Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 172-185.doi: 10.11978/2021151CSTR: 32234.14.2021151
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative study on zooplankton community structure in Pearl River Estuary based on morphological and DNA identification
YIN Tianqi1( ), WANG Qing1(
), WANG Qing1( ), YANG Yufeng1,2, CEN Jingyi1
), YANG Yufeng1,2, CEN Jingyi1
- 1. College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai), Zhuhai 519000, China
-
Received:2021-11-05Revised:2021-12-15Published:2021-12-23 -
Contact:WANG Qing E-mail:yintianqi11235@163.com;wq2010@jnu.edu.cn -
Supported by:General project of Guangdong Natural Science Foundation(2022A1515011387);General project of Guangdong Natural Science Foundation(2021A1515010814)
CLC Number:
- Q958.8
Cite this article
YIN Tianqi, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng, CEN Jingyi. Comparative study on zooplankton community structure in Pearl River Estuary based on morphological and DNA identification[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 172-185.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Species composition of zooplankton in the Pearl River Estuary"
| 类别 | 种类 | Ⅰ型网 | Ⅱ型网 | Ⅲ型网 | 25#网 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 桡足类 | 红纺锤水蚤(Acartia erythraea) | + | + | + | |
| 太平洋纺锤水蚤(Acartia pacifica) | + | + | + | + | |
| 刺尾纺锤水蚤(Acartia spinicauda) | + | + | + | + | |
| 中华异水蚤(Acartiella sinensis) | + | + | + | + | |
| 拟矮隆水蚤(Bestiolina similis) | + | + | |||
| 叉胸刺水蚤(Centropages furcatus) | + | ||||
| 微刺哲水蚤(Canthocalanus pauper) | + | + | |||
| 精致真刺水蚤(Euchaeta concinna) | + | + | |||
| 卵型光水蚤(Lucicutia ovalis) | + | ||||
| 强额孔雀哲水蚤(Parvocalanus crassirostris) | + | + | + | + | |
| 小拟哲水蚤(Paracalanus parvus) | + | ||||
| 亚强次真哲水蚤(Subeucalanus subcrassus) | + | + | + | + | |
| 异尾宽水蚤(Temora discaudata) | + | ||||
| 锥形宽水蚤(Temora turbinata) | + | + | + | + | |
| 瘦歪水蚤(Tortanus gracilis) | + | ||||
| 近缘大眼剑水蚤(Corycaeus affinis) | + | ||||
| 平大眼水蚤(Corycaeus dahli) | + | + | |||
| 近邻剑水蚤(Cyclops vicinus) | + | + | + | ||
| 短角长腹剑水蚤(Oithona brevicornis) | + | + | + | ||
| 小长腹剑水蚤(Oithona nana) | + | + | + | + | |
| 瘦长毛猛水蚤(Macrosetella gracilis) | + | + | + | ||
| 小毛猛水蚤(Microsetella norvegica) | + | + | + | + | |
| 水母类 | 半口壮丽水母(Aglaura hemistoma) | + | + | + | |
| 不列颠高手水母(Bougainvillia britannica) | + | + | + | ||
| 双生水母(Diphyes chamissonis) | + | + | + | ||
| 短柄和平水母(Eirene brevistylus) | + | + | + | ||
| 球型侧腕水母(Pleurobrachia globosa) | + | + | + | ||
| 毛颚类 | 百陶带箭虫(Zonosagitta bedoti) | + | + | + | + |
| 肥胖软箭虫(Flaccisagitta enflata) | + | + | + | + | |
| 被囊类 | 异体住囊虫(Oikopleura longicaudata) | + | + | + | |
| 浮游幼虫 | 磷虾幼虫(Euphausiacea larva) | + | + | + | + |
| 蔓足类幼虫(Cirripedia larva) | + | + | + | + | |
| 莹虾幼虫(Lucifer larva) | + | + | + | + | |
| 长尾类幼虫(Macruran larva) | + | + | + | ||
| 多毛类幼虫(Polychaeta larva) | + | + | + | + | |
| 鱼卵 | 鱼卵(fish eggs) | + | + | + |
Tab. 2
Species dominance of zooplankton collected using different types of nets"
