| [1] |
李晓露, 2016. 一种海藻Laurencia okamurai和一种软体动物Glossodoris atromarginata的化学成分和生物活性的研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海药物研究所.
|
|
LI XIAOLU, 2016. Studies on alga Laurencia okamurai and nudibranch Glossodoris atromarginata: chemistry and bioactivities[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institutes of Materia Medica, CAS (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
李忠东, 2015. 神奇的海蛞蝓[J]. 青少年科技博览, (5): 9-10 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
林光宇, 张玺, 1965. 海南岛潮间带的后鳃类软体动物[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 7(1): 1-24.
|
|
LIN GUANGYU, ZHANG XI, 1965. Opisthobranchia from the inter-tidal zone of Hainan Island, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 7(1): 1-24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
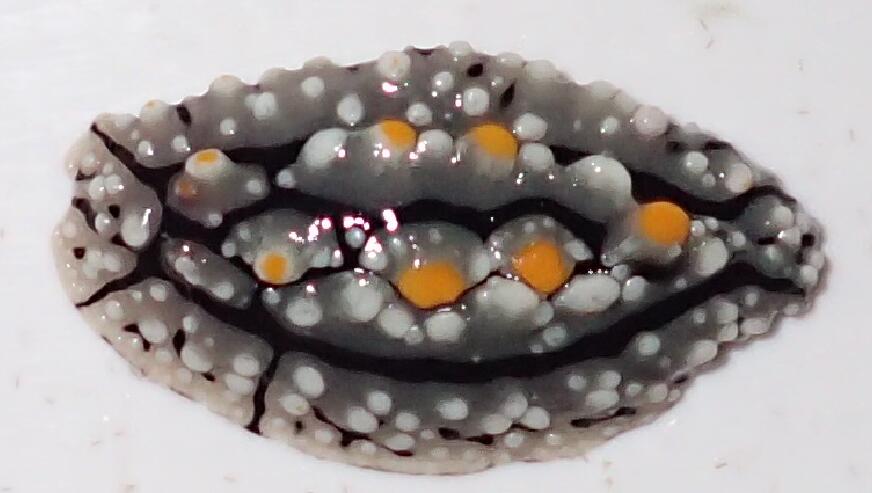
刘晓晖, 李晓萌, 李渊, 等, 2020. 南海叶海牛科的研究(异鳃亚纲, 裸鳃目)[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(3): 639-643.
|
|
LIU XIAOHUI, LI XIAOMENG, LI YUAN, et al, 2020. Studies on Phyllidiidae (Heterobranchia, Nudibranchia) in the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 51(3): 639-643 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
肖武汉, 张亚平, 2000. 鱼类线粒体DNA的遗传与进化[J]. 水生生物学报, 24(4): 384-391.
|
|
XIAO WUHAN, ZHANG YAPING, 2000. Genetics and evolution of mitochondrial DNA in fish[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 24(4): 384-391 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
谢金魁, 曹建国, 1997. 蛞蝓对人肺鳞癌、肺腺癌细胞抑癌作用初探[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 24(6): 344-346.
|
|
XIE JINKUI, CAO JIANGUO, 1997. Preliminary study of slug on non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 24(6): 344-346 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
张丽丽, 程起群, 2012. 鳀科鱼类线粒体全基因组序列结构特征及系统发育信息分析[J]. 海洋渔业, 34(1): 7-14.
|
|
ZHANG LILI, CHENG QIQUN, 2012. Mitochondrial genome characteristics and phylogenetic information of family Engraulidae (Clupeiformes: Clupeoidei) fishes[J]. Marine Fisheries, 34(1): 7-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
ALQUDAH A, SAAD S B, HADRY N F, et al, 2015. Identification and phylogenetic inference in different mollucs nudibranch species via mitochondrial 16S rDNA[J]. Brazilian Journal of Biological Sciences, 2(4): 295-302.
|
| [9] |
AOKI R, MATSUNAGA S, 2021. A photosynthetic animal: A Sacoglossan sea slug that steals chloroplasts[J]. Cytologia, 86(2): 103-107.
|
| [10] |
BRUNCKHORST D J, 1993. The systematics and phylogeny of phyllidiid nudibranchs (Doridoidea)[J]. Records of the Australian Museum, Supplement, 16: 1-107.
