Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 77-94.doi: 10.11978/2024224
• Marine Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of tourism disturbance on macrobenthic communities in intertidal zones of Quanfu Island and Yinyu Island, Xisha
WANG Yanyan1( ), SONG Danying1(
), SONG Danying1( ), CHEN Zhi2
), CHEN Zhi2
- 1. MTA Education Center, Tourism College, Hainan Tropical Ocean University, Sanya 572022, China
2. Key Laboratory of Utilization and Conservation for Tropical Marine Bioresources, Ministry of Education, Hainan Tropical Ocean University, Sanya 572022, China
-
Received:2024-11-28Revised:2024-12-10Online:2025-07-10Published:2025-07-31 -
Contact:SONG Danying -
Supported by:Hainan Provincial Philosophy and Social Sciences Planning Project Fund(HNSK(ZC)21-106); Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China(721RC596); National Natural Science Foundation of China(32002389)
CLC Number:
- P735
Cite this article
WANG Yanyan, SONG Danying, CHEN Zhi. Effects of tourism disturbance on macrobenthic communities in intertidal zones of Quanfu Island and Yinyu Island, Xisha[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(4): 77-94.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
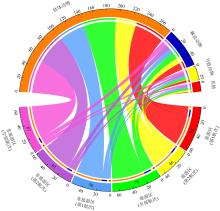
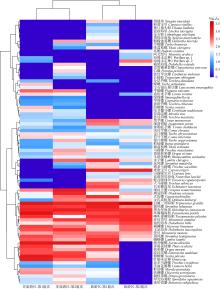
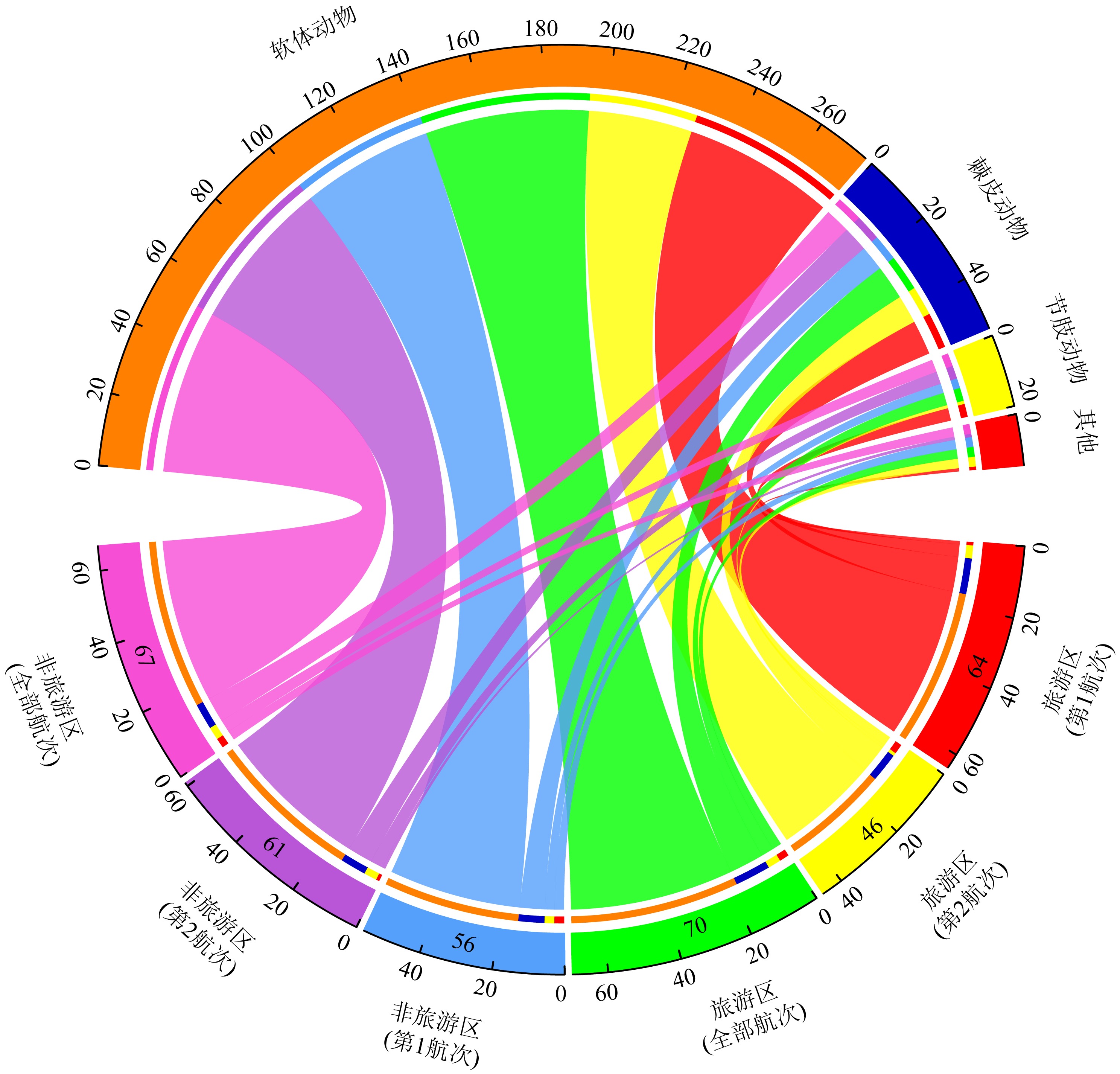
Fig. 1
Regional differences in species composition. The values in the lower semicircle represent the number of species across different regions, while the upper semicircle values show the cumulative sum of "species occurrences" (including repeated counts of the same species) across taxonomic phyla for each region"
Supplementary Tab. 1
Species list recorded in this study"
| 门类 | 物种名录 | 第1航次 | 第2航次 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种中文名 | 物种拉丁学名 | T1 | T2 | T3 | N1 | N2 | N3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | N1 | N2 | N3 | |