| 种类 | 浅水Ⅰ型网 | 浅水Ⅱ型网 | 浅水Ⅲ型网 | 25#浮游生物网 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优势度Y | 平均丰度/(ind·m-3) | 优势度Y | 平均丰度/(ind·m-3) | 优势度Y | 平均丰度/(ind·m-3) | 优势度Y | 平均丰度/(ind·m-3) | |
| 强额孔雀哲水蚤(Parvocalanus crassirostris) | 0.04 | 18 | 0.34 | 1070 | 0.15 | 666 | 0.24 | 2182 |
| 太平洋纺锤水蚤(Acartia pacifica) | 0.10 | 46 | <0.02 | / | <0.02 | / | <0.02 | / |
| 短角长腹剑水蚤(Oithona brevicornis) | <0.02 | / | <0.02 | / | 0.05 | 193 | 0.43 | 640 |
| 微刺哲水蚤(Canthocalanus pauper) | <0.02 | / | <0.02 | / | 0.04 | 1007 | <0.02 | / |
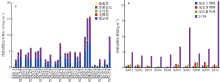
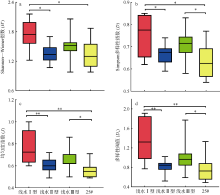
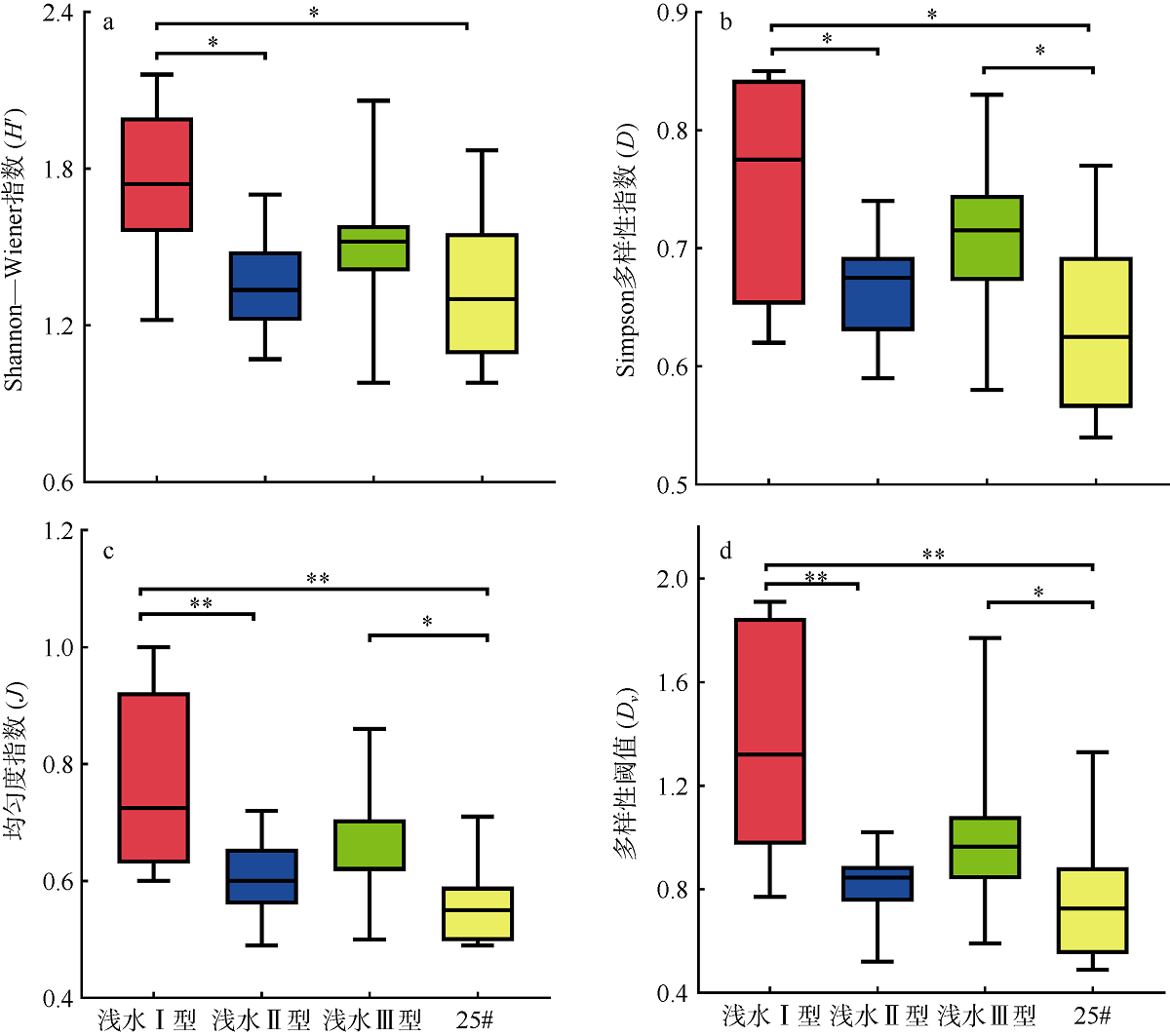
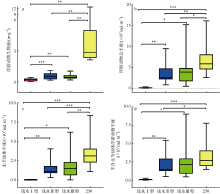
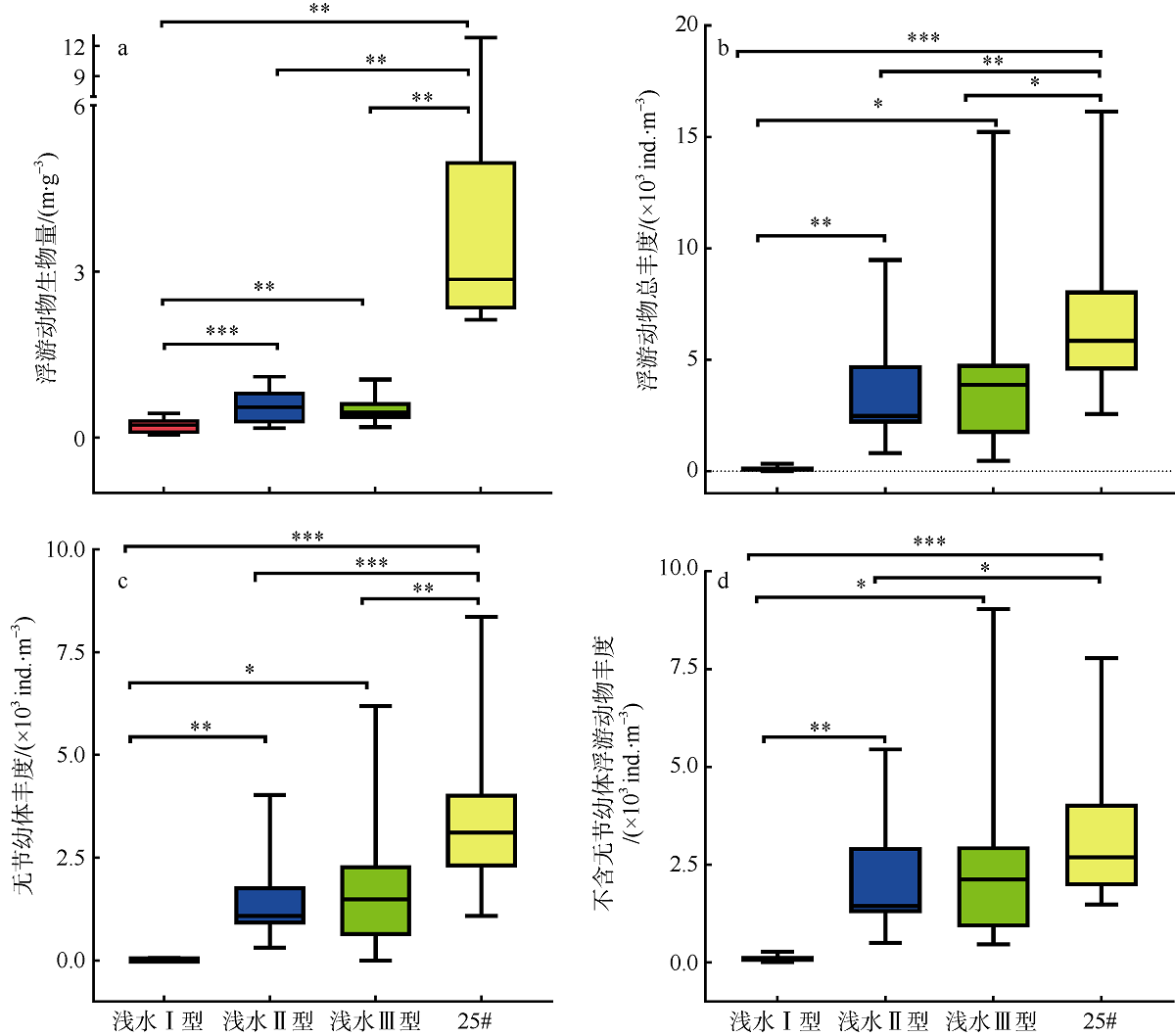
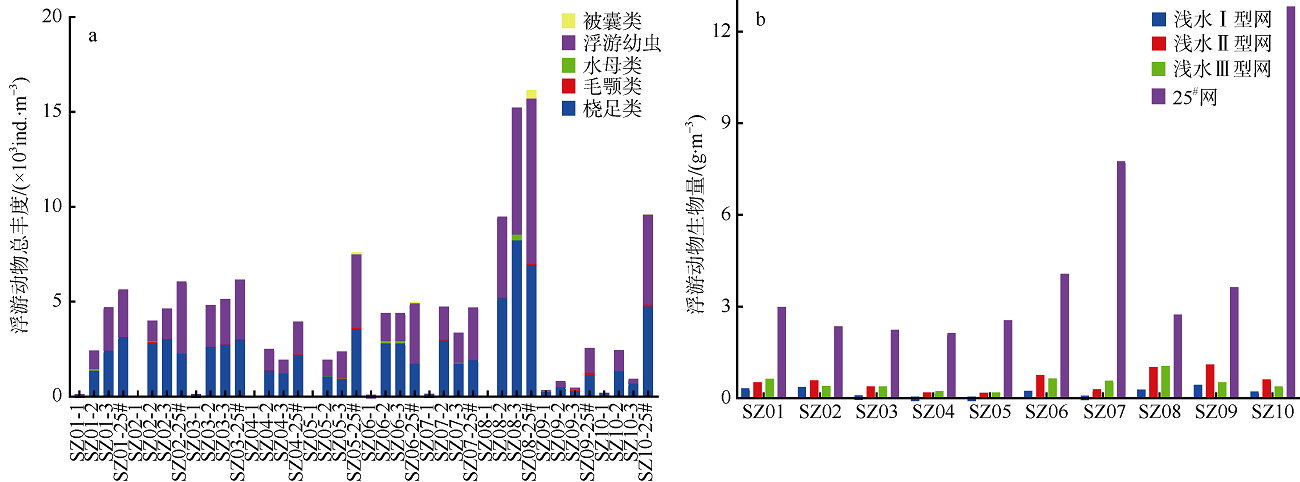
Fig. 4
Spatial variation of zooplankton abundance and biomass in the Pearl River Estuary (a) zooplankton abundance; and (b) zooplankton biomass. Site suffixes -1, -2, -3, and -25#, respectively, represent zooplankton samples collected by shallow water type I net, type Ⅱ net, type III net, and 25# plankton net at the sampling site"
Tab. 4
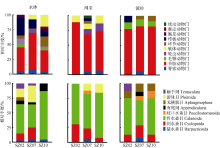
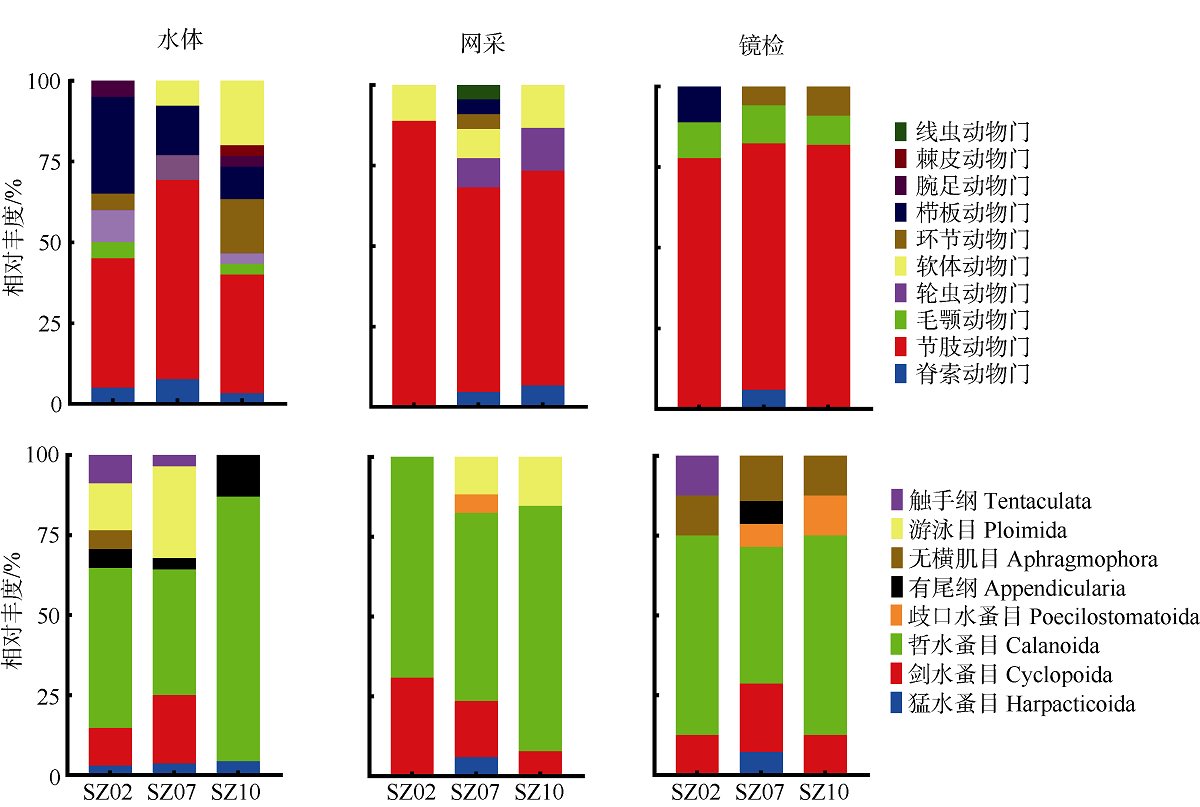
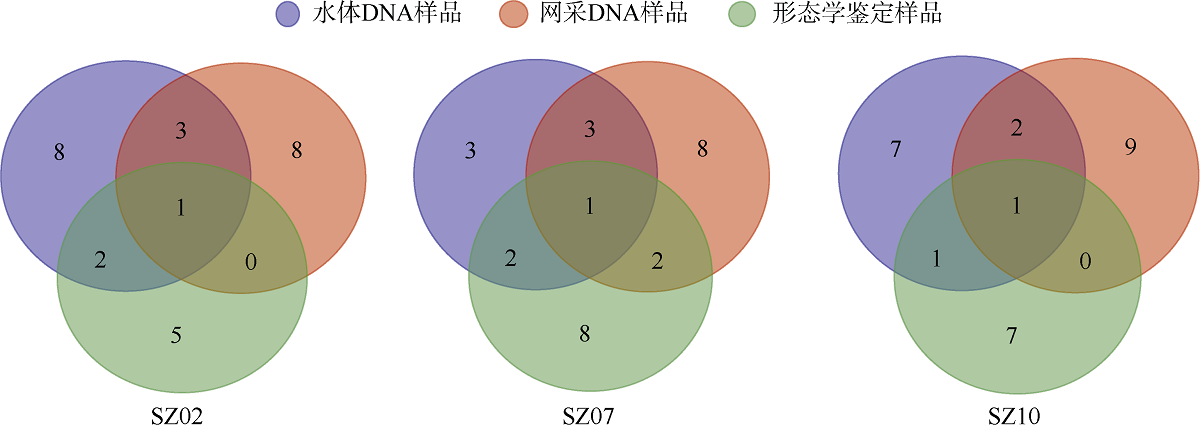
Zooplankton species in the water and net-collected samples through DNA sequencing and morphological identification"
| 种类 | 水体DNA样品OTU数 | 网采DNA样品OTU数 | 镜检种类数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZ02 | SZ07 | SZ10 | SZ02 | SZ07 | SZ10 | SZ02 | SZ07 | SZ10 | |
| 长纺锤水蚤(Acartia longiremis) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 太平洋纺锤水蚤(Acartia pacifica) | 3 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 刺尾纺锤水蚤(Acartia spinicauda) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 中华异水蚤(Acartiella sinensis) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 拟矮隆水蚤(Bestiolina similis) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 叉胸刺水蚤(Centropages furcatus) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 胸刺水蚤(Centropages hamatus) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 典型胸刺水蚤(Centropages typicus) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 强额孔雀哲水蚤(Parvocalanus crassirostris) | 5 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 伪镖水蚤(Pseudodiaptomus euryhalinus) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 指状伪镖水蚤(Pseudodiaptomus inopinus) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 中华华哲水蚤(Sinocalanus sinensis) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 强次真哲水蚤(Subeucalanus crassus) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 亚强次真哲水蚤(Subeucalanus subcrassus) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 异尾宽水蚤(Temora discaudata) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 锥形宽水蚤(Temora turbinata) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 瘦歪水蚤(Tortanus gracilis) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 近缘大眼剑水蚤(Corycaeus affinis) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 平大眼水蚤(Corycaeus dahli) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 近邻剑水蚤(Cyclops vicinus) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 半剑水蚤(Hemicyclops sp.) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 半剑水蚤(Hemicyclops tanakai) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 真刺唇角水蚤(Labidocera euchaeta) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 短角长腹剑水蚤(Oithona brevicornis) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 戴维斯长腹剑水蚤(Oithona davisae) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 小长腹剑水蚤(Oithona nana) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 长腹剑水蚤(Oithona sp.) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 矮小拟镖剑水蚤(Paracyclopina nana) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 小毛猛水蚤(Microsetella norvegica) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 拟双倍猛水蚤(Paramphiascella fulvofasciata) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 三角大吉猛水蚤(Tachidius triangularis) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 箭虫(无横肌目)(Aphragmophora) | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 百陶带箭虫(Zonosagitta bedoti) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 肥胖软箭虫(Flaccisagitta enflata) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 卵形无柄轮虫(Ascomorpha ovalis) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 萼花臂尾轮虫(Brachionus calyciflorus) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 梳状疣毛轮虫(Synchaeta pectinata) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 颤动毛轮虫(Synchaeta tremula) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 球型侧腕水母(Pleurobrachia globosa) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 斑点蝶水母(Ocyropsis maculata) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 住囊虫(Oikopleura sp.) | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Tab. 5
Comparison of zooplankton abundance and biomass in the Pearl River Estuary among different investigations"
| 采样时间 | 网具 | 丰度/(ind.·m-3) | 生物量/(mg·m-3) | 珠江口 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 浅水I型网 | / | 58~101 | 全国海洋普查(张达娟 等, |
| 1960 | 浅水I型网 | / | 33 | 全国海洋普查(张达娟 等, |
| 1981 | 浅水I型网 | / | 213~239 | 中国海湾志编纂委员会, |
| 1995 | 浅水I型网 | / | 2423 | 郑奕麟, |
| 1996 | 浅水I型网 | 5.01~606.5 | / | 刘玉 等, |
| 2002—2003 | 浅水I型网 | 700~1131 | 203~382 | 李开枝 等, |
| 2002—2003 | 浅水I型网 | 73~185 | / | 李开枝 等, |
| 2004 | 浅水I型网 | / | 152.34~571.54 | 张达娟 等, |
| 2005 | 浅水I型网 | / | 444.77~656.18 | 张达娟 等, |
| 2006 | 浅水I型网 | / | 712.94~874.5 | 张达娟 等, |
| 2006—2007 | 浅水I型网 | 2288~28013 | 10.03~132.95 | 高原 等, |
| 2009 | 浅水I型网 | 423.46 | / | 国家监测中心, 2009 |
| 2012—2013 | 浅水I型网 | / | 20~375 | 彭鹏飞 等, |
| 2015 | 浅水I型网 | 20.5~1035 | 2.5~417 | 徐姗楠 等, |
| 2004 | 浅水Ⅱ型网 | 3900~13000 | / | Tan et al, |
| 2009 | 浅水Ⅱ型网 | 4131.92 | / | 吴玲玲 等, |
| 2015 | 浅水Ⅱ型网 | 36~896 | / | 刘华雪 等, |
| 2013—2014 | 浅水Ⅱ型网 | 72.90~35128.57 | / | 黄彬彬 等, |
| 1985 | 浅水Ⅲ型网 | 31.37~71.68 | 69~204.73 | 宋盛宪, |
| 2006—2007 | 25#浮游生物网 | 1430~154450 | 6.3~277.3 | 高原 等, |
