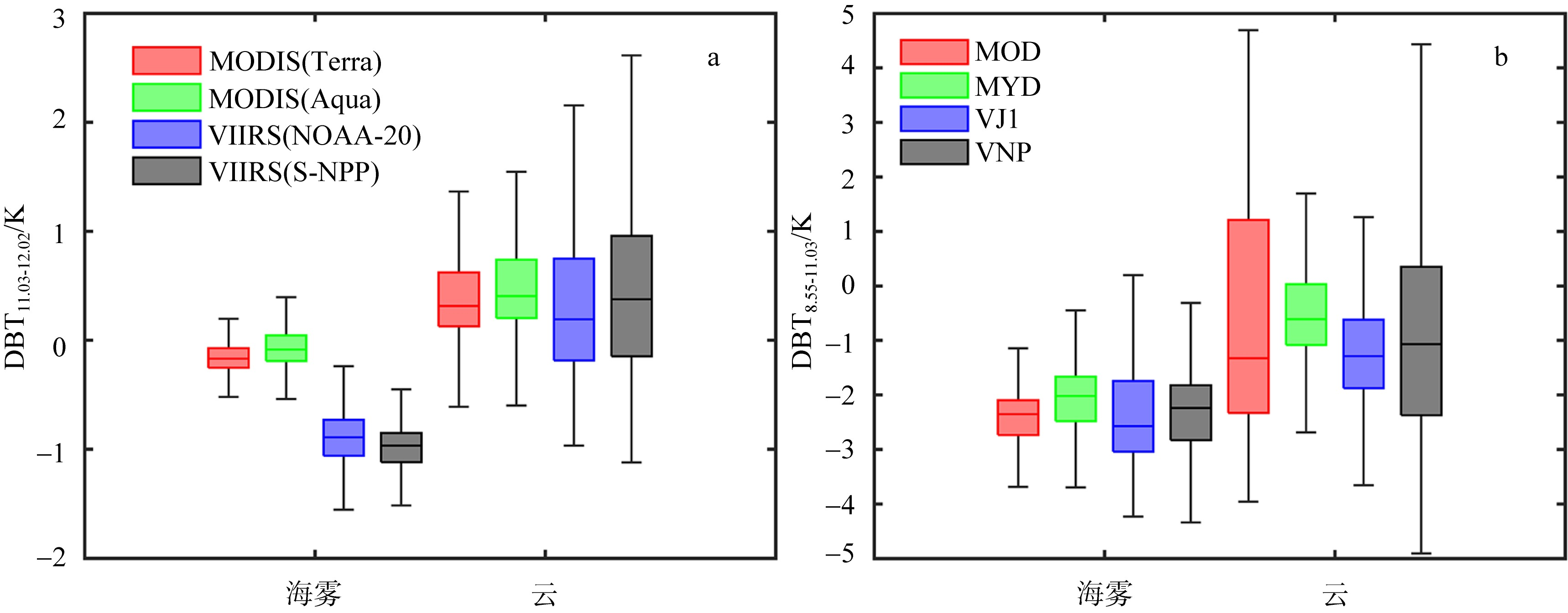
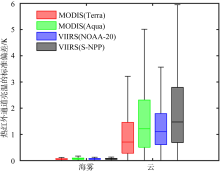
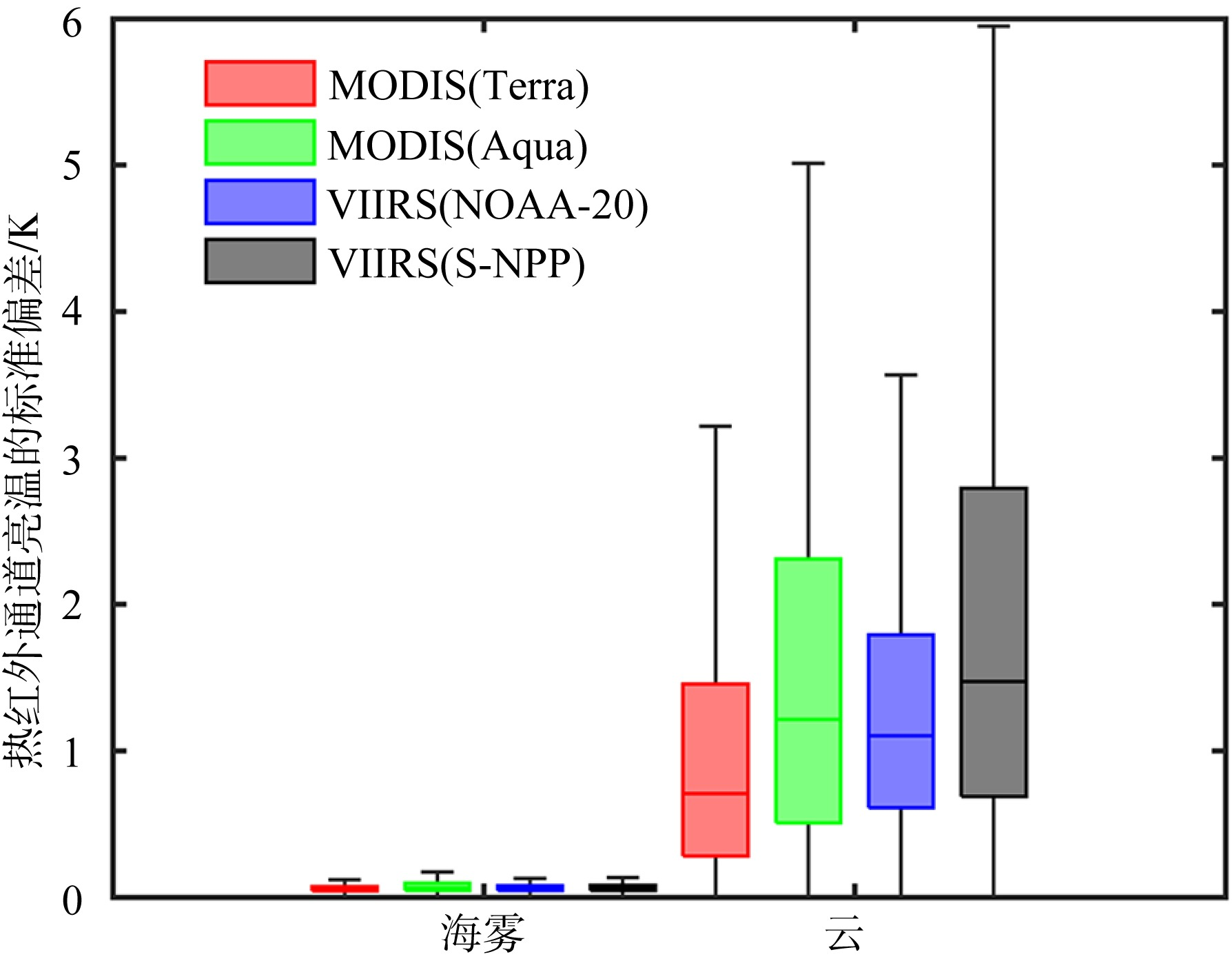
Fig. 4
Box plot of the standard deviation of brightness temperature in thermal infrared channel of sea fog and cloud in Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. The five horizontal lines in box plot from top to bottom represent the maximum value, upper quartile, median, lower quartile, and minimum value, respectively, while the vertical lines indicate the range of data variation"
Tab. 4
Cross-correction parameters between MODIS(Aqua) and VIIRS(S-NPP) on May 1st, 2015"
| 校正数据 | MODIS波段 | MODIS中心波长/μm | VIIRS中心波长/μm | 拟合斜率 | 拟合截距 | 决定系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 反射率 | 1 | 0.645 | 0.672 | 1.03 | 0.01 | 0.87 |
| 3 | 0.469 | 0.488 | 1.01 | 0.01 | 0.87 | |
| 7 | 2.13 | 2.25 | 1.12 | 0.00 | 0.84 | |
| 辐亮度 | 20 | 3.75 | 3.70 | 0.99 | -0.03 | 0.72 |
| 亮温 | 29 | 8.55 | 8.55 | 0.85 | 39.90 | 0.72 |
| 31 | 11.03 | 10.763 | 0.86 | 39.70 | 0.72 | |
| 32 | 12.02 | 12.013 | 0.85 | 43.17 | 0.70 |
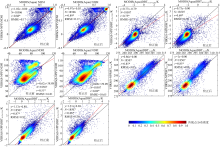
Fig. 5
Normalized difference snow index, normalized water vapor index, brightness temperature difference and brightness temperature in thermal infrared channel before and after calibration, where the solid black line is the 1:1 line, the solid red line is the regression line, and the asterisk (*) indicates passing the 95% significance test"

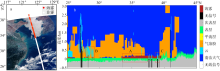
Fig. 9
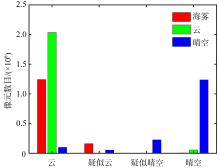
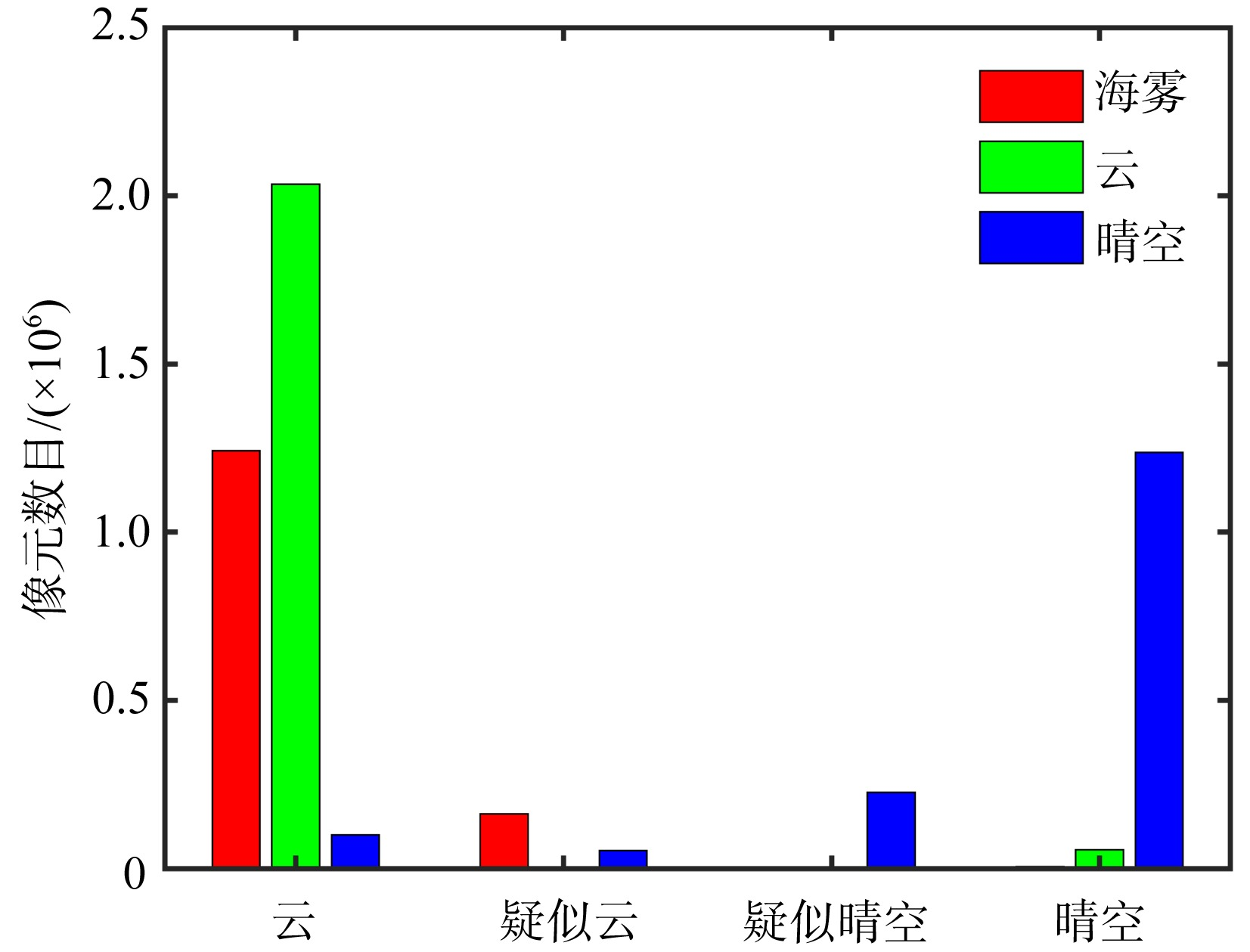
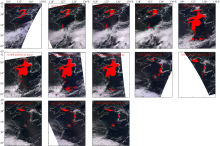
VIIRS (S-NPP) color-composite image with sea fog points extracted by CALIOP at 04:45 on March 25, 2021 (a) and sea fog detection result based on data of CALIOP on March 25, 2021(b). In figure (b), A is sea fog directly measured by CALIOP, B is sea fog under clouds, C is the misjudged points due to the inability to transmit through the thicker sea fog of CALIOP"