| 软体动物门 | 斑凤螺 | Strombus lentiginosus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 篱凤螺 | Strombus luhuanus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 花凤螺 | Strombus mutabilis | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 蜘蛛螺 | Lambis lambis | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 水字螺 | Lambis chiragra | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 耳鲍 | Haliotis asinina | √ | ||||||||||||
| 虎斑宝贝 | Cypraea tigris | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 山猫眼宝贝 | Cypraea lynx | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 蛇首眼球贝 | Erosaria caputserpentis | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 货贝 | Monetaria moneta | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 环纹货贝 | Monetaria annulus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 卵黄宝贝 | Cypraea vitellus | √ | ||||||||||||
| 阿文绶贝 | Mauritia arabica | √ | ||||||||||||
| 甲胄螺 | Casmaria erinaceus | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 软体动物门 | 结节蟹守螺 | Cerithium nodulosum | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 直管楯桑葚螺 | Clypeomorus petrosus | √ | ||||||||||||
| 大马蹄螺 | Trochus niloticus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 马蹄螺 | Trochus maculantus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 褶条马蹄螺 | Trochus sacellum | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 近亲马蹄螺 | Trochus creniferus | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 蝾螺 | Turbo petholatus | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 金口蝾螺 | Turbo chrysostomus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 银口蝾螺 | Turbo argyrostomus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 节蝾螺 | Turbo brunerus | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 肋蜒螺 | Nerita costata | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 褶蜒螺 | Nerita plicata | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 渔舟蜒螺 | Nerita albicilla | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 波纹滨螺 | Littorarina undulata | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 平轴螺 | Planaxis sulcatus | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 波纹甲虫螺 | Cantharus undosun | √ | ||||||||||||