| 2019 | 浅水I型网 | 9~331 | 45~444 | 本研究 |
| 2019 | 浅水Ⅱ型网 | 811~9474 | 170~1100 | 本研究 |
| 2019 | 浅水Ⅲ型网 | 460~15221 | 190~1050 | 本研究 |
| 2019 | 25#浮游生物网 | 2560~16140 | 2130~12820 | 本研究 |
| [1] | 陈清潮, 黄良民, 尹建强, 等, 1994. 南沙群岛海区浮游动物多样性研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 42-50. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | 国家海洋局南海环境监测中心 2009. 2009年珠江口生态监控区监测报告[R]. 广州: 国家海洋局南海环境监测中心. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | 高原, 赖子尼, 王超, 等, 2008. 2006年夏季珠江口浮游动物群落结构特征分析[J]. 南方水产, 4(1): 10-15. |
| GAO YUAN, LAI ZINI, WANG CHAO, et al, 2008. Community characteristics of zooplankton in Pearl River Estuary in summer of 2006[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 4(1): 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 黄彬彬, 郑淑娴, 蔡伟叙, 等, 2017. 珠江口枯水期和丰水期中小型桡足类种类组成、丰度分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 56(6): 852-858. |
| HUANG BINBIN, ZHENG SHUXIAN, CAI WEIXU, et al, 2017. Species composition and abundance distribution of meso-and micro-copepods and their relationships with environmental factors during dry and wet seasons in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 56(6): 852-858. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 李开枝, 尹健强, 黄良民, 等, 2005. 珠江口浮游动物的群落动态及数量变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 24(5): 60-68. |
| LI KAIZHI, YIN JIANQIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2005. Dynamic variations of community structure and quantity of zooplankton in Zhujiang river estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 24(5): 60-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 李开枝, 尹健强, 黄良民, 等, 2007. 珠江口浮游桡足类的生态研究[J]. 生态科学, 26(2): 97-102. |
| LI KAIZHI, YIN JIANQIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2007. Study on planktonic copepods ecology in the Pearl River estuary[J]. Ecologic Science, 26(2): 97-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 李开枝, 柯志新, 王军星, 等. 2021. 西沙群岛珊瑚礁海域浮游动物群落结构初步分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(2): 121-131. |
| LI KAIZHI, KE ZHIXIN, WANG JUNXING, et al, 2021. Preliminary study on the community structure of zooplankton in coral reef waters of Xisha Islands[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(2): 121-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 连光山, 王彦国, 孙柔鑫, 等, 2018. 中国海洋浮游桡足类多样性[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 40-747. |
| LIAN GUANGSHAN, WANG YANGUO, SUN ROUXIN, et al, 2018. Species diversity of marine planktonic copepods in China's seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press: 40-747. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 连喜平, 谭烨辉, 刘永宏, 等, 2013. 两种浮游生物网对南海北部浮游动物捕获效率的比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(3): 33-39. |
| LIAN XIPING, TAN YEHUI, LIU YONGHONG, et al, 2013. Comparison of capture efficiency for zooplankton in the northern South China Sea, using two plankton mesh sizes[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(3): 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 刘华雪, 许友伟, 陈作志, 等, 2016. 水母旺发对珠江口鱼类资源量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 35(6): 68-73. |