Tab. 5
Validation of daytime sea fog detection model based on CALIOP data"
| 卫星 | 评价指标 | 时间窗口/h | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | ||
| MODIS(Terra) | 雾点数目 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 1855 | 1977 |
| 召回率 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.97 | 0.94 | |
| 准确度 | 0 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.90 | |
| MODIS(Aqua) | 雾点数目 | 98 | 1958 | 1994 | 1994 | 1994 | 1994 |
| 召回率 | 0.66 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | |
| 准确度 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | |
| VIIRS(S-NPP) | 雾点数目 | 2056 | 2081 | 2185 | 2185 | 2185 | 2185 |
| 召回率 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | |
| 准确度 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | |
| VIIRS(NOAA-20) | 雾点数目 | 210 | 211 | 327 | 327 | 327 | 327 |
| 召回率 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.57 | |
| 准确度 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | |
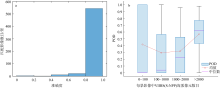
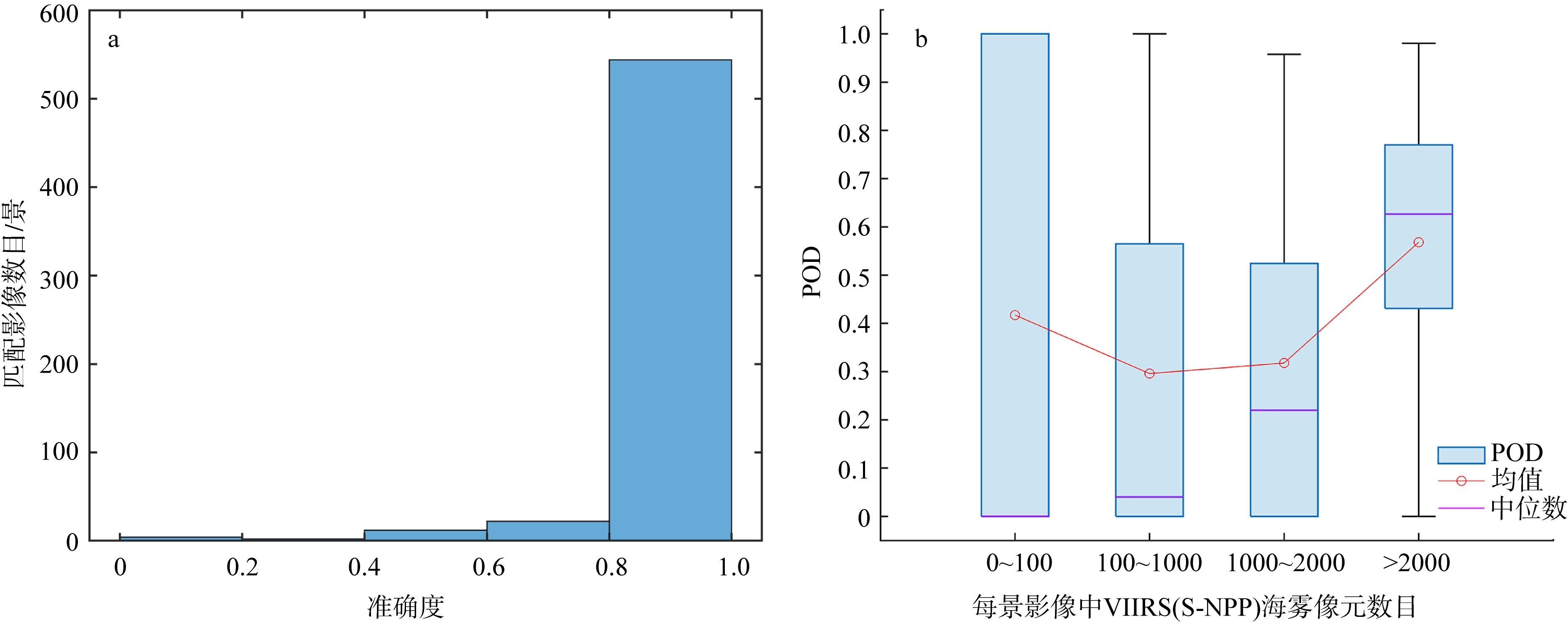
Fig. 10
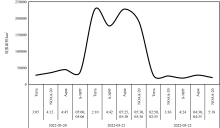
Distribution of sea fog detection accuracy of VIIRS (NOAA-20) in matched images between VIIRS (NOAA-20) and VIIRS (S-NPP) (a) and the box plot of the distribution of the number of sea fog pixels with probability of detection (POD) of VIIRS (S-NPP) in each matched image (b). The five horizontal lines in box plot from top to bottom represent the maximum value, upper quartile, median, lower quartile, and minimum value, respectively, while the vertical lines indicate the range of data variation"
| [1] | 傅刚, 王菁茜, 张美根, 等, 2004. 一次黄海海雾事件的观测与数值模拟研究——以2004年4月11日为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 34(5): 720-726, 926. |