| 刺荔枝螺 | Thais echinata | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 多角荔枝螺 | Thais aculeate | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 疣荔枝螺 | Thais clavigera | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 绿珠螺 | Smaragdinella sp. | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 核果螺 | Drupa morum | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 刺核果螺 | Drupa grossularia | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 黄斑核果螺 | Drupa ricinus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 粒结螺 | Morula granulata | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 草莓结螺 | Morula uva | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 粒蛙螺 | Bursa granularis | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 褐棘螺 | Chicoreus brunneus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 焦棘螺 | Chicoreus torrefactus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 犬齿螺 | Vasum turbinellus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 信号芋螺 | Conus litteratus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 加勒底芋螺 | Conus chaldaeus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 希伯来芋螺 | Conus striatus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 浅纹芋螺 | Conus ebraeus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 黑芋螺 | Conus marmoreus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 宝石银山黧豆螺 | Leucozonia smaragdula | √ | ||||||||||||
| 罫纹笋螺 | Terebra maculata | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 分层笋螺 | Terebra dimidiata | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 黄斑笋螺 | Terebra chlorata | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 金石蛏 | Lithophaga zitteliana | √ | ||||||||||||
| 细肋钳蛤 | Isognomon perna | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 厚壳海菊蛤 | Spondylus squamosus | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 牡蛎未定种 | Ostrea sp. | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 紫口猿头蛤 | Chama limbula | √ | ||||||||||||