| LIU HUAXUE, XU YOUWEI, CHEN ZUOZHI, et al, 2016. Impact on fish stock by jellyfish bloom in Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 35(6): 68-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 刘玉, 李适宇, 董燕红, 等, 2001. 珠江口伶仃水道浮游生物及底栖动物群落特征分析[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 40(S2): 114-118. |
| LIU YU, LI SHIYU, DONG YANHONG, et al, 2001. Community characteristics of plankton and benthos in the Lingding waterway of the Pearl River mouth[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 40(S2): 114-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 彭鹏飞, 李绪录, 蔡钰灿, 2015. 珠江口万山群岛海域秋春季浮游动物的分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 安徽农业科学, 43(18): 170-174. |
| PENG PENGFEI, LI XULU, CAI YUCAN, 2015. Distributing characteristics of zooplankton and its relationship to environmental factors in Wanshan islands sea of the pearl river estuary in fall and Spring[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 43(18): 170-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 司悦悦, 2018. 珠江口及南海中北部中型浮游动物摄食生态与繁殖研究[D]. 厦门大学. |
| SI YUEYUE, 2018. Study on mesozooplankton grazing and reproduction in Pearl River estuary and north-central South China Sea[D]. Xiamen University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 宋盛宪, 1991. 珠江口浮游生物的初步研究[J]. 海洋渔业, 13(1): 24-27. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | 孙松, 李超伦, 程方平, 等, 2015. 中国近海常见浮游动物图集[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 15-79. |
| SUN SONG, LI CHAOLUN, CHENG FANGPING, et al, 2015. Atlas of common zooplankton of the Chinese coastal seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press: 15-79. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 王荣, 王克, 2003. 两种浮游生物网捕获性能的现场测试[J]. 水产学报, 27(S1): 98-102. |
| WANG RONG, WANG KE, 2003. Field test of capture capabilities of two plankton nets[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 27(S1): 98-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 吴玲玲, 朱艾嘉, 郭娟, 等, 2012. 珠江口夏季中、小型浮游动物生态特征研究[J]. 海洋通报, 31(6): 689-694. |
| WU LINGLING, ZHU AIJIA, GUO JUAN, et al, 2012. Ecological study on meso-zooplankton and micro-zooplankton in the Pearl River Estuary in summer[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 31(6): 689-694. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 徐姗楠, 龚玉艳, 詹凤娉, 等, 2017. 珠江口海域南沙段浮游动物群落生态特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (6): 82-90. |
| XU SHANNAN, GONG YUYAN, ZHAN FENGPIN, et al, 2017. Ecological characteristics of zooplankton community structure in Nansha Area of Pearl River Estuary[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (6): 82-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 徐旭华, 黄国林, 胡莉娜, 等, 2021. 一种污染桉树组培苗的霉菌形态学及分子生物学鉴定[J]. 现代园艺, 44(9): 24-25, 30. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | 徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿, 1989. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 8(4): 13-15, 19. |