|
| [11] |
DO T D, CHOI T J, JUNG D W, et al, 2019a. The complete mitochondrial genome of Phyllidiella pustulosa (Cuvier, 1804) (Nudibranchia, Phyllidiidae)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 4(1): 771-772.
|
| [12] |
DO T D, KIM J I, JUNG D W, et al, 2019b. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Hermissenda emurai (Baba, 1937) (Nudibranchia, Facelinidae)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 4(1): 860-861.
|
| [13] |
FURFARO G, D′ELIA M, MARIANO S, et al, 2022. SEM/EDX analysis of stomach contents of a sea slug snacking on a polluted seafloor reveal microplastics as a component of its diet[J]. Scientific Reports, 12(1): 10244.
|
| [14] |
GOMES N G M, FERNANDES F, MADUREIRA-CARVALHO Á, et al, 2018. Profiling of heterobranchia sea slugs from Portuguese coastal waters as producers of anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory agents[J]. Molecules, 23(5): 1027.
|
| [15] |
KARAKAIDOS P, RAMPIAS T, 2020. Mitonuclear interactions in the maintenance of mitochondrial integrity[J]. Life, 10(9): 173.
|
| [16] |
LARKIN M F, SMITH S D A, WILLAN R C, et al, 2018. Diel and seasonal variation in heterobranch sea slug assemblages within an embayment in temperate eastern Australia[J]. Marine Biodiversity, 48(3): 1541-1550.
|
| [17] |
MA M L, ZHANG HAIQIANG, JIANG PEIYONG, et al, 2019. Topologic analysis of plasma mitochondrial DNA reveals the coexistence of both linear and circular molecules[J]. Clinical Chemistry, 65(9): 1161-1170.
|
| [18] |
MEHROTRA R, MONCHANIN C, SCOTT C M, et al, 2019. Selective consumption of sacoglossan sea slugs (Mollusca: Gastropoda) by scleractinian corals (Cnidaria: Anthozoa)[J]. PLoS One, 14(4): e0215063.
|
| [19] |
MELO CLAVIJO J, DREWS F, PIRRITANO M, et al, 2021. The complete mitochondrial genome of the photosymbiotic sea slug Berghia stephanieae (Valdés, 2005) (Gastropoda, Nudibranchia)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 6(8): 2281-2284.
|
| [20] |
MITOH S, YUSA Y, 2021. Extreme autotomy and whole-body regeneration in photosynthetic sea slugs[J]. Current Biology, 31(5): R233-R234.
|
| [21] |
NASS M M K, 1969. Mitochondrial DNA: I. Intramitochondrial distribution and structural relations of single-and double-length circular DNA[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 42(3): 521-528.
|
| [22] |
RICHLY E, 2003. Structural and functional genomics in semi-autonomous organelles: composition and origin of proteomes of chloroplasts and mitochondria and related transcriptomics[D]. Köln: Universität zu Köln.
|
| [23] |
SALES L, MARIAN J E A R, 2020. Functional morphology of the sperm-containing chambers of the sea slug Okenia polycerelloides in the context of sexual selection[J]. Journal of Morphology, 281(10): 1296-1312.
|
| [24] |
SEVIGNY J L, KIROUAC L E, THOMAS W K, et al, 2015. The mitochondrial genomes of the nudibranch mollusks, Melibe leonina and Tritonia diomedea, and their impact on gastropod phylogeny[J]. PLoS One, 10(5): e0127519.
|
| [25] |
VARNEY R M, BRENZINGER B, MALAQUIAS M A E, et al, 2021. Assessment of mitochondrial genomes for heterobranch gastropod phylogenetics[J]. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 21(1): 6.
|
| [26] |
XIANG PENG, LIN MAO, WANG YU, et al, 2016. The complete mitogenome of sea slug, Phyllidia ocellata (Mollusca: Phyllidiidae)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 1(1): 96-97.
|
| [27] |
YU C, KIM H, KIM H J, et al, 2018. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Oriental sea slug: Chromodoris orientalis (Nudibranchia, Chromodorididae)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 3(2): 1017-1018.
|
 ), ZHANG Huixian2(
), ZHANG Huixian2( ), LIU Xinman3, LIN Qiang2, SHEN Pingping1(
), LIU Xinman3, LIN Qiang2, SHEN Pingping1( )
)