| FU GANG, WANG JINGQIAN, ZHANG MEIGEN, et al, 2004. An observational and numerical study of a sea fog event over the Yellow Sea on 11 April, 2004[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 34(5): 720-726, 926 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 耿丹, 刘婷婷, 李超, 2022. 结合FY-4A卫星及随机森林的日间沿海海雾识别模型的研究[J]. 海洋预报, 39(3): 83-93. |
| GENG DAN, LIU TINGTING, LI CHAO, 2022. Research on a daytime sea fog identification model based on FY-4A satellite data and random forest algorithm[J]. Marine Forecasts, 39(3): 83-93 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 郝姝馨, 郝增周, 黄海清, 等, 2021. 基于Himawari-8数据的夜间海雾识别[J]. 海洋学报, 43(11): 166-180. |
| HAO SHUXIN, HAO ZENGZHOU, HUANG HAIQING, et al, 2021. Nighttime sea fog recognition based on Himawari-8 data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 43(11): 166-180 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 胡晨悦, 丘仲锋, 廖廓, 等, 2022. 福建海雾的CALIOP遥感监测及基于Himawari-8的云下雾光谱特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报: 1-10. |
| HU CHENYUE, QIU ZHONGFENG, LIAOKUO, et al, 2022. CALIOP remote sensing monitoring of Fujian sea fog and spectral characteristics analysis of cloud fog based on Himawari-8[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography: 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 刘照民, 康琮, 2011. 琼州海峡船舶雾航安全管理[J]. 中国海事, (2): 28-30. |
| LIU ZHAOMIN, KANG ZONG, 2011. Safety control of ships navigating in the Qiongzhou Strait in foggy weather[J]. China Maritime Safety, (2): 28-30 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 史得道, 黄彬, 吴振玲, 2018. 2016年春季一次黄渤海明显海雾过程的大气海洋特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 35(5): 85-92. |