| 砗蠔 | Hippopus hippopus | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 鳞砗磲 | Tridacna squamosa | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 番红砗磲 | Tridacna crocea | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 长砗磲 | Tridacna maxima | √ | ||||||||||||
| 长棱蛤 | Trapezium oblongum | √ | ||||||||||||
| 石磺 | Peronia peronii | √ | ||||||||||||
| 蓝斑背肛海兔 | Notarchus leachii | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 黑指纹海兔 | Aplysia dactylomela | √ | ||||||||||||
| 截尾海兔 | Dolabella scapula | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 棘皮动物门 | 黑赤星海参 | Holothuria cinerascens | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 黄疣海参 | Holothuria hilla | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 玉足海参 | Holothuria leucospilota | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| 斑锚参 | Synapta maculata | √ | ||||||||||||
| 棘皮动物门 | 环棘偏海胆 | Parasalenia poehli | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 喇叭毒棘海胆 | Toxopneustes pileolus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 白棘三列海胆 | Tripneustes gratilla | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 刺冠海胆 | Diadema setosum | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 蓝指海星 | Linckia laevigata | √ | ||||||||||||
| 吕宋棘海星 | Echinaster luzonicus | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 金氏真蛇尾 | Ophiura kinbergi | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 节肢动物门 | 细纹方蟹 | Grapsus tenuicrustatus | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| 粗糙蚀菱蟹 | Daldorfia horrida | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 美丽花瓣蟹 | Liomera bella | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 球形铠蟹 | Banareia subglobosa | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 其他 | 叉斑锉鳞鲀 | Rhinecanthus aculeatus | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 海绵未定种1 | Porifera | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 海绵未定种2 | Porifera | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