| XU ZHAOLI, CHEN YAQU, 1989. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in Autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 8(4): 13-15, 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 杨宇峰, 王庆, 陈菊芳, 等, 2006. 河口浮游动物生态学研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 26(2): 576-585. |
| YANG YUFENG, WANG QING, CHEN JUFANG, et al, 2006. Research advance in estuarine zooplankton ecology[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(2): 576-585. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 詹金钰, 呼晓庆, 郑玥熙, 等, 2021. 山西翅果油树上三种重要鳞翅目害虫的形态和分子鉴定及生活史观察[J]. 昆虫学报, 64(5): 618-626. |
| ZHAN JINYU, HU XIAOQING, ZHENG YUEXI, et al, 2021. Morphological and molecular identification and life history observation of three important lepidopteran pests on Elaeagnus mollis (Elaeagnaceae) in Shanxi Province, North China[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 64(5): 618-626. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 张达娟, 闫启仑, 王真良, 2008. 典型河口浮游动物种类数及生物量变化趋势的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 39(5): 536-540. |
| ZHANG DAJUAN, YAN QILUN, WANG ZHENLIANG, 2008. Variation in species number and biomass of zooplankton in typical Estuaries of China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 39(5): 536-540. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 张武昌, 陶振铖, 赵苑, 等, 2019. 中国海浮游桡足类图谱[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| ZHANG WUCHANG, TAO ZHENCHENG, ZHAO YUAN, et al, 2019. An illustrated guide to marine planktonic copepods in China seas[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 郑奕麟, 1995. 珠江口(唐家湾)浮游生物调查[J]. 水产科技, (1): 3-5. (in Chinese) |
| [26] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会 2008a. GB 17378.1-2007 海洋监测规范第7部分:近海污染生态调查和生物监测 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2008a. GB 17378.1-2007 The specification for marine monitoring-Part 7: Ecological survey for offshore pollution and biological monitoring[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会 2008b. GB/T 12763.1-2007 海洋调查规范第1部分: 总则[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2008b. GB/T 12763.1-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey-Part 1: general[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 中国海湾志编纂委员会 1998. 中国海湾志第十四分册[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 66-75. |
| Compilation Committee of China Gulf chronicles 1998, China Bay chronicle Volume 14. Beijing: Ocean Press, 66-75. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | BRYANT P, AREHART T, 2021. Diversity and life-cycle analysis of Pacific Ocean zooplankton by video microscopy and DNA barcoding: crustacea[J]. Journal of Aquaculture & Marine Biology, 10(3): 108-136. |
| [30] |
BUCKLIN A, PEIJNENBURG K T C A, KOSOBOKOVA K N, et al, 2021. Toward a global reference database of COI barcodes for marine zooplankton[J]. Marine Biology, 168(6): 78.