| SHI DEDAO, HUANG BIN, WU ZHENLING, 2018. Analysis of atmosphere and sea characteristics under an obvious sea fog process over the Bohai and Yellow Sea in spring 2016[J]. Marine Forecasts, 35(5): 85-92 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 苏婧, 2019. 基于主被动遥感的海雾探测方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东):19-21. |
| SU JING, 2019. Research on sea fog detection method based on active and passive remote sensing[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China): 19-21 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 张苏平, 鲍献文, 2008. 近十年中国海雾研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 359-366. |
| ZHANG SUPING, BAO XIANWEN, 2008. The main advances in sea fog research in China[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 38(3): 359-366 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | AMEUR Z, AMEUR S, ADANE A, et al, 2004. Cloud classification using the textural features of Meteosat images[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(21): 4491-4503. DOI: 10.1080/01431160410001735120. |
| [10] | BADARINATH K V S, KHAROL S K, SHARMA A R, et al, 2009. Fog over Indo-Gangetic Plains—A study using multisatellite data and ground observations[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2(3): 185-195. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2009.2019830. |
| [11] | BENDIX J, CERMAK J, THIES B, 2004. New perspectives in remote sensing of fog and low stratus-TERRA/AQUA-MODIS and MSG[C/OL]. Cape Town, South Africa:3rd Int. Conf. on Fog, Fog Collection and Dew, 11-15 Oct. 2004 [2023-02-08]. https://www.researchgate.net/deref/https%3A%2F%2Fwww.researchgate.net%2Fpublication%2F228860444_New_perspectives_in_remote_sensing_of_fog_and_low_stratus-TERRAAQUA-MODIS_and_MSG?_tp=eyJjb250ZXh0Ijp7ImZpcnN0UGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIiwicGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIiwicHJldmlvdXNQYWdlIjoicHVibGljYXRpb24ifX0 |