Tab. 4
Species abundance and biomass between the two voyages"
| 航次 | 调查区域 | 站位 | 丰度 | 生物量 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原始数值/(ind·m-2) | 标准值 | 原始数值/(g·m-2) | 标准值 | |||
| 第1航次 | 旅游区 | T1 | 186.462 | — | 6717.752 | — |
| T2 | 137.517 | — | 5138.364 | — | ||
| T3 | 166.321 | — | 3272.911 | — | ||
| 非旅游区 | N1 | 136.585 | — | 3513.495 | — | |
| N2 | 317.192 | — | 6040.827 | — | ||
| N3 | 144.434 | — | 2462.782 | — | ||
| 第2航次 | 旅游区 | T1 | 119.328 | 0.640 | 4130.929 | 0.615 |
| T2 | 108.905 | 0.792 | 3231.653 | 0.629 | ||
| T3 | 75.402 | 0.453 | 2217.342 | 0.677 | ||
| 非旅游区 | N1 | 84.718 | 0.620 | 2565.483 | 0.730 | |
| N2 | 214.506 | 0.676 | 5569.814 | 0.922 | ||
| N3 | 168.693 | 1.168 | 2819.682 | 1.145 | ||
Tab. 7
Dominant species and their corresponding relative importance index"
| 物种 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1航次 | 第2航次 | |||
| 旅游区 | 非旅游区 | 旅游区 | 非旅游区 | |
| 篱凤螺(Strombus luhuanus) | 1211.792* | 713.521 | 268.372 | 493.397 |
| 虎斑宝贝(C. tigris) | 1026.912* | 0 | 1104.636* | 0 |
| 褶蜒螺(Nerita plicata) | 102.047 | 1583.423* | 0 | 565.705 |
| 渔舟蜒螺(N. albicilla) | 542.821 | 1707.195* | 0 | 1658.676* |
| 牡蛎未定种(Ostera sp.) | 212.248 | 1290.244* | 0 | 339.510 |
| 黑赤星海参(Holothuria cinerascens) | 862.821 | 979.464 | 697.080 | 1278.623* |
| 环棘偏海胆(Parasalenia poehli) | 457.812 | 2067.219* | 626.899 | 528.991 |
| 白棘三列海胆(T. gratilla) | 1467.049* | 1913.999* | 4875.299* | 1129.563* |
| 细纹方蟹(Grapsus tenuicrustatus) | 222.088 | 254.567 | 28.554 | 1264.442* |
Tab. 8
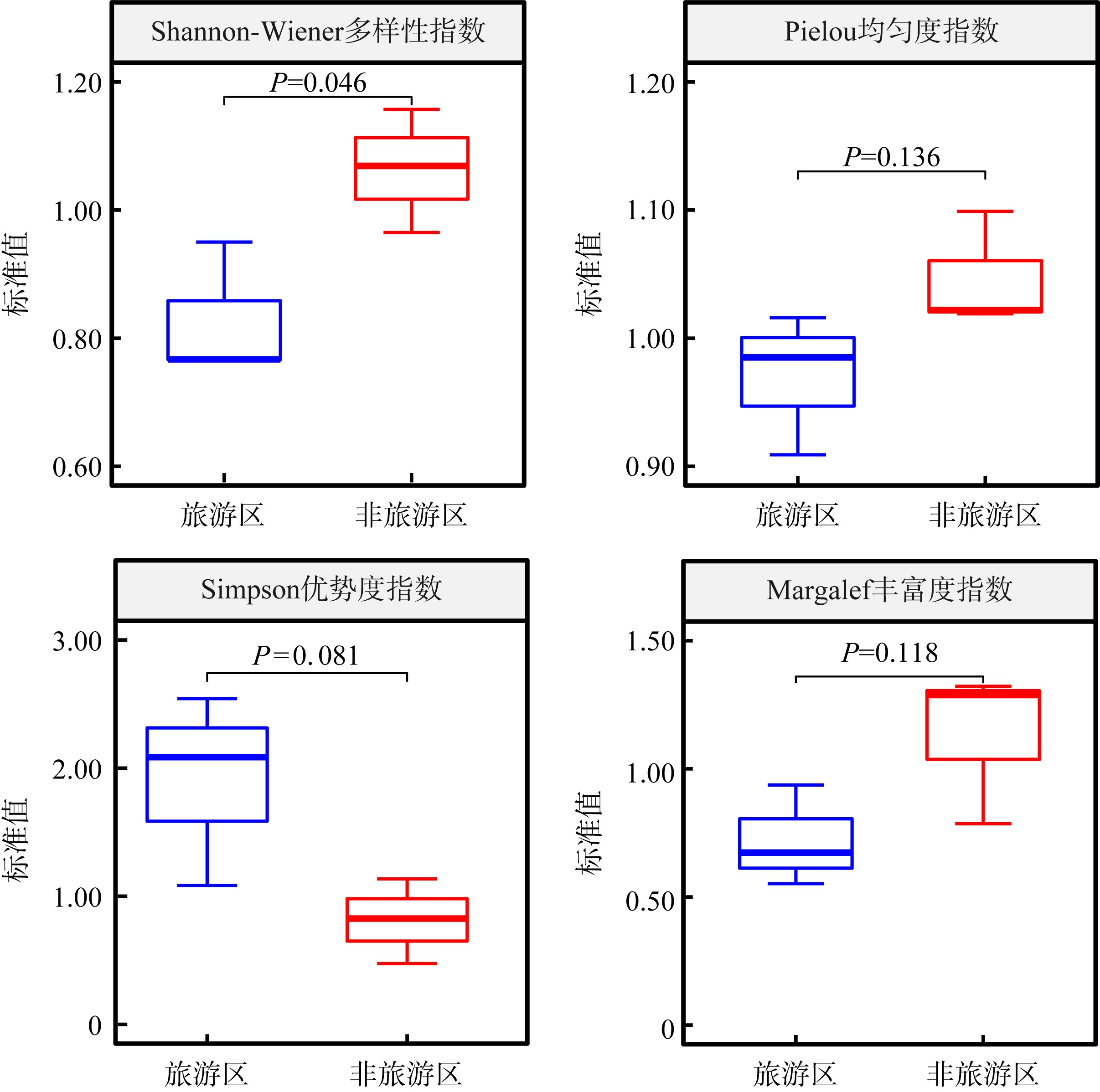
Species diversity indices at different sampling sites"
| 调查航次 | 调查区域 | 调查站位 | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H') | Pielou均匀度指数(E) | Simpson优势度指数(C) | Margalef丰富度指数(DMG) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原始值 | 标准值 | 原始值 | 标准值 | 原始值 | 标准值 | 原始值 | 标准值 | |||
| 第1航次 | 旅游区 | T1 | 3.194 | — | 0.914 | — | 0.048 | — | 6.124 | — |
| T2 | 3.298 | — | 0.882 | — | 0.047 | — | 7.838 | — | ||
| T3 | 3.105 | — | 0.854 | — | 0.058 | — | 7.238 | — | ||