doi: 10.1007/s00227-021-03887-y |
| [31] |
CHEN HONGJU, YU HAO, LIU GUANGXING, 2016. Comparison of copepod collection efficiencies by three commonly used plankton nets: a case study in Bohai Sea, China[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 15(6): 1007-1013.
doi: 10.1007/s11802-016-3122-6 |
| [32] |
CHEUNG M K, AU C H, CHU K H, et al, 2010. Composition and genetic diversity of picoeukaryotes in subtropical coastal waters as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing[J]. The ISME journal, 4(8): 1053-1059.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.26 |
| [33] | COGUIEC E, ERSHOVA E A, DAASE M, et al, 2021. Seasonal variability in the zooplankton community structure in a sub-Arctic fjord as revealed by morphological and molecular approaches[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 8: 705042. |
| [34] |
DI MAURO R, CAPITANIO F, VIÑAS M D, 2009. Capture efficiency for small dominant mesozooplankters (Copepoda, Appendicularia) off Buenos Aires Province (34ºS-41ºS), Argentine Sea, using two plankton mesh sizes[J]. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 57(3): 205-214.
doi: 10.1590/S1679-87592009000300004 |
| [35] |
ELBRECHT V, LEESE F, 2015. Can DNA-based ecosystem assessments quantify species abundance? Testing primer bias and Biomass-Sequence relationships with an innovative metabarcoding protocol[J]. PLoS One, 10(7): e0130324.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130324 |
| [36] |
ERSHOVA E A, WANGENSTEEN O S, DESCOTEAUX R, et al, 2021. Metabarcoding as a quantitative tool for estimating biodiversity and relative biomass of marine zooplankton[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 78(9): 3342-3355.
doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsab171 |
| [37] |
HARVEY J B J, JOHNSON S B, FISHER J L, et al, 2017. Comparison of morphological and next generation DNA sequencing methods for assessing zooplankton assemblages[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 487: 113-126.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2016.12.002 |
| [38] |
HOOGENDOORN C, SMIT N J, KUDLAI O, 2020. Resolution of the identity of three species of Diplostomum (Digenea: Diplostomidae) parasitising freshwater fishes in South Africa, combining molecular and morphological evidence[J]. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 11: 50-61.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2019.12.003 |
| [39] |
LINDEQUE P K, PARRY H E, HARMER R A, et al, 2013. Next generation sequencing reveals the hidden diversity of zooplankton assemblages[J]. PLoS One, 8(11): e81327.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081327 |
| [40] |
MARS BRISBIN M, BRUNNER O D, GROSSMANN M M, et al, 2020. Paired high-throughput, in situ imaging and high-throughput sequencing illuminate acantharian abundance and vertical distribution[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 65(12): 2953-2965.