| [12] | CERMAK J, BENDIX J, 2011. Detecting ground fog from space - a microphysics-based approach[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(12): 3345-3371. DOI: 10.1080/01431161003747505. |
| [13] | DOZIER J, PAINTER T H, 2004. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing of alpine snow properties[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 32(1): 465-494. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120404. |
| [14] | HAN J H, SUH M S, YU H Y, et al, 2020. Development of fog detection algorithm using GK2A/AMI and ground data[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(19): 3181. DOI: 10.3390/rs12193181. |
| [15] |
JEON J, KIM S, YANG CHANSU, 2016. Fundamental research on spring season daytime sea fog detection using MODIS in the Yellow Sea[J]. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(4): 339-351.
doi: 10.7780/kjrs.2016.32.4.1 |
| [16] | LIU LIANGMING, WEN XIONGFEI, GONZALEZ A, et al, 2011. An object-oriented daytime land-fog-detection approach based on the mean-shift and full lambda-schedule algorithms using EOS/MODIS data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(17): 4769-4785. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2010.489067. |
| [17] | QU J J, GAO WEI, KAFATOS M, et al, 2006. Earth science satellite remote sensing[M]. Beijing, China: Tsinghua University Press. |
| [18] | THIES B, NAUSS T, BENDIX J, 2008. Precipitation process and rainfall intensity differentiation using Meteosat Second Generation Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 113(D23). DOI: 10.1029/2008JD010464. |
| [19] | WEN XIONGFEI, HU DUNMEI, DONG XINYI, et al, 2014. An object-oriented daytime land fog detection approach based on NDFI and fractal dimension using EOS/MODIS data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(13): 4865-4880. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2014.930564. |