| 非旅游区 | N1 | 2.717 | — | 0.825 | — | 0.095 | — | 5.293 | — | |
| N2 | 3.008 | — | 0.839 | — | 0.069 | — | 6.078 | — | ||
| N3 | 3.128 | — | 0.860 | — | 0.059 | — | 7.445 | — | ||
| 第2航次 | 旅游区 | T1 | 2.447 | 0.766 | 0.831 | 0.909 | 0.122 | 2.542 | 4.120 | 0.673 |
| T2 | 3.132 | 0.950 | 0.896 | 1.016 | 0.051 | 1.085 | 7.345 | 0.937 | ||
| T3 | 2.383 | 0.767 | 0.841 | 0.985 | 0.121 | 2.086 | 3.993 | 0.552 | ||
| 非旅游区 | N1 | 3.144 | 1.157 | 0.907 | 1.099 | 0.045 | 0.474 | 6.997 | 1.322 | |
| N2 | 3.215 | 1.069 | 0.855 | 1.019 | 0.057 | 0.826 | 7.827 | 1.288 | ||
| N3 | 3.018 | 0.965 | 0.879 | 1.022 | 0.067 | 1.136 | 5.855 | 0.786 | ||
Tab. 9
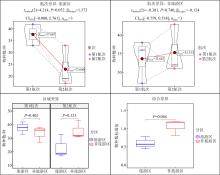
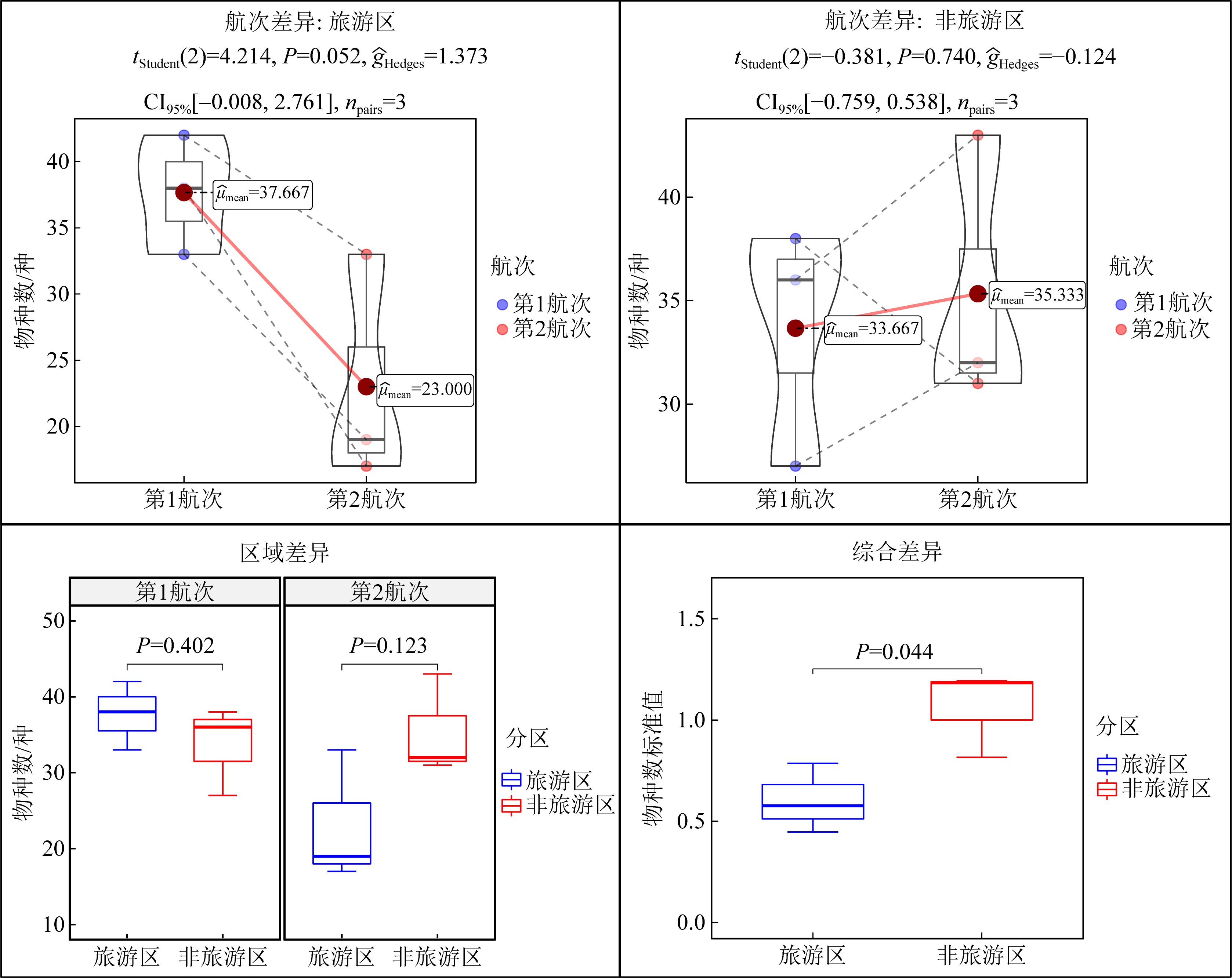
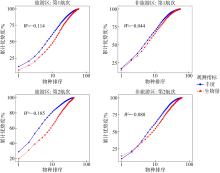
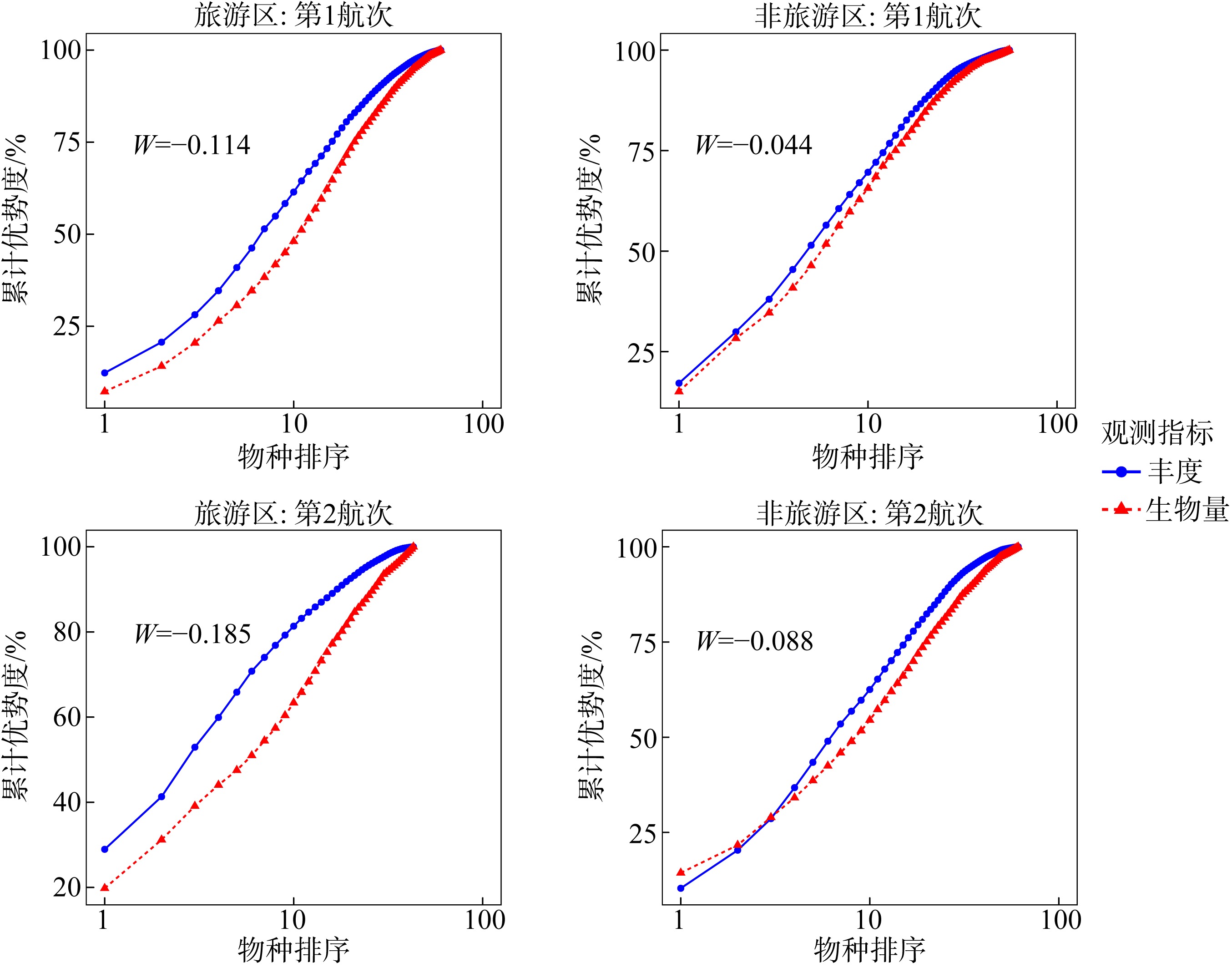
Summary of P-values for all measured parameters in this study"
| 检测指标 | 旅游区航次差异P | 非旅游区航次差异P | 第1航次区域差异P | 第2航次区域差异P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种数 | 0.052 | 0.740 | 0.402 | 0.123 |
| 丰度 | 0.076 | 0.360 | 0.585 | 0.245 |
| 生物量 | 0.053 | 0.451 | 0.515 | 0.701 |
| W统计量 | 0.133 | 0.250 | 0.973 | 0.079 |
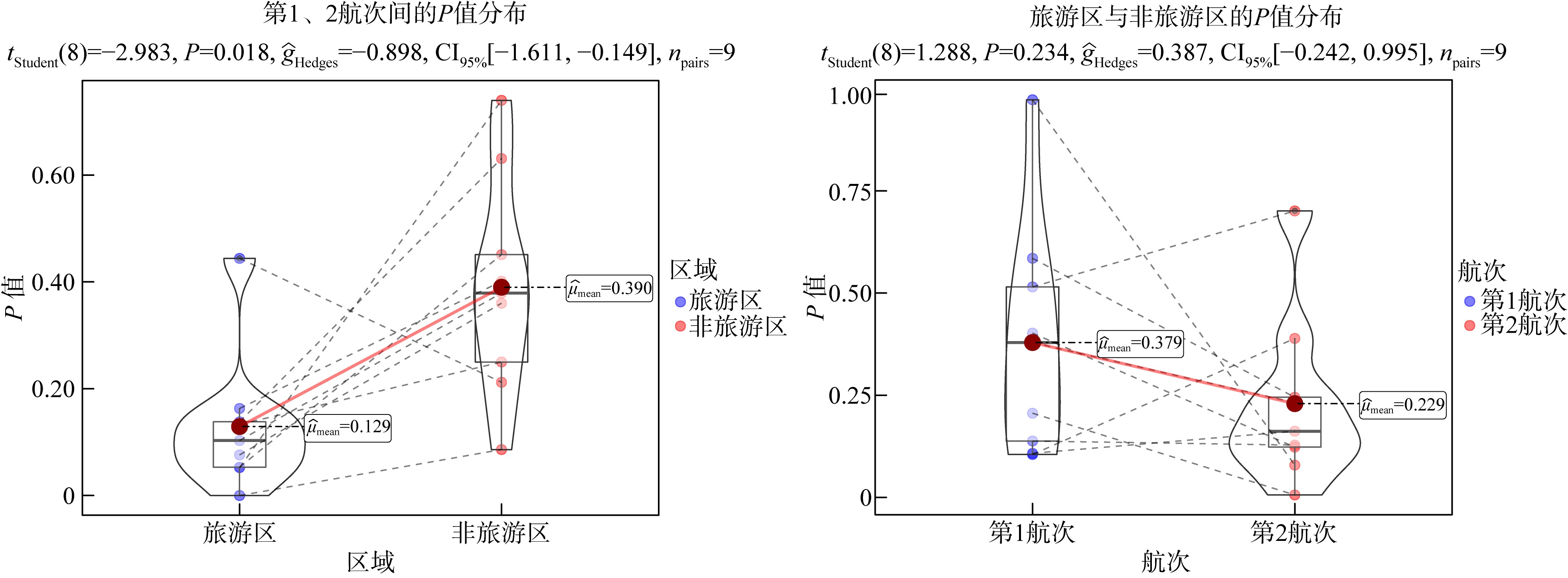
| 相对重要性指数 | 0 | 0.086 | 0.206 | 0.006 |
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 | 0.103 | 0.379 | 0.138 | 0.128 |
| Pielou均匀度指数 | 0.444 | 0.212 | 0.105 | 0.389 |
| Simpson优势度指数 | 0.163 | 0.401 | 0.108 | 0.162 |
| Margalef丰富度指数 | 0.138 | 0.631 | 0.379 | 0.232 |
| [1] |
毕耜瑶, 2016. 南麂列岛海洋自然保护区潮间带软体动物群落结构及其演替规律[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈金锋, 吴欣静, 林海, 等, 2023. 《国家重点保护野生动物名录》和其他保护名录对比分析[J]. 生物多样性, 31(6): 22639.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2022639 |
|
doi: 10.17520/biods.2022639 |
|
| [3] |
丁兰平, 王雨昕, 刘金梅, 等, 2024. 我国西沙群岛仙掌藻属Halimeda (绿藻门钙扇藻科)的分类学研究[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 44(3): 28-36.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
冯明, 韩庆喜, 严润玄, 2021. 浙江韭山列岛岩礁潮间带大型底栖动物群落特征和功能性状[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(5): 1469-1477.