doi: 10.1002/lno.11567 |
| [41] | NOVOTNY A, ZAMORA-TEROL S, WINDER M, 2021. DNA metabarcoding reveals trophic niche diversity of micro and mesozooplankton species[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 288(1953): 20210908. |
| [42] |
PEARMAN J K, IRIGOIEN X, 2015. Assessment of zooplankton community composition along a depth profile in the central Red Sea[J]. PLoS One, 10(7): e0133487.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133487 |
| [43] |
PIELOU E C, 1966. Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 10(2): 370-383.
doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90133-0 |
| [44] |
QUESTEL J M, HOPCROFT R R, DEHART H M, et al, 2021. Metabarcoding of zooplankton diversity within the Chukchi Borderland, Arctic Ocean: improved resolution from multi-gene markers and region-specific DNA databases[J]. Marine Biodiversity, 2021, 51(1): 1-19.
doi: 10.1007/s12526-020-01125-0 |
| [45] |
RATHNASURIYA M I G, MATEOS-RIVERA A, SKERN-MAURITZEN R, et al, 2021. Composition and diversity of larval fish in the Indian Ocean using morphological and molecular methods[J]. Marine Biodiversity, 51(2): 39.
doi: 10.1007/s12526-021-01169-w |
| [46] |
RENZ J, MARKHASEVA E L, LAAKMANN S, et al, 2021. Proteomic fingerprinting facilitates biodiversity assessments in understudied ecosystems: a case study on integrated taxonomy of deep sea copepods[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21(6): 1936-1951.
doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13405 |
| [47] |
SCHROEDER A, STANKOVIĆ D, PALLAVICINI A, et al, 2020. DNA metabarcoding and morphological analysis - Assessment of zooplankton biodiversity in transitional waters[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 160: 104946.
doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.104946 |
| [48] | SHANNON C E, WEAVER W, 1950. The mathematical theory of communication[J]. Physics Today, 3(9): 31-32. |
| [49] |
SIMPSON E H, 1949. Measurement of diversity[J]. Nature, 163(4148): 688.
doi: 10.1038/163688a0 |
| [50] |
SINGH S P, GROENEVELD J C, HUGGETT J, et al, 2021. Metabarcoding of marine zooplankton in South Africa[J]. African Journal of Marine Science, 43(2): 147-159.
doi: 10.2989/1814232X.2021.1919759 |
| [51] |
TAN YEHUI, HUANG LIANGMIN, CHEN QINGCHAO, et al, 2004. Seasonal variation in zooplankton composition and grazing impact on phytoplankton standing stock in the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(16): 1949-1968.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.018 |
| [52] | TURNER J T, 2004. The importance of small planktonic copepods and their roles in pelagic marine food webs[J]. Zoological Studies, 43(2): 255-266. |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [3] | ZHANG Lanlan, CHENG Xiawen, XIANG Rong, QIU Zhuoya, CHANG Hu. Changes of radiolarian community structure with depth in the central Bay of Bengal in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [4] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [5] | LI Ruofei, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, LIU Jiaxin, TAN Yehui. Vertical distribution of zooplankton in the “Haima” cold seep region based on ZooScan image analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 87-96. |
| [6] | TANG Ling, NIE Yuhua, WANG Ping, TANG Chaolian. Trend analysis of marine heatwaves variability in the outer Pearl River estuary from 1974 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 143-150. |
| [7] | SHANG Bowen, WU Yunchao, JIANG Zhijian, LIU Songlin, HUANG Xiaoping. Characteristics and sources of organic matter in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary: Carbon storage implications [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 16-28. |
| [8] | YIN Jianqiang, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui. Bathyconchoecia nanshaensis sp. nov. (Myodocopa, Halocyprididae), a new species of ostracod from the southern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 193-197. |
| [9] | ZENG Dianting, LI Junyi, XIE Lingling, YE Xiaomin, ZHOU Da. Analysis of temporal characteristics of chlorophyll a in Lingding Bay during summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 16-25. |
| [10] | LI Kaizhi, KE Zhixin, WANG Junxing, TAN Yehui. Preliminary study on the community structure of zooplankton in coral reef waters of Xisha Islands* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [11] | SHUAI Yiping, CHEN Yinchao, LIU Zijia, GE Zaiming, MA Mengzhen, ZHANG Yuanfang, LI Qian. Distribution of Pearl-River diluted water and its ecological characteristics during spring monsoon transitional period in 2016* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 63-71. |
| [12] | NI Yugen, LI Jianguo, XI Long. Discussion on grain-size grading scale and sediment classification for marine sand and gravel [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 143-151. |
| [13] | LAN Xuan, LI Feng, ZHANG Chao, DONG Hanying, YANG Qingshu, YU Minghui, WEN Rubing, YANG Yujie. Ecological risk assessment of thallium in Pearl River Estuary and network based on the SOM model [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 132-142. |
| [14] | LI Kaizhi, REN Yuzheng, KE Zhixin, LI Gang, TAN Yehui. Vertical distributions of epipelagic and mesopelagic zooplankton in the continental slope of the northeastern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 61-73. |
| [15] | CAI Jiannan, LIU Hailong, JIANG Bo, CHEN Yinhui, LI Jiehong, WU Sixiao, LIANG Jianxia, HUANG Hua, XING Qianguo. Retrieval of non-optically active water quality parameters by hyperspectra for river network waters in the Pearl River estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 58-64. |
|
||