| [20] | WU DONG, LU BO, ZHANG TIANCHE, et al, 2015. A method of detecting sea fogs using CALIOP data and its application to improve MODIS-based sea fog detection[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 153: 88-94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2014.09.021. |
| [21] | WU XIAOJING, LI SANMEI, 2014. Automatic sea fog detection over Chinese adjacent oceans using Terra/MODIS data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(21): 7430-7457. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2014.968685. |
| [22] |
YUAN YIBO, QIU ZHONGFENG, SUN DEDONG, et al, 2016. Daytime sea fog retrieval based on GOCI data: a case study over the Yellow Sea[J]. Optics Express, 24(2): 787-801. DOI: 10.1364/OE.24.000787.
pmid: 26832463 |
| [23] | ZHANG SUPING, YI LI, 2013. A comprehensive dynamic threshold algorithm for daytime sea fog retrieval over the Chinese adjacent seas[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 170(11): 1931-1944. DOI: 10.1007/s00024-013-0641-6. |
| [1] | LIAO Kuo, LI Kailin, DANG Haofei, LIN Bin, ZHAO Dongzhi, LI Hui. Process and characteristics of occurrence and dissipation of sea fog in the west coast of the Taiwan Strait based on coastal automatic weather station* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 79-93. |
| [2] | HU Chenyue, QIU Zhongfeng, LIAO Kuo, ZHAO Dongzhi, WU Daomao. CALIOP remote sensing monitoring of the Fujian sea fog and spectral characteristics analysis of subcloud fog based on Himawari-8 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 104-112. |
| [3] | YANG Qi, OU Jian-jun, LI Yong-ping. An objective forecast method for sea fog over the Yangshan Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 59-64. |
|
||