|
|
doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202105.007 |
|
| [5] |
海南省发展和改革委员会, 2022. 关于海南省2021年国民经济和社会发展计划执行情况与2022年国民经济和社会发展计划的报告[EB/OL]. (2022-02-10) [2024-12-18]. https://plan.hainan.gov.cn/sfgw/fzgh/202202/9a8544b20fc3490998bf72bc4ad6d31a.shtml
|
| [6] |
何溪澄, 丁一汇, 何金海, 2008. 东亚冬季风对ENSO事件的响应特征[J]. 大气科学, 32(2): 335-344.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
何鑫, 2020. 南海诸岛旅游环境脆弱性综合评价研究——以西沙群岛为例[D]. 海口: 海南大学.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
黄晖, 董志军, 练健生, 2008. 论西沙群岛珊瑚礁生态系统自然保护区的建立[J]. 热带地理, 28(6): 540-544.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
黄晖, 练健生, 黄小平, 等, 2006. 用珊瑚覆盖率作为干扰指标——永兴岛石珊瑚生物多样性研究[J]. 科学通报, 51(S3): 108-113 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
黄晖, 尤丰, 练健生, 等, 2011. 西沙群岛海域造礁石珊瑚物种多样性与分布特点[J]. 生物多样性, 19(6): 710-715.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06132 |
|
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06132 |
|
| [11] |
蒋文贤, 张明伟, 刘晓收, 2024. 不同污染压力对青岛董家口邻近海域大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 44(17): 7830-7843.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
焦海峰, 彭小明, 尤仲杰, 等, 2011. 渔山岛岩石相潮间带大型底栖动物物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 19(5): 511-518.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08021 |
|
|
|
| [13] |
雷明凤, 余克服, 廖芝衡, 等, 2024. 西沙群岛银屿珊瑚礁的生态快速退化及其对鱼类的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(3): 87-99.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
李北兴, 黎傲雪, 董建宇, 等, 2023. 湛江湾潮间带大型底栖动物的群落结构及其受干扰程度[J]. 南方水产科学, 19(2): 12-20.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李晶晶, 史本伟, 彭忠, 等, 2024. 台风“梅花”对潮滩大型底栖动物群落的影响研究[J]. 海洋学报, 46(7): 29-40.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
李梦蝶, 王立龙, 晋秀龙, 2022. 旅游干扰对植物多样性的影响研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 41(6): 230-236.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
李明峰, 2014. 游憩活动对沙滩潮间带大型底栖动物的影响研究—以福建省东山岛为例[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
李莎, 姜伟, 李博, 等, 2024. 长江葛洲坝坝下江段鱼类群落结构及多样性[J]. 水生态学杂志, 45(3): 121-130.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
李文杰, 潘婉雯, 宋河有, 2014. 旅游对环境影响研究的意义与展望[J]. 安全与环境工程, 21(2): 94-99.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
李新正, 2020. 中国常见海洋生物原色图典节肢动物[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [21] |
李亚芳, 杜飞雁, 王亮根, 等, 2016. 南海中沙西沙海域海樽类群落结构特征研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 12(4): 64-70.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
李映灿, 陈治文, 黄广传, 等, 2021. 西沙群岛主要岛屿鸟类和小型兽类群落调查研究[J]. 生态学报, 41(18): 7189-7203.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
廖彬彬, 蔡永立, 谢长坤, 等, 2013. 南海永兴岛珊瑚岛礁生境格局动态研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 32(5): 746-751.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
刘瀚仁, 廖一波, 寿鹿, 等, 2021. 浙江苍南无居民海岛岩相潮间带生物群落多样性研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 39(2): 68-79.
|
|
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.02.008 |
|
| [25] |
刘鸿雁, 张金海, 1997. 旅游干扰对香山黄栌林的影响研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 21(2): 191-196.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
刘世栋, 高峻, 2013. 旅游活动对滨海浴场水环境影响研究中国环境监测, 29(2): 1-4.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
刘岳含, 黎松松, 郑伟, 等, 2020. 旅游干扰下山地草甸光谱特征及其与冠层特征的关系[J]. 中国草地学报, 42(2): 83-94.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
鲁庆彬, 游卫云, 赵昌杰, 等, 2011. 旅游干扰对青山湖风景区植物多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(2): 295-302.
pmid: 21608239 |
|
pmid: 21608239 |
|
| [29] |
罗庆华, 2019. 旅游干扰对张家界大鲵生境和种群的影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
罗庆华, 宋英杰, 向昌国, 等, 2017. 旅游干扰对野生动物的影响研究进展[J]. 湖南农业科学, (9): 128-131.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
牛莉芹, 王紫彦, 王垚垚, 等, 2023. 基于旅游干扰的历山自然保护区游径附近森林群落生态环境承载力[J]. 自然资源学报, 38(4): 995-1009.
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20230411 |
|
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20230411 |
|
| [32] |
曲方圆, 于子山, 隋吉星, 等, 2009. 丰度生物量比较法应用局限性[J]. 海洋科学, 33(6): 118-121.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
全秋梅, 王腾, 刘永, 等, 2021. 南海典型岛礁的鹦嘴鱼群落结构组成[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(7): 2133-2145.
|
|
doi: DOI: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202107.029 |
|
| [34] |
三亚市旅游发展局, 2024. 2023年三亚旅游市场特征分析报告[EB/OL]. (2024-01-18)[2024-12-18]. https://www.visitsanya.com/display.php?id=998
|
| [35] |
孙晓东, 林冰洁, 2021. 中国邮轮产业有形之手: 政策创新与产业演化[J]. 旅游科学, 35(6): 67-91.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
唐明艳, 杨永兴, 2014. 旅游干扰下滇西北高原湖滨湿地植被及土壤变化特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(5): 1283-1292.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
王腾, 李纯厚, 王广华, 等, 2024. 西沙群岛七连屿珊瑚礁鱼类的物种组成与演替[J]. 生物多样性, 32(6): 23481.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2023481 |
|
doi: 10.17520/biods.2023481 |
|
| [38] |
望元庆, 2022. 旅游干扰下沙漠化地区社会-生态复合系统脆弱性研究—以额济纳旗为例[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
吴倩倩, 朱永恒, 白钰鹏, 等, 2024. 旅游活动对土壤健康的影响研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 43(5): 223-230.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
吴钟解, 陈春华, 丁翔宇, 2011. 三亚蜈支洲珊瑚礁观光旅游活动对珊瑚及其生态的影响探讨[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 28(3): 57-60 (in Chinese).
|
| [41] |
熊飞, 郭祺, 张伟, 等, 2024. 金沙江下游向家坝库区鱼类群落结构空间格局[J]. 水生态学杂志, 45(4): 82-91.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
阎根齐, 吴昊, 2024. 中国人对西沙群岛历史认知与风力、潮流、海浪作用下的变迁研究[J]. 热带地理, 44(2): 258-268.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003822 |
|
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003822 |
|
| [43] |
晏宏, 孙立广, 刘晓东, 等, 2010. 近50年来南海西沙群岛海域气候异常的ENSO效应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(5): 29-35.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.05.029 |
|
| [44] |
游长江, 李欣达, 陈海鹰, 2018. 西沙群岛旅游环境区域承载力测度研究[C]// 第九届海洋强国战略论坛论文集. 北海: 中国海洋学会, 中国太平洋学会: 162-167 (in Chinese).
|
| [45] |
曾晓起, 李洪武, 2020. 中国常见海洋生物原色图典腔肠动物、棘皮动物[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社: 1-165 (in Chinese).
|
| [46] |
张素萍, 2008. 中国海洋贝类图鉴[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-363 (in Chinese).
|
| [47] |
张颖, 杨栎潼, 苏南, 等, 2024. 西沙海域长棘海星潜在鱼类捕食者鉴定[J]. 海洋学报, 46(7): 73-87.
|
|
|
|
| [48] |
赵中伟, 赵璇, 陈天然, 等, 2024. 西沙群岛珊瑚礁2015—2023海岸地貌演化与其区域海洋环境特征的关联性研究[J/OL]. 热带海洋学报. (2024-06-05) [2024-11-18]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1500.p.20240604.0956.002.html.
|
|
|
|
| [49] |
甄文全, 张金凤, 杨明柳, 等, 2023. 利用潮间带大型底栖动物群落评估茅尾海生态环境质量[J]. 动物学杂志, 58(3): 390-401.
|
|
|
|
| [50] |
周雅君, 何明郡, 刘聪, 等, 2024. 基于Sentinel-2卫星影像的海南西岛珊瑚礁识别和变化分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 55(1): 65-76.
|
|
|
|
| [51] |
朱芳, 白卓灵, 2015. 旅游干扰对鄱阳湖国家湿地公园植被及土壤特性的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 22(3): 33-39.
|
|
|
|
| [52] |
pmid: 17681552 |
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
pmid: 17813173 |
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [1] | ZHAO Zhongwei, ZHAO Xuan, Chen Tianran, LI Wei. A study of the correlation between coastal morphological changes and oceanographic conditions of coral reef islands in the Xisha Islands from 2015 to 2023 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(4): 25-44. |
| [2] | XIAO Haiting, HUANG Rongyong, LIU Yi, YU Kefu. Spatiotemporal changes of lime-sand islands in the Xisha Islands under the impacts of typhoons [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 157-177. |
| [3] | LIU Jiehong, WANG Pengcheng, WANG Zhihao, XIA Wentong, XIE Songguang, SONG Yiqing. Preliminary study on the reproductive biology of crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster solaris) in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 160-169. |
| [4] | XIE Hongyu, LIU Yong, LI Chunhou, ZHAO Jinfa, SUN Jinhui, SHEN Jianzhong, SHI Juan, WANG Teng. Species composition and evolutionary characteristics of coral reef fish in the Langhua Reef, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 114-128. |
| [5] | LEI Mingfeng, YU Kefu, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Biao, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Xiaoyan. The rapid ecological degradation and its impact on fish of the Yinyu Island in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [6] | GAO Jie, YU Kefu, XU Shendong, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Biao, WANG Yonggang. Content and source analysis of organic carbon in the outer slope sediments of the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [7] | CHEN Shu, XU Hong, LU Shushen, Zhang Haiyang, MA Yazeng, LUO Jinxiong. The framework, reservoir characteristics and reef formation model of Miocene algal reef dolomite in the Xisha Islands* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 140-153. |
| [8] | ZHAO Jinfa, LIU Yong, LI Chunhou, WANG Teng, SHI Juan, XIAO Yayuan, WU Peng, SONG Xiaoyu. Study on species composition and distribution of fish eggs in Yongle Atoll and Dongdao Island by high-throughput sequencing technology [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 127-136. |
| [9] | FENG Ying-ci, ZHAN Wen-huan, YAO Yan-tao, SUN Jie, LIU Shou-jin, LI Jian. Analysis of tectonic movement and activity in the organic reef region around the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(3): 48-53. |
| [10] | CHEN Qi-dong, DENG Ru-ru, CHEN Lei, QIN Yan, HE Ying-qing, TIAN Jian-lin. Atmospheric correction of WorldView-2 data for the Xisha Islands and reefs imagery [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(3): 88-94. |
| [11] | DENG Xiao-dong, LIU Jun-liang, CAI Shu-qun. Analyses of the tidal current characteristics on the continental shelf of the Xisha Islands in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(4): 8-12. |
| [12] | YAN Hong,SUN Li-guang,LIU Xiao-dong,QIU Shi-can. Relationship between ENSO events and regional climate anomalies around the Xisha Islands during the last 50 years [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(5): 29-35. |
|
||